含有双层衍射光学元件的中波/长波消热差光学系统的设计
2019-10-15杨亮亮赵勇兵袁得银
杨亮亮,赵勇兵,陈 凤,袁得银
(盐城师范学院 新能源与电子工程学院,江苏 盐城 224007)
Introduction
With the continuous development of infrared optical systems in the fields of military affairs and national defense, a single waveband infrared imaging system can no longer satisfy the requirements of detective system. Dual-band focal plane array and dual infrared optical system enable simultaneous imaging onto the same detector in two spectral wavebands[1-3]. In order to prevent the change of ambient environmental temperature from affecting the performance of the infrared optical system, it is generally required to realize athermalization within a certain temperature range. It is difficult to obtain good imaging quality, and hard to achieve athermalization because the optical materials that can be used for the infrared dual-band optical system are very limited. Diffractive optical elements (DOEs) can provide some degree of freedom in infrared optical system due to its special negative dispersion and thermal expansion properties[4-5]. The diffraction efficiency of single-layer DOEs or harmonic diffractive elements (HDEs) drops rapidly as the wavelength deviates from the design wavelength. The working waveband of the optical system with DOEs is narrow as the modulation transfer function is proportional to the diffraction efficiency of DOEs[6]. Accompanied with the appearance of multi-layer DOEs (MLDOEs) which can achieve a high diffraction efficiency over a wide spectral range, the optical systems working in wide waveband are studied a lot[7-9].
A refractive-diffractive hybrid infrared optical system working at 8 μm~12 μm is designed, which can realize athermalization over the temperature range from -40 ℃to 60 ℃ in Ref. [10]. An uncooled optical system working at 3 μm~5 μm and 8 μm~12 μm dual infrared waveband is designed, which can realize athermalization over the temperature range from -50 ℃ to 60 ℃ in Ref. [11]. All the above designed optical system is uncooled. A four-channel cooled infrared dual-band optical system working at 3.5 μm~4.8 μm and 7.8 μm~9.8 μm is designed in Ref.[12], each optical system of imaging channel is designed to be double imaging configuration, and the structure of this optical system is complicated.
Based on the special properties of DOEs, a cooled infrared dual-band optical system with double-layer DOEs is designed in this paper. The working waveband is the mid-wave infrared (MWIR) 3.7 μm~4.8 μm and the long-wave infrared (LWIR) 7.9 μm~9.5 μm. The cooled focal plane array is 320×256 and the pixel pitch is 30 μm. The designed optical system realizes athermalization over the temperature range from -55℃ to 71℃. The polychromatic integral diffraction efficiency (PIDE) of double-layer DOEs is above 99.15% over the whole working wavebands. The comprehensive PIDE of the double-layer DOEs are 99.81% and 97.36% for the MWIR and LWIR waveband, respectively.
1 Theoretical diffraction efficiency of MLDOEs
Diffraction efficiency is an important parameter for evaluating DOEs and refractive-diffractive hybrid optical system with DOEs. The magnitude of diffraction efficiency determines the possibility of application and the working waveband of the DOEs. MLDOEs, composed ofNHDEs with different dispersion materials. The general formula of phase retardation of MLDOEs as a function of incident angle is[13-14]

(1)
wherediis the designed microstructure height of theith HDEs,nij(λ) andnit(λ) are the refractive index of the incident medium and emergent medium of theith HDEs at the wavelength of λ respectively,θijandθitare the incident and emergent angles of theith HDEs. After a mathematical derivation, the relationship of diffraction efficiency of MLDOEs and incidence angle is expressed as
(2)
where sinc(x)=sin(πx)/(πx) ,mis the diffraction order. The PIDE of the mth diffraction order is
(3)
whereλminandλmaxare respectively the minimum wavelength and maximum wavelength for the working waveband, and all the wavelengths are considered to be equally weighted. For MLDOEs working within a range of incident angle, the comprehensive PIDE is
(4)
whereθminandθmaxare the minimum and maximum incident angles, respectively. According to Eq. (4), the comprehensive PIDE of MLDOEs working within a range of incident angle is calculated. When the imaging optical system with MLDOEs working with a few separate field of views, for example, the zoom system, the comprehensive PIDE is expressed as
(5)
whereθiminandθimaxare the minimum and maximum incident angles respectively for theith field of view,ωiis the weight factor for theith field of view,Kstands for the number of field of view. If the imaging quality of the hybrid refractive-diffractive optical system is analyzed equally for each field of view, the weight factor for every field of view is equal, namely,ω1=ω2=…=ωk=1/K.
2 Design of infrared dual-band optical system
For the infrared dual-band imaging optical system working within the MWIR 3.7 μm~4.8 μm and LWIR 7.7 μm~9.5 μm, it is demanded to satisfy three equations, the focal power distribution equation, achromatic equation and athermalized equation, to realize athermalization and achromatism simultaneously for the two wavebands. The three equations are
(6)
(7)
(8)
wherehiis the incident height of the first paraxial ray on theith lens ,Φiis the focal power of theith lens;Φis the total focal power of the optical system;fbis the back focal length (BFL) of the optical system;ωiis the dispersion factor of theith lens, which is the relative change of focal power due to dispersion, and equal to the inverse of the Abbe number of the optical material[15];xiis the thermal expansion coefficient of theith lens ;αhis the linear expansion coefficient of the total system;Lis the length of the mechanical structure.
2.1 Athermal design of infrared dual-band optical system with double-layer DOEs
Based on the unique achromatic and athermalized properties of DOEs, an infrared dual-band optical system with double-layer DOEs is designed working within the two wavebands of 3.7 μm~4.8 μm and 7.7 μm~9.5μm. The focal length is demanded to be 200 mm, based on the configuration of Petzval objective, the structure of the designed infrared dual-band optical system is secondary imaging configuration as shown in Fig. 1, with only six lenses, three infrared optical materials, Ge, ZnSe and ZnS. The front group of the optical system are three separated lenses, and the rear group are double-layer DOEs and one single lens. F # is 2. The cooled focal plane array is 320×256 and the pixel pitch is 30 μm. The field of view is ±1.76°.

Fig.1 Structure of infrared dual-band optical system
2.2 Performance of designed optical system
The modulation transfer function (MTF) curves of MWIR and LWIR of the optical system at 20 ℃ are shown in Fig. 2 (a) and (b), respectively. The MTF is higher than 0.70 and 0.55 at the frequency of 17 lp/mm for MWIR and LWIR. The MTF curves of MWIR and LWIR of the optical system at -55 ℃ and 71℃ are shown in Fig. 3. Table 1 shows the minimum MTF for MWIR and LWIR at some different temperatures. The MTF is higher than 0.66 and 0.54 at the frequency of 17 lp/mm for MWIR and LWIR, with the imaging quality close to the diffraction limit. The designed infrared dual-band optical system realizes athermalization within the temperature range of -55℃~71℃.

Fig.2 MTF curves of MWIR and LWIR at 20 ℃
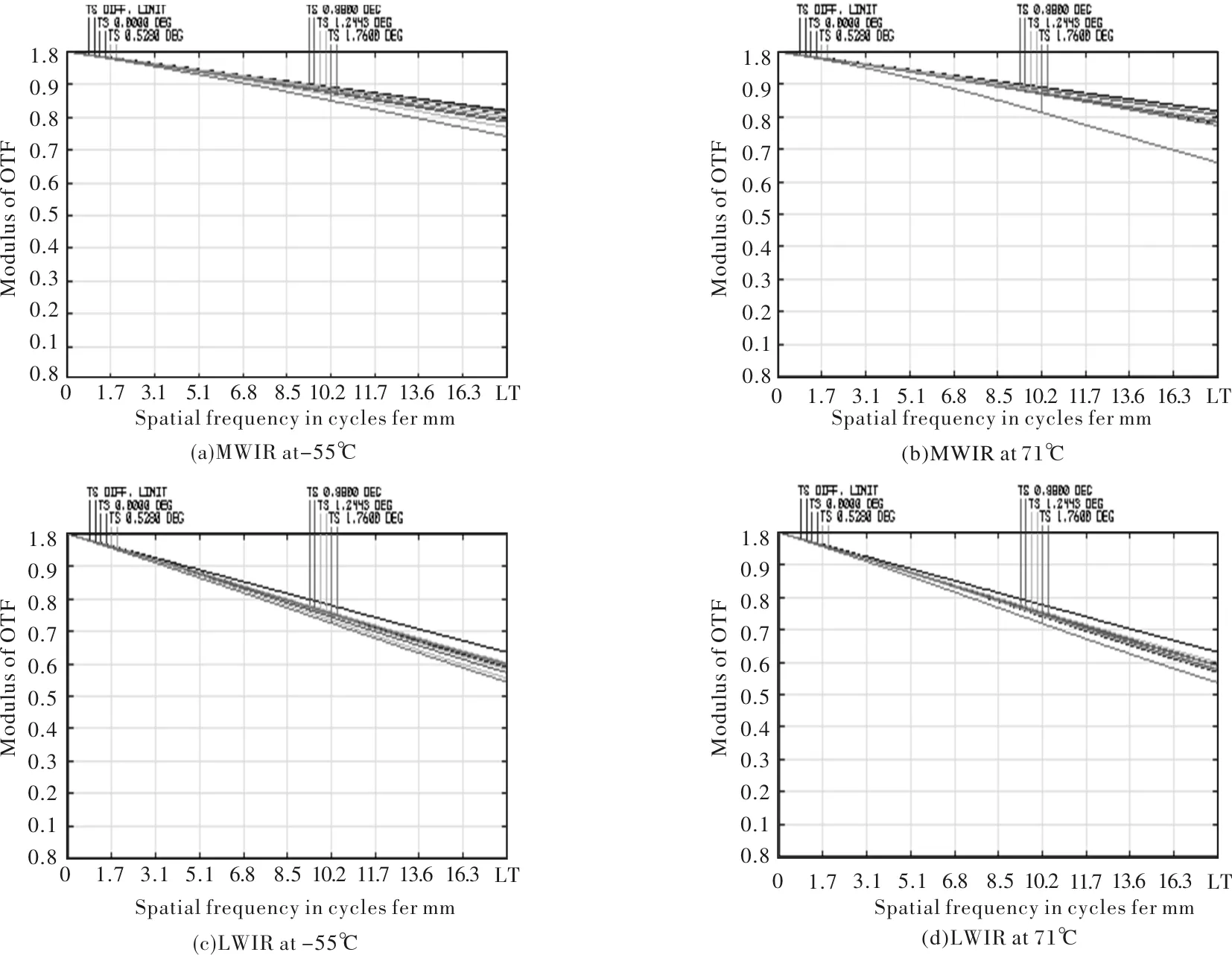
Fig.3 MTF curves of MWIR and LWIR at -55℃ and 71℃

Table 1 Minumum MTF at different temperatures
The RMS radius of MWIR and LWIR are respectively 11.503 μm and 8.332 μm at 20℃ as shown is Fig. 4(a) and (b), both less than the pixel size 30 μm. For different field of view, the RMS radius of the full field of view is the maximum. Table. 2 is the RMS radius of the full field of view at some different temperatures. The maximum RMS radiuses are less than 11.702 μm and 9.021 μm for the MWIR and LWIR waveband, respectively, which are both smaller than the pixel size 30 μm.
Table 3 shows the wavefront errors at some different temperatures. The maximum wavefront error is 0.191 7λat 71℃ for the MWIR waveband, and 0.132 8λ at 71℃ for the LWIR waveband, both smaller than 0.25λ, so the image quality is great.

Fig.4 Spot diagram of MWIR and LWIR at 20 ℃

Temperature/℃-55-29.8-4.62045.971RMS radius of MWIR/μm9.69410.45911.09511.50311.70211.702RMS radius of LWIR/μm9.0218.5328.3888.3328.2488.105
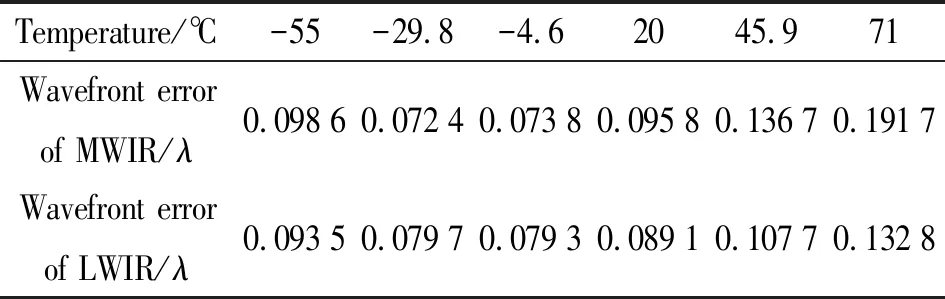
Table 3 Wavefront error at some different temperatures
The focus depths of the designed optical system are ±33.6 μm and ±71.2 μm for the MWIR and LWIR waveband, respectively. The defocus at different temperatures is compared to that at 20℃, as shown in Table.4. The maximal defocus from the temperature range from -55℃ to 71℃ are 10.48 μm and 9.79 μm respectively for the MWIR and LWIR waveband, the maximal defocus is less than focus depth.
Table4Defocusofdesignedopticalsystematdifferenttemperatures

Temperature/℃-55-29.8-4.62045.971DefocusMW/μm3.20-1.14- 1.9404.3310.48DefocusLW/μm4.14-0.05-1.6103.999.79
3 Diffraction efficiency of double-layer DOEs
The substrate materials of the double-layer DOEs are ZnSe and ZnS. The relationship of PIDE and wavelength for the double-layer DOEs is shown in Fig. 5. The PIDE of the double-layer DOEs over the whole working waveband is above 99.15%[16], which can be widely used in infrared dual-band optical system. The incident angle upon the diffractive surface is within the range of 0°~5.19°. Assuming the weight factor for every field of view is equal, the comprehensive PIDE of the double-layer DOEs are 99.81% and 97.36% for the MWIR and LWIR waveband, respectively.

Fig.5 PIDE of double-layer DOEs
4 Conclusion
The analysis model of comprehensive PIDE for MLDOEs working within a range of incident angle is established. MLDOEs can achieve a high diffraction efficiency over a wide waveband, an infrared dual-band optical system with double-layer DOEs working at 3.7 μm~4.8 μm and 7.7 μm~9.5 μm dual infrared waveband is designed. The cooled focal plane array is 320×256 and the pixel pitch is 30 μm. The maximal RMS radius of the designed optical system is less than 11.702 μm, the wavefront error is smaller than 0.191 7λ, and the absolution of maximal defocus is less than 10.48 μm. The designed optical system realizes athermalization over the temperature range from -55℃ to 71℃. The PIDE of double-layer DOEs is above 99.15% over the whole working wavebands. The incident angle upon the diffractive surface is within the range of 0°~5.19°. Assuming the weight factor for every field of view is equal, the comprehensive PIDE of the double-layer DOEs are 99.81% and 97.36% for the MWIR and LWIR waveband, respectively. The optical system can be applied to infrared dual-band detection system and has broad application prospect in the infrared thermal imaging system in military and defense fields.
