微晶化处理对Fe-Cr合金氧化性能的影响
2019-07-22马静王晓婕王瑞阳
马静 王晓婕 王瑞阳
摘要:为提高Fe-Cr合金的抗高温抗氧化性能,采用电火花沉积技术对不同Cr含量的Fe-Cr合金表面进行微晶化处理,研究了铸态和微晶化合金在900 ℃空气中的抗高温氧化行为。氧化动力学曲线、物相分析、表面和截面形貌表明,当Cr含量较低时,微晶化处理提高了Cr的扩散速度,但不足以生成连续的氧化膜,氧化性能变差;当Cr含量较高时,微晶化处理降低了形成保护性氧化膜的临界含量,微晶化处理的Fe-9Cr和Fe-13Cr合金抗氧化性能明显提高。微晶化处理Fe-13Cr合金的抗高温氧化性能最好,这是由于微晶化处理后13%(质量分数)的Cr可以形成连续致密的保护性氧化膜。因此,微晶化处理是提高材料抗高温氧化性能的有效方法,可应用于高温氧化领域。
关键词:材料失效与保护;微晶化处理;Fe-Cr合金;高温氧化; 电火花沉积; 氧化动力学
中圖分类号:TG17432文献标志码:A
MA Jing, WANG Xiaojie, WANG Ruiyang.Effect of microcrystallization on the oxidation resistance of Fe-Cr alloy[J].Journal of Hebei University of Science and Technology,2019,40(3):259-264.Effect of microcrystallization on the oxidation
resistance of Fe-Cr alloy
MA Jing1,2, WANG Xiaojie1, WANG Ruiyang1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Hebei University of Science and Technology, Shijiazhuang, Hebei 050018, China; 2.Hebei Key Laboratory of Material Near-Net Forming Technology, Shijiazhuang, Hebei 050018, China)
Abstract:In order to improve the high temperature oxidation resistance of Fe-Cr alloy, cast Fe-Cr alloys with different Cr contents are treated by electrospark deposition to get microcrystalline structure. The oxidation behavior of as-cast and microcrystalline Fe-Cr alloys at 900 ℃ in air is studied. Oxidation kinetics curves, phase analysis,surface and cross section morphology results show that the diffusion rate of chromium is enhanced by microcrystallized treatment when Cr content is low. Yet the content of Cr is not enough to form continuous oxide film so that the oxidation resistance of Fe-5Cr alloy is decreased. The critical Cr content to form protective oxide scale is reduced by microcrystallized treatment when Cr content increases. The oxidation resistance of microcrystalline Fe-9Cr and Fe-13Cr alloys is obviously improved. The high temperature oxidation resistance of microcrystalline Fe-13Cr alloy is the best, which is due to the formation of continuous dense protective oxide scale on the surface after microcrystallized treatment. Therefore, Microcrystallization treatment is an effective way to improve high temperature oxidation resistance of materials which can be applied in the field of high temperature oxidation.
Keywords:materials failure and protection; microcrystallization; Fe-Cr alloy; high temperature oxidation resistance; electrospark deposition; oxidation kinetics
合金在高温下的抗氧化性能通常取决于表面是否能形成选择性氧化膜。致密、稳定、缓慢生长以及附着性良好的氧化膜,如Al2O3,Cr2O3或SiO2,将有效降低氧化速率,防止合金氧化[1-2]。表面处理可改变氧化初期氧化膜的生成,从而改善高温氧化性能[3-9]。其中微晶化处理是改善合金抗高温氧化性能的重要途径[10-13]。电火花沉积技术工艺简单、加工成本低,热输入量低,沉积层残余应力低,产生的变形也小,基体与沉积层为冶金结合,能够在较低温度下快速凝固,从而在表面获得微晶结构的合金[14-18]。
河北科技大学学报2019年第3期马静,等:微晶化处理对Fe-Cr合金氧化性能的影响Fe-Cr合金具有良好的耐高温、耐腐蚀性能,被广泛地应用到各个领域[19-20]。含Cr量不同,合金的抗高温氧化性能也不同。在常温下,通常Fe-Cr合金表面形成保护性的钝化膜需要Cr含量最低为13%(质量分数,下同),然而在高温下,即使13%的Cr含量的Fe-Cr合金抗高温氧化性能仍然较差。微晶化处理可改变合金的氧化行为,本文采用电火花沉积法对不同Cr含量的Fe-Cr合金表面进行微晶化处理,并研究其抗高温氧化性能的差异。
1实验方法
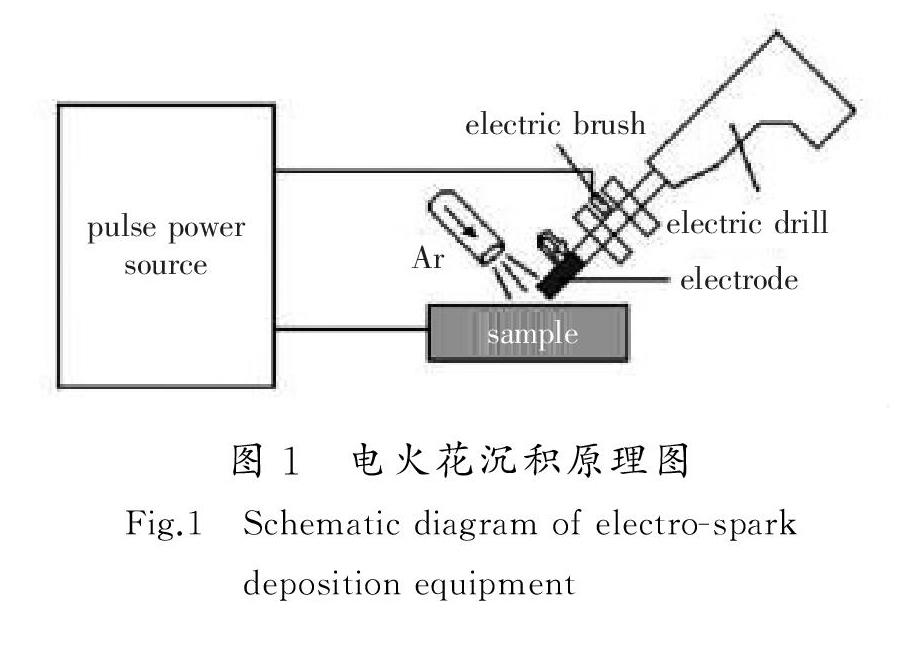
Fe-Cr合金由纯度为99.9%(质量分数,下同)的Fe和纯度为99.95%的Cr用非自耗真空电弧炉反复熔炼3次,得到Cr理论含量分别为5%,9%,13%的Fe-Cr合金,经800 ℃扩散退火12 h使成分均匀化,Cr实际含量分别为4.88%,9.28%,12.69%。将熔炼好的合金锭线切割成尺寸为10 mm×5 mm×1 mm的片状试样,用丙酮超声波清洗后,分别采用280#,600#,800#砂纸打磨,为微晶化处理做准备。将合金锭线切割Φ3 mm×40 mm棒状Fe-Cr合金,在片状铸态合金表面采用同种成分的棒状电极进行电火花微晶化处理,如图1所示。
将铸态和微晶化处理(以下简称微晶化)的Fe-Cr合金在900 ℃空气中进行100 h的高温循环氧化实验。为减小误差,实验前将坩埚放入900 ℃热处理炉中10 h,达到恒重。将Fe-Cr合金试样放入坩埚,在热处理炉中进行氧化实验,每隔10 h取出,静置20 min后采用精度为0.000 1 g的电子天平称量“坩埚+试样”以及空坩埚的质量,得到氧化动力学曲线。
用扫描电镜观察铸态和微晶化Fe-Cr合金的表面氧化膜和截面形貌,采用XRD对氧化膜进行物相分析。
2结果与讨论
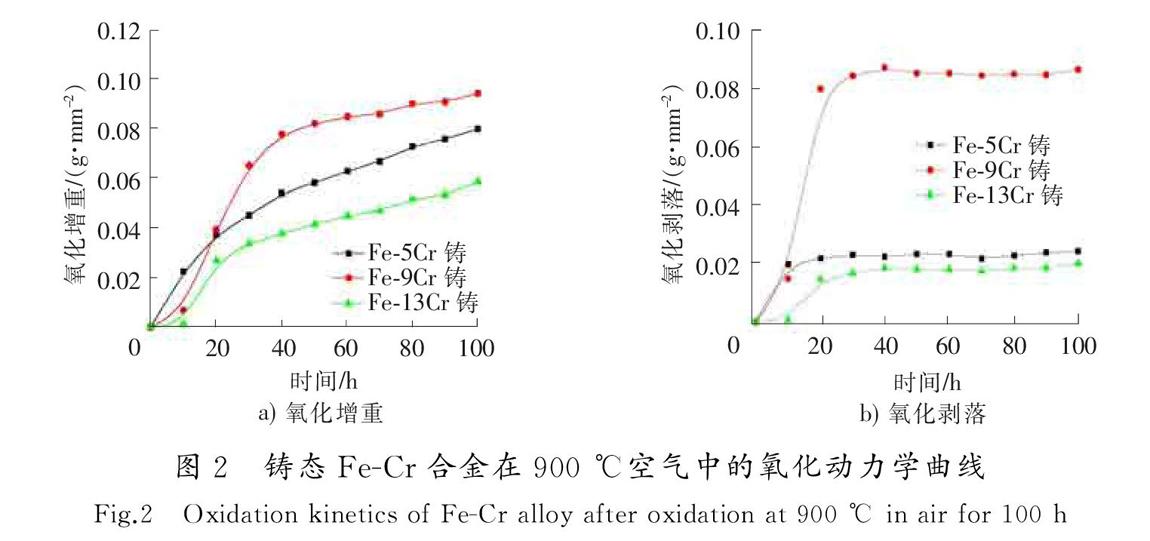
图2—图3分别为铸态和微晶化Fe-Cr合金高温氧化的动力学曲线。铸态和微晶化合金氧化规律相似。铸态合金氧化增重和氧化剥落由高到低为Fe-9Cr,Fe-5Cr,Fe-13Cr。随着Cr含量的增加,合金抗高温氧化性能先降低后增加,这是因为在合金表面形成了不同类型的氧化膜。当Cr含量较低(5%~9%)时,表面生成了以氧化铁为主的氧化膜,内层形成了氧化铁和铁铬尖晶石类的氧化层,不能有效地抑制氧向合金内部扩散,随着Cr含量增加,内氧化加剧,因此氧化速率增加。当Cr含量较高(13%)时,表面仍生成2层氧化膜,外层为氧化铁,内层为铁铬尖晶石类的氧化层,内层氧化膜具有较强的保护作用,可以有效地阻止氧向合金内部扩散,因此氧化速率降低。
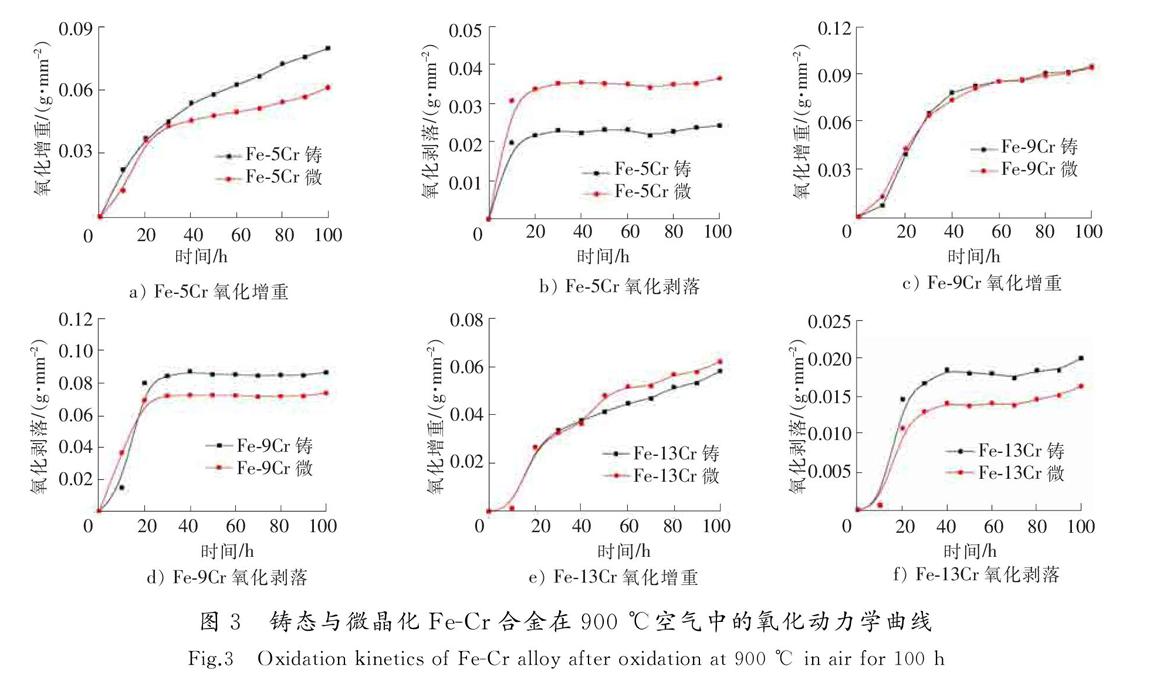
与铸态相比,微晶化Fe-5Cr合金氧化增重降低,氧化膜剥落量增加;微晶化的Fe-9Cr和Fe-13Cr合金氧化增重基本和铸态相当,氧化膜剥落量明显降低。微晶化处理可以降低发生选择氧化所需的Cr的临界含量,因此微晶化Fe-9Cr和Fe-13Cr合金的抗高溫氧化性能较铸态合金得到了改善。Cr含量较低时,微晶化处理后表面生成了很多的晶界,增加了氧向合金内部扩散的通道,因此抗高温氧化性能变差。
图4—图6为铸态及微晶化Fe-Cr合金在900 ℃氧化100 h后的表面SEM形貌。铸态和微晶化Fe-Cr合金表面均形成了Fe的氧化膜,其形貌却相差较大。铸态Fe-5Cr合金表面氧化膜不致密,表面可以看到较多的孔隙,Fe-9Cr和Fe-13Cr合金表面形貌比较相似,表面均形成了较为厚实的Fe2O3膜,Fe-9Cr合金表面的缝隙较多,Fe-13Cr合金表面较为密实,存在少量的缝隙。截面照片(见图7)显示Cr含量为9%的Fe-Cr合金表面形成的氧化膜较厚,而含量为5%和13%的氧化膜较薄,这是因为Cr含量为9%时,不能形成有效的保护膜,而相对于5%含量而言,Cr含量较多,在900 ℃,Cr的氧化速度比Fe快,所以氧化膜较厚。
微晶化Fe-Cr合金表面氧化膜不平整,微晶化Fe-5Cr合金表面生成了较多片状氧化物,氧化膜不致密,Fe-9Cr合金氧化膜很不平整,上面有较多的微孔,Fe-13Cr合金表面膜较为致密,孔隙少。截面照片(见图8)显示,与铸态相比,微晶化Fe-5Cr和Fe-13Cr合金氧化膜较薄,Fe-9Cr合金氧化膜较厚。与铸态相比,微晶化处理的作用在于细化后的晶粒间较多晶界的存在,提高了Cr原子的扩散,有助于形成保护性的氧化膜(Cr2O3)。
对于Fe-Cr合金而言,900 ℃的氧化温度比较高,可以看到合金表面都生成了较厚的氧化膜,XRD分析(见图9)表明,表面氧化膜的主要成分为Fe2O3,并没有看到有Cr2O3的峰。这是因为表面生成的Fe2O3膜较厚,XRD检测只能检测到表面的氧化物。
3结论
采用电火花沉积方法在Fe-5Cr,Fe-9Cr和Fe-13Cr合金表面沉积了同种成分的微晶化涂层,并进行了900 ℃循环氧化动力学测试、XRD分析以及表面和截面的形貌观察,结果表明:
1)当Cr含量较低时,微晶化处理提高了Cr的扩散,微晶化晶界增加了氧向合金内部扩散的通道,微晶化处理的Fe-5Cr合金表面不能形成连续的保护性氧化膜,抗高温氧化性能较差;
2)微晶化处理可以降低发生选择氧化所需的Cr的临界含量,有利于生成连续的保护性氧化膜,微晶化处理的Fe-9Cr和Fe-13Cr合金的抗高温氧化性能较铸态合金得到了明显改善。微晶化处理的Fe-13Cr合金抗高温氧化性能最佳;
3)微晶化处理是提高合金抗高温氧化性能的有效途径,电火花沉积微晶涂层可望应用于高温氧化领域。
参考文献/References:
[1]朱日彰,何业东,齐慧滨. 高温腐蚀及耐高温腐蚀材料[M]. 上海:上海科学技术出版社,1993: 160-193.
[2]WAGNER C. Formation of composite scales consisting of oxides of different metals[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1956(11): 627-633.
[3]马静, 何业东, 胡建文,等. 喷丸及退火处理对1Cr18Ni9Ti合金抗高温氧化性能的影响[J]. 河北科技大学学报, 2005, 26(2): 130-132.
MA Jing, HE Yedong, HU Jianwen, et al. Effect of annealing on the oxidation behavior of peened 1Cr18Ni9Ti alloy[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2005, 26(2): 130-132.
[4]马静, 陈维视, 何业东.电沉积-热解法制备Ce2O3薄膜的抗氧化性能研究[J].河北科技大学学报, 2006, 27(3): 224-226.
MA Jing, CHEN Weishi, HE Yedong. Effects of thin Ce2O3 coating on the oxidation resistance[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2006, 27(3): 224-226.
[5]马静,郭俐聪, 张彦超, 等. 喷丸处理对1Cr13 钢选择氧化的作用[J].河北科技大学学报, 2007, 28(3): 226-229.
MA Jing, GUO Licong, ZHANG Yanchao, et al. Effects of shot peening on the selective oxidation of 1Cr13 alloy[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2007, 28(3): 226-229.
[6]马静, 何业东, 王文青, 等. 喷丸与ZrO2/Al2O3 叠层对Cr5Mo 合金高温氧化性能的影响[J]. 河北科技大学学报, 2004, 25(4): 33-36.
MA Jing, HE Yedong, WANG Wenqing, et al. Effect of shot peening and ZrO2/Al2O3 terrace coating on the high-temperature oxidation resistance of Cr5Mo alloy[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2004, 25(4): 33-36.
[7]馬静, 何业东, 王俊, 等. Y2O3薄膜处理对3Cr25Ni7N合金的抗高温氧化性能的影响[J].中国稀土学报, 2007, 25(6): 765-768.
MA Jing, HE Yedong, WANG Jun, et al. Effect of Y2O3 thin film on oxidation resistance of 3Cr25Ni7N alloy[J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2007, 25(6): 765-768.
[8]马静, 孟凡曼,焦世坤. 电沉积-热解法制备Cr2O3薄膜及其抗高温氧化性能[J]. 材料保护, 2015, 48(4): 30-32.
MA Jing, MENG Fanman, JIAO Shikun. Preparation of Cr2O3 film on stainless steel by electrodeposition-pyrolysis method and evaluation of high-temperature oxidation resistance[J]. Material Protection, 2015, 48(4): 30-32.
[9]马静, 孟凡曼. 电沉积-热解法制备的Al2O3薄膜的抗高温氧化性能研究[J]. 河北科技大学学报, 2015, 36(4): 413-418.
MA Jing, MENG Fanman. Research on oxidation resistance of Al2O3 thin film prepared by electrodeposition-pyrolysis[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2015, 36(4): 413-418.
[10]YAO Hongrui, BAO Zebin, SHEN Mingli, et al. A magnetron sputtered microcrystalline β-NiAl coating for SC superalloys. Part Ⅱ. Effects of a NiCrO diffusion barrier on oxidation behavior at 1 100 ℃[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 407: 485-494.
[11]LI Yuanshi, NIU Yan, GESMUNDO F, et al. Grain size effects on the oxidation of two-phase Cu-Fe alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 2002,44(7): 1457-1468.
[12]侯少军. 磁控溅射β-NiAl微晶涂层的制备与其在1 100 ℃下抗高温氧化行为的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学,2015.
HOU Shaojun. Fabrication and Oxidation Behavior of A Magnetron Sputtering Microcrystalline-NiAl Coating at 1 100 ℃ in Air [D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2015.
[13]MA Jing, HE Yedong, WANG Deren, et al. Oxidation of two-phase Cu-50 Cr alloy at low oxygen pressure[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2006,434(1/2): 141-146.
[14]MA Jing, HE Yedong, GAO Wei, et al. The effect of micro-crystallizing on the oxidation resistance of Cu-Cr alloy in air[J].Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2008, 488(1/2): 311-317.
[15]MA Jing, HE Yedong, SUN Baode, et al. The oxidation of micro-crystalline Co-Cr alloys under balanced oxygen pressure of Co2O3/Co powders[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2008, 202(1/2/3): 457-463.
[16]馬静,何业东,王俊,等. 电脉冲沉积铝化物微晶涂层的高温腐蚀行为[J].中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(1): 13-18.
MA Jing, HE Yedong, WANG Jun, et al. High temperature corrosion behavior of microcrystalline aluminide coatings by electro-pulse deposition[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008,18(1): 13-18.
[17]MA Jing, HE Yedong, WANG Jun, et al. High temperature corrosion behaviour of microcrystalline aluminide coating on Q235 steel[J]. Corrosion Engineering Science and Technology, 2009, 44(2): 157-160.
[18]XU Qiang, HE Yedong, QI Huibin, et al. Oxidation behavior of micro- and nano-crystalline coatings deposited by series double-pole electro-pulse discharge[J]. Materials Letters, 2002, 56(1/2): 85-92.
[19]王志民, 刘光明, 吴世强, 等. 热处理对S30432喷丸不锈钢抗高温水蒸汽氧化性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2019,40(2): 124-132.
WANG Zhimin, LIU Guangming, WU Shiqiang, et al. Effect of heat treatment on high temperature steam oxidation resistance of shot blasted S30432 stainless steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2019,40(2): 124-132.
[20]MA Jing, HE Yedong, WANG Deren, et al. The effects of pre-oxidation and thin Y2O3 coating on the selective oxidation of Cr18-Ni9-Ti steel[J].Materials Letters, 2004, 58(5): 807-812.第40卷第3期河北科技大学学报Vol.40,No.3
2019年6月Journal of Hebei University of Science and TechnologyJune 2019
