Analysis of China's Nano andMicrosatellite Industry Development
2019-05-15MANXuan
MAN Xuan
China Aerospace Science & Technology Consulting Co., Ltd., Beijing 100054
Abstract: Nano and microsatellites have been widely used in communications, remote sensing, electronics, reconnaissance and other fields, and have become one of the important directions in future aerospace. On the basis of systematically clarifying the concept and scope of the nano and microsatellite industry, this paper analyses the development process of the nano and microsatellite industry. Starting from the nano and microsatellite current development status,this paper summarizes the characters of nano and microsatellites industry professional entities, and then forecasts the trend for nano and microsatellites development in terms of technological development, commercial launching, investment and financing channels.
Key words: nano and microsatellite industry, professional entities, forecast
1 INTRODUCTION
At present, there is no international agreement with regard the definition of nano and microsatellites. However in practice, it is generally defined according to the weight of the Nano and microsatellite. In this paper, satellites between 1 and 100 kg are considered as nano and microsatellites as seen in the classification criterion used by NASA. Nano and microsatellites have many advantages, such as small size, light weight, good performance, short development cycle, low cost, flexible launch mode and so on. nano and microsatellites have been widely applied in areas such as communication, remote sensing, navigation and science exploration and have demonstrated economic and social benefits. Nano and microsatellites have become one of important development directions in space.
All space powers all round the world placed high value on the nano and microsatellite industry. The United States and Britain were the first two entering the field of nano and microsatellites. The University of Surrey manufactured the UOSAT“University Satellite” series and launched UOSAT-1 successfully in 1981, which set off a global upsurge in nano and microsatellite development and application. In 1993, the concept of nanosatellite was put forward by the United States. At present, the United States, Russia, France, Britain, Italy and other countries have established nano and microsatellite platforms or constellations. India, South Korea, Sweden, Denmark, Brazil, Spain, Israel and other countries have taken nano and microsatellite as the starting point to promote the development of space technology,thereby improving the overall strength of their space industries.In 2017, of the 473 spacecrafts launched worldwide, 316 nano and microsatellites accounted for 66.8% of the total number of spacecrafts[1]. In the future, with a large number of nano and microsatellites being launched, the framework of world space will be changed gradually.
China's nano and microsatellite industry started late. It began to develop rapidly until 2015, launching 30 nano and microsatellites. In 2018, the number of nano and microsatellites launched accounted for 46.2% of the total number of spacecraft launched by China. The nano and microsatellite field in China is changing from that of technology development to business development, and becoming a supplement to traditional satellites and even the main force in space innovation. Although China's nano and microsatellite industry has made great progress, there is still a long way to go to catch up with developed countries.Driven by the construction and operation of constellations, the next five to ten years will be the golden period for China's nano and microsatellites industry.
2 ANALYSIS OF CHINA'S NANO AND MICROSATELLITES DEVELOPMENT
2.1 Development History of China's Nano and Microsatellites Industry
2.1.1 Summary
As of December 31st, 2018, the number of satellites under 100 kg launched by China was 128. Among them, there were 12 foreign satellites piggybacked by China. Of the 128 satellites under 100 kg launched, there are 8 pico-satellites, which is a satellite under 1 kg, and 120 nano and microsatellites. From the perspective of the rate of annual nano and microsatellites launched, the average number was no more than 1 from 1999 to 2005. Thereafter, 2006 onwards, the number of nano and microsatellites launched by China began to increase significantly year by year. Since 2015, the number reflected rapid growth.In general, the number of nano and microsatellites launched by China shows an increasing trend year on year.
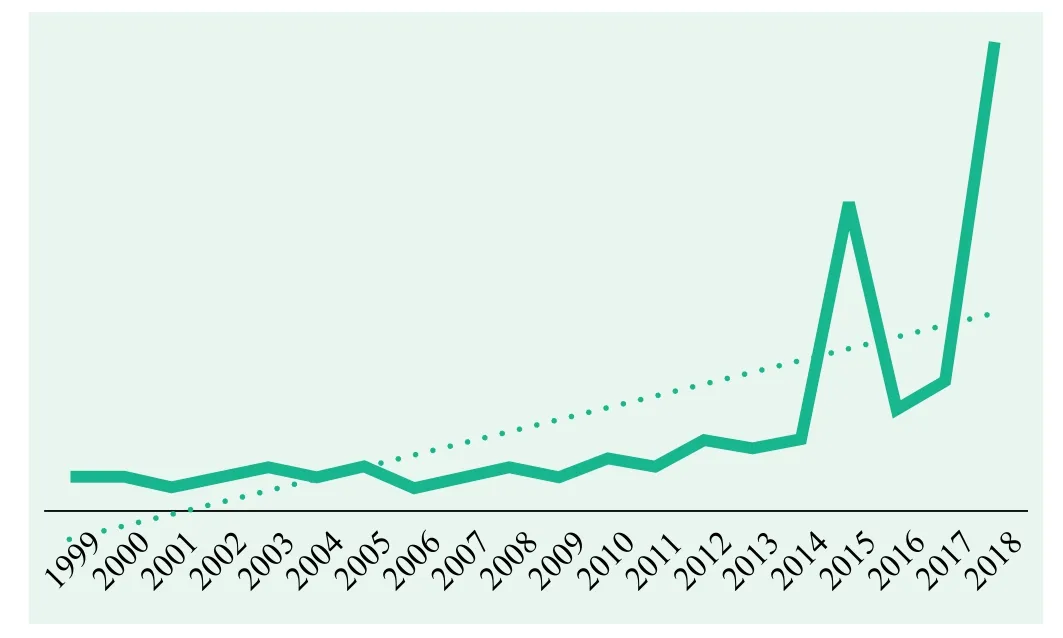
Figure 1 Quantity of nano and microsatellites launched by China
2.1.2 Emerging stage (1999 - 2005)
In the late 1990s, China's nano and microsatellite industry witnessed its first wave of development. Satellite manufacture technologies have improved and developed greatly. Launching of the Brazilian Science Application Satellite 1 in 1999 and Tsinghua Satellite 1 in 2000 marked the beginning of the nano and microsatellite industry in China. The total number of nano and microsatellites launched was 8 in this period. These satellites were all used for technology development.
Aerospace Tsinghua Satellite Technology Co., Ltd., cooperating with University of Surrey in the UK, jointly developed the Tsinghua Satellite 1, which was the first real nano and microsatellite in China. Aerospace Tsinghua Satellite Technology Co., Ltd., invested in by CASIC, Tsinghua University Enterprise Group, Tsinghua Tongfang Co., Ltd. and China Yintai Investment Co., Ltd., has clear intellectual property rights, an advanced organization and management system plus a market-oriented operation, and has established the strategy of improving civil aerospace development as its responsibility. The emergence of this company brought ideological innovation to China's aerospace industry.
2.1.3 Application stage (2006 - 2014)
During this period, China's nano and microsatellite industry developed steadily. Nano and microsatellites began to be applied in various fields. In nine years from 2006 to 2014, the number of nano and microsatellites launched by China was 23.Among them, there were 5 foreign satellites piggybacked by China. Of 18 Chinese nano and microsatellites, there were 9 nano and microsatellites used for Earth observation, communications, and scientific exploration. There were also 9 nano and microsatellites used for the testing and verification of new technologies. These new technologies involved satellite multimedia communications, satellite platform verification, micro-electromechanical systems, satellite orbit attitude expansion, space exploration, constellation and formation flight, which laid a foundation for wider applications in more fields. nano and microsatellites were changing from technology development to business development.
2.1.4 Prosperity stage (2015 - )
In 2014, China's policies about encouraging commercial capital to enter the aerospace industry were published, which promoted the development of the commercial space industry and brought a boom for Chinese private enterprises to enter the industry. Since 2015, China's nano and microsatellite industry began to expand. There were 30 nano and microsatellites launched by China in 2015. In the past four years, China has launched more than 20 nano and microsatellites annually. In 2018, China launched 48 nano and microsatellites, reaching a record high. Market sectors for national, industry and consumer use are taking shape. The nano and microsatellite industry ushered in a new wave of development, due to the prosperity of the new market sectors. The application fields for nano and microsatellites are constantly deepening and expanding. With the rapid development of traditional military, civilian and commercial markets, the consumer application market for the masses has become a new focal point. During this period, a series of nano and microsatellite constellation plans have been launched one after another, which means the industry is entering the prosperity stage driven by constellation construction.
2.2 Analysis of Active Nano and Microsatellites
2.2.1 Summary
Active nano and microsatellites, where active means providing the user some active capability. This usually means the satellite is able to communicate and to maneuver itself on-orbit.
Of 128 satellites under 100 kg launched by China, 92 actively operating satellites account for 71.9%, which is 10 percentage higher than the proportion of global active satellites for satellites launched into orbit[2]. Among them, the longest active nano and microsatellite is Innovation 1-01, which has been on orbit for more than 15 years.
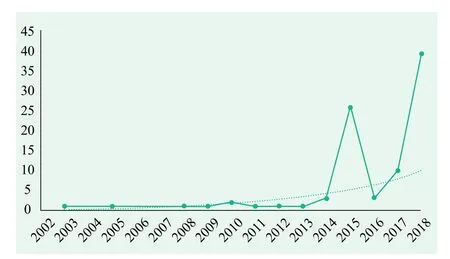
Figure 2 Launch year of active nano and microsatellites
2.2.2 Analysis of weight
Among active nano and microsatellites, satellites between 1 and 10 kg account for 34.6%, followed by satellites above 90 kg, accounting for 22.2%. Together they account for more than half of the total active nano and microsatellites. On the one hand, as satellite manufacture technologies are continuously developing, requirements for the missions and applications for nano and microsatellites are constantly increasing. The weight of the nano and microsatellite is increasing. To counter this due to the continuous progress with intelligent technologies, the weight of nano and microsatellite (especially for technology development) is actually decreasing. In the future, the proportion of satellites about 50 kg will increase significantly.
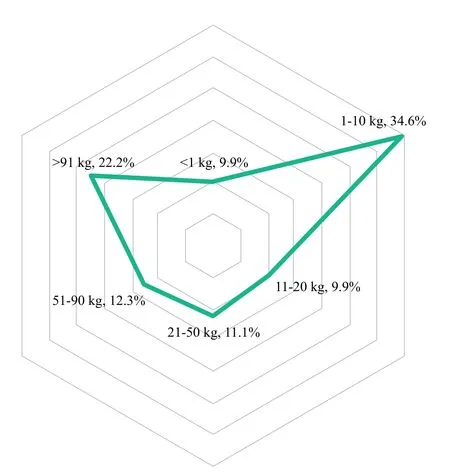
Figure 3 Weight distribution of nano and microsatellites
2.2.3 Analysis of application
According to the classification of satellite use, nano and microsatellites fall into three categories: scientific satellites, technology development satellites and application satellites. Application fields fall into communication, remote sensing, navigation and comprehensive applications. Among active nano and microsatellites, technology development satellites have the highest proportion, accounting for 46.6%, which means a large number of nano and microsatellites and constellations will be put into use in the future. Among the application satellites, remote sensing satellites have the highest proportion, with communication satellites next.
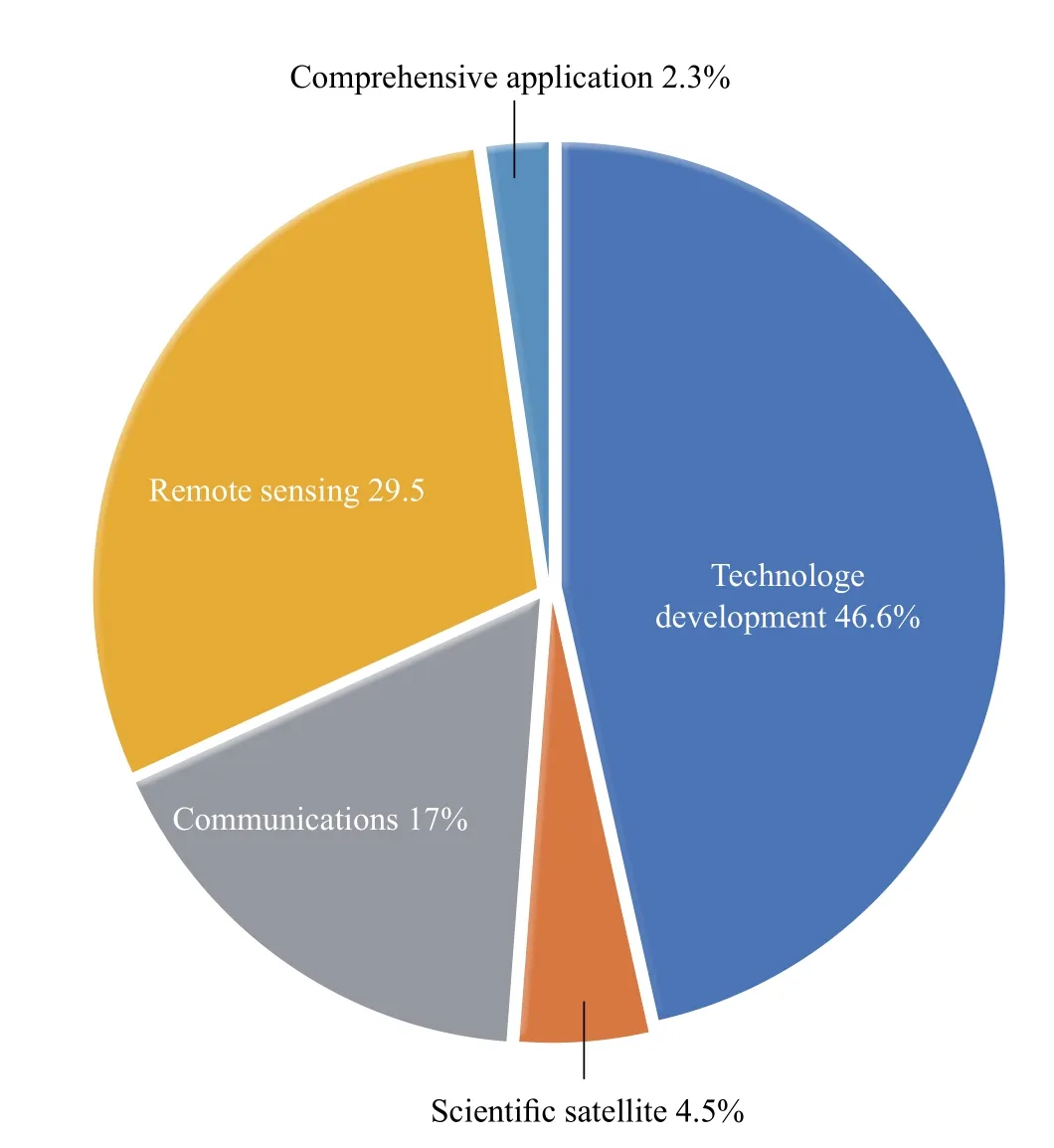
Figure 4 Usage of active nano and microsatellites
2.3 Analysis of Launch Service
Nearly 90% of nano and microsatellites launched by China were carried on Long March launch vehicles, of which 42.1%were carried on Long March 2 rocket, 19% carried on Long March 6 rocket, and 15.1% carried on Long March 11 rocket.The Long March launch vehicles are still the most important force for nano and microsatellites launching.

Figure 5 Vehicles of nano and microsatellites launched by China
3 ANALYSIS OF CHINA'S NANO AND MICROSATELLITES INDUSTRY PROFESSIONAL ENTITIES
3.1 Analysis of Professional Entities
According to the nature of the entity, China's nano and microsatellites Industry professional entities can fall into three categories: institutions, enterprises and others. Among them, institutions can be divided into universities and research institutes, and enterprises can be divided into traditional aerospace enterprises and emerging aerospace enterprises.
According to our statistics, there are 86 nano and microsatellite unities in China. Their business scope includes launching,manufacturing, operation and application of nano and microsatellites. In terms of quantity, the emerging aerospace enterprises account for 44% of all the unities in nano and microsatellite industry, the highest proportion, with traditional aerospace enterprises and research institutes next.
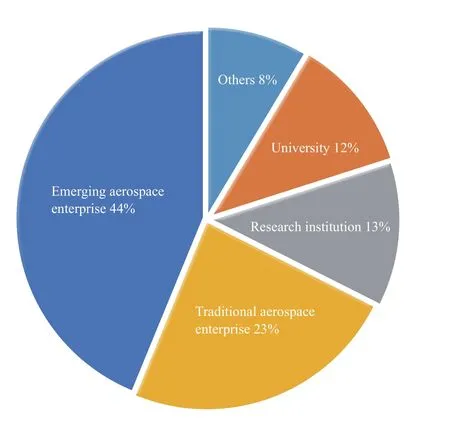
Figure 6 Nature of professional entities in nano and microsatellite industry
3.2 Analysis of Geographical Distribution
Professional entities in China's nano and microsatellites industry are located in 19 cities throughout the country (as shown in the Figure below). Nearly 70% of the professional entities are located in Beijing, followed by Shanghai, Nanjing and Changsha.At present, most of nano and microsatellite industrial professional entities are still located in the first-tier cities, but the nano and microsatellite industry has also blossomed in the second,third even fourth-tier cities.
3.3 Analysis of Nano and Microsatellite Manufacturer
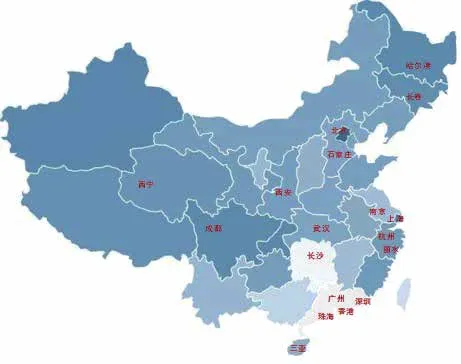
Figure 7 Geographical distribution of professional entities
According to the nature of nano and microsatellite Manufacturers, nearly half of the manufacturers are emerging aerospace enterprises, accounting for 49%. University and traditional aerospace enterprise are next, accounting for 25% and 18%respectively. Emerging aerospace enterprises are the main force in nano and microsatellite manufacture.
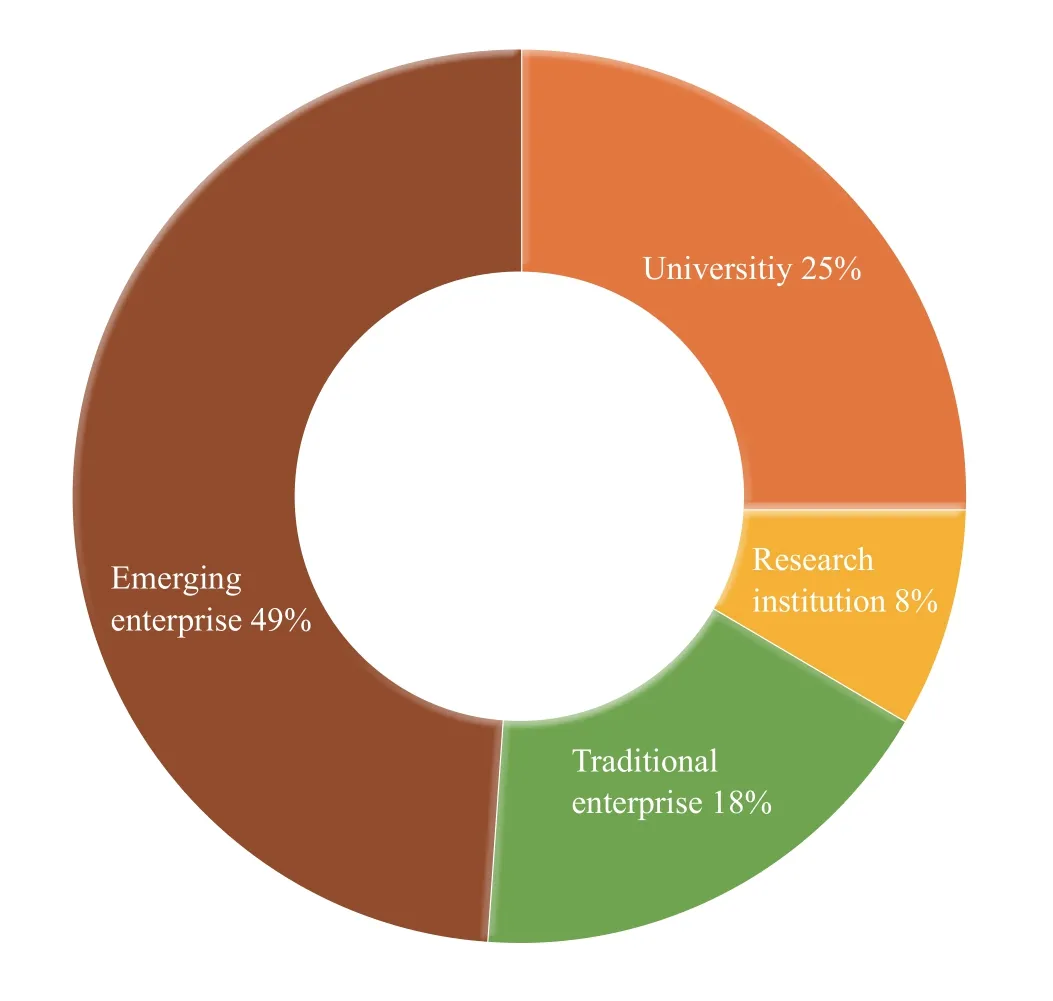
Figure 8 Nature of nano and microsatellite manufacturer
In terms of staff structure, more than 70% of employees have master's degree or above; personnel engaged in nano and microsatellite manufacturing are involved in a wide range of professions, while they have rich experience in aerospace engineering.
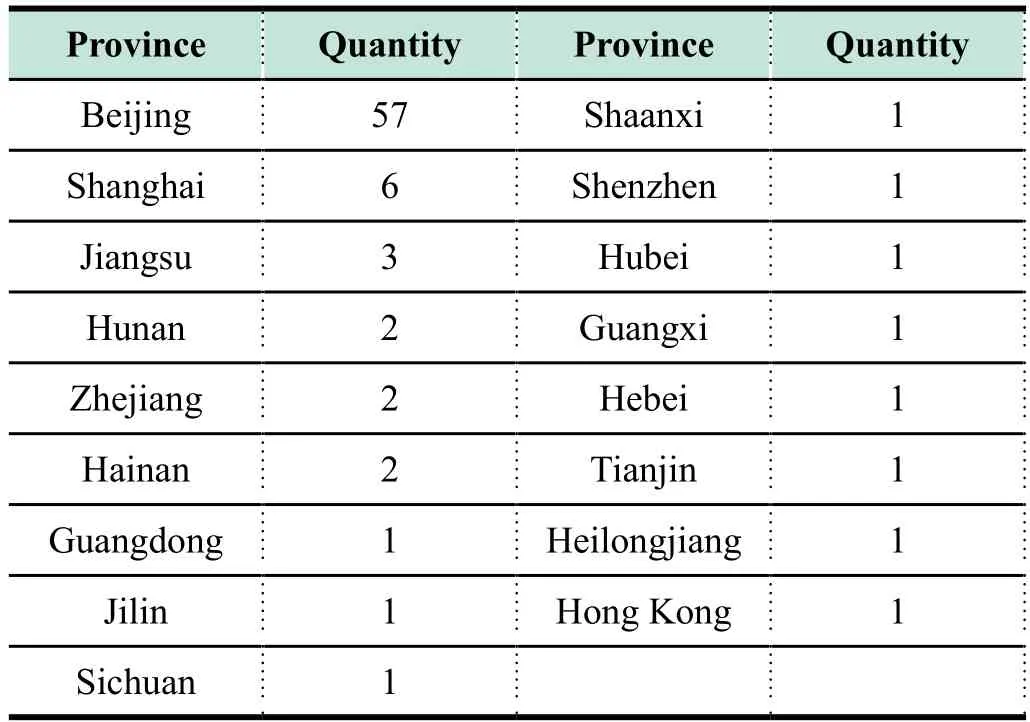
Table 1 Geographical distribution of professional entities and quantity
3.4 Analysis of Nano and Microsatellite Operators
Emerging aerospace enterprises account for 42% of all nano and microsatellite operators, the highest proportion. Traditional aerospace enterprise and research institution are next,accounting for 25% and 12% respectively. Emerging aerospace enterprises have been established only for a short time, 75%of them have been for less than five years, which means the market potential for the nano and microsatellite industry will be huge in the future.
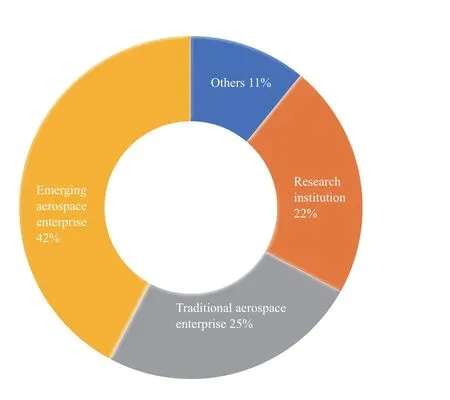
Figure 9 Nature of nano and microsatellite operator
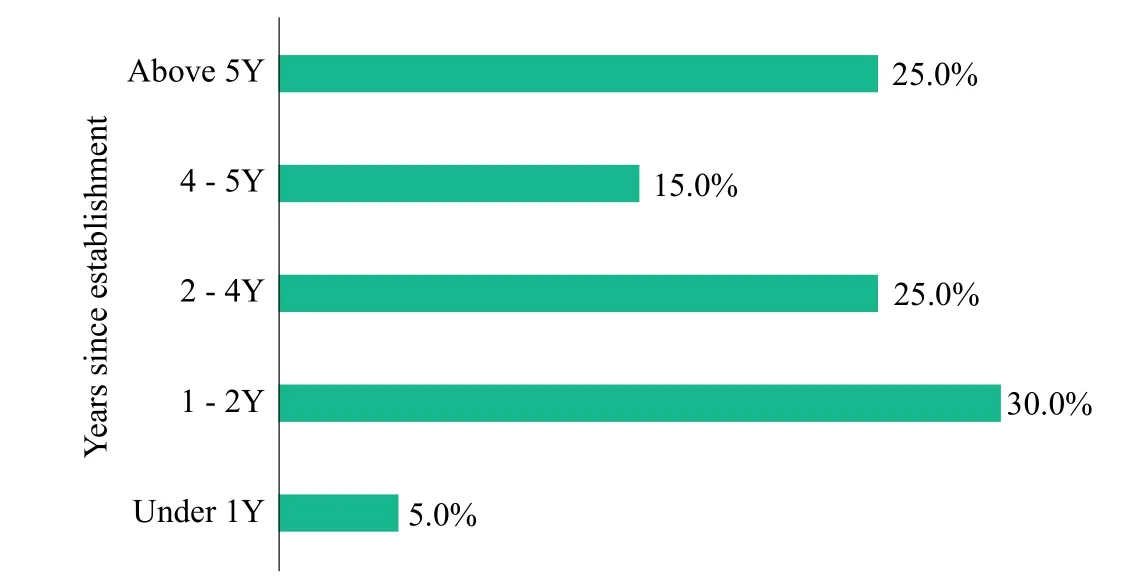
Figure 10 Nano and microsatellite operators - number of years since establishment
4 PROSPECTS FOR CHINA'S NANO AND MICROSATELLITE INDUSTRY DEVELOPMENT
4.1 Nano and Microsatellite Constellation Plan
There have been 20 nano and microsatellite constellation plans launched by 17 professional entities, involving thousands of nano and microsatellites. A part of the constellation plans aim at promoting regional economic and social development. Application fields with nano and microsatellites will expand constantly.In the future, nano and microsatellites will provide low orbit communications, high resolution remote sensing, navigation enhancement, scientific exploration, and even customization of satellite constellations according to new needs.
4.2 Prediction for China's Nano and Microsatellite in the Next Decade
According to the various nano and microsatellite constellation plans, the launch situation of China's nano and microsatellites over the next ten years is forecasted based on the business operation and application. Next decade, there will be 1382 nano and microsatellites launched by China. Over the next five years, the average annual growth rate for the number of nano and microsatellites launched by China will exceed 20%. After 2023, with the formation of satellite networks, the annual average growth rate will began to decrease.
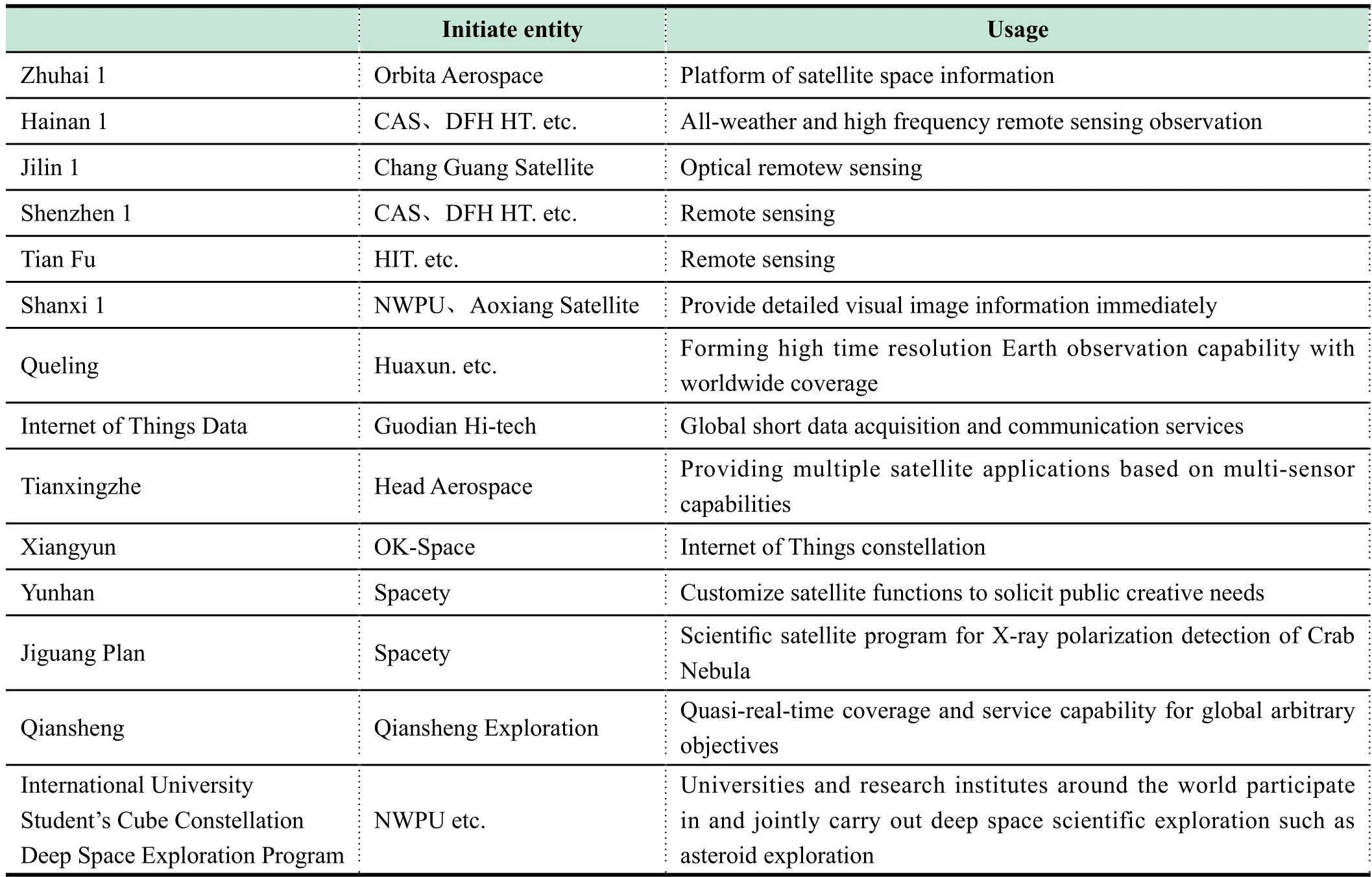
Table 2 Part of nano and microsatellite constellation plans
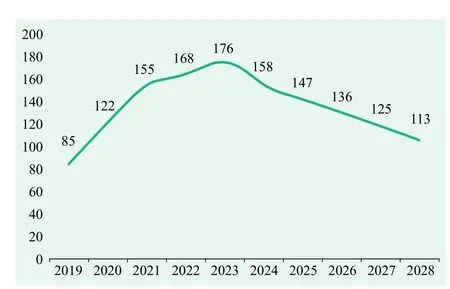
Figure 11 Prediction of China's nano and microsatellite launch in next decade
4.3 Forecast of Investment Scale of China's Nano and Microsatellite Industry Over the Next Decade
It is expected that the total investment in China's nano and microsatellite industry will reach 38.7 billion RMB in next ten years. In the early stage of satellite launching and networking during the next five years, the investment scale of nano and microsatellite industry will increase year by year. With the completion of constellation networks, of the next phase will be microsatellite constellation replenishment, hence the investment scale for the nano and microsatellite industry will decrease year by year.
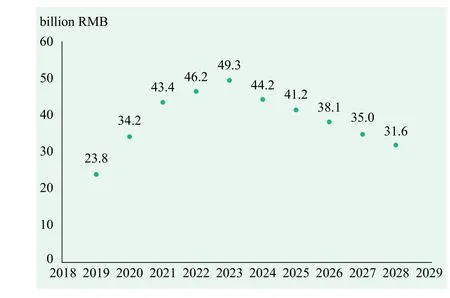
Figure 12 Forecast of investment scale of China's nano and microsatellite industry
4.4 Trend of China's Nano and Microsatellite Industry Development
Nano and microsatellite manufacturing technologies will continue improving. In the future, Nano and microsatellite networking will become the most important development direction. Constellation design will be the basis for dispatch and operation of satellite networks. The design and manufacture direction of nano and microsatellites will tend to be modularized and plug-in. Nano and microsatellites will be able to deal with a series of problems autonomously.
The nano and microsatellite industry will drive the vigorous development of China's commercial launch market. In order to meet the demand for large-scale launching of nano and microsatellites, delivery of products in different series and models will be committed to providing a faster response, higher frequency and more cost-effective launching services. Launch modes will be innovative constantly.
The operation mode of nano and microsatellite will continue to innovate. Because of their nature, nano and microsatellites can achieve more diverse applications at a lower cost. The application fields for nano and microsatellites will expand continuously, and the operation mode will be innovated constantly.
The financing channels for the nano and microsatellite industry will be more diversified. In the future, various types of capital, such as state-owned capital, private capital, various funds,venture capital, industrial capital and so on, will actively participate in China's nano and microsatellite industry development.
杂志排行
Aerospace China的其它文章
- China's Largest Thrust Solid Engine Hot Firing Test Succeeded
- Gaofen 5 and Gaofen 6 Satellites Put into Operation
- Major Test Completed on LM-9 Heavy Launch Vehicle Engine
- Commercial Opportunities for Broadband Maritime Satellite Communications in the Era of HTS Satellites
- A LM-3B Launches Tianlian 2-01 Satellite
- LM-3B Successfully Launches ChinaSat-2D
