海洋潮汐浪溅区混凝土表面氯离子浓度改进计算模型
2019-10-08蔡荣杨绿峰余波2
蔡荣 杨绿峰 余波2

摘 要:收集了世界不同地区304组海洋潮汐浪溅区混凝土的自然暴露的试验数据,据此分析了水胶比、胶凝材料种类和暴露时间对混凝土表面氯离子浓度Cs,ts的影响规律,进而结合二阶段多元非线性回归分析,分别确定了硅酸盐水泥、粉煤灰、矿渣和硅灰等胶凝材料对Cs,ts的修正系数,建立了海洋潮汐浪溅区Cs,ts的改进模型,并利用现有模型和试验数据对比,验证了该模型的适用性。分析表明:Cs,ts与水胶比之间近似呈线性关系,且胶凝材料种类对Cs,ts的影响显著;Cs,ts在前5 a内快速增长,随后逐渐趋于稳定,可以利用指数型函数来描述其时变规律。
关键词:潮汐浪溅区;混凝土;表面氯离子浓度;二阶段回归分析;胶凝材料种类
中图分类号:TU311.3 文献标志码:A 文章编号:
Abstract:The influences of water-to-binder ratio, binder type and exposure time on the surface chloride concentration Cs,ts of concrete exposed to marine tidal and splash zones were investigated respectively based on 304 sets of field test data selected from different sites. Then an improved model for Cs,ts was developed based on the two-phase multiple nonlinear regression technique by determining the correction factors of binder type including the ordinary Portland cement, fly ash, slag and silica fume respectively. Finally, the applicability of the improved model for Cs,ts was validated in comparison with existing models and field test data. Analysis results show that the surface chloride concentration increases with water-binder-ratio linearly, while the influence of binder type on Cs,ts cannot be ignored. Moreover, Cs,ts increases over exposure time exponentially, which appears a fast increase in the first 5 years and then becomes stable.
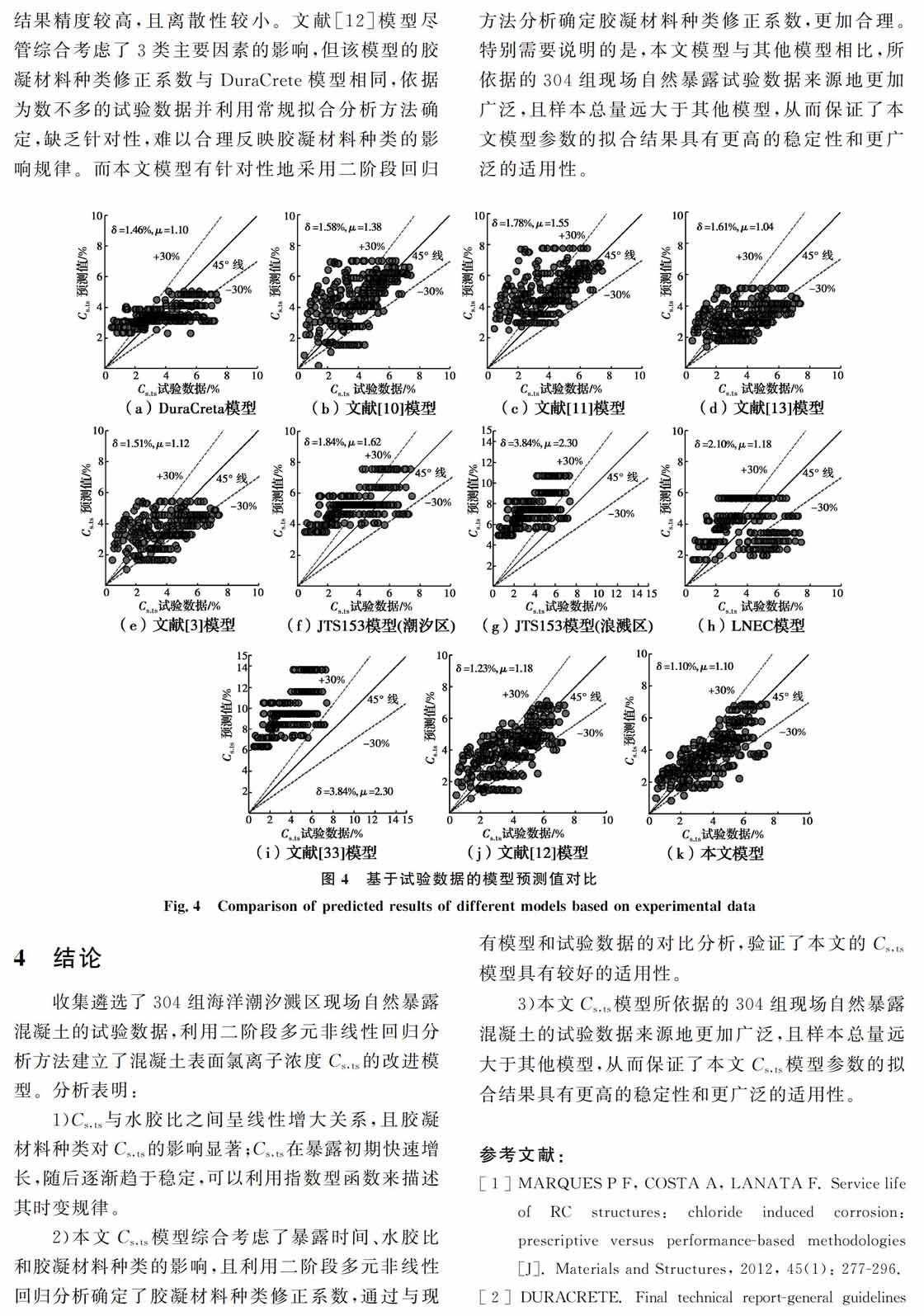
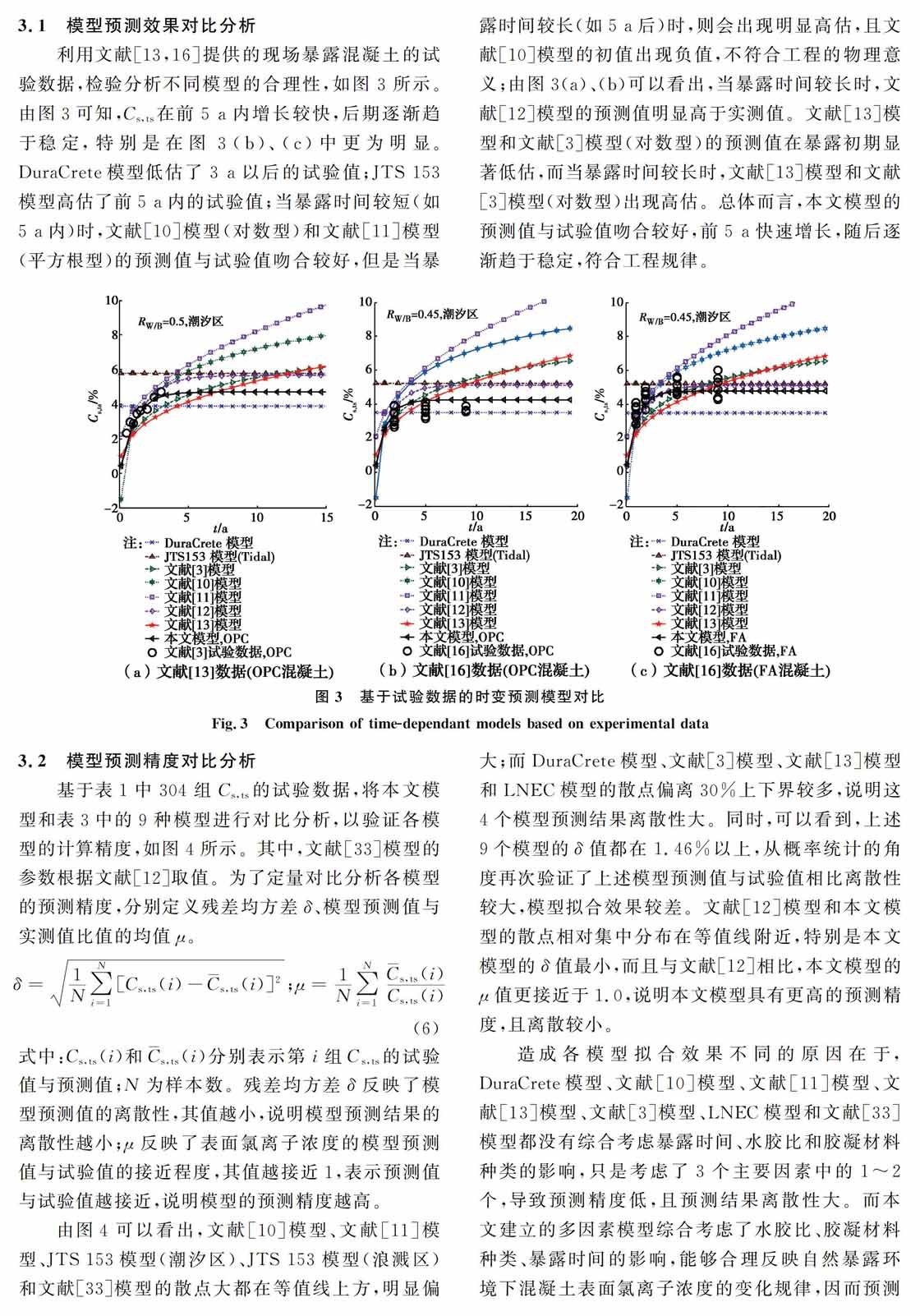
Key words:Tidal and splash zones; Concrete; Surface chloride concentration; Two-phase regression technique; Binder type海洋潮汐浪溅区是海洋混凝土结构耐久性劣化最为突出的区域,所以,有必要建立该区域混凝土表面氯离子浓度Cs,ts的计算模型,为混凝土结构的耐久性分析和设计提供量化边界条件。目前,学者们建立了多种表面氯离子浓度计算模型。其中,Marques等[1]建立了Cs,ts与水胶比之间的线性关系模型;DuraCrete[2]建立了考虑水胶比和胶凝材料种类影响的关系模型。上述模型只考虑了材料特性的影响,而忽略了暴露时间t的影响。由于水泥水化程度的发展,混凝土越来越密实,导致Cs,ts具有显著的时变特性。对此,文献[3-8]分别利用对数型、幂函数型、指数型等函数来描述了Cs,ts的时变规律,但无法合理描述初期增长较快、后期趋于稳定的时变规律。文献[9-11]建立了Cs,ts与水胶比和暴露时间之间的关系模型,但忽略了胶凝材料种类对表面氯离子浓度的影响。由此可见,Cs,ts不仅与水胶比和胶凝材料种类等材料参数密切相關,而且具有显著的时变特性,因此,有必要综合考虑水胶比、胶凝材料种类和暴露时间的影响,建立Cs,ts的多因素模型。蔡荣等[12]初步建立了Cs,ts与水胶比、胶凝材料种类和暴露时间之间的关系模型,但直接采用了DuraCrete模型[2]的胶凝材料种类修正系数,无法合理描述不同胶凝材料对Cs,ts的影响规律。
