血清let-7家族水平和大面积脑梗死的严重程度的相关性研究
2018-07-04洪有波
洪有波
急性缺血性脑卒中涉及颈动脉或大脑中动脉(MCA)整个血管分布区域可引起大面积脑梗死(MCI)[1],其短期和长期预后均较差,导致大多数患者死亡,即使生存也会遗留严重的神经功能损伤[2-4]。在所有MCA病变导致的脑梗死中MCI占10%~15%[5]。微小RNA(miRNA)是一组单链的非编码的RNAs,调节各种病理生理过程包括肿瘤发生、细胞增殖、造血、代谢、炎症、胚胎形成等[6-8]。let-7家族是在秀丽隐杆线虫中发现的第2个miRNA家族。后来的研究发现它具有重要的调控作用如细胞生长、分化和凋亡[9-11]。let-7表达异常与许多人类疾病如癌症和心血管疾病密切相关[12-13]。根据微阵列测定的结果,let-7家族在急性缺血性脑卒中患者体内表达异常[14-15]。慢性炎症一直被广泛认为在动脉粥样硬化形成过程中发挥重要作用[16],并且炎症标志物(例如IL-6)的水平与脑血管事件的风险存在一定的相关性[17-18]。本研究旨在评估急性大面积脑梗死(MCI)患者血清let-7家族水平与MCI严重程度的相关性。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
收集2014年1月-2017年6月在本院神经内科接受治疗的MCI患者88例。纳入标准:(1)年龄>18岁;(2)脑卒中48 h内入院;(3)根据CT或MRI表现,患者梗死面积占至少67%的MCA的分布区域[19]。排除标准如下:(1)患者由于代谢紊乱或药物治疗失去意识;(2)患者接受了任何镇静药物或手术治疗;(3)改良Rankin量表(mRS)的脑卒中术前评分>2; (4)合并可能影响患者临床结局的并发症如严重的心肺疾病。选取健康受试者(健康对照组,n=45),患有缺血性脑卒中而无MCI(IS无MCI组,n=40)和出血性脑卒中(ICH组,n=45)的患者作为对照组。对于没有严重心肺并发症的MCI患者,在发病2周后再次进行CT检查,确定发生出血性转化(HT)(n=22)和不存在HT(n=34)。
1.2 样本采集
采集静脉血5 mL,4℃,200 r/min×离心15 min,去除上清液在-80℃保存待测。
1.3 实时定量逆转录聚合酶链反应(real time qRT-PCR)
采用逆转录系统和Gotaq qPCR Master Mix(Promega)进行real time qRT-PCR。使用5s核糖体RNA(5s rRNA)作为标准化样品。按照试剂盒说明书使用LightCycler 1.5实时PCR系统(Roche)进行操作。采用比较周期阈值方法(Ct)进行qRT-PCR数据的比较。基因表达的相对变化使用Livak方法(也称为2-ΔΔCt方法)确定。所有反应重复进行3次。
1.4 统计学处理

2 结 果
2.1 2组患者的一般临床特征比较
在MCI组(48 h)、IS无MCI组,ICH组和健康对照组之间年龄和性别无明显差异(P均>0.05)(表1)。在MCI患者人群中发生出血性转化(HT)(n=22)和不存在HT的患者之间的年龄和性别没有明显差异(P均>0.05)(表2)。

表1 入院48 h内各组患者的年龄和性别比较)

表2 入院2周后MCI组内患者的年龄和性别比较)
2.2 实时qRT-PCR检测48 h各组Let-7家族mRNA表达水平
为了证实由微阵列鉴定的基因表达的变化,8种miRNA(let-7a,let-7b,let-7c,let-7d,let-7e,let-7f,let-7g,miR-98)被选择用于实时qRT-PCR的分析。(1)MCI组let-7c(0.123±0.072)和let-7f(1.188×10-2±0.737×10-2)相对表达水平显著降低;(2)IS无MCI组的let-7b(7.382±1.112),let-7c(34.226±4.642),let-7d(7.214±1.321)和let-7f(17.852±2.656)的相对表达水平明显增加;(3)ICH组的let-7f(40.251±3.572)的相对表达水平明显增加;(4)与IS无MCI和ICH组比较,MCI和健康对照组的let-7f的相对表达水平明显降低(P<0.001)(图1)。
2.3 实时qRT-PCR检测2周各组Let-7家族mRNA表达水平
(1)与MCI无HT(48 h)患者人群比较(1.188×10-2±0.737×10-2),MCI无HT(2周)患者人群的let-7f(0.145±0.092)相对表达水平明显升高(P<0.01);(2)与MCI无HT(2周)患者人群比较,MCI合并HT(2周)患者人群的let-7f(40.668±4.601)相对表达水平明显升高(P<0.01)。另外,在MCI无HT(48 h)和(2周)组let-7f相对表达水平与GCS正相关(r=0.639,P<0.01)(图2)。
2.4 Let-7f表达水平与hs-CRP的相关性
脑卒中的常规危险因素包括收缩压、舒张压、高密度脂蛋白(HDL)、低密度脂蛋白(LDL)、甘油三酯、空腹血糖水平、同型半胱氨酸和hs-CRP水平在MCI和IS无MCI组间无显著性差异(表3)。另外,hs-CRP的水平与let-7f的相对表达水平呈负相关(r=-0.673,P<0.01)。

图1 实时qRT-PCR检测48 h各组Let-7家族mRNA表达水平 A为与健康对照组比较,MCI组let-7c和let-7f相对表达水平显著降低(#P<0.01,*P<0.05);B为与健康对照组比较,IS无MCI组的let-7b、let-7c、let-7d以及let-7f的相对表达水平显著增加(#P<0.01,*P<0.05);C为与健康对照组比较,ICH组的let-7f的相对表达水平显著增加(#P<0.01);D为与IS无MCI和ICH组比较,MCI和健康对照组的let-7f的相对表达水平明显降低(#P<0.01);与ICH组比较,*P<0.01
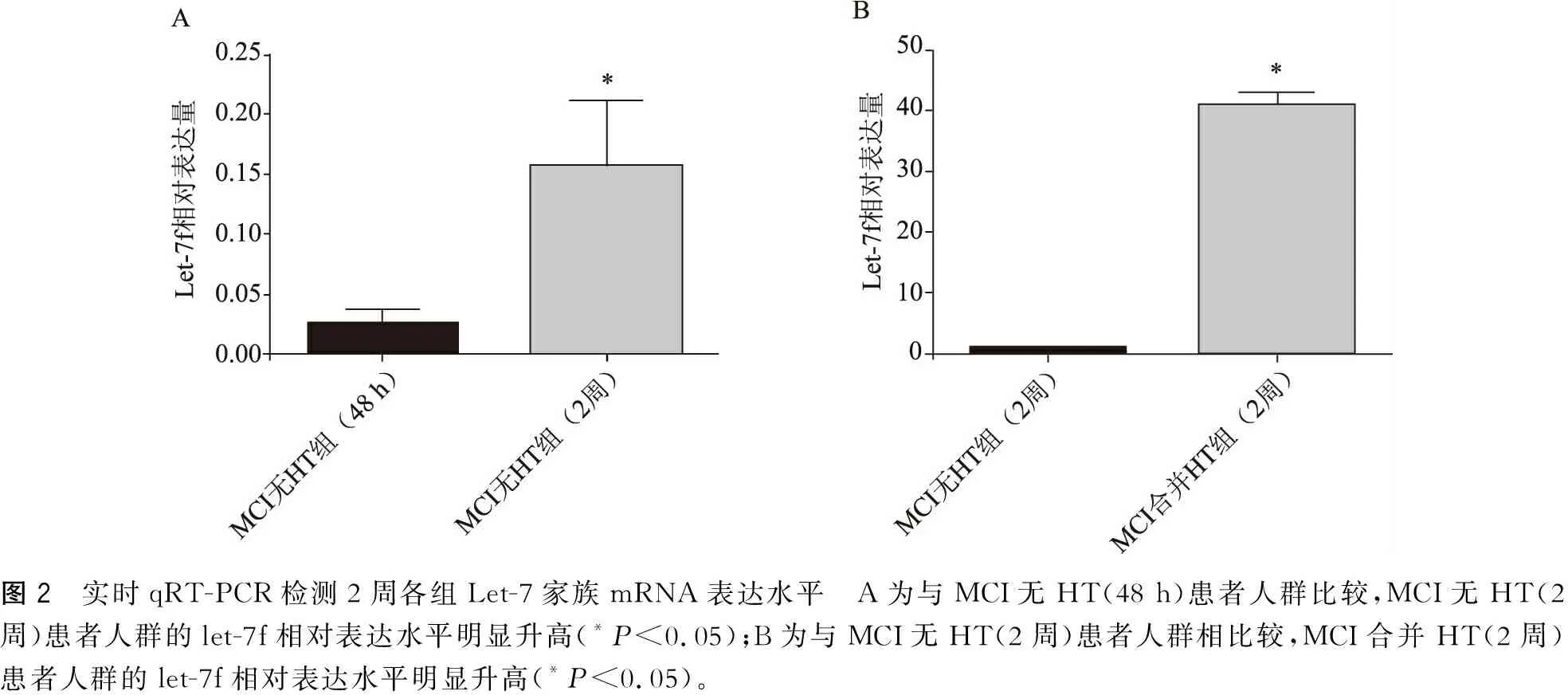
图2 实时qRT-PCR检测2周各组Let-7家族mRNA表达水平 A为与MCI无HT(48 h)患者人群比较,MCI无HT(2周)患者人群的let-7f相对表达水平明显升高(*P<0.05);B为与MCI无HT(2周)患者人群相比较,MCI合并HT(2周)患者人群的let-7f相对表达水平明显升高(*P<0.05)。
3 讨 论
本研究结果显示,与健康对照组和IS无MCI组患者比较,MCI患者的let-7f表达水平明显降低。此外,在MCI组中let-7f表达水平与hs-CRP水平呈负相关。另外,在MCI无HT患者人群中let-7f水平随着患者病情的改善而升高,与GCS呈正相关。
大量有关缺血性脑卒中的研究结果显示,炎症因子特别是IL-6影响继发性损伤和恢复的过程[20]。由于脑梗死过程中的缺氧和缺血性损伤而超量产生的ROS诱导IL-6上调[21]。此外,IL-6是炎症反应的早期和中枢性调控分子,通过引起内皮功能失调、平滑肌细胞增殖和迁移以及炎症细胞的募集和激活来促进动脉粥样硬化的发生发展[22]。作为IL-6的靶向分子,NF-κB作为转录因子促进iNOS的表达。iNOS在炎症期间高度表达,并导致NO的产生增加,导致大脑受到氧化性损伤[23]。此外,作为IL-6的下游分子,STAT3的激活与ROS产生有关,可能进一步增加IL-6的生成量。有研究发现,抑制STAT3激活能够减小局灶性脑缺血的梗死体积,减轻缺血/再灌注损伤。以前的研究表明,IL-6可能会造成缺血性脑卒中患者的神经功能障碍。除了IL-6外,其他的let-7f靶基因包括MYH9[24]、CYP19A1[25]、IGF-1R[13]、HMGB1[10]、胃蛋白酶原C[26]、IL-23R[27]、THBS1[28]、骨膜素[29]均参与了脑卒中的发生发展。
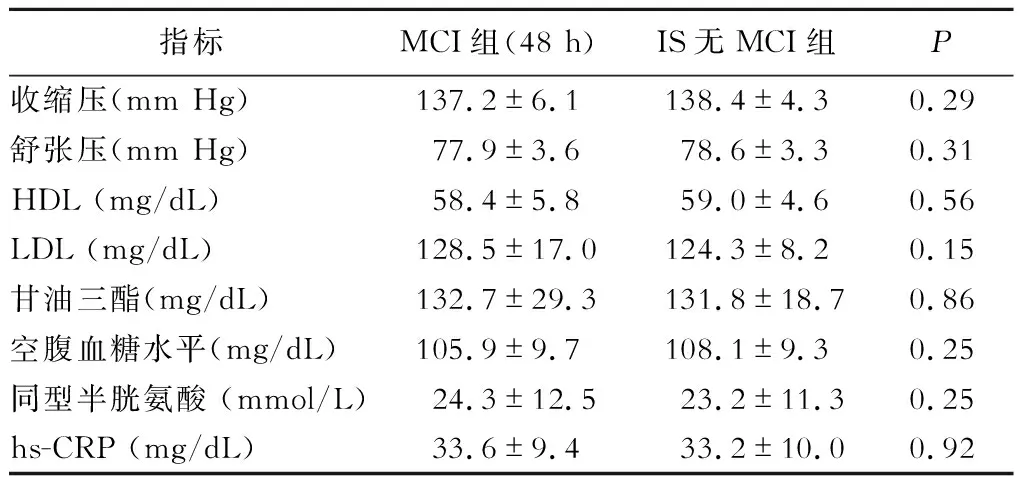
表3 MCI和IS无MCI组间脑卒中的常规危险因素的比较
大量体内和体外研究结果显示,let-7能够诱导神经元死亡,并且导致中枢神经系统损伤。最近的一项研究报道了炎症信号刺激的调节通路导致NF-kB核转位[30]。此外,本研究的实时qRT-PCR检测结果显示,与MCI无HT组(48 h)患者人群比较,MCI无HT组(2周)患者人群的let-7f相对表达水平明显升高(P<0.01);与MCI无HT组(2周)患者人群比较,MCI合并HT组(2周)患者人群的let-7f相对表达水平明显升高(P<0.01)。出血、局部炎症反应以及血管生成过程是HT的重要因素。O'Carroll等[31]发现促炎症因子TNF-α和人脑微血管内皮细胞(hCMVECs)的IL-1β活化是参与血脑屏障损伤的重要免疫介质。
综上所述,本研究发现与健康受试者、IS无MCI以及ICH患者比较,MCI无HT患者人群的Let-7f表达水平明显降低。此外,与健康受试者比较,MCI合并HT患者的Let-7f表达水平明显增加,这提示Let-7f可能参与了MCI过程中HT的发生发展。因为let-7f可以抑制IL-6的表达。因此,Let-7f在无HT的MCI患者中的水平降低可能会引起炎症反应。
[1] Sakai K,Iwahashi K,Terada K,et al.Outcome after external decompression for massive cerebral infarction[J].Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo),1998,38(3):131-135; discussion 135-6.
[2] Jeon SB,Koh Y,Choi HA,et al.Critical care for patients with massive ischemic stroke[J].Journal of stroke,2014,16(3):146-160.
[3] Subramaniam S,Hill MD.Massive cerebral infarction[J].Neurologist,2005,11(3):150-160.
[4] Caso V,Agnelli G,Alberti A,et al.High diastolic blood pressure is a risk factor for in-hospital mortality in complete MCA stroke patients[J].Neurol Sci,2012,33(3):545-549.
[5] Moulin D,Lo R,Chiang J,et al.Prognosis in middle cerebral artery occlusion[J].Stroke,1985,16(2):282-284.
[6] Budhu A,Ji J,Wang X.The clinical potential of microRNAs[Z],2010:37.
[7] Leeper N, Cooke J. MicroRNA and mechanisms of impaired angiogenesis in diabetes mellitus[J].Circulation,2011,123(3):236-238.
[8] Wang G,Van Der Walt JM,Mayhew G,et al.Variation in the miRNA-433 binding site of FGF20 confers risk for Parkinson disease by overexpression of alpha-synuclein[J].Am J Hum Genet,2008,82(2):283-289.
[9] Davoodian N,Lotfi AS,Soleimani M,et al.Let-7f microRNA negatively regulates hepatic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells[J].J Physiol Biochem,2014,70(3):781-789.
[10] Pannuru P,Dontula R,Khan AA,et al.miR-let-7f-1 regulates SPARC mediated cisplatin resistance in medulloblastoma cells[J].Cell Signal,2014,26(10):2193-2201.
[11] Ge W,Yu DC,Li QG,et al.Expression of serum miR-16, let-7f, and miR-21 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and their clinical significances[J].Clin Lab,2014,60(3):427-434.
[12] Sathe A,Patgaonkar MS,Bashir T,et al.MicroRNA let-7f: a novel regulator of innate immune response in human endocervical cells[J].Am J Reprod Immunol,2014,71(2):137-153.
[13] Hu W,Li T,Hu R,et al.MicroRNA let-7a and let-7f as novel regulatory factors of the sika deer (Cervus nippon) IGF-1R gene[J].Growth Factors,2014,32(1):27-33.
[14] Li PF,Teng FM,Gao F,et al.Identification of circulating MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for detecting acute ischemic stroke[J].Cell Mol Neurobiol,2015,35(3):433-447.
[15] Wang W,Sun G,Zhang L,et al.Circulating microRNAs as novel potential biomarkers for early diagnosis of acute stroke in humans[J].J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis,2014,23(10):2607-2613.
[16] Hansson G. Inflammation, atherosclerosis,and coronary artery disease[J].N Engl J Med,2005,352(16):1685-1695.
[17] Miwa K,Tanaka M,Okazaki S,et al.Association between interleukin-6 levels and first-ever cerebrovascular events in patients with vascular risk factors[J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2013,33(2):400-405.
[18] Manso H,Krug T,Sobral J,et al.Variants in the inflammatory IL6 and MPO genes modulate stroke susceptibility through main effects and gene-gene interactions[J].J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,2011,31(8):1751-1759.
[19] Wardlaw JM,Sellar R.A simple practical classification of cerebral infarcts on CT and its interobserver reliability[J].AJNR Am J Neuroradiol,1994,15(10):1933-1939.
[20] Titov BV,Barsova RM,Martynov MIu,et al.Polymorphic variants of genes encoding interleukin-6 and fibrinogen, the risk of ischemic stroke and fibrinogen levels[J].Mol Biol (Mosk),2012,46(1):93-102.
[21] Bowler RP,Sheng H,Enghild JJ,et al.A catalytic antioxidant (AEOL 10150) attenuates expression of inflammatory genes in stroke[J].Free Radic Biol Med,2002,33(8):1141-1152.
[22] Libby P, Ridker P, Maseri A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis[J].Circulation,2002,105(9):1135-1143.
[23] Niyazoglu M,Baykara O,Koc A,et al.Association of PARP-1, NF-κB, NF-κBIA and IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α with Graves Disease and Graves Ophthalmopathy[J].Gene,2014,547(2):226-232.
[24] Liang S,He L,Zhao X,et al.MicroRNA let-7f inhibits tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting MYH9 in human gastric cancer[J].PLoS One,2011,6(4):e18409.
[25] Shibahara Y,Miki Y,Onodera Y,et al.Aromatase inhibitor treatment of breast cancer cells increases the expression of let-7f, a microRNA targeting CYP19A1[J].J Pathol,2012,227(3):357-366.
[26] Liu WJ,Xu Q,Sun LP,et al.Expression of serum let-7c, let-7i, and let-7f microRNA with its target gene, pepsinogen C, in gastric cancer and precancerous disease[J].Tumour Biol,2015,36(5):3337-3343.
[27] Newcomb DC,Cephus JY,Boswell MG,et al.Estrogen and progesterone decrease let-7f microRNA expression and increase IL-23/IL-23 receptor signaling and IL-17A production in patients with severe asthma[J].J Allergy Clin Immunol,2015,136(4):1025-34.e11.
[28] Tao WY,Liang XS,Liu Y,et al.Decrease of let-7f in low-dose metronomic Paclitaxel chemotherapy contributed to upregulation of thrombospondin-1 in breast cancer[J].Int J Biol Sci,2015,11(1):48-58.
[29] Yan S,Han X,Xue H,et al.Let-7f inhibits glioma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting periostin[J].J Cell Biochem,2015,116(8):1680-1692.
[30] Gerard C,Gonze D,Lemaigre F,et al.A model for the epigenetic Switch linking inflammation to cell transformation:deterministic and stochastic approaches[Z],2014:e1003455.
[31] O'carroll S,Kho D,Wiltshire R,et al.Proinflammatory TNF alpha and IL-1beta differentially regulate the inflammatory phenotype of brain microvascular endothelial cells[J].J Neuroinflammation, 2015,12(3):131.
