手机召车软件影响下城市出租车运营平衡模型探讨
2019-09-10曹祎朱海
曹祎 朱海



摘要:手机召车软件深刻变革了城市出租车系统,为供需双方搭建了信息平台,出租车空驶时,需完成双层选择。上层为选择使用手机召车软件的网约模式或者不使用手机召车软件的巡游模式;下层为选择下一乘客的起点小区,下层区域选择受上层模式选择特征影响。文章分析了模式选择与区域选择的关系,构建基于出租车选择行为的出租车运营平衡模型,并探讨两种模式对应的乘客在等待过程上的差异,以便于计算基于小区特征的等待时间。算例结果表明:网约模式的出租车搜索时间比巡游模式受出租车规模影响小;出租车规模较小时,巡游模式的利用率较网约模式低;随着规模增大,巡游模式利用率下降6.2%,网约模式利用率下降13.1%,且此时网约模式的利用率较低,乘客等待时间的差距缩短。可见,手机召车软件可有效改善信息不对称,但在出租车规模较大时边际效应明显。
关键词:城市出租车系统;均衡模型;手机召车软件;出租车搜索行为;乘客等待时间
The ehailing software has profoundly changed the urban taxi system,and builds an information platform for both the supply and demand sides,and,when the taxi is empty,it needs to complete the doublelayer selection,the upper layer is to select the online reservation mode of ehailing software or not using the cruise mode of ehailing software,the lower layer is to select the starting community of next passenger,and the lowerlayer area selection is affected by the upperlayer mode selection feature.This article analyzes the relationship between mode selection and region selection,constructs a taxi operation equilibrium model based on taxi selection behavior,and discusses the difference of corresponding passenger waiting process under the two modes,in order to calculate the waiting time based on community characteristics.The calculation results show that the taxi search time of online reservation mode is less affected by the taxi scale than the cruise mode.When the taxi scale is small,the utilization rate of cruise mode is lower than online reservation mode.As the scale increases,the cruise mode utilization rate is decreased by 6.2%,and the utilization rate of online reservation mode is decreased by 13.1%.At this time,the utilization rate of online reservation mode is lower,and the gap between passenger waiting times is shortened.It can be seen that the ehailing software can effectively improve the information asymmetry,but the marginal effect is obvious when the taxi scale is large
Urban taxi system;Equilibrium model;Ehailing software;Taxi search behavior;Passenger waiting time
0 引言
“互聯网+”城市交通为城市公共出行服务的供给侧改革和优化带来了机遇,需要重新审视基于信息平台的城市出租车系统。面对技术革新与行业演化,急需理清出租车系统中传统与新型两种模式的差异,把握信息背景下的市场运转机制特征。
Yang和Wong在Douglas[1]提出在经典出租车固定需求的框架上开创出租车市场均衡问题[2-3]。Wong
认为空驶出租车的选择由两个子模型构成[4-5]。以上研究均设定在传统出租车市场的背景下以讨论空驶行为的随机性。然而在信息环境下,空驶车可通过手机召车软件提前获知需求分布信息,基于自身利益最大化动态调整搜索策略,传统研究难以完整涵括这种转变过程。
目前,已有学者注意到出租车市场变化态势:Zhao采用纽约的出租车信息平台数据,得出手机召车软件这一技术创新为制度革新提供了可行性[6];Xia构建了出租车行业评价指标体系[7];Hai认为互联网专车是出租车的有效补充[8];He讨论了出租车司机及乘客的双边选择均衡问题[9]。以上研究多集中于对手机召车软件这一技术手段本身的探讨,较少涉及系统运转机制及内生变量的变化。
通过以上分析可知,空驶出租车的搜索行为,是区分新型与传统出租车系统的关键。将使用手机召车软件完成出租车服务的召车模式称为网约模式,反之为巡游模式。假设所有出租车均已配备手机召车软件,在上一乘客下车后,可自由选择下一乘客。本文拟量化出租车选择行为,构建信息环境下出租车系统重构的运营平衡模型,旨在为决策部门掌握手机召车软件特性及制定管控方案提供理论参考。
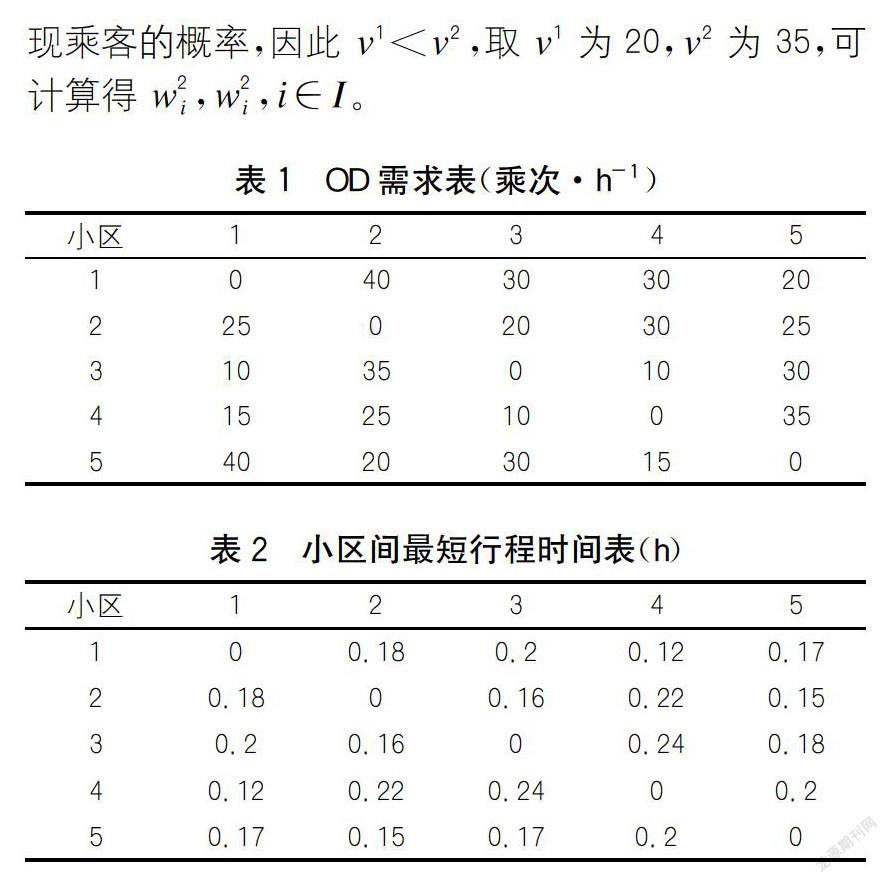
随着出租车规模增加,结合图2(a)、图2(c)可知:巡游车搜索时间总增幅为51%,出租车规模增加意味着市场中出租车运力增加,即总运营时间增加,在需求固定的情况下,巡游车搜索对象为路网中的任一乘客,因此搜索时间增加,整体利用率降低了6.2%;网约车搜索时间不受出租车规模影响,这是由于网约车的服务对象为路网中的特定的已预约乘客,搜索时间只由供需双方的距离等路网特征决定,搜索时间稳定,整体利用率降低了13.1%,比巡游车更为敏感。由图2(b)可知:随着出租车规模的增加,巡游车乘客更容易扬招到出租车,等待时间下降明显;参考式(7)、式(8)可知,随着巡游车的负效用增加,而网约车搜索时间未变,网约车的负效用也不变,出租车更倾向于选择网约模式;由式(18)可知,网约车乘客等待时间则间接降低。此外,在出租车规模较小时,网约模式的乘客等待时间短,同时利用率也高;规模较大时,网约车与巡游车乘客等待时间接近,此时巡游模式的利用率较高,说明此时手机召车软件边际效应有限。
5 结语
在手机召车软件广泛使用的背景下,本文确定了空驶出租车选择行为的多层次结构。上层为模式选择(巡游模式或网约模式);下层为区域选择(下一乘客的起点小区)。并依次量化了选择效用,建立了考虑空间路网特征的出租车市场平衡模型。在平衡状态时,空驶出租车不可通过改变选择行为以增加效用。通过算例分析可知,在一定的规模下,巡游模式在出租车搜索时间及乘客等待时间上,受租车规模影响的波动性更大,证实了手机召车软件在规模较小时对信息不对称的改善作用;但在规模较大时,该作用十分有限。本文的研究是在出租车总需求固定的前提下进行的,对于弹性需求的变化,将是下一步的研究方向。
参考文献:
[1]Douglas G W,Douglas G W.Price Regulation and Optimal Service Standards:The taxicab Industry [J].Journal of Transport Economics and Policy,1972(20):116-127.
[2]Yang H,Wong S C.A network model of urban taxi services [J].Transportation Research Part B Methodological,1998,32(4):235-246.
[3]Yang H,Wong K I,Wong S C.Modeling urban taxi services in road networks:Progress,problem and prospect [J].Journal of Advanced Transportation,2001,35(3):237-258.
[4]Wong R C P,Szeto W Y,Wong S C.A twostage approach to modeling vacant taxi movements [J].Transportation Research Part C Emerging Technologies,2015(59):147-163.
[5]Wong R C P,Szeto W Y,Wong S C.Behavior of taxi customers in hailing vacant taxis:a nested logit model for policy analysis:[J].Journal of Advanced Transportation,2015,49(8):867-883.
[6]Zhao J.Humanizing Travel:How Ehail Apps Transform Stakeholder Relationships in the U.S.Taxi Industry[C].Transportation Research Board 94th Annual Meeting,2015.
[7]Xia T.Evaluation of Efficiency of Taxi Industry:Effects of TaxiCalling Mobile Apps[C].Transportation Research Board Annual Meeting 94th Annual Meeting,2015.
[8]Hai D J,Yang Y J,Li W F,et al.How the Chauffeured Cars Affect the Taxi Market? A Case Study in Xiamen,China[C].Presented at the 95th Annual Meeting of the Transportation Research Board,Washington,D.C.,2016.
[9]He F,Shen Z J M.Modeling taxi services with smartphonebased ehailing applications [J].Transportation Research Part C Emerging Technologies,2015(58):93-106.
[10]Wang X L,He F,Gao O.Pricing Strategies for an Ehailing Platform in Taxi Service [C].Presented at the 95th Annual Meeting of the Transportation Research Board,Washington,D.C.,2016.
[11]曹 祎,陶竑宇,羅 霞.打车软件使用率对出租车社会福利的影响[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2015,15(3):1-6.
[12]Shi Y,Lian Z.Optimization and Strategic Behavior in a Passengertaxi Service System[J].European Journal of Operational Research,2016(249):1024-1032.
