Correlation of Commonly Used Anthropometric Parameters with FPG, FPG-CV and HbA1C
2019-04-23YaNanZhaoRuiHuaWangLiJuanZhangQiangXuYanFenLi
Ya-Nan Zhao, Rui-Hua Wang, Li-Juan Zhang, Qiang Xu, Yan-Fen Li*
1Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin,China.
2The Second Affiliated Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin,China.
3Laiyuan Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Baoding,Hebei, China.
Abstract Objective: To investigate the relationship between body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), hip circumference (HC),waist-hip ratio (WHR), waist height ratio (WHtR), fasting blood glucose (FPG), fasting blood glucose variation (FPG-CV) and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C) to provide a reference for predicting the risk and development trend of diabetes mellitus.Methods: From October 2016 to December 2017, 111 subjects from the Second Affiliated Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine were selected to measure their height and weight. BMI, WHR and WHtR were calculated and the concentrations of FPG and HbA1C were detected. Statistical analysis was carried out with SPSS21.0 software, and the data were processed by multiple linear regression analysis.Results: The concentration dependence of WHtR, FPG, FPG-CV and HbA1C were more closely related. There was a significant difference between WHtR and FPG, FPG-CV and HbA1C by multiple linear regression analysis (t = 8.531, 6.910 and 6.905,respectively, P < 0. 01), and the correlation coefficient was 0. 633, 0.552 and 0. 552 respectively (P < 0. 01).Conclusion: There is a significant correlation between WHtR and FPG, FPG-CV and HbA1C. Therefore, measuring the height and waist circumference for the predictive potential of diabetes needs to be emphasized and intensified.
Key words: Fasting blood glucose, Fasting glucose variation,Glycosylated hemoglobin, Human parameters, Correlation
Introduction
T he World Health Organization(WHO) predicted that global number of patients with diabetes will exceed 300 million in 2025[1]. Diabetes has become the third serious chronic disease that threatens human health after cancer and cardiovascular disease [2]. In order to improve the effectiveness of diabetes prevention, it is necessary to explore the key factors for diabete prevention.Diabetes diagnostic criteria in the Diabetes Care Guide developed by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) is FPG ≥ 7.0 mmol/L; OGTT ≥ 11.1mmol/L; HbA1C ≥ 6.5% [3], Qiu Ying et al [4]considered that weightrelated parameters have a certain correlation with fasting plasma glucose (FPG). Body mass index(BMI), waist circumference (WC),waist hip ratio (WHR) and waist height ratio (WHtR) all increased with the increase of FPG value,especially when FPG was more than 5.6 mmol/L, but Han Qi [5]considered that the relationship between BMI and FPG was not significant, and some studies [6-7]pointed out that the correlation of WHR and WC with FPG was better than BMI. Combined BMI, WC,hip circumference (HC), WHR and WHtR predicted FPG is more accurately than either one alone. Wang Yu [8]pointed out that WC contributed the most to human body measurement indexes and was closely related to blood glucose level. However, reports about the relationship of HbA1C and FPG are little and the conclusions are also different. For example,Yang Chunfeng [9]believed that HbA1C might be affected by BMI, WHR and FPG, and regular detection of HbA1C was of great significance for monitoring the occurrence and development of diabetes. On the contrary, Wu Yanxiang [10]considered that the gender,age, BMI, and WC levels of type 2 diabetes were not related to HbA1C. The main criteria for clinical control of diabetes are the standard of FPG and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C), but studies [11]have shown that the development of diabetes and its complications is also significantly associated with glucose variability(GV), which is an independent risk factor for the prognosis of diabetes. It is also an independent predictor of all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and cancer mortality in diabetic patients, and an independent risk factor for predicting death and an effective parameter for managing patients with type 2 diabetes. FPG variability is usually assessed in FPG coefficient of variation (FPG-CV) in clinical studies[12]. We hypothesized that human-related parameters are associated with FPG, HbA1C, and FPG-CV.However, there was no complete report on the clinic,whether can we monitor human-related parameters to forecast FPG, HbA1C, and FPG-CV? If that, patients'condition can be estimated more comprehensive and systematic, timely prevented and treated, so that we can reduce the incidence and the risk of diabetes and reduce diabetes-related mortality. Therefore, this subject has a further discussion on the relationship of BMI, WC, HC,WHR and WHtR with FPG, FPG-CV and HbA1C.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 General information
111 subjects were from Second Affiliated Hospital of Tianjin Traditional Chinese Medicine University from October 2016 to December 2017, aged 21-68 years.Average age is 44.5 ± 23.5 years old. Each subject would conduct questionnaires (including general conditions, past history, etc.), physical examination(height, weight, WC, HC, laboratory FPG and HbA1C testing). All subjects must volunteer to participate in the study and sign informed consent.
1.2 Detection method
1.2.1 Measurement of BMI
Height and weight measurement used DST-600 ultrasonic height and weight meter producted by Dong Huayuan medical device company. The subject wore light clothes and shoes on an empty stomach, standing upright on the physical examination machine. The unit of length is cm, the unit of mass is kg, and keep one decimal place behind the decimal point. WC was measured by flexible ruler and by full-time personnel.The subject was required to stand naturally, with the feet separated by 25-30 cm, so that the body mass is evenly distributed. Their arms were folded across the chest, and the eyes were flat in front. The tester faces the subject and measures the circumference of 1.0 cm on the umbilicus when the subject is breathing smoothly. The value of the ruler crossing the "0" is the measured value[13]. The value of HC was calculated from the pubic symphysis and the most convex part of the gluteus maximus behind [14]by the tape ruler horizontally, with subjects' both legs closed and both arms naturally drooping. BMI= weight (kg)/ height2(m); WHtR = WC (cm)/ height (cm). WHR= WC (cm)/HC (cm). Blood glucose coefficient variation (FPG-CV)= mean FPG/standard deviation of FPG.
1.2.2 Measurement of FPG and HbA1C
All subjects were required to fast but could drink water after 22:00 on the night before the physical examination. Venous blood was collected on an empty stomach and submitted to the clinical laboratory department of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. HbA1C was detected by electrochemical analysis. FPG was measured by glucose oxidase method at 8:00 am every monday for 4 weeks.
1.2.3 Statistical method
The database was established by EpiData 3.0. The data was double-entered and checked, and analyzed by SPSS21.0 statistical software. Multiple linear regression models were used to calculate the five indexes (BMI, WC, HC, WHR, and WHtR) and the correlations of FPG, FPG-CV, and HbA1C. P<0.05 was statistically significant.
2 Result
Based on the anthropometric parameters of all subjects, it was found that the concentration change of WHtR and FPG is more closely, and the same with FPG-CV and HbA1C. Multiple linear regression analysis results of FPG, FPG-CV, and HbA1C are respectively t = 8.531, 6.910 and 6.905. Both relationship of WHtR with FPG and FPG-CV with HbA1C has a linear correlation, and the correlation coefficients were statistically significant, at 0.633,0.552, and 0.552, respectively (P<0.01). The specific results are as follows.
The correlation coefficients of between mean fasting blood glucose and body weight, BMI,WC, HC and WHR were T=0.709 and P=0.385, T=0.732 and P=0.419, T=0.107 and P=0.583, T=0.077 and P=0.521,T=0.196 and P=0.392 respectively.
The correlation coefficients of between FPGCV and body weight, BMI,WC, HC and WHR were T=0.633 and P=0.34, T=0.013 and P=0.326,T=0.784 and P=0.531, T=0.6 and P=0.424, T=1.976 and P=0.457 respectively.
The correlation coefficients of between HbA1C and body weight, BMI,WC, HC and WHR were T=0.441 and P=0.327, T=0.933 and P=0.387, T=0.670 and P=0.527, T=0.368 and P=0.469, T=0.503 and P=0.364 respectively.
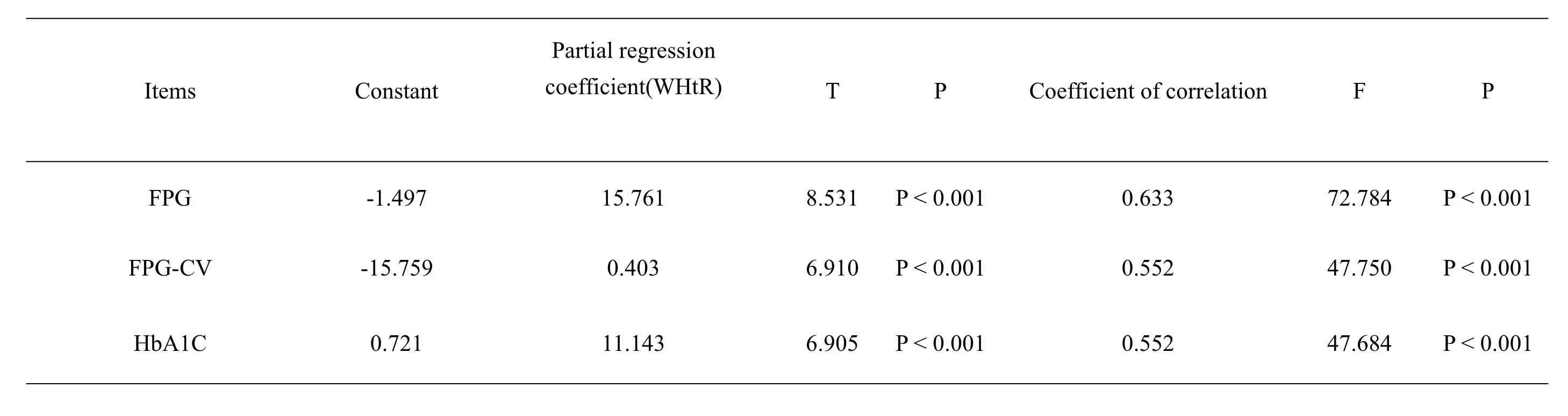
Table 1: Multiple linear regression analysis of individual anthropometric parameters
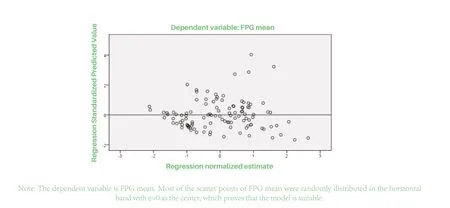
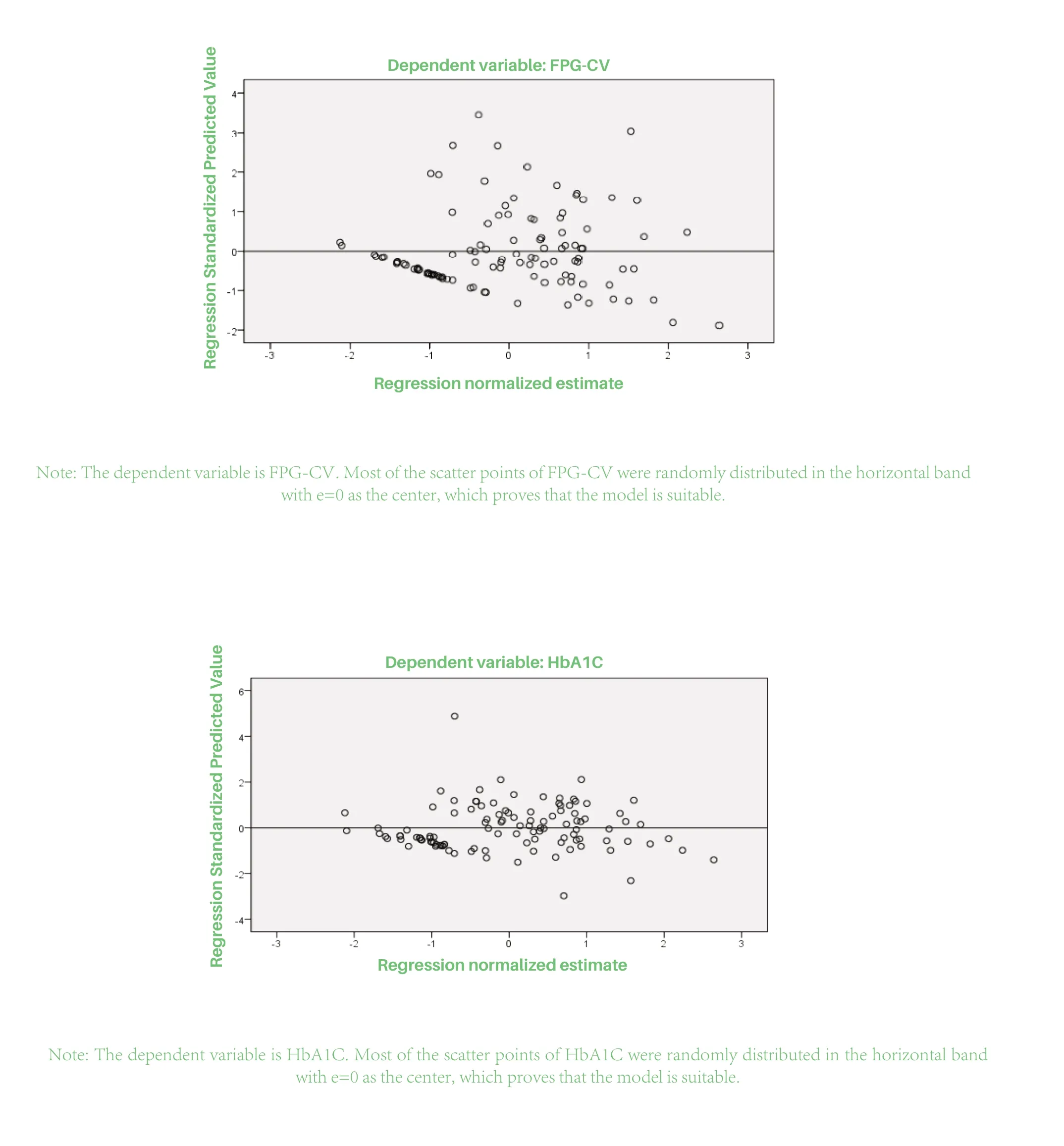
Figure 1 : Multiple linear regression residuals test
3 Discussion
In this experiment, we analyzed the correlation factors of all variables via multiple linear regression,and then showed the correctness of the results via residual test. According to the above analysis, WHtR is significantly correlated with FPG, CV and HbA1C.This is consistent with Hazen's report [15]that WHtR is a better indicator of abdominal obesity and has a higher predictive value for diabetes. However, weight,BMI, WC, HC, WHR are also correlated with FPG,CV and HbA1C to some extent, but the correlation coefficient was not large. There may be many factors influencing these parameters or the factors are lack of representativeness. For example, it has been reported[16]that WC, HC and age are correlated, while WHtR is not, and there is no gender difference. Therefore,measuring WHtR can forecast FPG, HbA1C and CV,screen diabetes faster and help identify people at high risk in an early time, so that patients could be educated and carried out to intervene their life way, physical exercise and so on. It has important social significance to avoid metabolic abnormalities and reduce the incidence, complications, poor prognosis, and economic burden. The role of prevention and detection of diabetes mellitus is often ignored in actual clinical practice, so this study hopes that the society can pay attention to human parameters, especially height and WC. In the future, it is necessary to strengthen the exploration of large clinical samples related to the prediction potential of diabetes. The shortcomings of our study are that the number of observation cases is small, the time is short and there is no gender comparison. In the future, multicenter and prospective studies are needed to further explore and verify the above conclusions.
