Application of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: A concise review
2019-05-17AiTongWangYingFengHongHongJiaMengZhaoHaoYu
Ai-Tong Wang,Ying Feng,Hong-Hong Jia,Meng Zhao,Hao Yu
Abstract
Key words: Osteoarthritis;Mesenchymal stem cells;Stem cell therapy;Clinical trials
INTRODUCTION
Osteoarthritis (OA) refers to a common chronic degenerative joint disease,namely the degenerative injury of articular cartilage caused by still multiple factors (e.g.,aging,obesity,fatigue injury,trauma,joint congenital abnormalities,joint deformity,etc).Pathological changes largely include articular cartilage destruction,subchondral osteosclerosis and synovial hyperplasia[1].OA occurs primarily after middle age,and it is more widespread in women than in men.Clinical manifestations include joint pain,joint stiffness and loss of function,which impairs patient mobility,and OA will turn out to be the fourth most disabling disease by 2020[2,3].The cartilage has poor selfrepair and regeneration abilities since the hyaline cartilage tissue on the joint surface has no nerves nor blood vessels,and it is hard to recover by itself once damaged.At present,the main clinical treatment methods for OA include non-drug therapy,drug therapy and surgical treatment,which is only capable of relieving pain,and can to a certain extent improve symptoms,delay illness and correct malformation.Nevertheless,the progressive degeneration of articular cartilage cannot be thoroughly delayed for patients with OA disease[4-8].Autologous chondrocyte transplantation has been successfully employed to repair damaged cartilage,yetin vitrocultured chondrocytes show dedifferentiation and decreased chondrocyte-specific gene expression,thereby affecting its therapeutic effect.In recent years,new stem cellbased therapies for OA have aroused increasing attention.Mesenchymal stem cells(MSCs) have the potential of self-renewal and directional differentiation,which can repair cartilage tissue and suppress chondrocyte secretion of inflammatory factors and homing characteristics,which make MSCs the ideal seed cells for gradual OA treatment.This study reviews the potential applications of MSCs in preclinical models,as well as the clinical applications of OA.
CHARACTERISTICS OF MSCS
MSCs are adult stem cells that are not hematopoietic stem cells,and exist in various tissues (e.g.,bone marrow,umbilical cord,placenta,tendon,periodontal,adipose,and many other tissues)[9].In the 1970s,Friedenstein isolated MSCs from whole bone marrow cultures,and the cells were subsequently extensively studied.In 1995,Lazaruset al[10]reported in the journal of bone marrow transplant the first clinical study of bone marrow derived from MSCs for the treatment of marrow transplant patients.The international society for cell therapy (ISCT) defines MSCs with three criteria:(1) Plastic-adherent;(2) Expression of CD105,CD73 and CD90,and lack of CD45,CD34,CD14 or CD11b,CD79α or CD19 and HLA-DR surface molecules;and(3) MSC must differentiate into osteoblasts,adipocytes and chondroblastsin vitro[11].Besides their differentiation potential,MSCs also express enzymes and secrete numerous nutritional factors involved in paracrine activities,including growth factors,cytokines and chemokines[12],which nourish cartilage by activating cellular and angiogenesis pathways.Moreover,it is noteworthy that MSCs participate in the local immune regulation mechanism,which can suppress T cell proliferation,dendritic cell maturation,as well as the activation,proliferation and antibody secretion of B cells,thereby affecting the polarization of macrophages and the differentiation of antibody-secreting cells,thus essentially eliminating the risk of rejection and disease transmission[13].However,the immunomodulatory function of MSCs may vary among individuals,species,tissue sources,culture conditions and activation states.ISCT proposed the standardization of MSC immunomodulatory characteristics[14].Finally,MSCs also play a homing role,actively migrating to cartilage ischemia or damaged sites under the action of the microenvironmentin vivo.Besides,repair and reconstruction can be performed by secreting growth factors,cytokines and extracellular matrix[15].In brief,further understanding of MSC function will have therapeutic significance for slowing cartilage degeneration in OA patients.
HOW MSCS CAN TREAT OA DISEASE IN PRECLINICAL TRIALS?
In vivoexperiments on various animal models have been performed in the literature.These studies include the following models:Sodium iodoacetate (MIA) model in guinea pigs/rabbits,oophorectomy in rats,and anterior cruciate ligament amputation in rats/rabbits (ACLT).In addition,some chemical agents (e.g.,papain,quinolone and collagenase) can induce the OA model in animals[16,17].ACLT on the anterior feet of rabbits is one of the classic ways to build an OA model in rabbits.This type of rabbit model has been successfully modeled in 3 to 8 wk,which also exhibits similar biochemical and pathological variations to those of humans[17].It was reported in animal experiments that local intra-articular injection of MSCs,MSC-derived exosomes,implants with MSC-laden scaffolds,and MSC suspensions with carrier media can effectively alleviate OA disease.
Use of MSCs seeded on scaffolds in articular cartilage repair
MSCs can serve as cartilage progenitor cells or regenerative cells,which can be seeded onto three-dimensional scaffolds in order to repair damaged cartilage through the stimulation of endogenous cells[18].MSCs can be differentiated into chondrocytesin vitro,which is similar to the structural characteristics of hyaline cartilage.However,there are differences in the chondrocyte differentiation capacity of MSCs derived from different sources,cells can tend to hypertrophy during differentiation,and the phenotypic stability of mature chondrocytes remains difficult to ensure[19].Many previous experiments have verified that connective tissue growth is vital for cartilage repair,i.e.,it can promote cartilage and extracellular matrix repair.Accordingly,studies show that tissue growth factors can be loaded onto scaffolds to assist cartilage repair and increase the degree of integration of new cartilage units with surrounding tissues[20,21].However,this method is usually employed to repair the small area cartilage defect model,yet it does not address the large area of cartilage defects related to OA.At present,several scaffolds [polylactic-co-glycolic acid,polyethylene glycol,polylactic acid,polyglycolic acid,collagen,gelatin,hyaluronic acid (HA),and fibrin] are applied for the implantation of articular cartilage defects in experimental animal models[22].They are still not used as routine treatments in clinical practice,although several studies have shown the safety and efficacy of MSC-based tissue engineering methods.This is largely because:(1) Since both allogeneic MSCs and scaffold materials may cause unnecessary graft-versus-host reactions,the acquisition and culture of autologous MSCs and the selection of scaffold materials are major limitations to clinical application;and (2) At present,the selection of cytokines is more diversified,and the function of promoting chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation is also favored by researchers.However,studies have demonstrated that different levels of growth factors have bidirectional effects on promoting chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation.How to minimize osteogenic differentiation in the new cartilage area while maximizing chondrogenic differentiation ability remains one of the problems to be solved.Thus,more studies are required to prove their effectiveness in larger groups of OA patients before they can be implemented at a large scale.
Therapeutic MSC exosomes
In recent years,a growing number of researchers think that exosomes secreted by MSCs also play a role in the treatment of OA[23].Exosomes are generally hypothesized to be intercellular communication vehicles and function to transfer lipids,nucleic acids (mRNAs and microRNAs) and proteins between cells to elicit biological responses in recipient cells that are reflective of the cargo contents[24].MSC exosomes are abundant in a considerable amount of microRNA,which can specifically bind to transcribed mRNA from their target genes,thereby silencing the expressed target genes or forming an interaction network of multiple signals[24-26].Accordingly,microRNA may be vital to mediate the efficacies of MSC exosomes in the treatment of OA[27-30].For example,Taoet al[30]reported that exosomes derived from human synovial MSCs overexpressed with microRNA-140-5p can promote cartilage regeneration and suppress OA in rat models,suggesting that miroRNA-140 may be a protective factor in the pathogenesis of OA.It can also prevent and alleviate OA by upregulating the expression of SOX9 and aggrecan (ACAN) to maintain cartilage homeostasis[27-30].Tohet al[23]reported that microRNA-23b,92a,125b,320,145,22 and 221 were involved in the regulation of chondrogenesis and homeostasis.Besides,MSC exosomes are rich in ECM proteins and enzymes,thereby regulating and restoring ECM balance.The increase in enzyme activity is proportional to the loss of normal equilibrium,i.e.,exosome-based enzymes promote tissue repair and regeneration by restoring homeostasis during injury and disease.In contrast,homeostasis was restored,and exosome enzyme activity was terminated after subsided injury[31].According to the study on both the pathogenesis of OA and the drug treatment of OA,MSC exosomes exhibit infinite potential,with a good tolerance and minimal risk of immunogenicity and toxicity.However,how to obtain large-scale purified exosomes,as well as how to improve the utilization efficiency,biosafety and therapeutic efficacy of exosomes,should be further explored and studied.The study on the effect and mechanism of MSC exosomes on OA will remain one of the important hotspots for future research.In brief,MSC exosomes will soon become the main treatment modality for clinical OA with the continuous innovation of technology and in-depth research.
Local intra-articular injection of MSCs and mixed injections
In recent years,local intra-articular injection of MSCs has been reported to promote the regeneration and repair of cartilage tissue and alleviate the degeneration caused by OA.MSCs are capable of significantly improving local microenvironmental,immune-regulation and anti-inflammatory biological activities through the secretion of exosomes,growth factors,cytokines,anti-inflammatory factors and other bioactive molecules,thereby gradually becoming the simplest and easiest method to treat OA.For example,Zhouet al[32]found that local intra-articular injection of adipose-derived MSCs (AD-MSCs) can effectively alleviate the condition in rat OA models through autophagy induction to reduce the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines.Toghraieet al[33]reported the establishment of an OA model by resection of anterior cruciate ligaments in rabbits.Radiology revealed OA symptoms after 12 wk,and then a single dose of 1 × 106/mL AD-MSCs was injected into the joint cavity of the OA model.It was found that cartilage tissue was significantly repaired and improved as the result of imaging,morphology and histology at 20 wk.In the meantime,platelet-rich plasma(PRP) with the active substance can promote cell proliferation,collagen synthesis and inflammatory chemotaxis.Thus,it is conducive to tissue repair and can assist tissue reconstruction.Pre-clinical studies have verified that PRP/MSCs can also improve knee joint function,and the repaired tissue exhibits good compatibility with the original articular facial cartilage tissue by MRI analysis.Additionally,HA combined with MSCs can effectively repair damaged cartilage,and its mechanism may be to promote the repair of damaged cartilage by suppressing the inflammatory response and apoptosis of chondrocyte.It has been reported that PRP/MSCs or HA/MSCs has a significantly better effect on the repair of damaged cartilage than the individual treatment group in the OA animal model (HA,PRP or MSCs were used alone,respectively).Table 1 shows the summary of pre-clinical trials of MSCs in the treatment of the OA animal model from 2015 to 2018.
Mechanism of MSCs in the treatment of OA
Immunomodulatory effects of MSCs is one of the vital mechanisms of its treatment of OA.MSCs can be activated by inflammatory factors,then the secretion of PGE2,IDO,NO and other factors by MSCs can directly or indirectly suppress immune cells[40].For instance,PGE2secreted by MSCs can promote the production of immunosuppressive IL-10 by binding EP2 and EP4 receptors on macrophages,and participate in the regulation of CD4+ effector T cells[41].Moreover,MSCs have been shown to suppress T cell proliferation and induce T cell apoptosis,resulting in fragments that stimulate phagocytes to produce tumor growth factor beta and increase the number of regulatory T cells[42].MSCs also regulate innate immunity by inhibiting dendritic cell maturation and reducing natural killer (NK) cytotoxicity[43].MSCs can also reverse the polarization of macrophages from pro-inflammatory (M1) to anti-inflammatory (M2)phenotypes[44].Joet al[45]found that MSCs can interact with macrophages to suppress the activation of macrophages and the secretion of IL-1β,TGF-α and another inflammatory factors.
The supernatant from MSCs stimulated by INF-γ and IL-1β can increase the expression of arginine,IDO and nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in macrophages,which lead to the transformation of macrophages from M1 to M2 types.MSCs also secrete an abundant of chemokines (SDF-1α,MCP-1 and MCP-2),which can attract monocytes,macrophages,lymphocytes and dendritic cells,etc,and then these cells are recruited to sites of injury and inflammation by chemotaxis,which participate in the repair of tissue injury[46].A study reported that mature chondrocytes and the secretion of cytokines can promote the differentiation of MSCs into chondrocytes.In the meantime,cytokines secreted by MSCs can also promote the proliferation ofchondrocytes and the synthesis of an ECM matrix,which can repair damaged bone and cartilage[47,48].It has been reported that cytokines secreted by MSCs can target synovial membranes and chondrocytes,which can regulate anabolic and catabolic factors,as well as induce the expression of anti-inflammatory and chondrogenic molecules[49].However,in recent years,most studies have suggested that MSCs primarily regulate local inflammation,apoptosis and proliferation of cells through paracrine mechanisms,rather than directly differentiating into chondrocytes to participate in tissue repair (Figure 1).Barry and Murphy thought that endogenous MSCs contribute to the maintenance of healthy tissues by acting as reservoirs for cell repair or as immunomodulatory sentinels to reduce inflammation,but also,paracrine signaling by MSCs might be more important than differentiation in stimulating repair responses[50].In other words,MSCs are not specifically designed to replace damaged and lost cartilage,but rather coordinate and enhance this repair response.
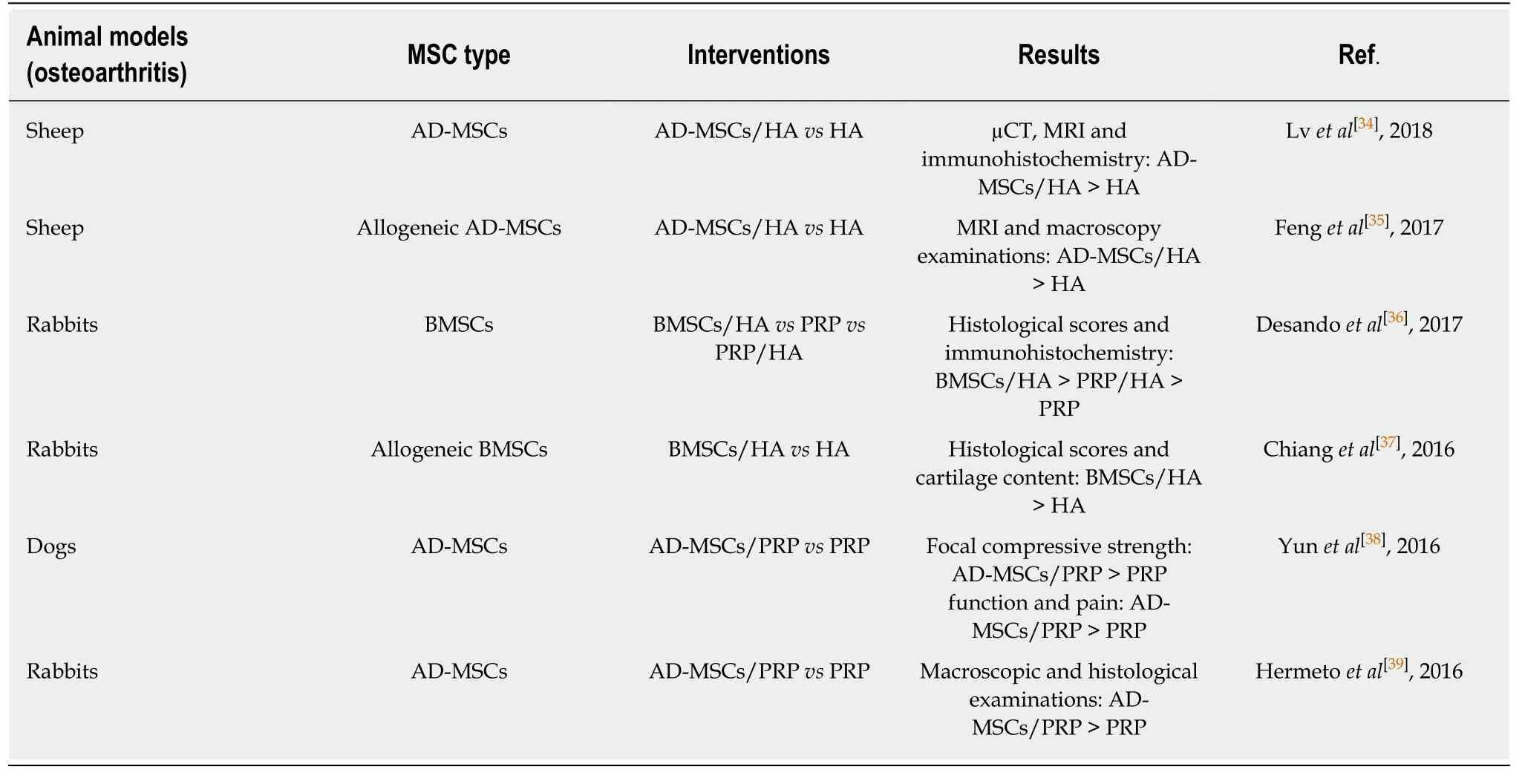
Table 1 Summary of mesenchymal stem cell preclinical trials in osteoarthritis animal models from 2015 to 2018
CLINICAL TRIALS OF MSC-BASED THERAPY IN OA DISEASE
Local intra-articular injection of MSCs and mixed injections
Mixed injections means that MSCs are combined with growth factors,cytokines and scaffolds in order to improve efficacy.The commonly used support scaffolds are polymer scaffolds such as HA,fibrin gel,and nutrient-rich liquid such as serum platelet rich plasma (PRP).Among them,there are many studies on the treatment of OA by injecting MSCs/PRP suspensions into the articular cavity.Details of the case report of MSCs combined with PRP in the treatment of OA are shown in Table 2.It is generally known that PRP is an autologous tissue,rich in chondrogenic growth factors (e.g.,TGF-β and platelet-derived growth factor).It can serve as a source of tissue for the treatment of damaged cartilage[51].PRP composite scaffolds have high osteogenic induction activity,and are capable of promoting bone healing.The combination of PRP with MSCs (adipose MSCs:AD-MSCs/vascular stroma of adipose tissue:SVF) is used for treating knee OA,which can create a suitable microenvironment for MSC growth (promote the supplying of blood,reduce the responding of local inflammatory),promote the synthesis of cartilage matrix,and also improve the therapeutic effect of MSCs in knee arthritis[52-54].The problem of PRP still lies in its preparation and the variability of the synthesis number of bioactive factors it expresses.Some growth factors secreted in PRP (e.g.,vascular endothelial growth factor) may have adverse effects on both joints and MSCs[51,52].
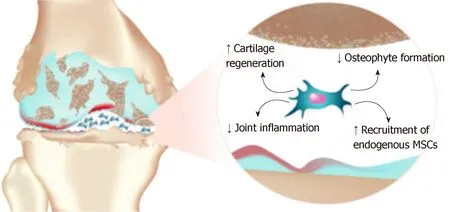
Figure 1 Paracrine activity of mesenchymal stem cells in an osteoarthritis articular environment(Professional illustration by Matilde Bongio,GoArts - lstituto Ortopedico Galeazzi).
Clinical trials using MSCs for OA disease
MSCs were first proposed to reside in bone marrow and have since been demonstrated to exist in other tissues (e.g.,fat,placenta,umbilical cord,dental pulp,peripheral blood,and synovium)[60,61].With the increase in evidence for the application of stem cell technology in animal andin vitroexperiments,the application of MSCbased transplantation technology in the treatment of OA to achieve cartilage regeneration has shown promise.Thus far,clinical studies on mesenchymal stem cell therapy for OA have been conducted globally,and 74 of them have been registered on clinicaltrial.gov,some of which have completed clinical trials as well as preliminary evaluations of safety and efficacy.In China,research on the treatment of OA with MSCs is also in full swing.Currently,there are six studies registered on clinicaltrial.gov,taking up 8.1%,four of which (one UC-MSCs and three AD-MSCs)focus on the treatment of OA have been completed,and one study (UC-MSCs) is in the recruitment state.According to the results of the completed studies,mesenchymal stem cell (bone marrow,adipose and umbilical cord) therapy shows highly efficacy in the research of OA diseases,and has great potential to replace traditional therapies in the future.PubMed,Wiley,Elsevier ScienceDirect,Springer,Taylor and Francis were searched for the relevant studies published from 2015 to 2018.The search strategy included the keywords “mesenchymal stem cells”,“bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs)”,“umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs)”,“adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (AD-MSCs)”,“stem cell therapy”,“osteoarthritis” and “clinical trial”.Inclusion criteria:(1) Clinical research journal articles or reviews were included;(2) The content of this study closely links to the application of MSC therapy in OA treatment;and (3) Select articles that have been recently published or published in an authoritative journal in the same field.Exclusion criteria:(1) Non-English literature in foreign languages;(2) Literature with repetitive content;and (3) Cannot get the full text of the document.In the end,14 studies were included here,including eight on the clinical study of BM-MSCs in OA treatment (Table 3),three on the clinical study of UC-MSCs in OA treatment (Table 4),and three on the clinical study of AD-MSCs in OA treatment (Table 5).
Bone marrow is the most common and earliest effective source of MSCs for the treatment of OA diseases.BM-MSCs have achieved a promising effect in the clinical repair of knee articular cartilage using stem cell transplantation technology.In 2008,Centenoet al[62]reported a case of severe OA of the knee joint.Bone marrow MSCs in suspension culture with phosphate buffered saline were injected for treatment,and 10% platelet lysate (PL) and 10 ng dexamethasone injection were supplemented for cartilage stimulation.Six months after injection,MRIs showed the significant growth of articular cartilage and meniscus,ROM score increased and the pain score of modified VAS decreased.A single injection of BM-MSCs into the articular cavity without using adjuvant analgesics,anti-inflammatory drugs or immunosuppressants has also achieved positive results[62,63].Studies have shown that BM-MSC transplantation is more effective than either autologous chondrocyte transplantation or no transplantation,with relatively fewer complications.Finally,though BM-MSCs have been extensively studied and its effectiveness and safety have been confirmed,further clinical application of BM-MSCs is limited by the fact that it is difficult to obtain sufficient numbers of primary generations due to factors such as trauma and differentiation ability affected by donor age.Intra-articular injection of AD-MSCs was also used in the treatment of OA.It is usually obtained by liposuction or is subpatellarfat pad-derived,and then the liposome is centrifuged and digested by collagenase I to prepare concentrated AD-MSCs[52,57,64].It has been reported that intra-articular injection of 1.0 × 108AD-MSCs can significantly improve knee joint pain (P< 0.001)and function (P< 0.001) without adverse events.Patients in the medium dose group(5.0 × 107) showed some improvement in clinical results,while those in the low dose group (1.0 × 107) showed no improvement in most outcome indicators[45].These results suggest that intra-articular injection of MSCs has a significant dose-response effect,and that further large-scale trials are needed to confirm the long-term safety and clinical advantages of high-dose injection.However,comparative studies have shown that AD-MSCs have lower chondrogenic potential,lower cartilage specificity of matrix protein production,and low expression rate of the collagen type I gene as compared with BM-MSCs.Thus,scholars should work to further optimize the chondrogenic potential of AD-MSCs[65].Umbilical cord-derived MSCs (UC-MSCs) are a type of pluripotent stem cell existing in neonatal umbilical cord tissues,which can be obtained from discarded umbilical cord or umbilical cord blood banks.At present,clinical trials have shown that injecting human umbilical cord-derived MSCs into the joint cavity for the treatment of degenerative knee OA can significantly improve the joint function and quality of life of patients[66].In January 2012,the Korean Food and Drug Administration approved the manufacture and sale of Cartisem in South Korea as a safe and effective stem cell drug (containing UC-MSCs and sodium hyaluronate)for treating degenerative OA and cartilage injury.Since it was listed in South Korea in 2012,more than 5,000 patients have been treated at an effective rate of 97.67%,and the treatment effect is not limited by the age of the patients.More importantly,Cartistem uses allogeneic stem cells rather than autologous stem cells,and has become the world’s first user of allogeneic stem cells to produce therapeutic drugs.Cartistem utilizes umbilical cords to isolate and cultivate UC-MSCs that meet the needs of clinical treatment,and they are implanted into damaged cartilage.In the microenvironment of the implanted location,UC-MSCs coordinate and enhance the repair response of damaged cartilage tissue by a paracrine mechanism,thereby creating a new avenue for the treatment of OA.UC-MSCs are a little backwards compared with other MSCs because of their unique properties,whereas they are expected to be widely used in clinical practice and will make an important contribution to the repair of damaged cartilage,which will be the focus of future research.
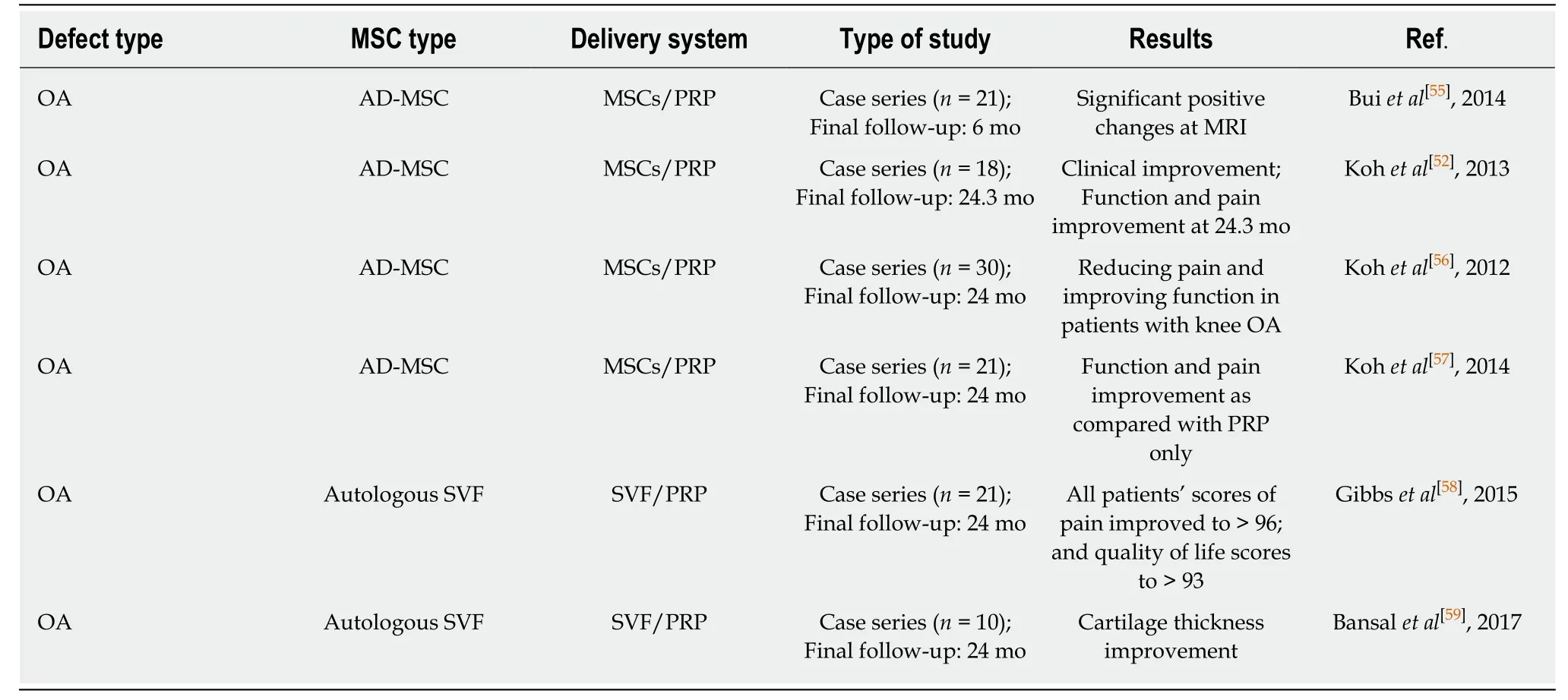
Table 2 Summary of mesenchymal stem cells/platelet-rich plasma clinical trials in osteoarthritis patients from 2012 to 2018
Although the initial efficacy of intra-articular MSC injections in patients with severe knee OA deserves to be confirmed,prospective and placebo-controlled studies are still needed to verify the effectiveness of this method.New clinical trials should focus on the efficacy of MSC injections in patients with moderate OA and early radiology.Kohet al[67]showed that the effects of MSC implantation in level 3 OA patients were better than those in level 4 OA patients.Accordingly,MSC-based therapies should be more effective in preventing or limiting the progression of early stages of OA disease.Another important question is the optimal dose of the experimental cells.Cell dosages range from 2 × 106to 3 × 108,with significant differences between clinical trials.However,the dose described by different researchers for the improvement of pain function and histological scores is also different,so there is still no clinical criteria for guiding treatment.
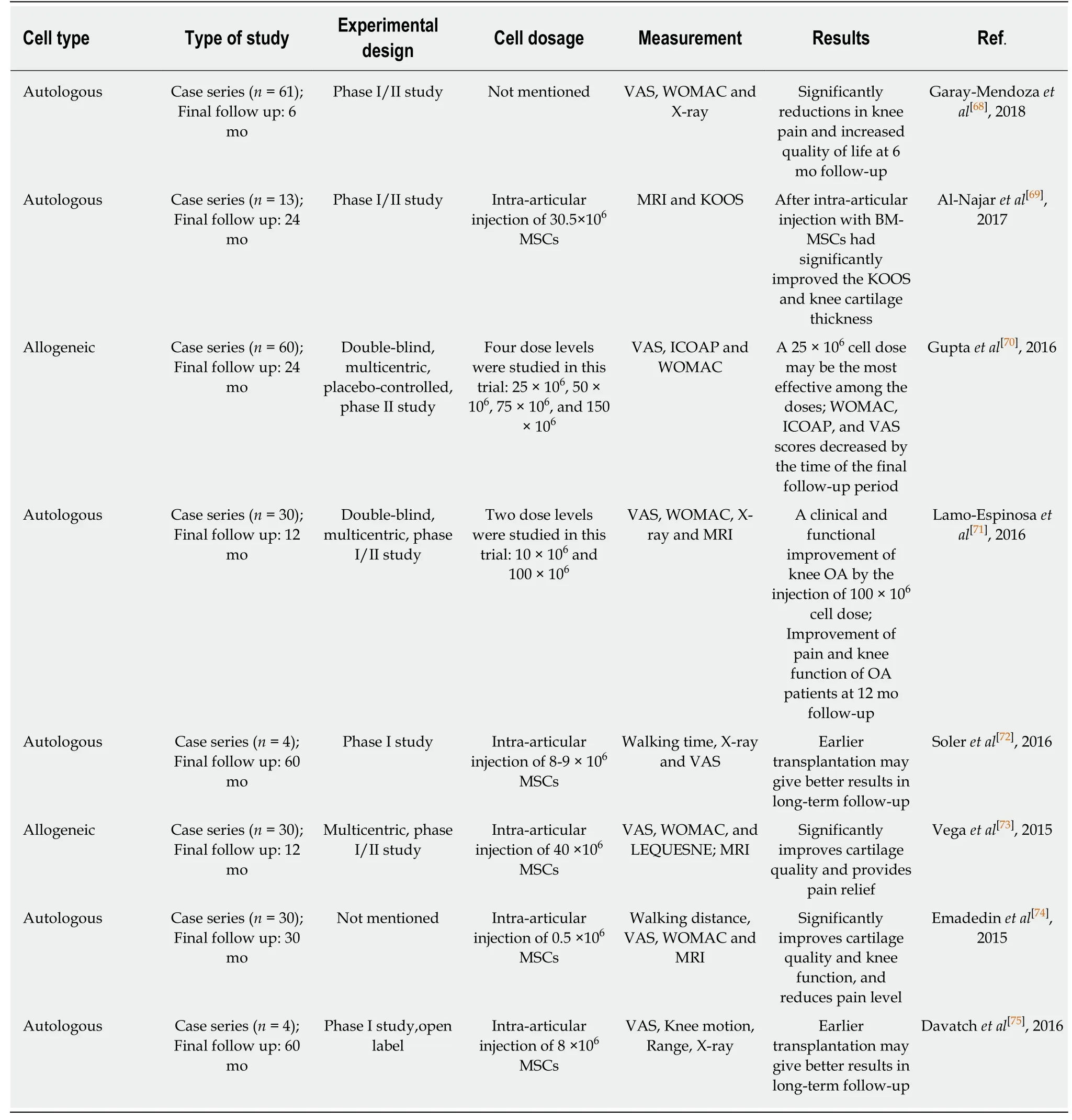
Table 3 Summary of intra-articular injection of expanded bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in knee osteoarthritis treatment(2015-2018)
SAFETY AND QUESTIONS
As early as 2005,Rubioet al[81]transplanted AD-MSCs into immunodeficient mice,and the results suggested that spontaneous stem cell transformations and malignant tumors occurred in mice.Later,several studies revealed that this malignanttransformation is due to cell line contamination,and is therefore not correlated with MSCs themselves.Thus,this study was withdrawn[81,82].In recent years,numerous animal studies have reported that intra-articular injection of MSCs can promote cartilage regeneration and reduce joint inflammation to improve the OA function of joints,and no malignant transformation of MSCs has been found.A total of 14 studies reported intra-articular injection of MSCs for the treatment of OA in clinical trials from 2015 to 2018.In general,whether intra-articular injection of autogenous and allogeneic MSCs (bone marrow,adipose and umbilical cord) were used,the clinical manifestations,radiological and histological scores of OA patients were improved,no graft-related death,tumorigenesis and infection occurred,and no serious adverse reactions were observed.However,there are still some problems with the intraarticular injection of MSCs for the treatment of OA in clinical trials:(1) It has been reported that MSCs could promote cartilage repairviathe secretion/stimulation of biomolecules,and if these results are true,the duration of stimulation and whether the biomolecules secreted by MSCs can be characterized as drugs and used accumulatively should be considered;(2) How to improve the effectiveness of MSCs in the OA microenvironment.Also,the transfer of cells fromin vitroatmospheric culture conditions to thein vivoniche may affect the survival rate of MSCs after transplantation;(3) How to accurately assess the progress of OA repair.There are many different clinical scoring systems that have been widely used until now,but the popularity of scoring systems and the debate over their relative merits suggest that they do not accurately assess the progression of OA disease;(4) How to eliminate the blindness of clinical research.While MSCs are usually packaged into syringes,there is a tendency for cells to aggregate and become fuzzy at the bottom of the syringe,which may affect the results of blind clinical trials compared with transparent placebos;and (5) Transport problem:how can cells be effectively transported from the laboratory to OA patients without losing their efficacy and quantity.

Table 4 Summary of intra-articular injection of expanded umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in knee osteoarthritis treatment (2015-2018)
CONCLUSION
Since analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs often cause gastrointestinal,liver,kidney and heart problems,many common side effects arise from current arthritis treatments,which may cause significant injury to the patient.Also,ACI surgery may cause morbidity in the donor site,and requires two operations under general anesthesia.With the advancement of research on the characteristics,pre-clinical and clinical applications of MSCs,regenerative medicine based on stem cell therapy hasgradually presented its advantages in the treatment of OA disease.Previous studies have injected bone marrow-,umbilical cord- and adipose-derived MSCs into the joint cavity using the ultrasound detection technique.This study summarizes the contents of preclinical and clinical trials in the recent three years as follows:intra-articular injection of MSCs can lead to the reduction of index-pain,improve the function and significantly increase the volume of cartilage.

Table 5 Summary of intra-articular injection of expanded adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in knee osteoarthritis treatment(2015-2018)
Despite many researchers’ initial worries about mesenchymal stem cell therapy,a systematic review of clinical trials has suggested that MSCs are relatively safe for both intravascular and intra-articular injection.It is noteworthy that umbilical cord MSCs can serve as allogeneic stem cell drugs,which can replace damaged tissue in the microenvironment of the implanted site,which creates a new approach for OA treatment.Finally,although these initial studies show promising therapeutic effects,their long-term therapeutic effects need further investigation.Furthermore,more reliable studies with larger sample sizes and randomized controls are also required for higher levels of evidence,and to comprehensively standardize and optimize MSC therapy in the treatment of OA diseases.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by Cell products of National Engineering Research Center and National Stem Cell Engineering Research Center.
