北京市顺义区学龄儿童少年体重指数与体脂百分比关系的研究
2019-06-09黄晓凤张悦吕金昌
黄晓凤 张悦 吕金昌
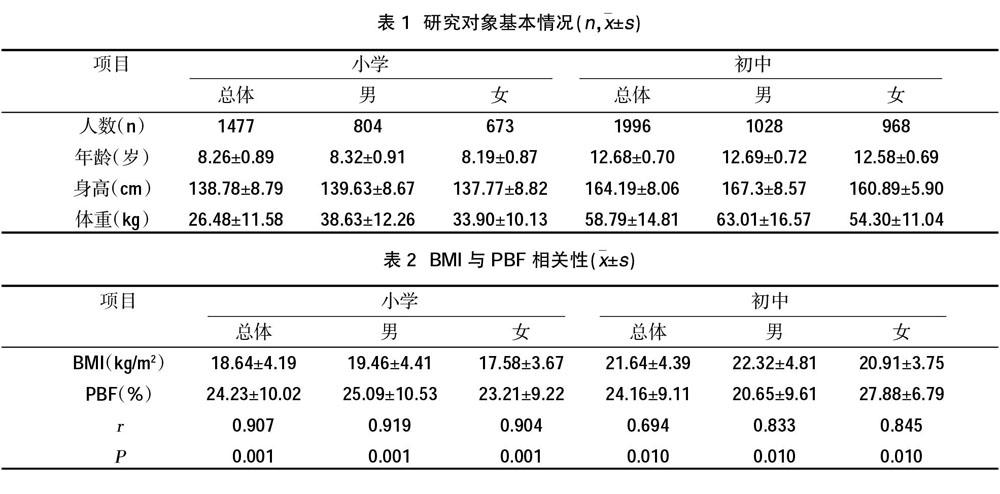
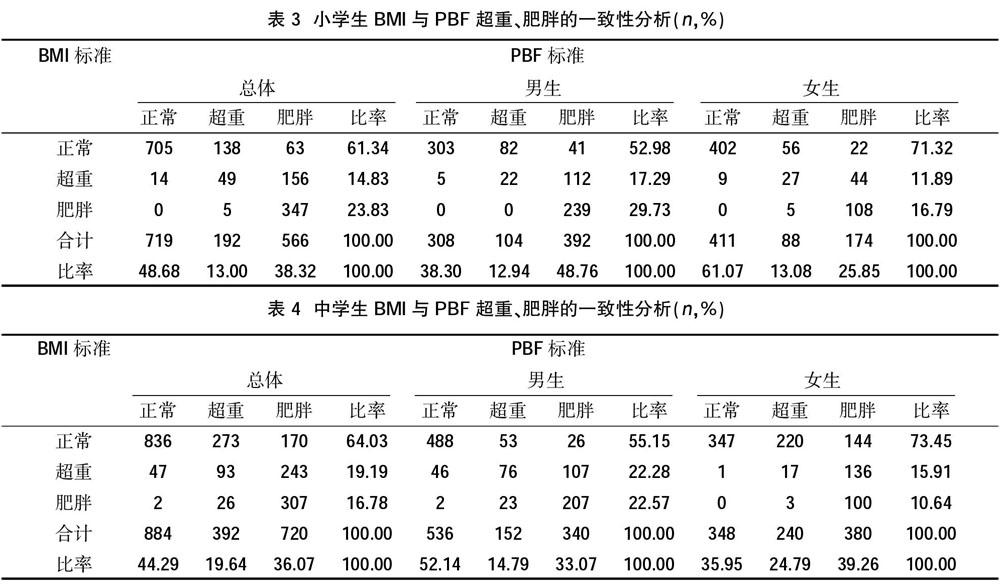
摘要:目的 分析北京市順义区儿童少年体重指数(BMI)和体脂百分比(PBF)的关系。方法 采用整群抽样法抽取顺义区小学生1477人,其中男生804人,平均年龄8.3岁,女生673人,平均年龄8.2岁;初中生1996人,其中男生1028人,平均年龄13.7岁,女生968人,平均年龄13.6岁,使用人体成分分析仪H-Key350测定PBF,并计算BMI,比较两者判定超重、肥胖的一致性。结果 北京市顺义区中小学生BMI与PBF两者呈正相关,小学生总体、男生、女生BMI与PBF均呈高度正相关,相关系数分别为0.907、0.919和0.904;初中生总体、男生、女生BMI与PBF的相关系数分别为0.694、0.833和0.845;与BMI标准判定超重相比,PBF判定的超重有较高特异度,小学和初中分别为84.71%和80.47%;而灵敏度差为14.42%和20.24%;与BMI标准判定肥胖相比,PBF判定的肥胖有较高灵敏度,小学和初中分别为99.86%和91.93%,而特异度差,只有73.56%和61.27%。结论 用PBF判断超重标准对于确定顺义区初中生和小学生超重和肥胖分别有较高特异度和灵敏度,可以使用PBF对学龄儿童开展超重和肥胖的筛查。
关键词:体重指数;体脂百分比;儿童;青少年;
中图分类号:R179 文献标识码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2019.07.040
文章编号:1006-1959(2019)07-0134-03
Abstract:Objective To analyze the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and body fat percentage (PBF) in children in Shunyi District, Beijing. Methods A total of 1477 primary school students in Shunyi District were selected by cluster sampling method, including 804 male students, with an average age of 8.3 years and 673 female students, with an average age of 8.2 years. There were 1996 junior high school students, including 1028 male students, with an average age of 13.7 years and 968 female students. The average age was 13.6 years. The PBF was measured using the body composition analyzer H-Key350, and the BMI was calculated. The two were compared to determine the consistency of overweight and obesity. Results There was a positive correlation between BMI and PBF in primary and middle school students in Shunyi District of Beijing. The BMI and PBF of primary school students, boys and girls were highly positively correlated, with correlation coefficients of 0.907, 0.919 and 0.904 respectively. Junior high school students, boys, girls BMI and PBF. The correlation coefficients are 0.694, 0.833, and 0.845, respectively. Compared with the BMI standard, the overweight of PBF has higher specificity, 84.71% and 80.47% for primary and junior high schools respectively, and 14.42% and 20.24% for sensitivity. Compared with obesity judged by BMI standard, obesity determined by PBF has higher sensitivity, 99.86% and 91.93% in primary and junior high school, respectively, and poor specificity, only 73.56% and 61.27%. Conclusion Using PBF to judge the overweight criteria has higher specificity and sensitivity for determining the overweight and obesity of junior high school students and primary school students in Shunyi District. PBF can be used to screen overweight and obesity in school-age children.
