Prediction and Countermeasures for Reuse and Reclamation of Urban Sewage in Ningxia
2019-07-30,2,3*
,2,3*
1. School of Civil Engineering and Hydraulic Engineering, Ningxia University, Yinchuan 750021, China; 2. Engineering Research Center of the Ministry of Education for the Modern Utilization of Modern Agricultural Water Resources in Arid Areas, Ningxia University, Yinchuan 750021, China; 3. Innovation Team of Ministry of Education for Modern Utilization of Modern Agricultural Water Resources in Arid Areas, Ningxia University, Yinchuan 750021, China
AbstractA Logistic equation gray prediction model was established for prediction of reuse and reclamation rate of urban sewage in Ningxia. Based on the data of reuse and reclamation of urban sewage in Ningxia in 2006-2013, it analyzed and predicted the development trend of reuse and reclamation of urban sewage in the whole region of Ningxia. The prediction results indicate that: according to the current development trend, the reuse and reclamation rate of the whole region of Ningxia has become close to saturation, the development space is limited, there is a huge gap with the planned objectives, thus it is required to actively adjust the development strategies. On this basis, the main limiting factors affecting the reuse and reclamation of urban sewage in Ningxia were determined by analytic hierarchy process (AHP) method, in order to provide a reference for the rapid development of reuse and reclamation of urban sewage in Ningxia.
Key wordsLogistic equation gray prediction, Reuse and reclamation rate, Limiting factors
1 Introduction
Urban sewage belongs to potential water resources with stable water volume and reliable supply. As an effective approach to expanding sources, reducing water pollution, improving ecological environment and solving the problem of urban water shortage, recycling of urban sewage is receiving closer and closer attention. Ningxia is located in arid and semi-arid areas. The reuse of reclaimed water has always been a key promotion project in the field of water resources. The reuse and reclamation of urban sewage directly determines the scale and capacity of reuse and reclamation of urban sewage. Limited by many factors, the reuse and reclamation of urban sewage develops slowly in Ningxia. By 2016, compared with the average sewage treatment rate of the whole region (75%), the average reuse and reclamation rate was as low as 14.6%. Therefore, exploring the regional development trend of reuse and reclamation rate of urban sewage, predicting the reuse and reclamation rate and accordingly finding out countermeasures for reuse and reclamation rate of urban sewage are important parts of the development plan for reuse and reclamation of urban sewage. In this study, using the Logistic equation, we firstly established a gray prediction model. Taking the reuse rate of reclaimed water as the gray quantity, based on the data of the recent 10 years, we predicted the reuse rate of sewage reclamation. Besides, combined with the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) method and with reference to the existing research findings, we analyzed main factors limiting the development of reuse of regional sewage reclamation. It is intended to provide a certain reference for planning of full use of urban reclaimed water.
2 Building of Logistic equation gray prediction model
GM (1, 1) gray prediction model is a common prediction method. This method is characterized by less data demand, simple calculation, and high reliability[1-3], so it is widely applied. The Logistic equation has also been widely used in the simulation research and prediction of animal and plant breeding, cultivation, resources, ecological and environmental protection[4]. The Logistic model established with the gray modeling method has the advantage that all parameters can be determined in one time. Due to simple calculation, this solution method is widely used in many literatures[4-6].
The gray GM (1,1) differential equation and Logistic equation are as follows:
(1)
(2)
whereydenotes the growth of reuse and reclamation rate of sewage;Ldenotes the upper limit of growth;bdenotes the free growth rate of reuse and reclamation rate of sewage to be measured;tdenotes the growth time of reuse and reclamation rate of sewage;
Then, we combined equations (1) and (2) together, and applied the gray system theory to make the gray estimation for the parameters of the Logistic equation[5-6], and established the gray prediction model of the Logistic equation. Letx=1/y;B=1/Lin the Equation (2), then we can express the Logistic equation as:
x=B(1+ae-tb)
(3)
Then, we calculated the derivative oftin both sides of Equation (3):
(4)
Ifλ=b,u=Bb, we can express the Logistic equation in the same form as the gray GM (1, 1) prediction model. Namely, the Formula (1). Then, according to the calculation step of the gray GM (1, 1) prediction model, we calculatedλandu, wherexis the reciprocal of the indexyto be measured. The specific steps are as follows:
(λ,u)=(XTX)-1XTxN
(5)
(6)
(7)
According to equations (5), (6), and (7),b=λ,L=1/B=λ/u,a=(L/y0-1)ebt0in Logistic equation, we established the Logistic gray equation prediction model for prediction of reuse and reclamation rate of sewage.
3 Prediction for reuse and reclamation of urban sewage in Ningxia
3.1 Comparison of prediction methodsTaking the data of the reuse and reclamation rate of sewage in the whole region of Ningxia in 2006-2013 as the data for building the model, using the gray GM (1,1) prediction model and Logistic equation gray prediction model, we predicted the reuse and reclamation rate of sewage in the whole region of Ningxia in 2020-2025. Then, we compared the accuracy of two methods. The original data of reuse and reclamation rate of sewage are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Reuse and reclamation rate of urban sewage in the whole region of Ningxia in 2006-2013
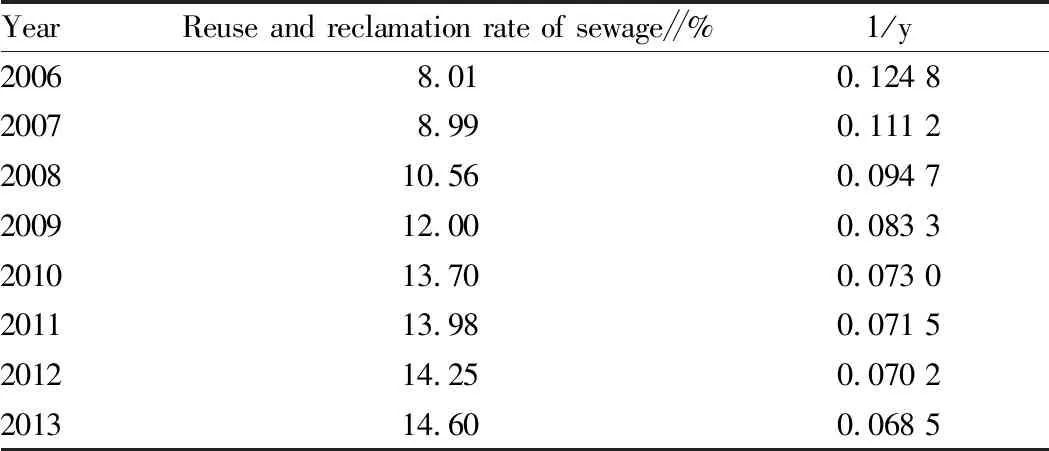
YearReuse and reclamation rate of sewage∥%1/y20068.010.124 820078.990.111 2200810.560.094 7200912.000.083 3201013.700.073 0201113.980.071 5201214.250.070 2201314.600.068 5
In accordance with the above method, the calculation of prediction model is as follows:
3.1.1Gray GM (1,1) prediction model.
Through calculation, (λ,u)=(-0.071, 9.152 4)

=8.018e0.071k-0.008
(8)
According to one time degression, we obtained the simulated value of the reuse and reclamation rate of urban sewage in Ningxia in 2006-2013 (Table 2).
Table 2 Prediction results of gray GM (1,1) prediction model

YearActualvalue∥%GM simulationdata∥%Relativeerror∥%20068.018.01-20078.9910.0712.05200810.5610.812.41200912.0011.613.24201013.712.479.01201113.9813.384.28201214.2514.370.82201314.615.425.65Mean value--5.35
From the calculations in the above table, we can obtain the gray GM (1,1) prediction model simulation results: the relative error was in the range of 12.05-0.82, and the average relative error was 5.35. The model simulation value was close to the actual value, so the accuracy was very high.
3.1.2Logistic equation gray prediction model. Through calculation, (λ,u) =(0.294 249 3, 0.017 198),λ=b=0.294 249 3;L=λ/u=17.109 665;a=(L/y0-1)ebt0, wherey0=8.01,t0=1, thusa=1.524 697.
(9)
The simulation results are shown in Table 3. From the simulation results, the relative error of reuse and reclamation rate of urban sewage in Ningxia was 7.5-0.52 in 2006-2013, and the average relative error was 2.86. The error between model prediction and actual value was smaller than the gray prediction model, so the accuracy of prediction was higher. Thus, the gray prediction model of logistic equation to predict the reuse and reclamation rate of urban sewage in Ningxia is better than the gray GM (1,1) model, as shown in Fig.1.
Table 3 Prediction and test for reuse and reclamation rate of urban sewage in Ningxia by Logistic equation parameter gray modeling method
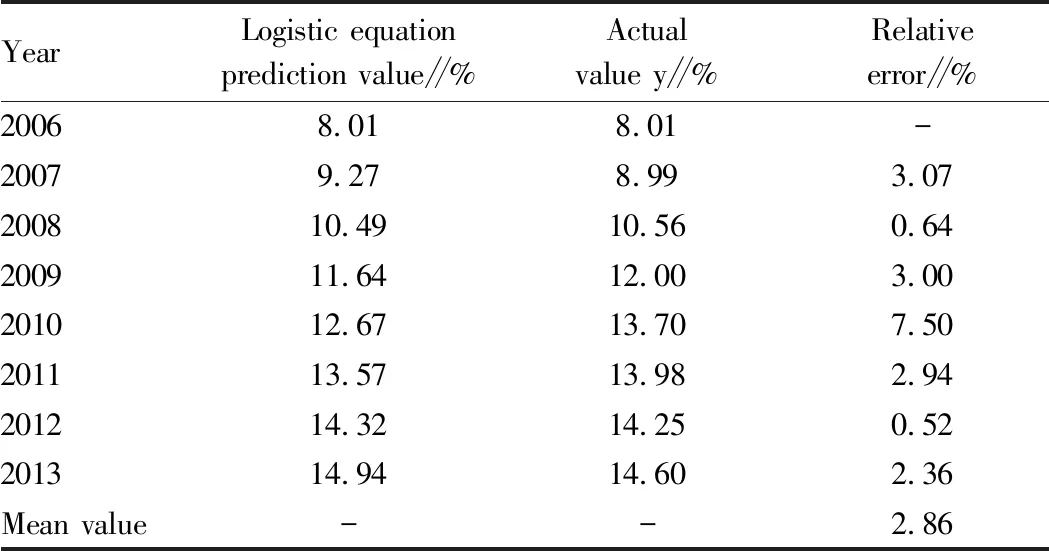
YearLogistic equationprediction value∥%Actualvalue y∥%Relativeerror∥%20068.018.01-20079.278.993.07200810.4910.560.64200911.6412.003.00201012.6713.707.50201113.5713.982.94201214.3214.250.52201314.9414.602.36Mean value--2.86
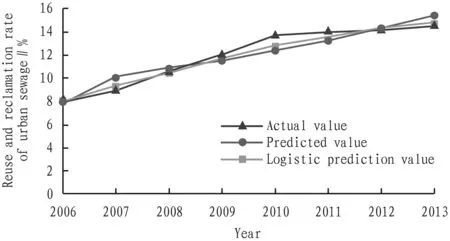
Fig.1 Line chart for prediction of reuse and reclamation rate of urban sewage in Ningxia based on Logistic equation parameter gray modeling method
3.2 Prediction for reuse and reclamation of urban sewage in NingxiaThe accuracy of Logistic equation gray prediction model is higher than that of the simple gray model. Therefore, we used this method to estimate the reuse and reclamation rate of urban sewage in Ningxia in 2020 and 2025. The prediction results are listed in Table 4. Comparing the prediction results and the planned objectives, according to the current development trend, the future development of reuse and reclamation rate in Ningxia will be very slow. It will be only 17% in 2025, showing a huge gap with the planned objectives.
This indicates that the current development trend is far to meet the development requirements. It is required to find out limiting factors, actively improve the current situations, and adjust the development strategies, so as to adapt to the requirements of economic and social development for the reuse and reclamation of urban sewage.
Table 4 Prediction results of reuse and reclamation rate of urban sewage in the whole region of Ningxia in 2020 and 2025

YearLogistic equation gray predictionPlanned objectives[7]202016.69625202517.01330
4 Analysis on factors limiting the reuse and reclamation of urban sewage in Ningxia
According to the above prediction results, for Ningxia, the current development of reuse and reclamation of urban sewage is very slow and is far to meet the development requirements. At such development rate, it is very difficult to realize the planned objectives. Factors influencing the potential of reuse of urban sewage mainly include water resources, economy, technology, policies, and social recognition degree. Specifically, the economic factors mainly set down requirements for decision making of project for reuse and reclamation from the benefits of sewage reclamation. The economic factors considered include: water saving benefit, environmental benefit, and social benefit; the technical condition mainly considers the degree of satisfaction of water volume and water quality required for reuse and reclamation engineering technology[7]. The main indicators include technological advancement, water volume, and water quality guarantee. The reclaimed water reuse project, as secondary use of water resources, belongs to public welfare industry, enjoys the support of government policy and investment and benefit of enterprise operation and management, as well as reasonable water price system. Thus, it is necessary to select investment, operation expenses, and water price factors. Besides, the reclaimed water is the secondary water that is different from fresh water. Whether it can be accepted by common people and widely replace the fresh water are influenced by such social recognition as urban water shortage, general public acceptance, willingness to pay, environmental awareness, so it should be considered separately[7]. In this situation, we established 16 indicators and three hierarchies for the potential of reuse of regional reclaimed water. Through the expert consultation and survey, using AHP, we calculated the combined weight for the influence of each indicator on the factor. The calculation results indicate that the potential of reuse of reclaimed water in Ningxia is mainly influenced by economic benefits, policy support, and regional water shortage, and less influenced by technical feasibility and social recognition. The improvement of construction of urban pipe network system and government investment are decisive factors[7]. Fundamentally, the development of reclaimed water requires the construction of a separate pipe network. Therefore, the degree of perfection of the supporting pipe network still depends on the government investment in environmental protection and the investment capacity of the municipal infrastructure. In the period of the Twelfth Five-Year Plan, the whole society’s environmental investment of the whole region of Ningxia was 23.6 billion yuan, accounting for 2.5% of the GDP in the same period, which was 0.3 percentage points higher than that in the period of the Eleventh Five-Year Plan. The objective of the Thirteenth Five-Year Plan is about 3%. In terms of proportion, the proportion of environmental protection investment in Ningxia has risen from 0.16% in the early stage of reclaimed water development to about 2.5% at present, and it has developed rapidly. However, Ningxia is a small province in China, and its total GDP is still relatively small. On the whole, the government’s policy investment proportion has a higher restriction to the reuse of reclaimed water (Fig.2).
Factors influencing the potential of reuse of urban reclaimed water of Yinchuan City at the target hierarchy are mainly water resource condition (P1), economic benefits (P2), technical feasibility (P3), policy support (P4), and social recognition degree (P5), and their weights were 0.201 8, 0.269 6, 0.197 2, 0.216 2, and 0.115 2, respectively. These indicate that the potential of reuse of reclaimed water in Yinchuan City is mainly influenced by economic benefits, policy support, and Yinchuan City water shortage, and less influenced by technical factors and social recognition. From the perspective of the three-level evaluation indicators, the evaluation results show that the urban pipe network system, investment, benefits and safety reliability indicators are major factors influencing the utilization of reclaimed water resources in Yinchuan City, especially the pipe network supporting situation and investment, the sum of both weights was up to 0.216, belonging to the decisive factors. These indicate that the potential of use of reclaimed water in Yinchuan City is greatly influenced by these two factors.
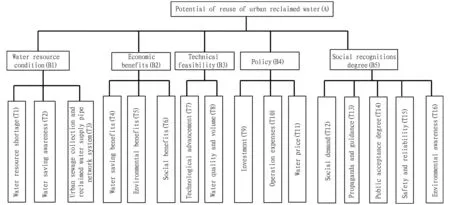
Fig.2 Potential of reuse of urban reclaimed water
5 Conclusions
(i) Gray GM (1,1) prediction model and Logistic equation gray prediction model based on the gray system theory require less data, the calculation is simple, and the prediction result is very accurate. (ii) From the perspective of prediction results: both prediction models meet the accuracy requirements. Especially, the relative error of Logistic equation gray prediction is smaller than that of the gray GM (1,1) model, the accuracy is the highest, and the model simulation value is the closest to the actual value. According to the prediction results of the model, at the current development status and trend, the upper limit of reuse rate of reclaimed water is only 17.2%. However, the reuse rate has been close to 15% in 2014, indicating that the space for the growth of the reuse rate is very limited. (iii) Compared with the planned objective value, the results of both prediction models are much lower, indicating that for Ningxia, it is far insufficient to realize rapid development of reuse of sewage reclamation at the current development scale and trend. The development of reuse of reclaimed water mainly experiences four stages: starting stage, growth stage, mature stage, and saturation stage. At present, the development has become close to the saturation stage. Therefore, the internal adjustment and rapid development of the reuse system of the urban sewage reclamation system will be the main and difficult works of the current reuse of the sewage reclamation in Ningxia. Otherwise, it is very difficult to guarantee the realization of the planned objectives. (iv) Many development factors influence the reuse and reclamation of urban sewage, such as policy investment, treatment capacity of sewage treatment plants, collection capacity of urban drainage, supporting pipe network construction for reuse of reclaimed water, and residents’ recognition and acceptance degree of the reuse of reclaimed water,etc. Through analysis, it is found that factors influencing the reuse of reclaimed water of urban sewage in Ningxia mainly include the perfection degree of urban supporting pipe network and government investment, and their development speed depends on the government’s investment in environmental protection and the investment capacity of urban infrastructure investment. Therefore, it is recommended to make larger investment to improve the big environment of reuse of reclaimed water, promote the development of reclaimed water, so as to match the regional water resource status and economic and social development.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Personnel Cultivation Program for Innovative and Entrepreneurial Biopharmaceutical Discipline under the Credit System
- Poverty Alleviation Model of "Three Stresses and Three Commentaries" to Stimulate Endogenous Motivation in Xundian County
- Study on Cost of Environmental Degradation Based on Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Study on Agricultural Intellectual Property Protection and High-Quality Development of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Ginseng
- Cost-benefit Analysis of Land Development Projects Based on Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Model
- Does Rapid Urbanization Trigger Significant Increase of Cumulative Heavy Rains in China?
