围麻醉期右美托咪定的应用对老年患者PFN术后认知功能障碍的影响
2019-09-30闫焱
闫焱


[摘要] 目的 研究圍麻醉期右美托咪定(Dex)的应用对老年患者股骨粗隆间骨折行髓内钉(PFN)术后认知功能障碍(POCD)的影响。 方法 选取2018年1~12月广州市第一人民医院南沙医院收治的股骨粗隆间骨折,在椎管内麻醉下择期行PFN手术的老年患者60例为研究对象,采用随机数字表法分为Dex组(D组,n = 30)和对照组(C组,n = 30)。D组患者麻醉前15 min静脉泵注Dex 0.3 μg/kg作为术前用药,10 min泵注完,术中泵注Dex 0.3 μg/(kg·h)至术终,术后Dex 1 μg/(kg·d)+舒芬太尼2 μg/(kg·d)行PCIA 48 h;C组患者围麻醉期静脉泵注生理盐水,术后舒芬太尼2 μg/(kg·d)行PCIA。检测麻醉前(T0)、术后24 h(T1)、术后48 h(T2)血清丙二醛(MDA)、8-异构前列腺素F2α(8-iso PGF2α)水平,并行简易精神状态评价量表(MMSE)评分。 结果 两组患者T1、T2的MDA、8-iso PGF2α水平高于T0,但D组低于C组同时点,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。两组患者T1、T2的MMSE评分低于T0,但D组高于C组同时点,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。C组T1和T2的VAS高于D组,按压次数、有效按压次数、舒芬太尼用量多于D组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。 结论 围麻醉期应用Dex,可降低老年患者PFN术后 POCD的发生率。
[关键词] 右美托咪定;术后认知功能障碍;围麻醉期;丙二醛;8-异构前列腺素F2α
[中图分类号] R687.4 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2019)07(a)-0117-04
Effects of Dexmedetomidine on postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly patients undergoing PFN in perianesthesia
YAN Yan
Department of Anesthesiology, the First People′s Hospital of Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510180, China
[Abstract] Objective To study the effects of Dexmedetomidine on postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly patients undergoing PFN in perianesthesia. Methods Sixty elderly scheduled for PFN surgery under spinal anesthesia were enrolled in Nansha Hospital of the First People′s Hospital of Guangzhou City from January to December 2018 were selected as study objects, and they were divided into Dexmedetomidine group (group D, n = 30) and control group (Group C, n = 30) by using random numeral table method. The patients in group D were intravenous infused 0.3 μg/kg Dexmedetomidine within 10 min as premedication 15 minutes before anesthesia, followed by 0.3 μg/(kg·h) infusion until the end of operation. The patients in group C received intravenous infusion of saline. Patient-controlled intravenous analgesia (PCIA) was started for all patients when they were transferred to the ward. The patients were given Sufentanyl 2 μg/(kg·d) as PCIA 100 mL in group C. Group D were given Dexmedetomidine 1 μg/(kg·d) + Sufentanyl 2 μg/(kg·d) as PCIA 100 mL. The levels of MDA and 8-iso PGF2α in serum were detected before anesthesia (T0), 24 h (T1) and 48 h (T2) after operation. The min-mental state examination (MMSE) scores were estimated at T0, T1 and T2. Results The levels of MDA and 8-iso PGF2α at T1 and T2 in two groups were higher than those at T0, but those in group D were lower than those in group C at the same time, the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). MMSE scores of T1 and T2 in two groups were lower than those of T0, but those in group D were higher than those in group C at the same time, the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). VAS of T1 and T2 in group C was higher than that in group D, and the times of pressing, effective pressing and the dosage of Sufentanil in group C were higher than those in group D, the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion Dexmedetomidine can reduce the incidence of postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly patients undergoing PFN in perianesthesia.
[Key words] Dexmedetomidine; Postoperative cognitive dysfunction; Perianesthesia; Malondialdehyde; 8-iso prostaglandin F2α
术后认知功能障碍(POCD)是患者在术后出现精神活动、人格、社交活动及认知能力的变化,65岁以上患者发病率达20%~50%[1]。在手术损伤时,往往同时发生炎症与氧化应激反应,脑组织的高代谢特性,导致其容易遭受氧化应激损伤,使神经元变性、坏死或凋亡,出现认知障碍[2]。盐酸右美托咪定(Dex)有镇静、抗焦虑、降低应激反应的作用,本研究对股骨粗隆间骨折行髓内钉(PFN)内固定术的老年患者,围麻醉期应用Dex,探讨Dex对POCD的影响。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2018年1~12月广州市第一人民医院南沙医院(以下简称“我院”)收治股骨粗隆间骨折,择期行PFN手术的老年患者60例为研究对象,采用随机数字表法分为Dex组(D组,n = 30)和对照组(C组,n = 30),其中男23例,女37例。纳入标准:①ASA分级Ⅰ~Ⅱ级;②年龄60~75岁;③初中以上文化;④术前无认知障碍,简易精神状态评价量表(MMSE)评分>23分。排除标准:①精神神经病史,服用精神类药物史;②严重心肺功能不全;③酗酒及长期使用镇静药或吸毒史;④术前不能完成MMSE测评。本研究经我院医学伦理委员会审查批准,参与研究者及家属签署知情同意书。
1.2 麻醉方法
患者入手术室后开放左上肢静脉,D组麻醉前15 min静脉泵注Dex(江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司,批号:181124BP,规格:2 mL∶200 μg/支)0.3 μg/kg作为术前用药,10 min泵注完。C组给予生理盐水。所有患者行椎管内麻醉,穿刺一次成功,蛛网膜下腔给予0.75%罗哌卡因1.7 mL(阿斯利康制药有限公司,批号:NAXY,规格:10 mL∶100 mg/支),控制麻醉平面T8以下。麻醉平面确切后,D组和C组分别泵注Dex 0.3 μg/(kg·h)和生理盐水至术终。维持术中平均动脉压(MAP)波动范围在基础值±20%,心率<50次/min者,静脉注射阿托品纠正。
1.3 自控静脉镇痛(PCIA)方法
D组:Dex 1 μg/(kg·d)+舒芬太尼(宜昌人福药业有限责任公司,批号:1180401,规格:5 mL∶250 μg/支)2 μg/(kg·d)+昂丹司琼(齐鲁制药有限公司,批号:HB2B8003,规格:2 mL∶4 mg/支)8 mg,C组:舒芬太尼2 μg/(kg·d)+昂丹司琼8 mg。设置总量为100 mL,连续背景输注量2 mL/h,单次给药量1.5 mL,锁定时间15 min。记录术后24 h和48 h视觉模拟评分(VAS)、镇痛泵参数及不良反应。
1.4 观察指标
麻醉前(T0)、术后24 h(T1)、术后48 h(T2)抽取外周静脉血3 mL,4℃,3000 r/min,离心半径13.5 cm,离心30 min(德国Sigma 1-15K),取上清液,-80℃冻存。酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)检测血清丙二醛(MDA,Abcam公司,ab238537)和8-异构前列腺素F2α(8-iso PGF2α,Abcam公司,ab133025)水平,操作按试剂盒说明书进行。
MMSE评分[3],从时间定向力、即刻记忆、延迟记忆、地点定向力、语言、注意力及计算力、视空间七个方面,评估被试者智力状态及认知功能缺损程度。25~30分为正常,20~24分可能认知障碍,<20分明确认知障碍。测试患者麻醉前及术后24 h和48 h的MMSE评分。
1.5 统计学方法
所有数据采用SPSS 20.0统计软件进行处理。计量资料用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,组间比较采用配对t检验,组内比较采用单因素方差分析,计数资料采用χ2检验,以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 两组患者一般情况比较
D组有4例因心率<50次/min,静脉注射阿托品0.5 mg纠正。两组患者性别、年龄、体重、身高、手术时间比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。见表1。
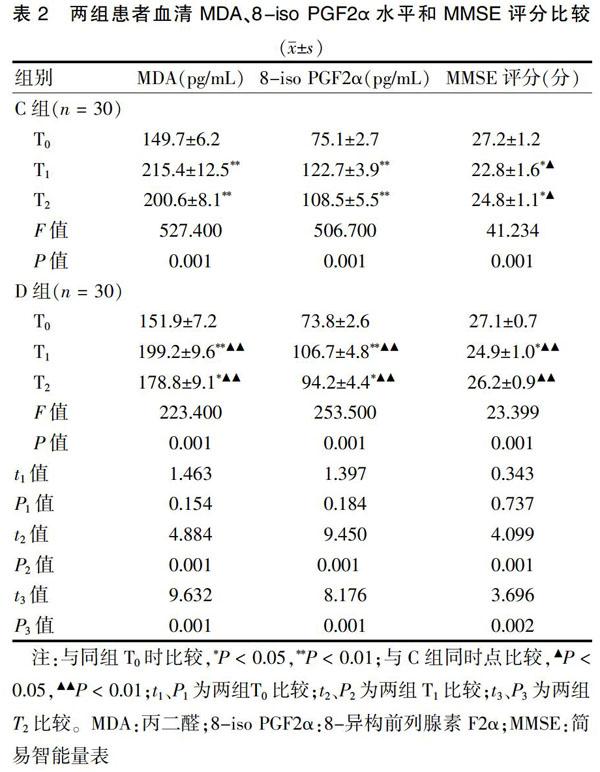
2.2 两组患者血清MDA、8-iso PGF2α水平和MMSE评分比较
两组患者T1、T2的MDA、8-iso PGF2α水平高于T0,但D组低于C组同时点,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。两组患者T1、T2的MMSE评分低于T0,但D组高于C组同时点,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表2。
2.3 两组患者VAS和PCIA参数比较
C组T1和T2的VAS高于D组,按压次数、有效按压次数、舒芬太尼用量多于D组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表3。C组恶心、呕吐6例,而D组仅有2例。
3 讨论
POCD是老年人术后常见并发症,通常认为全身麻醉手术,由于联合用药药物作用,诱发POCD的风险远远高于椎管内麻醉[4],而Coburn等[5]证明不同麻醉方式并不影响其发生率,一项多国研究[6]证明全身麻醉和椎管内麻醉患者术后3个月POCD发生率分别是14.3%和13.9%,无显著差异。本研究选择股骨粗隆间骨折老年患者,在椎管内麻醉下行PFN术,观察从术前用药、术中镇静至术后镇痛围麻醉期Dex应用对患者POCD的影响。
大脑对疼痛感知和认知的区域重叠,疼痛感受器超敏化状态加剧了术后疼痛,同时作用于认知区域。有研究[7]表明疼痛导致海马体积缩小,因此手术引起的术后疼痛是POCD的发生因素之一。Dex是高选择性α2肾上腺素能受体激动剂(α2∶α1比例为1620∶1)[8],用于镇静、镇痛及全身麻醉辅助用药,产生的睡眠-清醒镇静模式更接近生理状态,患者是可唤醒和合作的,能够降低谵妄的发生率[9]。Meta分析证实,Dex與阿片类联合PCIA安全有效[10],本研究应用Dex联合舒芬太尼行PCIA,发现其镇痛效果优于单纯舒芬太尼,降低恶心、呕吐的发生率,减少舒芬太尼用量,可达到更加满意的镇痛效果。
MMSE自1975年起用于評估认知功能[11],是应用最广泛的认知筛查量表,对认知功能的检测敏感,是临床POCD评估的常用方法[3]。Rohan等[12]发现,MMSE对大脑认知功能的测定,敏感度87%,特异度82%。本研究采用MMSE评估患者认知功能,两组患者术前评分无差异,术后24 h和48 h评分均低于麻醉前,对照组明显低于Dex组,因此Dex可降低POCD的发生率。
众所周知,术中缺氧、低血压等伤害性刺激引起脑损伤,可产生氧化应激反应,导致POCD[13]。8-iso PGF2α在体内经脂质过氧化由花生四烯酸衍生而成,是检测氧化应激的金标准[14],其含量在脑损伤患者大脑间质明显增加,反映脑损伤的严重程度及预后[15]。髋骨骨折患者术后血浆8-iso PGF2α含量增加,可独立预测POCD的发生,敏感度为82%、特异度为75%[16]。临床及基础研究均证实[17-19],Dex可降低氧化应激标志物含量,对氧化应激损伤具有保护作用,然而Dex对8-iso PGF2α的影响尚未见相关报道。本研究发现Dex可降低MDA和8-iso PGF2α水平,这与Rodríguez-González等[20]研究发现的Dex降低MDA水平,通过抗氧化应激发挥脑保护作用是一致的。脑干蓝斑核在伤害性神经递质调控中起着重要作用,是Dex的主要作用靶点[21],推测Dex可能通过作用于蓝斑核,调控伤害性神经递质的释放,从而降低伤害性刺激,抑制氧化应激反应,这需要进一步的研究证实。本研究中行PFN手术的老年患者在围麻醉期应用Dex,从术前用药至术后镇痛,维持Dex一定的血浆浓度,减少阿片类药物术后镇痛的用量,降低氧化应激反应,在围麻醉期的各个环节发挥POCD保护作用。
综上所述,围麻醉期应用Dex,可降低老年患者PFN术后POCD的发生率。
[参考文献]
[1] Carr ZJ,Cios TJ,Potter KF,et al. Does Dexmedetomidine ameliorate postoperative cognitive dysfunction? a brief review of the recent literature [J]. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep,2018,18(10):64-74.
[2] Joy T,Rao MS,Madhyastha S. N-acetyl cysteine supplement minimize tau expression and neuronal loss in animal model of Alzheimer′s disease [J]. Brain Sci,2018,8(10):185-199.
[3] Hemerka JN,Wu X,Dixon CE,et al. Severe brief pressure-controlled hemorrhagic shock after traumatic brain injury exacerbates functional deficits and long-term neuropathological damage in mice [J]. J Neurotrauma,2012, 29(12):2192-2208.
[4] Hui-Jian Shi,Xin-Hong Xue,Yue-Lan Wang,et al. Effects of different anesthesia methods on cognitive dysfunction after hip replacement operation in elder patients [J]. Int J Clin Exp Med,2015,8(3):3883-3888.
[5] Coburn M,Fahlenkamp A,Zoremba N,et al. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction:incidence and prophylaxis [J]. Anaesthesist,2010,59(2):177-184.
[6] Rasmussen LS,Johnson T,Kuipers HM,et al. Does anaesthesia cause postoperative cognitive dysfunction? A randomised study of regional versus general anaesthesia in 438 elderly patients [J]. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand,2003, 47(3):260-266.
[7] Apkarian AV,Mutso AA,Centeno MV,et al. Role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in persistent pain [J]. Pain,2016,157(2):418-428.
[8] Weerink MAS,Struys MMRF,Hannivoort LN,et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of Dexmedetomidine [J]. Clin Pharmacokinet,2017,56(8):893-913.
[9] Duan X,Coburn M,Rossaint R,et al. Efficacy of perioperative dexmedetomidine on postoperative delirium:systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomised controlled trials [J]. Br J Anaesth,2018,121(2):384-397.
[10] Peng K,Liu HY,Wu SR,et al. Effects of combining Dex-medetomidine and opioids for postoperative intravenous patient-controlled analgesia:a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Clin J Pain,2015,31(12):1097-1104.
[11] Folstein MF,Folstein SE,McHugh PR. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician [J]. J Psychiatry Res,1975,12(3):189-198.
[12] Rohan D,Buggy DJ,Crowley S,et al. Increased incidence of postoperative cognitive dysfunction 24 hr after minor surgery in the elderly [J]. Can J Anaesth,2005,52(2):137-142.
[13] An LN,Yue Y,Guo WZ,et al. Surgical trauma induces iron accumulation and oxidative stress in a rodent model of postoperative cognitive dysfunction [J]. Biol Trace Elem Res,2013,151(2):277-283.
[14] Owczarek D,Cibor D,Mach T. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA),symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA),arginine,and 8-iso-prostaglandin F2alpha (8-iso-PGF2alpha) level in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases [J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis,2010,16(1):52-57.
[15] Clausen F,Marklund N,Lewén A,et al. Interstitial F(2)-isoprostane 8-iso-PGF(2α) as a biomarker of oxidative stress after severe human traumatic brain injury [J]. J Neurotrauma,2012,29(5):766-775.
[16] Zheng YB,Ruan GM,Fu JX,et al. Postoperative plasma 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α levels are associated with delirium and cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients after hip fracture surgery [J]. Clin Chim Acta,2016,455(1):149-153.
[17] Akpinar H,Akpinar O. The effects of dexmedetomidine on biomarkers of oxidative stress and antioxidants in kidney [J]. Bratisl Lek Listy,2018,119(8):476-480.
[18] Yu J,Yang W,Wang W,et al. Involvement of miR-665 in protection effect of dexmedetomidine against Oxidative Stress Injury in myocardial cells via CB2 and CK1 [J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2019,115:108894.
[19] Li F,Wang X,Deng Z,et al. Dexmedetomidine reduces oxidative stress and provides neuroprotection in a model of traumatic brain injury via the PGC-1α signaling pathway [J]. Neuropeptides,2018,72:58-64.
[20] Rodríguez-González R,Sobrino T,Veiga S,et al. Neuroprotective effects of dexmedetomidine conditioning strategies:evidences from an in vitro model of cerebral ischemia [J]. Life Sci,2016,144(1):162-169.
[21] Vuyk J,Sitsen E,Reekers M,et al. Intravenous anesthetics [M]. Miller′s Anesthesia,2015:854-859.
