基于阴影域的搜索树检测算法
2019-08-01李小文范艺芳侯宁宁
李小文 范艺芳 侯宁宁
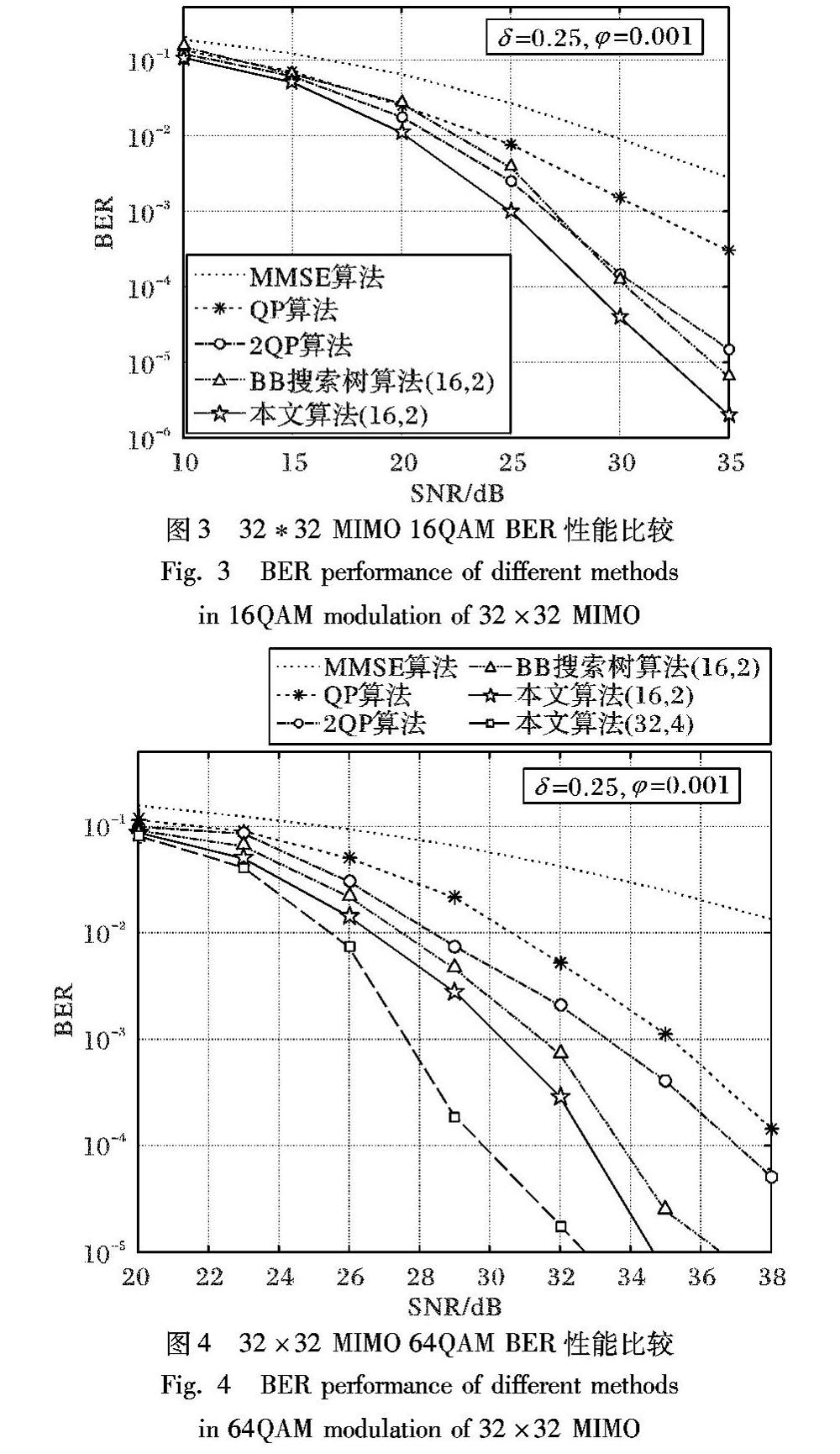
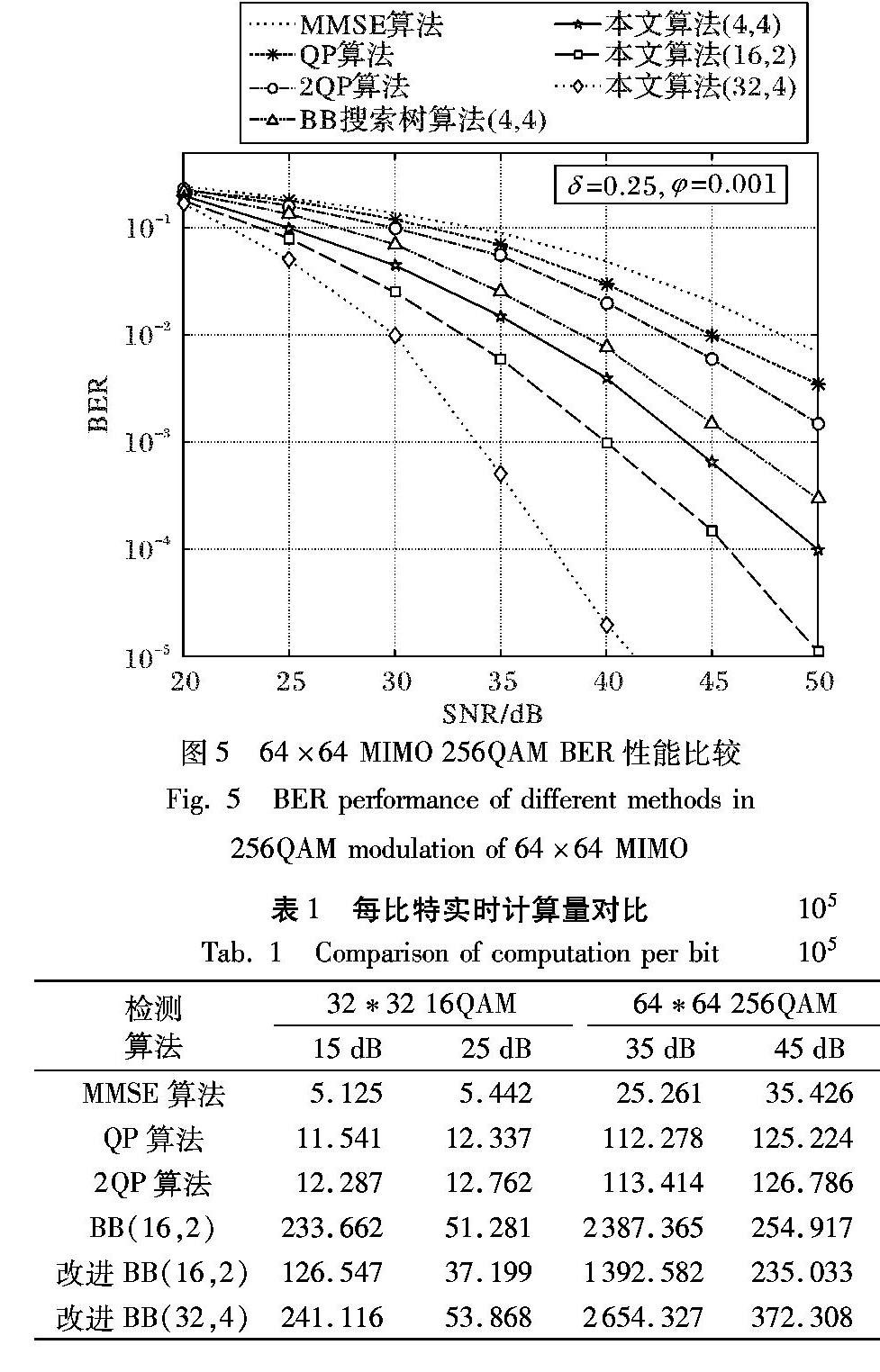
摘 要:大规模多输入多输出(MIMO)系统中,随着天线数目的增加,传统的信号检测算法的检测性能大幅度下降,复杂度呈指数增长,且不适用于高阶调制。针对大规模MIMO场景,基于阴影域思想提出一种结合二次规划(QP)与分支界限(BB)算法的搜索树检测算法。首先,构造QP模型,并针对一阶QP算法后的解向量,提取落入阴影域的不可靠符号; 然后,将落入阴影域的不可靠符号进行BB搜索树检测以求得最优解; 同时,为了降低复杂度,提出三种搜索树修剪策略,在性能和复杂度之间折中选择。仿真结果表明,在大规模MIMO场景下,在调制阶数为6的正交幅度调制(QAM)时,提出的基于阴影域搜索树检测算法比QP算法提升了约20dB的性能增益,在256QAM调制时,比QP算法提升了约21dB的性能增益,验证了算法对高阶调制的适应性,同时,与传统的搜索树算法相比,使用相同修剪策略,复杂度降低了50%左右。
关键词:多输入多输出;二次规划;阴影域;分支界限;高阶调制
中图分类号:TN929.5
文献标志码:A
Abstract: In massive MultipleInputMultipleOutput (MIMO) system, as the increse of antenna number, traditional detection algorithms have lower performance, higher complexity, and they are not suitable for high order modulation. To solve the problem, based on the idea of shadow domain, a search tree detection algorithm combining Quadratic Programming (QP) and Branch and Bound (BB) algorithm was proposed. Firstly, with QP model constructed, the unreliable symbols from solution vector of firstorder QP algorithm were extracted; then, BB search tree algorithm was applied to the unreliable symbols for the optimal solution; meanwhile three pruning strategies were proposed to reach a compromise between complexity and performance. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm increases 20dB performance gain compared with the traditional QP algorithm in 64 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) and increases 21dB performance gain compared with QP algorithm in 256 QAM. Meanwhile, applying the same pruning strategies, the complexity of the proposed algorithm is reduced by about 50 percentage points compared with the traditional search tree algorithm.
英文關键词Key words: MultipleInputMultipleOutput (MIMO); Quadratic Programing (QP); shadow domain; Branch and Bound (BB); high order modulation
0 引言
大规模多输入多输出(MultipleInputMultipleOutput, MIMO)是5G的关键技术之一[1],可实现更高的传输速率,提升系统容量。该系统在信道估计、天线相关性、硬件实现,以及低复杂度的信号检测方面是非常具有研究意义的[2-3]。人们在传统的MIMO系统中提出了许多线性检测和接近最大似然检测算法,例如,在文献[4]提出的多阶段球形译码检测算法与文献[5]提出的Kbest球形检测算法,能够达到近似最大似然(Maximum Likelihood, ML)检测算法的性能,但其复杂度随天线数目和调制阶数的增加呈指数增长;另一方面,低复杂度的检测算法,例如最小均方误差(Minimum Mean Square Error, MMSE)算法,其性能随天线数目的增加而恶化。
针对大规模MIMO系统,为了平衡因天线数目增加而带来的性能流失以及复杂度问题,主动禁忌搜索算法(Reactive Tabu Search, RTS)[6]以及似然上升搜索(Likelihood Ascend Search, LAS)检测算法[7]被提出,它们是基于一些良好的初始向量局部邻域的搜索,例如MMSE向量,当天线数目达到上百时,其也能达到接近单天线的加性高斯白噪声(Additive Gaussian White Noise, AWGN)性能,每个接收向量的复杂度为O(NT3)(NT为发射天线数量),但其性能随调制阶数的增加而恶化。文献[8]提出的似然搜索树检测(Likelihood Based Tree Search, LBTS)算法,相对于传统分支界限(Branch and Bound, BB)搜索树,避免了在每个节点求最优解,而是运用节点选择策略,在每个节点对符号出错概率进行评估,大幅降低了计算复杂度,当调制阶数增加时,性能恶化明显。文献[9]针对大规模多用户多输入多输出(MultiUser MIMO, MUMIMO)系统基站检测复杂度高的问题,提出了一种基于强迫收敛算法的可变节点全信息高斯消息传递迭代检测算法,降低了算法的复杂度,但带来了性能的相对损失,且在高阶调制时,性能流失严重。文献[10]提出的二阶二次规划(Twostage Quadratic Programing, 2QP)算法,在二次规划(Quadratic Programing, QP)的基础上,加入判定标准,对不可靠符号进行2QP算法,相对于一阶QP算法,提高了可靠性。文献[11]结合多种迭代算法,提出适用于大规模MIMO优化的近似迭代检测算法,以增加复杂度来换取迭代的优化,但性能随调制阶数增加而恶化。
本文結合QP与BB搜索树算法[12],并结合阴影域思想,提出一种基于阴影域的搜索树检测算法。首先构造QP模型,针对一阶QP算法后的解向量,提取落入阴影域的不可靠符号;然后将落入阴影域的不可靠符号进行BB搜索树检测;同时,为了降低复杂度,提出三种搜索树修剪策略,可调整修剪方案在复杂度和检测性能之间折中选择。通过仿真验证本文方案在性能和复杂度之间的折中优化以及在高阶调制下的性能优势。
4 结语
本文针对大规模MIMO系统,基于阴影域思想,并结合QP模型与BB搜索树算法,考虑了高阶调制的检测性能,提出了一种基于阴影域的搜索树检测算法:首先,根据ML最优算法模型构造QP算法模型;其次,结合阴影域思想,提取落入阴影域的不可靠符号;然后,将不可靠符号进行搜索树检测;同时,提出三种修剪策略,可以在复杂度和性能之间折中选择,增加了灵活性。仿真结果验证了本文算法不仅提升了性能增益,且可在复杂度和性能之间折中优化,且适用于高阶调制。
参考文献 (References)
[1] SHAFI M, MOLISCH A F, SMITH P J, et al. 5G: a tutorial overview of standards, trials, challenges, deployment and practice[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2017, 35(6): 1201-1221.
[2] YANG S, HANZO L. Fifty years of MIMO detection: the road to largescale MIMOs[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2015, 17(4): 1941-1988.
[3] RUSEK F, PERSSON D, LAU B K, et al. Scaling up MIMO: opportunities and challenges with very large arrays[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2012, 30(1): 40-60.
[4] CUI T, TELLAMBURA C. Approximate ML detection for MIMO systems using multistage sphere decoding[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2005, 12(3): 222-225.
[5] HAN S, CUI T, TELLAMBURA C. Improved Kbest sphere detection for uncoded and coded MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2012, 1(5): 472-475.
[6] DATTA T, SRINIDHI N, CHOCKALINGAM A, et al. Randomrestart reactive tabu search algorithm for detection in largeMIMO systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2010, 14(12): 1107-1109.
[7] LI P, MURCH R D. Multiple output selectionLAS algorithm in large MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2010, 14(5): 399-401.
[8] AGARWAL S, SAH A K, CHATURVEDI A K. Likelihood based tree search for low complexity detection in large MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2017, 6(4): 450-453.
[9] KHAN I. A robust signal detection scheme for 5G massive multiuser MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(10): 9597-9604.
[10] ELGHARIANI A, ZOLTOWSKI M D. Low complexity detection algorithms in largescale MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(3):1689-1702.
[11] TANG C, TAO Y, CHEN Y, et al. Approximate iteration detection and precoding in massive MIMO[J]. China Communications, 2018, 15(5): 183-196.
[12] ELGHARIANI A, ZOLTOWSKI M. Branch and bound with M algorithm for near optimal MIMO detection with higher order QAM constellation[C]// Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Military Communications Conference. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2012: 1-5.
[13] RAO C V. Application of interiorpoint methods to model predictive control[J]. Journal of Optimization Theory & Applications, 1998, 99(3): 723-757.
[14] GONDZIO J. Interior point methods 25 years later[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2012, 218(3): 587-601.
[15] COHEN A I, YOSHIMURA M. A branchandbound algorithm for unit commitment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus & Systems, 1983, PER3(2): 34-35.
