Clinical observation of traditional Chinese medicine nursing on recovery of gastrointestinal function in patients after abdominal operation
2019-08-30BaoLinYang
Bao-Lin Yang
1Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Liaoning,China.
ABSTRACT
Key words:Traditional Chinese medicine nursing,Patients after abdominal surgery,Gastrointestinal function,Clinical curative effect
1.INTRODUCTION
Clinically,we found that abdominal surgery patients often lead to postoperative gastrointestinal dysfunction due to surgical trauma,anesthesia,intestinal traction and other irritation or intestinal exposure,gauze,dressing covering for a long time or abdominal tear breakage,coupled with abdominal opening to cause heat emission and placement of abdominal drainage tube and other factors,resulting in gastrointestinal dysfunction after operation.The decline of gastrointestinal function is mainly manifested by weakened gastrointestinal motility,disappearance of bowel sounds,abdominal pain,abdominal distension,and stop of exhaustion and defecation [1 - 2].In this case,the patient can only temporarily ban the water,which is not only unfavorable for the recovery of the body,but also prolongs the hospitalization time of the patient,aggravating the patient's physical pain and financial burden,so how to restore gastrointestinal function and reduce complications as soon as possible after abdominal surgery and promoting the early recovery of patients is a major problem faced by medical staff.In response to this situation,our department gave Chinese medicine nursing intervention to 148 patients with abdominal surgery who were admitted from June 2013 to June 2014 on the basis of routine nursing,and achieved satisfactory results.The report is as follows.
2.MATERIALS
2.1 General information
A total of 148 patients who underwent abdominal surgery were selected from the general surgery department of our hospital from June 2013 to June 2014.There were 77 males and 71 females,aged 25 - 64 years old,with an average age of (42.3 ±5.63) years.They were divided into observation group and control group according to the random number table method,with 74 cases in each group.Among the observation group and the control group,29 cases were laparoscopic cholecystectomy,9 cases were radical gastrectomy,31 cases were appendicitis,and 5 cases were after intestinal tumor operation.The data of gender,age,type of surgery and related treatment of abdominal surgery in the two groups were statistically processed,and there was no statistical difference (P> 0.05),which was comparable.
2.2 Inclusion criteria
(1) From June 2013 to June 2014,patients admitted to the general surgery department of our hospital after abdominal surgery.(2) The patients aged less than 75 years had no serious dysfunction of heart,liver,kidney and other important organs.(3) No serious blood system,endocrine system disease or mental disorder.(4) This study passed the ethical review and followed the principle of voluntary informed consent of patients.
2.3 Exclusion standard
(1) The patients suffered from functional gastrointestinal diseases or took gastrointestinal motility drugs within 3 months.(2)There were active bleeding,trauma and other operations within 2 weeks.(3) Hemorrhagic disease or severe heart,liver,kidney,brain and other diseases.
3.METHODS
3.1 Nursing intervention
3.1.1 Control group.The vital signs of the patients were monitored,fasting water,continuous gastrointestinal decompression,nutritional support,correction of acid-base imbalance,disorder of water and electrolyte,early activity and other routine treatment and nursing care.
3.1.2 Observation Group.Acupuncture,application and pointer nursing were added to the control group.(1) Acupuncture treatment:Acupoint:Zusanli (ST36),Sanyijiao (SP6),Tianshu(ST25),Shangjuxu (ST37).The patient was placed in the supine position.After routine disinfection,the 0.32 mm×40 mm needle was used for straight puncturing.The Zusanli (ST36) line was used to supplement the method.The remaining points were used to fill the diarrhea method and the needle was kept for 20 minutes.The needle is taken once every 5 minutes during needle retention,once a day,7 days for a course of treatment.(2) Application:Dahuang(Radix et Rhizoma Rhei)10 g,Mangxiao(Natrii Sulfas)40 g,mix and apply appropriate amount of yellow wine blended and applied to the umbilicus [generally Guanyuan (CV4),Qihai (CV6),Zhongyu (CV12) and other points],cover it with gauze,fix it with tape,and apply it to a hot water bag for 10 minutes,1 time a day,7 days for a course of treatment.(3) Pointer treatment:Take Tianshu (ST25),Zusanli(ST36),Zhongyu (CV12) and other points,applying press method,push method,rub method to wait,each time apply art 5- 10 minutes,everyday 2 times,7 days are a course of treatment.
3.2 Observation index
Six hours after the operation,the bowel sounds,duration of ventilation,and defecation time were recorded every hour.Bowel sound recovery criteria:at least in the two auscultation areas,the bowel sounds are≥3 - 5 times/minute.The time of anal exsufflation is based on the time when the patient first feels that the gas is discharged from the anus.
3.3 Statistical analysis method
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 20.0 statistical software.The measurement data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (),and t-test was used for differences between groups.The count data was analyzed by Chi-square test.P< 0.05 indicates that the difference between the two groups is statistically significant.
4.RESULTS
4.1 Comparison of postoperative gastrointestinal function recovery between the two groups
The recovery time of bowel sounds,the time of first anal exhaust defecation,and the length of hospital stay were lower in the observation group than in the control group,the difference was statistically significant (P< 0.05).(Table1).
4.2 Comparison of postoperative complications between the two groups
The results showed that the incidence of postoperative abdominal pain,bloating,nausea,vomiting and constipation were significantly lower in the observation group than in the control group,and the difference was statistically significant (P< 0.05).See Table2.
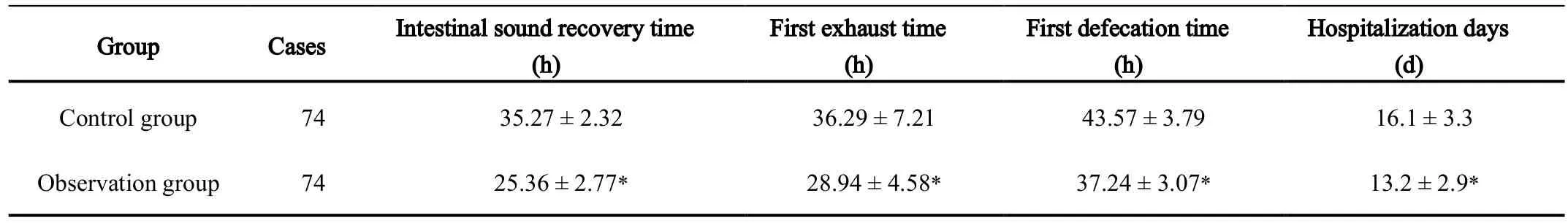
Note:*compared with the control group,P < 0.05
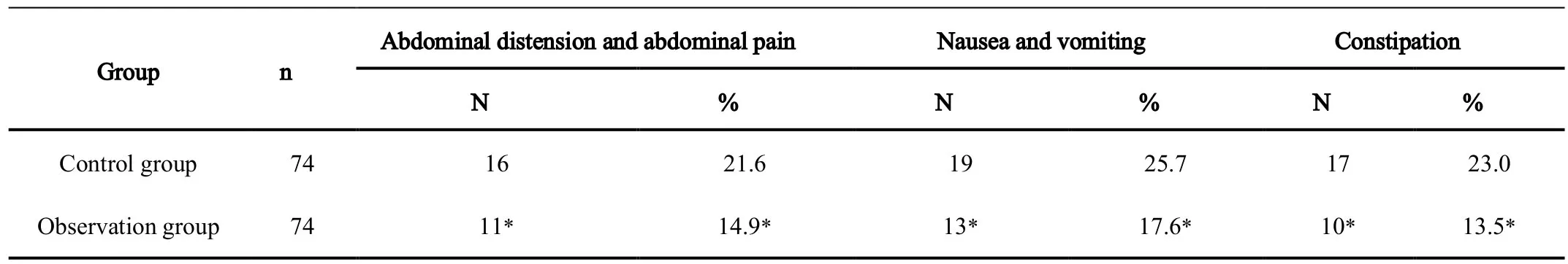
Table2.Postoperative abdominal distension,abdominal pain,nausea,vomiting and constipation in both groups (no shedding cases)
5.DISCUSSION
After abdominal surgery,gastrointestinal dysfunction caused by a variety of reasons,affecting the recovery of the patient's physical function,weakening the intestinal barrier ability,severe cases can lead to intestinal adhesions,intestinal obstruction,anastomotic leakage,abdominal wall incision and other complications.Compared with routine treatment and nursing,traditional Chinese medicine therapy has more advantages in promoting the recovery of gastrointestinal function after operation [1 - 3].In this study,acupuncture therapy,pointer massage and abdominal external application and other nursing measures,so that the bowel sounds recovery time,exhaust,defecation time is significantly shortened,abdominal pain,abdominal distension,nausea and vomiting and constipation and other complications are significantly reduced.Animal experiments show that acupuncture can improve the abnormal ultrastructure of postoperative intestinal mucosal epithelial cells,enhance the defense barrier function of intestinal mucosa,and have an important impact on gastrointestinal mucosal immunity and repair function [4].
5.1 Acupuncture therapy for acupoint selection
This study selected Zusanli (ST36),Sanyinjiao (SP6),Shangjuxu (ST37) and other points.Zusanli (ST36) is a stomach meridian he-sea pointand a stomach lower he-sea point.It has the effects of regulating spleen and stomach,strengthening Qi and activating blood,strengthening and consolidating body resistance.Shangjuxu (ST37) is a large intestine lower he-sea point,which can dredge the intestines and viscera.The Sanyinjiao (SP6) is the point of Taiyin Spleen Channel of Foot,which has the functions of “Invigorate the spleen,and stomach,dissipate dampness,soothe the liver and regulate blood”.Tianshu(ST25) is the alarm point of large intestine.It has the function of regulating intestines and organs,regulating qi,stagnation and digestion.
The above acupoints have the functions of strengthening the spleen and replenishing Qi,regulating stomach descending adverse Qi,promoting Qi to activate blood.Yi YZ,et al.took the abdominal surgery patients Zusanli (ST36),Shangjuxu (ST37),Xiajuxu (ST39),Yanglingquan (GB34),Sanyinjiao (SP6) and other points once a day,each time 30 minutes,5 times for a course of treatment.After 1 - 3 months,the total effective rate of gastrointestinal dysfunction was 93.2% [5].
5.2 Pointer therapy
The pointer stimulates the acupuncture points on the body surface,and is transmitted to the viscera through the meridians to achieve Qi and blood patency,which is beneficial to the recovery of postoperative intestinal peristalsis.Liu J massaged Zusanli (ST36) and Hegu (LI4) on gynecological laparoscopic patients 6 hours after operation,effectively promoted the recovery of gastrointestinal function,reduced the loss of appetite and constipation,and significantly improved the quality of life of patients [6].
5.3 Acupoint application therapy
Acupoint application therapy makes the external application through the fur,meridian and meridians,and achieves the purpose of consolidation of superficies,remove evil by acupoints,and strengthening the body.
Dahuamo(Pulvis rhei)has the effect of Purging heat and dredging intestines,cooling blood and detoxification.Modern research shown that Dahuang(Pulvis rhei)rice vinegar Shenque(CV8) acupoint application feedback to regulate gastrointestinal autonomic nerve function and promote intestinal peristalsis recovery after abdominal surgery [7].
In summary,the combination of routine nursing and traditional Chinese medicine has shortened the anal exhaust and defecation time,accelerated the recovery of gastrointestinal function,reduced the abdominal pain,nausea,vomiting,constipation and other complications,and shortened the hospitalization days.The method is simple and easy to use and is worthy of clinical promotion.
Acknowledgments
None.
Financial support and sponsorship
None.
Patient consent
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
杂志排行
Nursing Communications的其它文章
- The clinical effect observation of gastrointestinal function after colorectal cancer surgery with integrated of Chinese and western medicine nursing methods
- Effect of acupoint application combined with microwave treatment on the intestine barrier functional disturbance of moderately severe acute pancreatitis
- Study on the timing of intervention of gastrointestinal function recovery in patients after laparoscopic cholecystectomy with acupoint application of traditional Chinese medicine
- Effect of moxibustion combined with acupoint application on enteral nutrition tolerance in patients with severe acute pancreatitis