2014-2017年上海某社区糖尿病死亡特征分析
2019-02-18陈勇辉吴昊王云辉王伟
陈勇辉 吴昊 王云辉 王伟


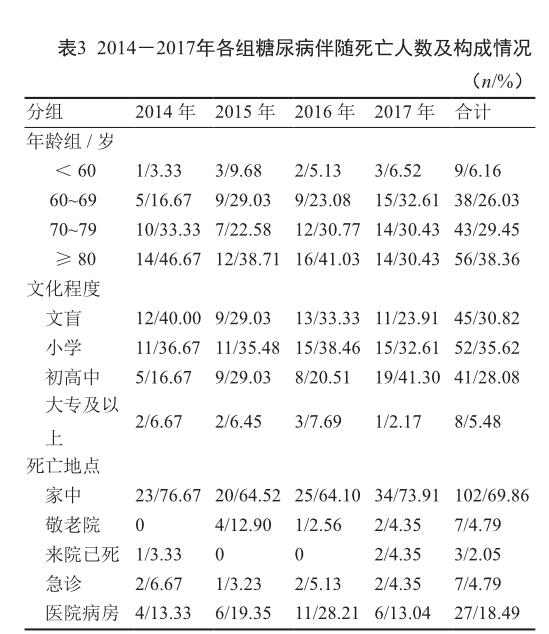
摘 要 目的:了解辖区户籍居民2014-2017年糖尿病死亡特征,为制定预防控制策略和措施提供依据。方法:采用描述统计方法计算和比较糖尿病相关的死亡率和构成比。结果:2014-2017年上海新桥镇户籍居民糖尿病年均粗死亡率为21.55/10万,标化死亡率为9.50/10万。其中,男性粗死亡率为14.36/10万,标化死亡率为6.88/10万,女性粗死亡率为28.75/10万,标化死亡率为12.10/10万。60岁及以上患者的死亡数开始明显增加,文化程度以文盲及小学文化程度为主,且多为院前死亡。高血压、恶性肿瘤和心脑血管疾病是主要伴发疾病。结论:老龄化对辖区糖尿病死亡率有较大影响,女性糖尿病死亡率高于男性。应加强社区糖尿病及其并发症的管理。
关键词 糖尿病;社区;死因
中图分类号:R587.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1006-1533(2019)02-0045-04
Analysis of death characteristics of diabetes mellitus in a community of Shanghai from 2014 to 2017
CHEN Yonghui, WU Hao, WANG Yunhui, WANG Wei(Prevention and Health Care Department of Xinqiao Community Health Service Center of Songjiang District, Shanghai 201612, China)
ABSTRACT Objective: To understand the death characteristics of diabetes among registered residents in the jurisdiction from 2014 to 2017 for providing basis for formulation of prevention and control strategies and measures. Methods: The descriptive statistical methods were used to calculate and compare the mortality and composition ratios associated with diabetes. Results: From 2014 to 2017, the average annual crude mortality rate of diabetes among registered residents in Xinqiao Community, Shanghai was 21.55/100 000, and the standardized mortality rate was 90.50/100 000. Among them, the crude mortality rate of males was 14.36/100 000, the standardized mortality rate was 68.88/100 000, the crude mortality rate of females was 28.75/100 000 and the standardized mortality rate was 12.10/100 000. The number of deaths among patients aged 60 years and older began to increase significantly; the culture was dominated by illiterate and primary school education, and most of them were pre-hospital deaths. Hypertension, malignant tumors, and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases were the major concomitant diseases. Conclusion: Aging has a greater impact on the mortality rate of diabetes in the jurisdiction, and the mortality rate of diabetes in women is higher than that in men. The management of diabetes mellitus and its complications in the community should be strengthened.
KEY WORDS diabetes; community; cause of death
隨着我国社会经济的发展和人们生活方式的改变,糖尿病正严重威胁着居民的健康,公共卫生问题本质日益浮现[1]。上海松江区新桥镇位于上海市西南外环以外的城乡结合部,本文旨在分析该地区居民2014-2017年糖尿病相关死亡的数据,为科学制定糖尿病社区防治策略和措施提供依据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 资料来源
人口资料来自上海市公安局松江分局新桥派出所户籍统计年报;死亡资料来自上海松江区卫生与计划生育委员会健康云平台户籍死亡数据库;标化死亡率计算采用2010年第六次全国人口普查数据为标准人口。
1.2 方法
社区生命统计条线人员每月按照国际疾病分类(ICD-10)方法对死亡单上登记的多个死因逐项进行疾病编码,结合调查推断,从死因链中摘选唯一的根本死因,由上海松江区疾病预防控制中心伤统科审核通过。本研究收集2014-2017年辖区户籍居民死亡资料中所有曾涉及糖尿病疾病编码(E10-E14.9)的死亡个案资料,计算死亡率,比较不同年龄组、文化程度、死亡地点的构成及伴发死因的情况。
