Effect of acupoint massage plus acupoint sticking therapy for the stress reaction during postoperative anesthesia recovery period in patients undergoing nasal endoscopic surgery
2018-10-22LuWeiyu陆伟钰ShenJuanfen沈娟芬ShenLiping沈丽萍ZhuJianfen朱建芬
Lu Wei-yu (陆伟钰), Shen Juan-fen (沈娟芬), Shen Li-ping (沈丽萍), Zhu Jian-fen (朱建芬)
Tongxiang City Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhejiang 314500, China
Abstract
Keywords: Tuina; Massage; Acupoint Sticking Therapy; Nasal Surgical Procedures; Anesthesia Recovery Period; Anesthesia,General; Drug-related Side Effects and Adverse Reaction
Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) has been widely used clinically for its clear view and convenience for fine operation; however it may cause a strong stimulation to patients.Therefore, it requires sufficient anesthesia to inhibit the stress reaction and maintain the stability of hemodynamics during surgery.After surgery, a nasal cavity blocking hemostasis method is also required.The patients should keep a rapid and stable awakening process during postoperative anesthesia recovery period, and avoid sharp fluctuation and restlessness which may lead to hemorrhage in surgery region[1-3].However, during general anesthesia resuscitation period, certain adverse reactions might be induced by anesthesia medication, surgery trauma,hyper-function of nerves, and pathophysiological specificity of patients.Common adverse reactions include nausea, vomiting, headache, restlessness,abnormal blood pressure, retardation of awakening,post anesthesia shiver and airway obstruction[4].We have used acupoint massage plus acupoint sticking therapy to treat stress reaction during postoperative anesthesia recovery period in patients undergoing nasal endoscopic surgery, and observed the stress reaction during anesthesia resuscitation period.The report is now given as follows.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Inclusion criteria
Patients undergoing nasal endoscopic surgery and under trachea intubation and general anesthesia.Graded I-II according to the American Society of Anesthesiologist (ASA) criteria; aged above 18 years,male or female; good compliance and informed consent.
1.2 Exclusion criteria
With heart, cerebral or lung diseases or abnormal liver and kidney functions; with hearing disorder or a history of allergy; skin lesion around acupoint massage or acupoint sticking regions; obvious abnormalities in pre-operation tests.
1.3 Statistical methods
All data were analyzed by SPSS version 17.0 software.Measurement data of normal distribution were described as mean ± standard deviation () and compared byt-test.Chi-square test was used for the enumeration data comparison.APvalue less than 0.05 indicated statistical significance.
1.4 General data
A total of 120 patients undergoing nasal endoscopic surgery were included, and all patients were under trachea intubation and general anesthesia.The patients were included between December 2016 and November 2017 in the clinic of Tongxiang City Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine.They were randomized allocated according to their visiting sequence by the random number table into an observation group and a control group, with 60 cases in each group.In comparisons of the gender, age, surgery time, amount of bleeding and body mass index (BMI), the differences showed no statistical significance (P>0.05), showing that the two groups were comparable (Table 1).

Table 1.Comparison of general data
2 Treatment Methods
2.1 Control group
The patients were restricted from drink and food during pre-operation period, with no medicine administrated.The left upper-limb vein was accessed before the operation.When the patient entered the operation room, the monitor was connected to measure non-invasive blood pressure (NIBP) of the right arm, electrocardiograph (ECG) and peripheral oxygen saturation (SPO2) on the tip of the left thumb.Then a combined anesthesia was conducted by an anesthetist according to the unified standard and all vital signs were kept in the range of ±20% of those before the operation.Anesthesia supply was stopped 10 min before the end of the operation.After the operation, patients were transferred to a post-anesthesia care unit (PACU).After the secretion in mouth and trachea was cleared away,AIR LIQUIDE ventilator (Model MONNAL T75) was connected with SIMV mode.The heart rate (HR), ECG,systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure(DBP) and SPO2of the patient were monitored.When the patient restored awareness, and had a respiratory frequency >10 times/min, spontaneous exhaled tidal volume (Spon Vt) >350 mL and SPO2>95% under air breathing condition, sputum was sucked and tracheal tube was removed, and then a oxygen maskwas applied at 3 L/min until the patient left the PACU.Conducted follow-up visit twice in 24 h after the operation.
2.2 Observation group
On the basis of the conventional treatment as for the control group, acupoint massage and acupoint sticking therapy were added.All nurses in the operation room were trained for acupoint massage and acupoint sticking manipulation and passed the examination.
2.2.1 Acupoint massage
Acupoints: Hegu (LI 4) and Neiguan (PC 6) on the right side.
Methods: When the patient was sent to PACU and started anesthesia resuscitation, acupoint massage was given immediately.The nurse was standing on one side of the patient, with the left hand holding the patient’s forearm, and the right hand selecting the acupoint.Used one-thumb Tui-pushing manipulation (took finger tip, finger print surface or radial side of the finger as the attachment to certain acupoint or location, and used elbow joint as the supporting point to conduct a coordinated swaying movement of waist joint and forearm, and flexion and extension movement of the thumb to function on certain location or acupoint)during acupoint massage[5-6].The massage was given for 2 min at each acupoint during the withdrawal of the tracheal tube and the following 5 min.
2.2.2 Acupoint sticking therapy
Medicinal herbs:Sheng Jiang(Rhizoma Zingiberis),Ban Xia(Rhizoma Pinelliae),Wu Zhu Yu(Fructus Evodiae)andRou Gui(Cortex Cinnamomi), 30 g of each ingredient.
Acupoints: Shenque (CV 8), Zhongwan (CV 12) and Danzhong (CV 17).
Methods: A mixture ofSheng Jiang(Rhizoma Zingiberis),Ban Xia(Rhizoma Pinelliae),Wu Zhu Yu(Fructus Evodiae) andRou Gui(Cortex Cinnamomi), 30 g of each ingredient, was ground into fine powder and mediated with sesame oil, and then the mixture was heated into paste and stored in a sealed pot.As for manipulation, took 2 g of the paste each time and smeared it on acupoint pastry, which was then pasted on the above acupoints 30 min before the end of the operation.Slightly kneaded the pastry and retained it for 4 h.
3 Therapeutic Efficacy Evaluation
3.1 Evaluation items
Changes in the HR, SBP and DBP were recorded at three time points including the end of the surgery (T0),the removal of the tracheal tube (T1) and 10 min after the removal of the tracheal tube (T2).Recorded the awakening and tube removal time, and happenings of choking cough and restlessness, and adverse reactions(dizziness, nausea and vomiting) in 24 h post-surgery period.All the observation in PACU was conducted by a senior and experienced anesthesia nurse; the observer had no access to the group allocation details.
3.2 Results
There were no adverse reactions or dropouts during the treatment period.
3.2.1 Comparisons of HR, SBP and DBP at each time point
There were no significant between-group differences in HR, SBP and DBP at T0 (allP>0.05).The betweengroup comparisons of HR, SBP and DBP at T1 and T2 showed statistical significance (allP<0.05).In the control group, HR, SBP and DBP at T1 and T2 showed statistical significance when compared with those at T0(allP<0.05), (Table 2).
Table 2.Comparison of HR, SBP and DBP between the two groups at each time point ()
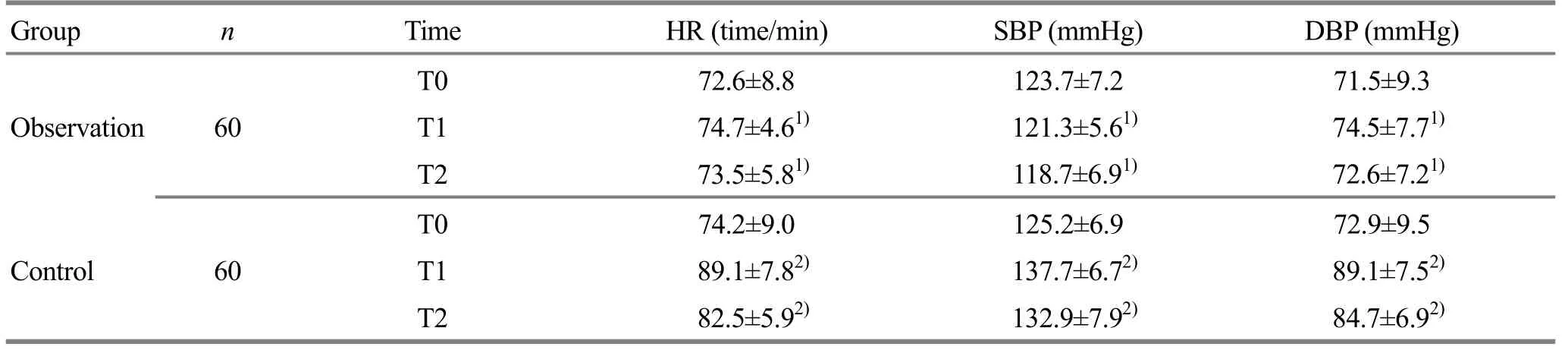
Table 2.Comparison of HR, SBP and DBP between the two groups at each time point ()
Note: Between-group comparison, 1) P<0.05; compared with that at T0 in the same group, 2) P<0.05
Group n Time HR (time/min) SBP (mmHg) DBP (mmHg)T0 72.6±8.8 123.7±7.2 71.5±9.3 Observation 60T1 74.7±4.61) 121.3±5.61) 74.5±7.71)T2 73.5±5.81) 118.7±6.91) 72.6±7.21)T0 74.2±9.0 125.2±6.9 72.9±9.5 Control 60T1 89.1±7.82) 137.7±6.72) 89.1±7.52)T2 82.5±5.92) 132.9±7.92) 84.7±6.92)
3.2.2 Comparisons of awakening time and tube removal time
The between-group comparisons of the awakening time and tube removal time showed statistical significance (allP<0.05), (Table 3).
3.2.3 Comparisons of occurrence rates of choking cough and restlessness
The incidences of choking cough and restlessness were 8.3% and 3.3% respectively in the observation group, versus 53.3% and 30.0% in the control group,and the between-group comparisons showed statistical significance (P<0.05), (Table 4).
Table 3.Comparisons of awakening time and tube removal time between the two groups (, min)
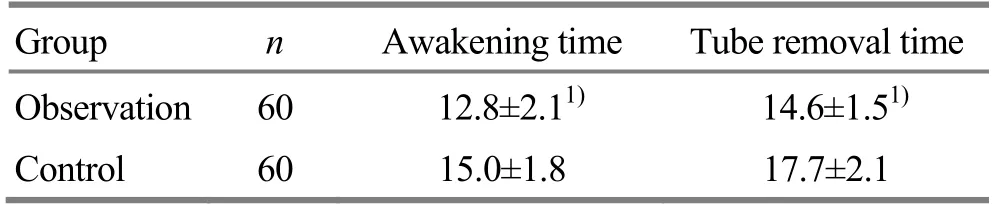
Table 3.Comparisons of awakening time and tube removal time between the two groups (, min)
Note: Between-group comparison, 1) P<0.05
Group n Awakening time Tube removal time Observation 60 12.8±2.11) 14.6±1.51)Control 60 15.0±1.8 17.7±2.1
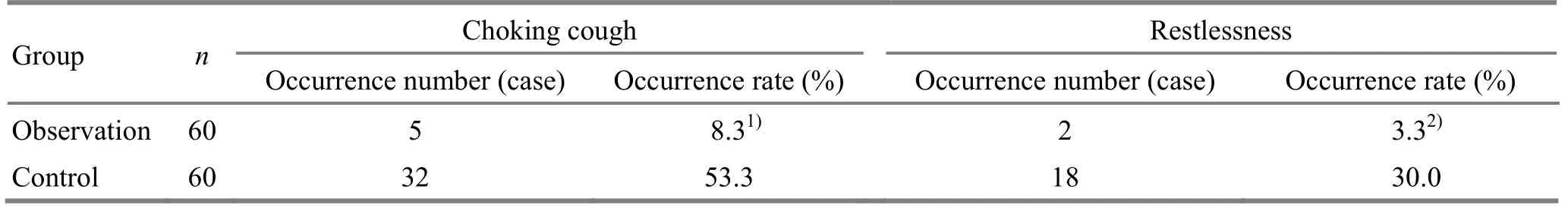
Table 4.Comparisons of occurrence rates of choking cough and restlessness at tube removal in the two groups
3.2.4 The incidence of adverse reaction in 24 h postsurgery period
The incidences of dizziness, nausea and vomiting in 24 h post-surgery period were 3.3%, 5.0% and 0.0%respectively in the observation group, versus 43.3%,33.3% and 25.0% in the control group, and the between-group comparisons showed statistical significance (allP<0.05), (Table 5).
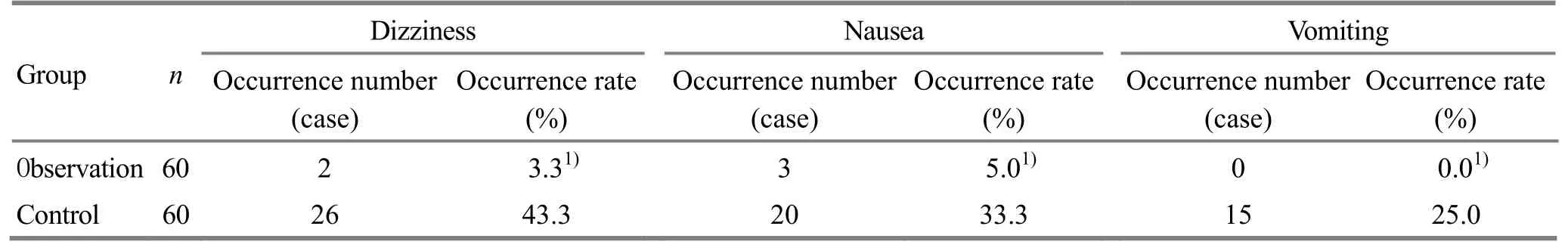
Table 5.The incidence of adverse reactions in 24 h post surgery
4 Discussion
Anesthesia resuscitation is a crucial step in the anesthesia management of nasal endoscopic surgery.Patients in this period are affected by the stimulation from tracheal tube, respiratory tract secretion, and nasal cavity blocking hemostasis, anesthetics, pain and sputum suction or other factors.Such stimulation can give rise to the stress response of the sympatheticparasympathetic nerve reflex, thus causing serious cyclical fluctuation and leading to adverse reactions including restlessness, choking cough, nausea and vomiting.To alleviate the stress response during the resuscitation period, medicines such as imidazole,propofol and opioid drugs are usually prescribed.However, these medicines usually prolong the awakening time or even increase the tube removal risks[7].Therefore, sedatives and analgesics are not recommended.Moreover, application of cardiovascular drugs may also cause adverse effects[8].
In this study, Hegu (LI 4) (the Yuan-Primary point of the Large Intestine Meridian) and Neiguan (PC 6) (the Yuan-Primary point of the Pericardium Meridian) were used for massage to calm the mind, relieve pain and stop vomiting[9].Reports showed that stimulation to Hegu (LI 4) can decrease the randomization and complexity of the brain[10].Neiguan (PC 6) has also been widely used in the anti-stress researches[11].Some researches showed that acupoint stimulation had the function of dredging meridians, facilitating qi and blood movement, and regulating the function of nerves and body fluid, and acupoint massage can regulate blood pressure and pulse rate of the patients to a relatively stable level[12].
Acupoint sticking therapy can exert the stimulation of both meridians and herbs, and thus has the function of regulating yin and yang and Zang-fu organs, and dredging meridian qi and blood.Such method has been widely used in the prevention and treatment of diseases[13].As an external treatment method, acupoint sticking therapy is both safe and cheap[14].In this study,we choseSheng Jiang(Rhizoma Zingiberis),Ban Xia(Rhizoma Pinelliae),Wu Zhu Yu(Fructus Evodiae) andRou Gui(Cortex Cinnamomi)for the acupoint sticking therapy.Sheng Jiang(Rhizoma Zingiberis) can warm the lung and suppress cough, warm the middle jiao and stop vomiting, and it has been used primarily for vomiting and cough[15];Ban Xia(Rhizoma Pinelliae) can direct qi downward to ease vomiting, and dry dampness to resolve phlegm, and it can also influence the vomiting-related nervous center;Wu Zhu Yu(Fructus Evodiae) can direct qi downward to stop vomiting and warming the middle jiao to relieve pain, and it can also dilate blood vessels at the same time;Rou Gui(CortexCinnamomi) can invigorate the stomach, activate blood flow and stop pain[16].Shenque (CV 8), Zhongwan(CV 12) and Danzhong (CV 17) were used in this study.Sticking at the aforementioned acupoints can directly reach the disease location, and relax stomach smooth muscle spasm, reduce throat stimulation, and stop nausea and vomiting[17].Shenque (CV 8) can warmand tonify original yang, fortify spleen and stomach and secure the prolapse[18-19]; Zhongwan (CV 12) is focusing on harmonizing the stomach and regulating qi;Danzhong (CV 17) is the Front-Mu point of the Pericardium Meridian, and the influential point of qi in the Eight Influential Points.Modern research has shown that Danzhong (CV 17) can regulate nerves, relax vascular smooth muscle and dilate coronary artery[20-22].Acupoint sticking therapy is a convenient method with a small dose of medication.It can effectively avoid the first-pass effect at the liver and inactivation of the intestine and stomach, and thus increase the therapeutic effect of the medicine and also lower the adverse reactions at the same time[23-25].
This study showed that acupoint massage plus acupoint sticking therapy can effectively regulate the stress response during postoperative anesthesia recovery period in patients undergoing nasal endoscopic surgery, and maintain a stable internal environment.Acupoint massage and acupoint sticking therapy are green treatment methods of traditional Chinese medicine[26-27].Such methods can give full play of the dual-regulation function of meridians and herbs.The two methods are mutually motivated, coordinated and overlaid with each other to regulate the stress response, maintain stable hemodynamics and increase safety in patients during postoperative anesthesia recovery period.
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Effect of liver-soothing and mind-regulating acupuncture on resting-state electroencephalographic signals in rats with post-traumatic stress disorder
- Effects of electroacupuncture of different frequencies on free radicals in hippocampus of mice with vascular dementia
- Experimental study on the influence of pressing force and time on thermal effect of An-pressing manipulation
- Clinical experience of Xiangxi Liu’s infantile tuina for exogenous fever in children
- Therapeutic observation of acupuncture plus tuina for cervical vertigo
- Clinical observation of sinew-regulating and bone-setting manipulation combined with functional exercise to treat rotator cuff injury
