Delimitation and Zoning of Natural Ecological Spatial Boundary Based on GIS
2019-06-27YonghaoWANG1HengjiLI2JunREN
Yonghao WANG1*, Hengji LI2, Jun REN
1. Gansu Academy of Natural Resources Planning, Lanzhou 730000, China; 2. Global Change Research Information Center, Lanzhou Information Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou 730000; 3. Qinghai University, Xining 810016, China
Abstract In order to improve the control of land use in China, taking Sunan Yugur Autonomous County in the Qilian Mountains area as an example, this paper explores the method of national ecological space delimitation and zoning based on ARCGIS platform. Three kinds of space division techniques are formed to unify natural resources survey data, carry out land spatial suitability evaluation, delimit three kinds of space and optimize natural ecological space division. According to existing laws in China, based on ecological protection red line, natural ecological space is divided into ecological protection red line and general ecological space. According to the regulation requirements and the functional division of various protected areas, the red line area of ecological protection is divided into core protected area, ecological restoration area, traditional utilization and recreation area with the area of 3 947.28, 3 216.89 and 6 936.56 km2, respectively. In view of the prominent problems in the process of delimitation and zoning of natural ecological space, some suggestions are put forward, such as unification of chassis, optimization of ecological protection red line and coordination and unification of management boundary.
Key words Territorial space, Natural ecological space, Ecological protection red line, General ecological space
1 Introduction
The establishment of the Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China marks that the land use control system has been upgraded to an unprecedented national strategic level[1]. The existing land space use control mainly focuses on land use control system, forest and wetland management system, grassland, water area management system, urban and rural construction planning permit system, various nature reserves, parks and scenic spots management system,etc. It only covers cultivated land, forest land, urban and rural construction land,etc., and has not covered all natural ecological space such as natural reserves and tidal flats[2-4]. Therefore, it is of great significance to conduct in-depth research on the natural ecological space control system. At present, relevant research pays more attention to the investigation and evaluation of natural resources, the registration of rights, the regulation of use, the management of assets, and the supervision, lacking the research on the method of delimitation of ecological space boundaries. The delimitation of natural ecological space boundaries is the basis for the regulation of natural ecological space use[5-8]. Qilian Mountain is a water conservation area in the Hexi Corridor and the western part of Inner Mongolia. It is also an important ecological security barrier in western China. Sunan Yugur Autonomous County is a key county for the rectification of ecological and environmental problems in Qilian Mountain. Currently, affected by factors such as temperature changes, human life and production activities, the natural ecological environment is deteriorating and the carrying capacity of eco-system is declining year by year. Taking Sunan Yugur Autonomous County in Qilian Mountain area as an example, this paper explores the method of delimitation of natural ecological space boundaries, so as to provide a basis for improving the control of the use of natural ecological space and provide reference for the establishment of land space zoning methods.
2 Overview of study area
Sunan Yugur Autonomous County is named after its location in the south of Suzhou (Jiuquan), and is the only Yugur autonomous county in China. It is located in the northeast of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, the middle of the Hexi Corridor and the north foothill of the Qilian Mountain. The east-west length is 650 km, and the south-north width is 120-200 km, with the total area of about 20 100 km2, accounting for 75% of the total area of the northern foothill of Qilian Mountain and 59% of the total area of the Qilian Mountain National Nature Reserve. There are only 37 800 people. The area is sparsely populated, but resources such as minerals, water conservancy and tourism are abundant.
3 Data sources and research methods
3.1 Data sourcesLand use master plan data, permanent basic farmland delimitation data and geological park data are derived from Gansu Academy of Natural Resources Planning, and other data such as resource and environmental survey evaluation data, national park data, ecological protection red line delimitation data and urban development boundary delimitation data are derived from Land Resources Bureau of Sunan Yugur Autonomous County and related functional departments. The positioning information of various vector, taster and graphic data is unified using the 2000 national geodetic coordinate system.
3.2 Research methodsThe first is to unify natural resource survey data. Based on the latest land use change data, using image interpretation as a guideline, assisted by geographical condition survey data, forestry survey data, grassland survey data, forest tenure scope and grassland use right scope, focusing on the overlap of forest and grassland, the land use change data are corrected, adjusted and supplemented using the literature method, interview method and field survey method to finally form the natural resource survey data.
The second is to carry out the evaluation of land space suitability. Based on the status of land and resources, the importance of ecological functions is evaluated from three aspects: ecological protection bottom line, importance of ecosystem services and ecological sensitivity. The suitability of agricultural functions is evaluated from the suitability of agricultural production and the suitability of rural settlements. The evaluation of urban construction suitability is carried out in terms of topography, geographical hazards, agricultural production restrictions, ecological protection restrictions, urbanization possibilities and location conditions.
The third is to delimit three types of space. First, one the basis of obtaining three types of functional suitability level maps, following the rules of " suitability → ecology→ agriculture", the dominant function of each unit is determined using superposition analysis to identify the three types of space. Second, cluster analysis of the three types of special units is carried out using the composite functional grid method to maintain the continuity and integrity of the space. Third, the overall strategy, goals and structure of the national land space are implemented. The development orientation, agricultural development characteristics and urban development law of each region are fully considered. Combined with the main function positioning, the grid layout of the ecological space is divided. Finally, based on the grid layout, the three types of space are refined into a natural resource survey database of 1∶10 000.
The fourth is to optimize the natural ecological space delimitation. Taking the ecological protection red line as the basis of the natural ecological space, the ecological space within and outside the red line is distinguished. At the same time, according to the regulatory requirements stimulated by existing laws and regulations and the functional division of various types of protected areas, the space within the red line is further divided into core protected area, ecological restoration area and traditional utilization and recreation area (Fig.1).
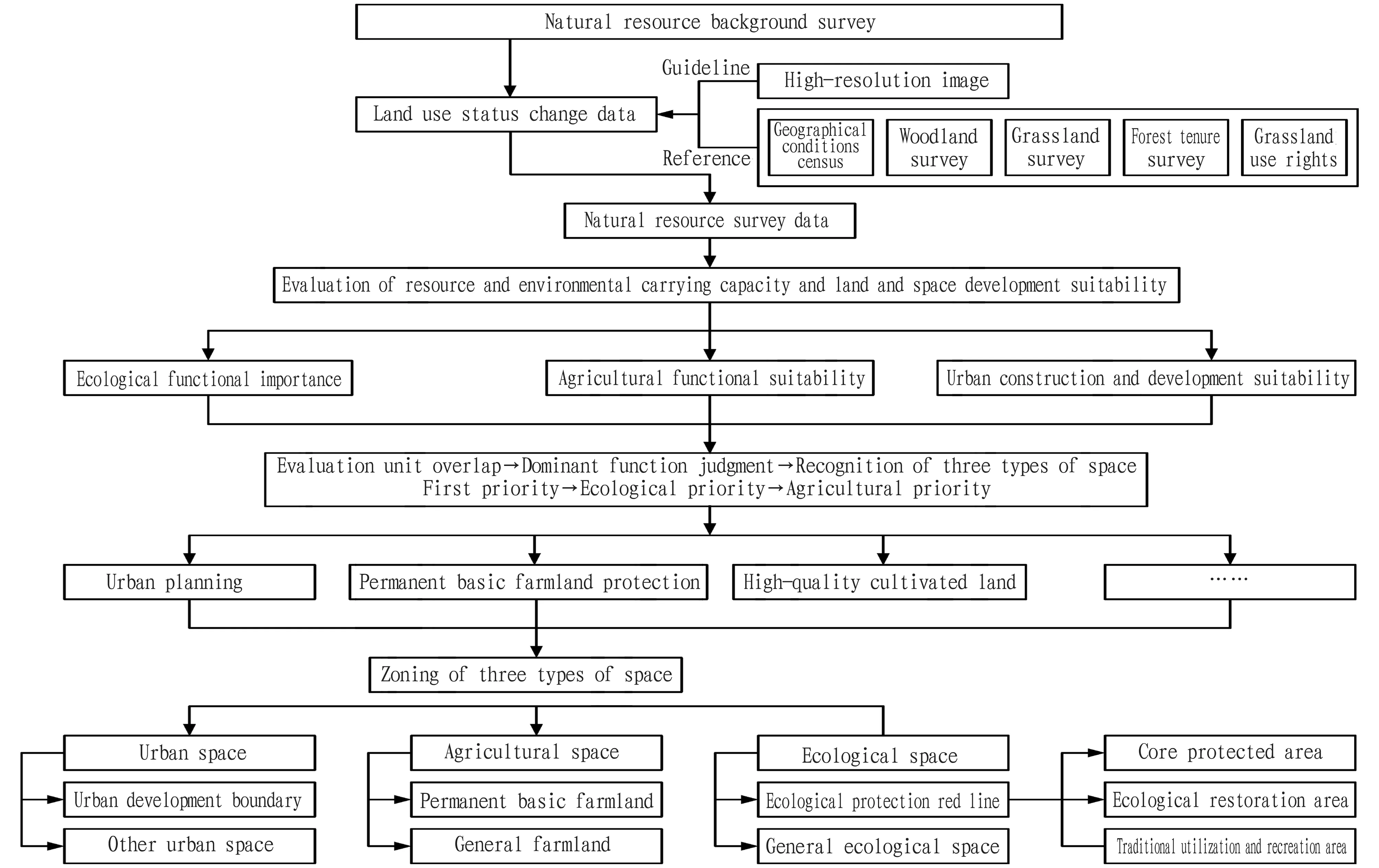
Fig.1 Delimitation of three types of space
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Unified natural resources survey dataThe various vector, raster and graphic data are positioned to the 2000 national geodetic coordinate system according to the uniform rules. Proofreading verification of land use change data was performed using ArcMap 10.4. According to theCurrentLandUseClassificationofChina(GBT21010-2017)[9], the natural resource survey data are finally formed. Among them, the area of cultivated land, garden land, forest land, grassland, urban village and industrial and mining land, transportation land, water and water conservancy facility land and other land is 136.35, 0.33, 2 790.26, 14 375.09, 20.48, 35.02, 927.08 and 1 890.08 km2, respectively.
3.2 Space suitability evaluationThe ecological function importance evaluation selects the natural reserve, ecological protection red line, NDVI index, important ecological land, river sensitivity and water source sensitivity as the indicators. In the evaluation of the importance of ecological functions, the bottom line of ecological protection is the highest level of ecological importance. The importance of ecosystem services, ecological sensitivity and ecological restoration necessity are based on the barrel principle, which determines the final suitability level according to the "short board" level of the factor. According to the evaluation system of the importance of ecological functions of land and space (Table 1), the ecological function suitability of Sunan County is divided into four levels: more important, important, less important and unimportant. The area is 15 641.13, 4 479.79, 1.77 and 52.02 km2, respectively.
Table 1 Evaluation system of importance of land spatial ecological function

Target layerSystematicnessIndicator layerIndicator classificationScoreEcological Bottom line of ecological protectionNature reserve D1Protected area1functional Non-protected area4suitabilityEcological protection red line D2Within the ecological protection red line1Outside the ecological protection red line4Importance of ecological services(NDVI index) S1 0.8-1.010.6-0.820.4-0.630-0.44Ecological sensitivityImportant ecological land M1Woodland, pasture land, wetland1Ecologically vulnerable area2Others4River sensitivity M2Area within 100 m1Area 100-200 m far2Area 200-300 m far3Area more than 300 m far4Water source sensitivity M3Water source and buffer zone within 500 m1Buffer zone within 500-1 000 m2Buffer zone within 1 000-2 000 m3Area more than 2 000 m4
Note: "1" represents more important, "2" represents important, "3" represents less important, and "4" represents unimportant. The same below.
The suitability evaluation of agricultural functions includes the suitability of agricultural production and the suitability of rural settlements. Agricultural production suitability evaluation selects permanent basic farmland protection area, cultivated land, garden land, pasture land, reserve resources, soil pollution level,etc. as indicators. The suitability evaluation of rural settlements selects slope, active faults, geological hazards hidden danger point, ecological and agricultural production restriction, urbanization possibility,etc. as the indicators. The agricultural production suitability level map and the rural settlement level map are combined into a level map of agricultural functional suitability. According to agricultural function suitability evaluation system (Table 2), the agricultural functional suitability is divided into four levels: more suitable, suitable, less suitable and unsuitable. The area is 1 127.44, 4 700.38, 1 506.69 and 12 840.19 km2, respectively.
Table 2 Suitability evaluation system of land space agricultural function

Target layerSystematicnessIndicator layerIndicator classificationScoreAgricultural Basic farmland protectionPermanent basic farmland protection Protected area1production area BNon-protected area4suitabilityCultivated land and backup resources Cultivated land grade S111, 12, 13, etc.1restriction evaluation14, etc.2Garden land, pasture land, backup Garden land1resources S2Pasture land2Concentrated contiguous backup resources3Non-concentrated contiguous backup resources4Soil pollution level S3Clean1Slightly and mildly polluted2Moderately polluted3Heavily polluted4Rural settlement Natural suitabilitySlope N10-8%1suitability8%-15%215%-25%3>25%4Active fault N21 000 m1800 m2500 m3200 m4Geological hazard hidden point N3Resistant area1Vulnerable area4Agricultural production restrictionBasic farmland protection BProtected area4Other area1Ecological protection restrictionEcological importance level EImportant4Others1Urbanization possibilityDegree of concentration contiguous JPlaque area<3 ha1Plaque area≥3 ha4
The indicators selected for the evaluation of urban construction natural suitability include topography (slope), active fault, hidden point of geological hazards,etc. The restriction of ecological and agricultural production mainly refers to the ecologically important and most suitable areas for agricultural production to be deducted. The concentrated contiguous suitable area less than a certain area is regarded as a suitable area for rural settlement, and is deducted from the suitable area for urban construction and development. The location conditions mainly consider the distance from the county town, the distance from township center and the distance from the main transportation hub. According to the land space development and construction suitability evaluation system (Table 3), the districts are divided into four levels, namely, more suitable, suitable, less suitable and unsuitable for urban development, with area of 1 122.36, 2 300.80, 48.38 and 16 703.16 km2, respectively.
Table 3 Suitability evaluation system of land space development and construction
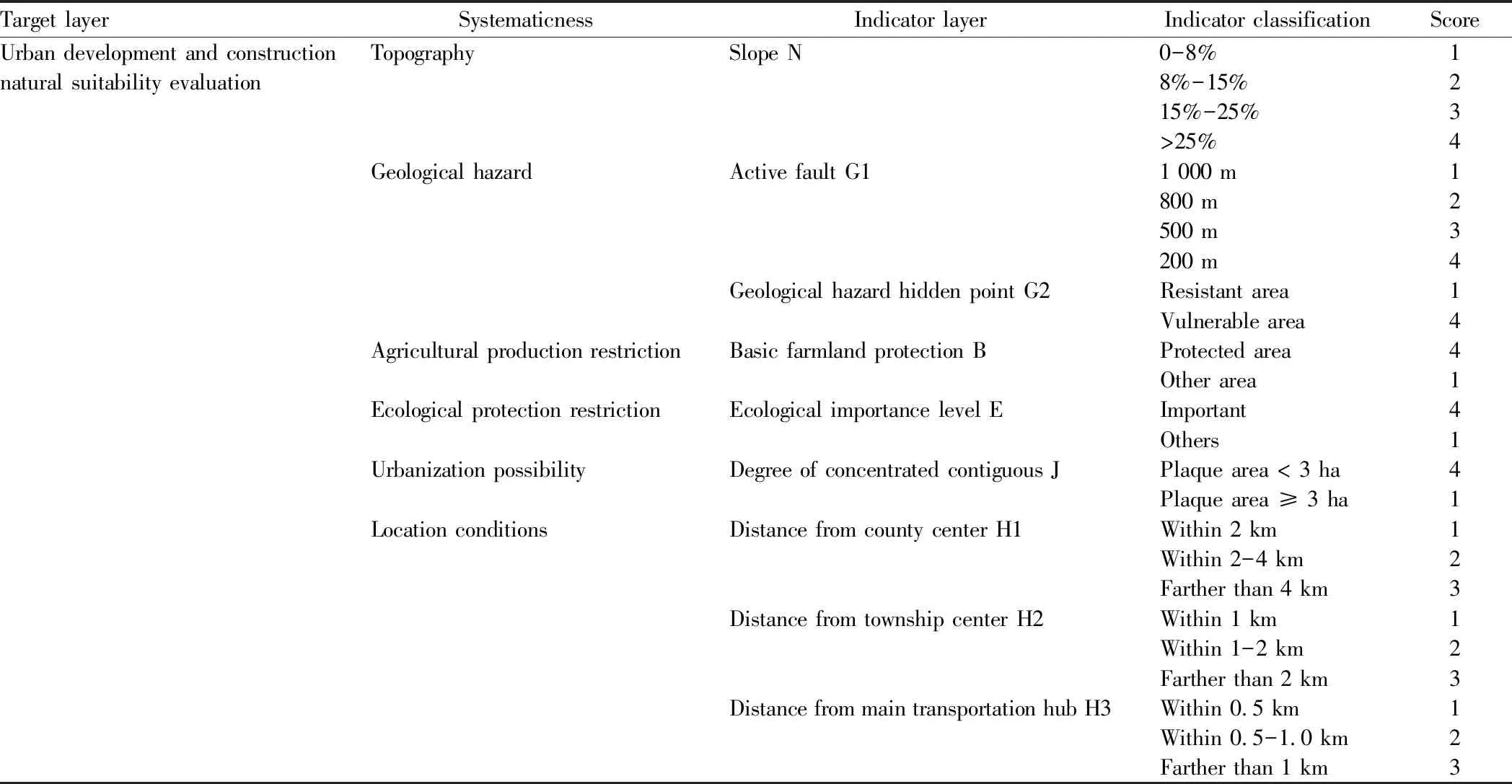
Target layerSystematicnessIndicator layerIndicator classificationScoreUrban development and construction TopographySlope N0-8%1natural suitability evaluation8%-15%215%-25%3>25%4Geological hazardActive fault G11 000 m1800 m2500 m3200 m4Geological hazard hidden point G2Resistant area1Vulnerable area4Agricultural production restrictionBasic farmland protection BProtected area4Other area1Ecological protection restrictionEcological importance level EImportant4Others1Urbanization possibilityDegree of concentrated contiguous JPlaque area < 3 ha4Plaque area ≥ 3 ha1Location conditionsDistance from county center H1Within 2 km1Within 2-4 km2Farther than 4 km3Distance from township center H2Within 1 km1Within 1-2 km2Farther than 2 km3Distance from main transportation hub H3Within 0.5 km1Within 0.5-1.0 km2Farther than 1 km3
3.3 Delimitation of three types of spaceUsing the Raster Calculator tool of ArcMap 10.4, the three layers of urban construction development suitability, agricultural function suitability and ecological function importance are superimposed and analyzed, thus the three types of spatial distribution maps are obtained. Cluster analysis is performed using the Block Statistics tool of ArcMap 10.4. Based on this, the evaluation results and the base map are spatially superimposed and analyzed, and the three types of space are refined to the natural resource survey database of 1∶10 000. After delimitation, the area of ecological protection space of Sunan County is 19 072.05 km2, accounting for 94.53% of the total area. The area of agricultural development is 1 082.98 km2, accounting for 5.37% of the total area. The area for urban construction is 19.67 km2, accounting for 0.10% of the total area.
3.3.1Zoning of ecological protection space. According to theTechnicalGuidelinesfortheDelimitationofEcologicalProtectionRedLine(Environmental Ecology[2017]No.48)[10]and theGuidelinesfortheDevelopmentofEcologicalCivilizationConstructionStandardSystem(2018-2020)[11], the natural ecological space is divided into ecological protection red line and general ecological space.
The ecological protection red line of Sunan County includes Qilian Mountain National Park, Qilian Mountain National Nature Reserve, Gansu Zhangye National Geological Park, Water Source Protection Area and first-class national public welfare forest, with a total area of 14 100.74 km2, accounting for 73.91% of the ecological space. According to the regulatory requirements stipulated by existing laws and regulations and the functional division of various types of protected areas, the red line is divid3ed into core protection area, ecological restoration area and traditional utilization and recreation area. The core protection area of Sunan County includes the core protection area of the national park and the core protection area of the nature reserve, with a total area of 3 947.28 km2, accounting for 20.69% of the ecological space. The ecological restoration area of Sunan County includes ecological conservation area of the national park, the buffer zone of the nature reserve, the geological heritage landscape area and natural ecological zone of the national geological park, and the protection area of the first-grade drinking water source, with a total area of 3 216.89 km2, accounting for 16.86% of the ecological space. Traditional utilization and recreation area of Sunan County includes the comprehensive service area of the national geological park, the quasi-protection area of the drinking water source, the second-grade national public welfare forest and other local public welfare forests, and other concentrated contiguous forests, waters, grasslands and wastelands with certain scale and important ecological functions, with a total area of 6 936.56 km2, accounting for 36.36% of the ecological space.
The general ecological space of Sunan County includes the comprehensive service area of the national geological park, quasi-protection area of the drinking water source, the second-grade national public welfare forest and other local public welfare forests, and other concentrated contiguous forests, waters, grasslands and wastelands with certain scale and important ecological functions, with a total area of 4 971.30 km2, accounting for 26.07% of the ecological space.
3.3.2Zoning of agricultural development space. Based on the results of permanent basic farmland delimitation and agricultural land classification, the agricultural space is divided into permanent basic farmland protection area and general farmland area. The area of permanent basic farmlands in Sunan County is 88.79 km2, accounting for 8.20% of the agricultural space; and the area of general farmlands is 994.20 km2, accounting for 91.80% of the agricultural space.
3.3.3Zoning of urban construction space. According to the results of the suitability evaluation of urban development planning, urban planning and construction development in Sunan County, the urban space is also divided into two levels: urban development boundary and other urban space. The area within the urban development boundary in Sunan County is 6.57 km2, mainly distributed in the central city and industrial concentration area of Sunan County, accounting for 33.40% of the urban space. The area of other urban space is 13.10 km2, accounting for 66.60% of the urban space (Fig.2).
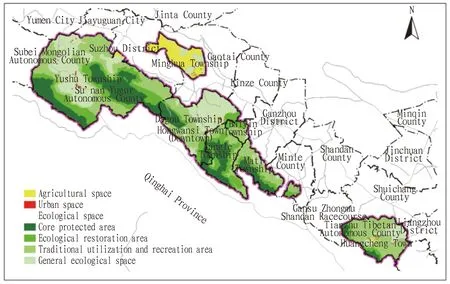
Fig.2 Zoning of three types of space
4 Conclusions and suggestions
Taking Sunan County as an example, from aspects of unifying natural resources survey data and carrying out evaluation of land space suitability, three types of ecological, agricultural and urban space were delimitated using the ARCGIS spatial superposition analysis tool. After delimitation, the area of ecological protection space is 19 072.05 km2, accounting for 94.53% of the total area; the area of agricultural development space is 1 082.98 km2, accounting for 5.37% of the total area; and the area for urban construction was 19.67 km2, accounting for 0.10% of the total area. The natural ecological space is divided into ecological protection red line and general ecological space, with area of 14 100.74 and 4 971.30 km2, respectively. The agricultural space is divided into permanent basic farmland protection area and general farmland area with area of 88.79 and 994.20 km2, respectively. The urban space is divided into urban development boundary and other urban space with area of 6.57 and 13.10 km2, respectively. The delimitation results are in accordance with local conditions, laying a foundation for developing ecological space regulation measures for the next step and establishing a differentiated use control system and providing reference for the delimitation of natural ecological space in other regions.
In view of the prominent problems that arise during the delimitation and zoning of natural ecological space, the following suggestions are proposed. First, the data of land use status survey, geographical survey, forestry survey and grassland survey have large differences due to land content and technical accuracy. Moreover, there are different degrees of misjudgment and misregulation. As a result, the natural resource survey data is difficult to connect. It is recommended to comprehensively identify the natural resource background by taking the opportunity of the third national and survey as the chassis and base of natural resource management. Second, the connotation and delimitation method of the ecological protection red line should highlight the status of the "bottom line" and "lifeline", and the control rules of the ecological protection red line should be coordinated with the control content of the functional zones of various protected areas. It is suggested to further link the connotation of the ecological protection red line with the functional zoning and control requirements of existing protected areas to optimize the ecological protection red line. Third, the boundaries of national park, ecological protection red line and nature reserves overlap with each other, so the boundaries of various types of protected areas need to be further identified. It is suggested to clearly define the scope of rights and integration of various types of protected areas to coordinate and unify management boundaries.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Pilot-scale Study on NCMBR Process for Upgrading of Sewage Treatment Plant in Industrial Park
- Career Planning Education Paths for Students of Aquatic Animal Medicine Discipline in the Context of the Belt and Road Initiative: A Case Study of Construction Achievement of Guangdong Ocean University
- Present Situation and Renovation Strategies of Farmhouses in Yingxi Village, Fuliang County, Jingdezhen
- Preliminary Exploration on Design of Green Landscape of Urban Streets: A Case Study of Guangchang East Road in Xihu District of Nanchang City
- Cultivation and Management Technologies for New Banana Cultivar ‘Refen 1’(Musa Spp. ABB, Pisang Awak Subgroup)
- Influence of Sino-US Agricultural Trade on China’s Total Agricultural Output Value Based on Cointegration Model
