A dual-antenna global positioning system(GPS)receiver based automated leveling system for tuber harvesters of Ophiopogon japonicus
2018-09-15ZHANGFangmingLIJiamingCHENJiasongSchoolofMechanicalandEnergyEngineeringNingboInstituteofTechnologyZhejiangUniversityNingbo500ZhejiangChinaNingboMicroagriTechnologyLtdNingbo500ZhejiangChinaThe8thInstituteofChinaElectronicS
ZHANG Fangming,LI Jiaming,CHEN Jiasong(.School of Mechanical and Energy Engineering,Ningbo Institute of Technology,Zhejiang University,Ningbo 500,Zhejiang,China;.Ningbo Microagri Technology Ltd.,Ningbo 500,Zhejiang,China;.The8th Instituteof China Electronic Science and Technology Group,Hefei0088,China)
Abstract Ophiopogon japonicus,a kind of local herbal remedies in Zhejiang,is usually grown on rectangular pieces of land.In harvesting season of O.japonicus when a tractor accidentally falls into any furrows,mechanical partsof the tuber harvester hitched behind areproneto break.To solvethisproblem,an automated leveling system,consisted of a field computer,an electronic control unit(ECU),a dual-antenna GPSreceiver,a rope-type sensor,a cylinder,and a hydraulic valve,was developed and tested so that the harvester remained level.The computer got rolling angle of the tractor and displacement of the cylinder in sequence,and then deduced rolling angle of the harvester.The system employed a proportion integration differentiation(PID)algorithm to calculate control quantity of the valve.The experimental results conducted in the fields of O.japonicus showed that the average elevation differenceof theleft and right pointswas1.04 cm,and thestandard deviation was2.39 cm.Therefore,the harvester could remain horizontal all thetime,and itsmechanical fracturewould nothappen again.
Key words automated leveling system;Ophiopogon japonicus;agricultural implement;dual-antenna GPS
Ophiopogon japonicus is a kind of local herbal remedies in Cixi City,Zhejiang Province,which takes three years growing from a seedling to a mature plant.Harvesting of this genus is a laborious and skilled physical work.A person should dig out the root while keeping the green plants on the ground,which will be cut apart and used as seedlings in the next turn.A tuber harvester,hitched behind a tractor by a three-point suspension mechanism,was used to dig out O.japonicus.In the first harvest season,it suffered from several mechanical failures,such as fracture of connecting rod and heavy wear of chainwheelsasshown in Fig.1.The main reason was serious roll of the tractor when its tires in one side fell into a furrow in the field and the connecting rod of this side undertook nearly the whole strain.Thus it is important to keep the harvester horizontal in thissituation.
Automated leveling system for agricultural machines had been developed for more than 10 years.The common approach is that one linkage rod of a tractor was replaced by a cylinders[1],which was governed by a control circuit according to the signal from the rolling angle sensor mounted on the harrow to maintain level.This kind of sensor and regulating cylinder was also used in our first-generation leveling system.Initial experiments showed that the sensor could not output correct and stable value due to violent jitter of the harvester.Literatures show that there are two other schemes to solve the issue.One scheme is to measure rolling angle of the tractor and displacement of the regulating cylinder,and then establish a conversion functiontoevaluatetherollingangleof theimplement[2-3].The other scheme is to use two ultrasonic sensors[4],mounted on each end of the sprayer to detect the height of spray boom,thereby controlling the hydraulic cylinders to keep level.Multi-antenna or dual-antenna global positioning system(GPS)was used to measure theattitudeanglesof aircraft early in the1990s[5-6].In the last 10 years,Chinese scholars had begun to research application of dual-antenna GPS,such as measurement of yaw angle of vehicle[7-8],ship’s attitude[9],missile attitude[10].In the missile test,the results showed the pitch angle error was less than 0.8°,and the yaw angle error was less than 0.7°,when the distance between the two antennas was 0.36 m.As a dual-antenna GPShad already been a part in previously developed guidance systems,we attempt to realize leveling control of agricultural implements by a dual-antenna GPSinstead of inclination sensor.

Fig.1 The1st-generation harvester
1 Materialsand methods
1.1 Leveling measurement and control method
The 2nd-generation of tuber harvester was a lengthened,double-layer vibrating machine(YJS-1,Dilong,China).A wheeled tractor(1204,Xingguang,China)was used as the power of the harvester.The harvester wasconnected with thetractor in a three-point suspension mode,as shown in Fig.2.The leveling system consisted of a field computer,an electronic control unit(ECU),a dual-antenna GPSreceiver(382,Beiyun,China),a rope-type sensor,and a hydraulic system.The left straight rod was replaced by the cylinder,whose action was controlled by the ECU.Two GPSantennas were mounted,which were one left and one right on the driver’s cab.The GPSreceiver output rolling angleswith precision of 0.08°per 2 m,wherethe precision was 0.15°in this application.The field computer received rolling angles from the GPS and sampled the displacement of cylinder from therope-type sensor.

Fig.2 Tractor,harvester,and leveling regulation system
A linear functional relationship of the elevation difference between pairs of the left and right end points of the implement and the data of rope sensor were established through an experiment.Before the experiment,the harvester was lifted from horizontal posture to a height of about 30 cm,and then the left end of the harvester was lifted to its highest position.An optical level,standing 5 m far behind,was used to read numbers on a ruler standing on the left or right end of the implement.The left end of the implement dropped bit by bit.The numbers on the ruler and the analog-to-digital(A/D)value of the rope sensors were read once every drop.When the left side reached to the nadir,a set of elevation differences and A/D values were obtained,as shown in Fig.3,which showed a linear relationship between these two data.Using the least square method,the relationship was established,asshown in formula(1):

Where,yˆ1is the estimated elevation difference caused by the cylinder,cm;x is the A/D value obtained from therope sensor.

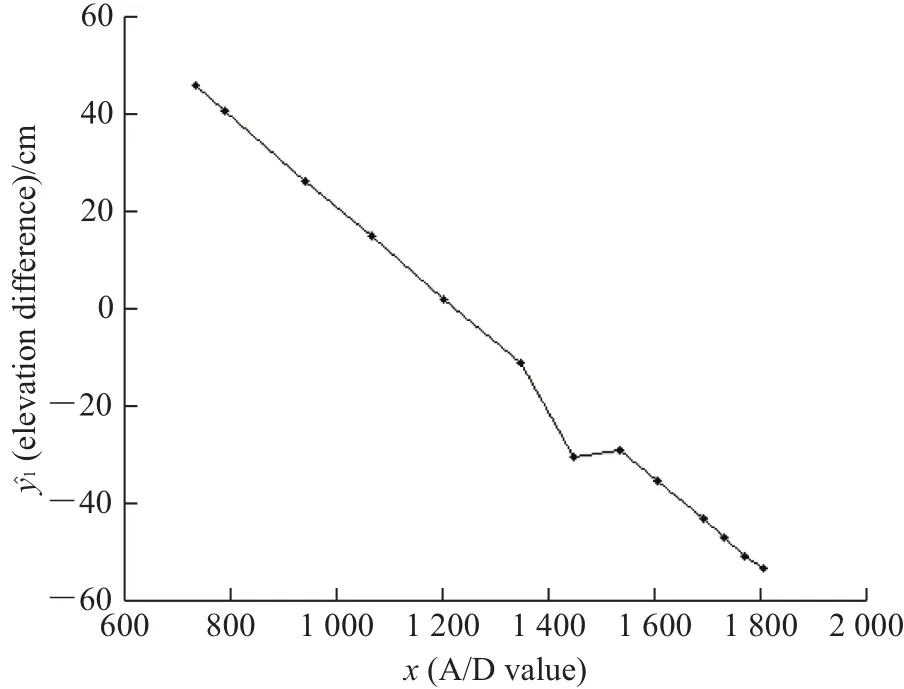
Fig.3 Measured relationship between elevation differences and A/D values
The elevation difference caused by tractor rolling could be calculated as the following equation:Where, yˆ2is the estimated elevation difference caused by tractor rolling,cm;W is the width of the implement,cm;γisthe rolling angle of the tractor.
These above two items constituted the total estimated elevation difference.The field computer calculated the elevation difference in every 200 ms,and produced the control quantity and moving direction of the cylinder through a proprotion integration differentiation(PID)algorithm.Finally,the ECU controlled the solenoid valve to adjust the expansion of thecylinder.
1.2 The hydraulic system
The hydraulic system was composed of a directional valve(FW-02,Hoyea,China),a spool-type cartridge relief valve(LADRV2-10,Ketai,China),and a cylinder(Shengli,China).Fig.4 shows the hydraulic schematic diagram,where the directional valve controls lifting or dropping action.
2 Field application test
Farmland condition:a dryland with ridges of 1.5 m widewasselected for testing.
Test processing:The machine was used for harvesting from May 4 to 10,2017.In the first two days,we recorded the control effect.Because it was difficult to measure the rolling attitude of the harvester directly,the leveling effect of the machine was evaluated by the land horizontal before and after harvesting.On the first day,the right tires fell into furrows,and the left tires fell into other furrows on the second day.Thus,the elevation measurements of each day were distinctly different,but this did not affect the elevation differences.Before harvesting,40 pairs of points were measured by the optical level at 3 m interval;after harvesting,the elevation was measured again with the level.
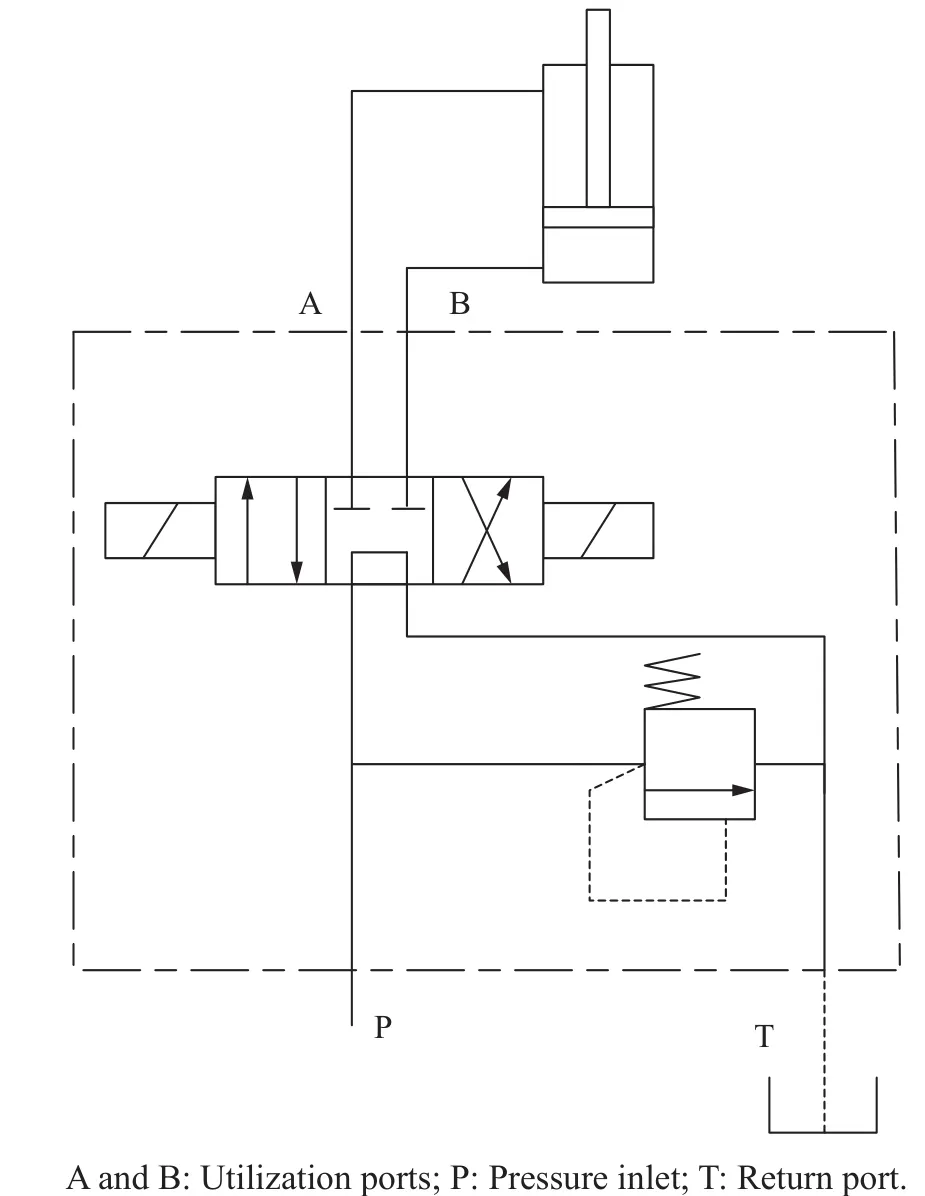
Fig.4 Hydraulic system
Data processing and analysis:Matlab software was used for data processing and graphic representation.The average value of the elevation difference represented the elevation difference,and the standard deviation represented the fluctuation degree of the elevation difference.Table 1 shows elevations before the harvest experiment,where the areais40 m×20 m,and thesampling interval is3 m.
Before harvesting, the average elevation differenceand standard deviation wereasfollows:

After harvesting,the 40 point-pairs were measured again,whose data were shown in Table2.
The average elevation difference and standard deviation were as follows:

3 Resultsand discussion
According to the data,the average elevation difference was improved significantly,and the rolling angle of the harvester was well controlled by this leveling system,thus the system greatly reduced the risk of structural fracture when harvesting.However,the elevation of land surface after balanced treatment was still a little fluctuating,which was caused by fluctuating surface in the moving direction.The nextstep is to measure the pitch angle of vehicle and the displacement of lifting cylinder in the whole suspension mechanism to estimate the elevation of the suspension and control thiscylinder.

Table 1 Sampling data before harvesting cm

Table2 Sampling data after harvesting cm
The PID algorithm used here only worked in the range of small elevation difference,which was set from-3 to 3 cm.When the difference was greater than 3 cm and less than 10 cm,the control output was 150 ms;and it was 200 ms when the difference was greater than 10 cm.Fig.5 shows a curve of the elevation difference estimated by the system.In most cases, the fluctuation range of the elevation difference was less than 3 cm;but when the rolling angle of the vehicle was obviously large,the elevation difference might be 5-20 cm in a short time.However,it could be controlled back to the level state in 5-10 sampling periods,or 1-2 s.

Fig.5 Continuously estimated elevation difference
During the field experiments,there were some cases out of control,which were caused by dust particles blocking the slide valve.After the slider was cleaned with diesel oil,the control system was restored.The hydraulic oil,obtained from hydraulic quick joint,was akind of hydraulic transmission dualpurpose oil.It might contain some dust after a long time use.Therefore,the cleanliness of oil is very important for the electromagnetic control system.
4 Conclusions
An automated leveling control system was added to the three-point suspension mechanism of a tractor for harvesting O.japonicus.The conclusions can be drawn:
1)The rolling posture of the harvester was no longer a rigid body with the tractor.Regardless of the rolling motion of tractor,the harvester can remain horizontal.The average elevation difference of the left and right points reduced from 30.66 to 1.04 cm,and the standard deviation was reduced from 6.32 cm to 2.39 cm.
2)The control frequency of 5 Hz can meet the requirementof leveling control.Thedual-antenna GPS receiver can reliably and accurately measure the rolling angle of the tractor.
3)Failure of connecting rod did not occur again in thisharvest season.
If the system is to be used in an 8 m wide paddy rake machine,a PWM(pulse width modulation)module will be used to control the solenoid valve to achievemore precisecontrol.
