Belt and Road Trade Figures,2013-2017
2018-11-26byYinXing
by Yin Xing
In September 2013, Chinese President Xi Jinping proposed the Silk Road Economic Belt followed by the introduction of the 21st-Century Maritime Silk Road that October, which together became known as the Belt and Road Initiative. Over the five years spanning from 2013 to 2017, the total trade volume between China and countries along the Belt and Road routes reached US$6.98 trillion with a growth rate much faster than that of Chinas overall foreign trade. China has become the largest trading partner for 25 nations and signed or updated five free trade agreements with 13 nations along the routes. Also over the past five years, Chinas direct investment in countries along the Belt and Road has exceeded US$70 billion at an annual growth rate of 7.2 percent. The value of new contracted projects in those countries surpassed US$500 billion at an annual growth rate of 19.2 percent.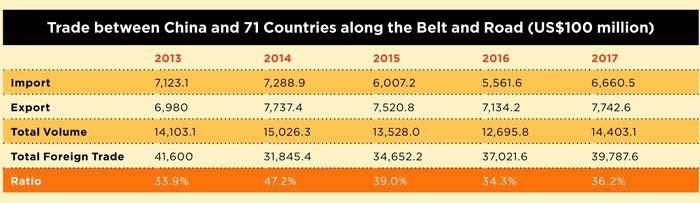
Chinas Top Ten Trading Partners along the Belt and Road, 2017
In 2017, Chinas top ten trading partners along the Belt and Road were South Korea, Vietnam, Malaysia, India, Russia, Thailand, Singapore, Indonesia, the Philippines and Saudi Arabia. The total volume of trade between China and those countries accounted for 68.9 percent of the total trade volume between China and countries along the Belt and Road.
Exceptionally high growth was seen between China and countries including Qatar, Montenegro, Mongolia and Kazakhstan, with an increase of over 35 percent compared to the previous year.

Top Ten Sources of Chinese Imports along the Belt and Road, 2017
In 2017, the top ten exporters to China along the Belt and Road were South Korea, Malaysia, Vietnam, Thailand, Russia, Singapore, Saudi Arabia, Indonesia, South Africa and the Philippines. The combined value of their exports to China accounted for 75.5 percent of Chinas imports from all nations along the Belt and Road.
Exceptionally fast growth in exports to China came from East Timor, Yemen, Maldives, Egypt and Montenegro, all expanding by over 100 percent.
Top Ten Destinations for Chinese Exports along the Belt and Road, 2017
In 2017, the top ten destinations for Chinese exports along the Belt and Road were South Korea, Vietnam, India, Singapore, Russia, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, the Philippines and the United Arab Emirates. Together, they imported 65.6 percent of the total value of Chinas exports to nations along the Belt and Road.
Chinas fastest-growing export destinations along the routes include Laos, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Moldova, Slovenia, Bhutan, Serbia, Armenia, Mongolia, Afghanistan, Lithuania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia, Montenegro and Cambodia, which all increased their imports from China by more than 20 percent from the previous year.
Trade Structure
In 2017, the exported commodities from China to countries along the Belt and Road were dominated by boilers, machinery, mechanical appliances and parts, electrical equipment and parts, audio recorders and television equipment, which accounted for 38.2 percent of all exports from China to those countries.
In 2017, the commodities imported by China from nations along the Belt and Road mainly included fossil fuels, mineral oils and related products, bituminous substances and mineral waxes, electrical equipment and parts, audio equipment and television equipment, which accounted for 50.3 percent of the total value of Chinas imports from those nations.
Main Trade Contributors
In terms of trade value, private Chinese companies were the primary contributors.
In 2017, trade volume between Chinas private enterprises and countries along the Belt and Road reached US$620 billion, accounting for 43 percent of the total, followed by foreignfunded enterprises (36.6%) and state-owned enterprises (19.4%).
In terms of growth rate of trade volume, state-owned enterprises led the trend with a year-on-year growth of 24.5 percent, contributing trade volume of US$279.6 billion with countries along the Belt and Road in 2017, followed by private companies(12.1%) and foreign-funded companies (10.2%).
Types of Trading
General trade dominated trading between China and countries along the Belt and Road. In 2017, the value of general trade reached US$840.76 billion, accounting for 58.4 percent of the total value, followed by processing trade with imported materials (19.5%), other trades (14.5%), processing and assembly with supplied materials (5.0%) and petty trade in the border areas (2.6%).
Petty trade in the border areas between China and countries along the Belt and Road saw a particularly rapid growth. In 2017, its value reached US$38 billion, up by 17.3 percent from 2016, followed by general trade (16.1%), processing trade with imported materials (12.9%), other trades (10.3%) and processing and assembly with supplied materials, which actually dropped by 4.5 percent.