Evaluation of Post-operative Anti-stress Response of Dexmedetomidine in Dogs
2018-06-14GuanWeiFengXiujingZhangLiangyuLuanLiWangJinyuTangYueshunLiuTaoandFanHonggang
Guan Wei, Feng Xiu-jing, Zhang Liang-yu, Luan Li, Wang Jin-yu, Tang Yue-shun, Liu Tao, and Fan Hong-gang*
1 Heilongjiang Key Laboratory for Animals and Comparative Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China
2 College of Veterinary Medicine, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China
3 College of Veterinary Medicine, Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning, China
Introduction
The surgery-induced stress response, including intense and fear in preoperative period, anesthesia operation,surgical trauma, pain and other aspects, exists in the whole perioperative process. Surgical trauma is the main factor which produces perioperative stress response. Dexmedetomidine, as the dextral isomers of medetomidine, is regarded as a newα2-adrenergic receptor agonist. Dexmedetomidine has many pharmacological effects, including sedation, muscle relaxation, analgesia, smooth hemodynamics, antistress, anti-tremor (side-effect caused by anesthetic)and decreasing the dosage of anesthetic (Parashchankaet al., 2014). In recent years, dexmedetomidine has been gradually applied in the field of clinical anesthesia in domestic and overseas, especially in the process of compound anesthesia and the induced anesthesia in small animals, such as dogs and cats(Canfránet al., 2016; Khenissiet al., 2016). In the effects of stress response, including the burn,surgical injuries and the pain, the body is under high metabolic conditions, glycogen breakdown, protein metabolism and accelerated fat mobilization. Besides,gluconeogenesis generates amino acids, fatty acids and lactic acids, which produce the glucose infiltrating into blood and result in increased blood sugar in bodies (Romanoet al., 2015; Srithunyaratet al.,2017). As the relative factor regulating the growth and development of adrenal cortex, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is also the important factor for animals expressing stress response. ACTH produced in the pre-pituitary is a kind of small molecule polypeptide consisting of amino acids. And the main physiological action is promoting the secretion and release of glucocorticoid (GCS) (Romanoet al., 2015).Cortisol (Cor), known as hydrocortisone, is a glucocorticoid produced by zona fasciculata of the adrenal gland secreting, with a wide range of anti-inflammatory effect. Cor mobilizes glucose, amino acids and fatty acids and other substances, then quickly generates energy for bodies to resist and avoid adverse stimuli during the stress response (Srithunyaratet al., 2017).The aim of this study was to explore the protective effects of dexmedetomidine on stress response induced by surgical trauma, which required to establish a dog trauma stress model and set up different groups, then administered low doses of dexmedetomidine and tilidine, respectively. Furthermore, blood glucose,serum Cor and ACTH contents were measured at different time points after operation.
Materials and Methods
Materials
Animals
A total of 32 healthy local female dogs aged from 11.3±2.4 months and weighting (7.7±2.2) kg. Vaccine immunization and conventional deworming were conducted before the experiment. Animals were fed with the complete formula feed of dog in the experimental animal room for 4 weeks. Physical examination was conducted one day before the test for details.
Drugs
Propofol injection (Fresenius Kabi AB, Lot 1505107),isoflurane (Hebei Nine Send Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd., batch number 111102), dexmedetomidine (trade name "Duomijing", Zoetis Animal Health Products Co., Ltd., batch number 1505107), tilidine (France,Granville Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., batch number 20155010801), dog cortisol ELISA kit (Suzhou Calvin Biotechnology Co., Ltd., batch number 20151010A),dog adrenal gland Corticosteroid ELISA kit (Beijing Lvyuan Bode Biotechnology Co., Ltd., batch number 20151005) and so on.
Equipments
YY-2 small animal breathing anesthesia machine(Jiangsu Kaitai Medical Equipment Co., Ltd.),continuous wavelength microplate reader (Gene Company Limited Medical Devices Co., Ltd.), micropipette and surgical instruments.
Methods
Animal grouping
A total of 32 dogs were randomly divided into four groups (n=8), including control group DZ (10 min after administration of intramuscular injection of 2 mL normal saline), group SQY (10 min before administration of intramuscular injection of 20 μg · kg-1dexmedetomidine), group SHY (10 min after admini-stration of intramuscular injection of 20 μg · kg-1dexmedetomidine) and group DLD (10 min after administration of intramuscular injection of 0.1 mL · kg-1tilidine). All the drugs were diluted to 2 mL by physiological saline. All the dogs of the four groups were performed hystero-oothecectomy. Then, the surgery trauma stress model was set up. After operation,normal and daily treatments were conducted. Dogs in the 4th group were administered with the same dosage of drugs as the first time between 6: 00-6: 15 a.m. on the 2nd day and the 3rd day after operation.
Pre-operation and anesthesia
Animals were fasting for solids and liquids for 12 and 6 h respectively before anesthesia. The experimental animals were brought in the disposal room to adapt to the environment 30 min before the anesthesia.Physiological basis values were measured, venous indwelling needles were placed and blood samples were collected. Then, atropine sulfate (0.02 mg · kg-1)was injected subcutaneous and anesthesia induction of intravenous injection of propofol injection (4 to 6 mg · kg-1) was pushed constantly after 15 min.Endotracheal intubation with isoflurane was conducted to maintain anesthesia.
Hystero-oothecectomy
The dog was immobilized with a supine condition. The hystero-oothecectomy was operated through the threeplier-way. Then, the surgical trauma stress model was established. All the surgical operations were carried out by one person.
Blood sample collection and detection
All the animals with limosis were taken brachial vein blood of 2 mL, which serum was collected from for measurement on the day of operation (3 h after operation), the 2nd day and the 3rd day (between 8:00 and 8:15 a.m.) and stored at -80℃ refrigerator.The blood glucose, Cor and absorbance of ACTH(OD) were measured at 450 nm by a microplate reader.The concentrations of blood glucose, Cor and ACTH were calculated.
Results
The results of blood glucose analyses showed that there were significant differences between group DZ and other groups at each time point except preoperative period and the 3rd day after operation with the comparison among groups (p<0.05). Group DZ had a similar trend to other groups with a variety of increasing first and then dropping with the comparison among groups (p<0.05). There were significant differences between the pre-operative period and the operation day, one day after, two day after, respectively(p<0.05). Specific results are shown in Fig. 1.
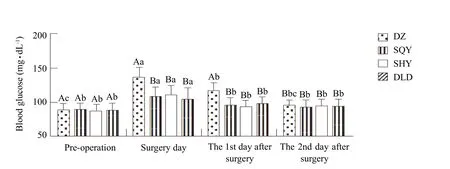
Fig. 1 Values of blood glucose of different groups (mg · dL-1, n=8)
The results of Cor analyses showed that there were significant differences between group DZ and other groups at each time point except pre-operative period with the comparison among groups (p<0.05). There were significant differences among groups SHY, SQY and DLD on the 2nd day and the 3rd day after operation (p<0.05). However, no significant differences were found in groups SQY and DLD, during the whole monitoring process (p>0.05). Group DZ had a similar trend to other groups with a variety of increasing first and then dropping with the comparison among groups(p<0.05). There were significant differences between the pre-operative period and the operation day, one day after, two day after, respectively (p<0.05). The specific results are shown in Fig. 2.
The results of ACTH analyses showed that there was no significant difference with the comparison among groups before and after operation (p>0.05).However, there were significant differences between group DZ and other groups on the day of surgery(p<0.05). Significant differences existed among group DZ and other groups (p<0.05), and no significant differences were found among the experimental groups (p>0.05). Group DZ had a similar trend to other groups with a variety of increasing first and then dropping with the comparison among groups (p<0.05).Some of the time points had significant differences.There were no significant differences between groups DZ and SQY (p>0.05). The specific results are shown in Fig. 3.
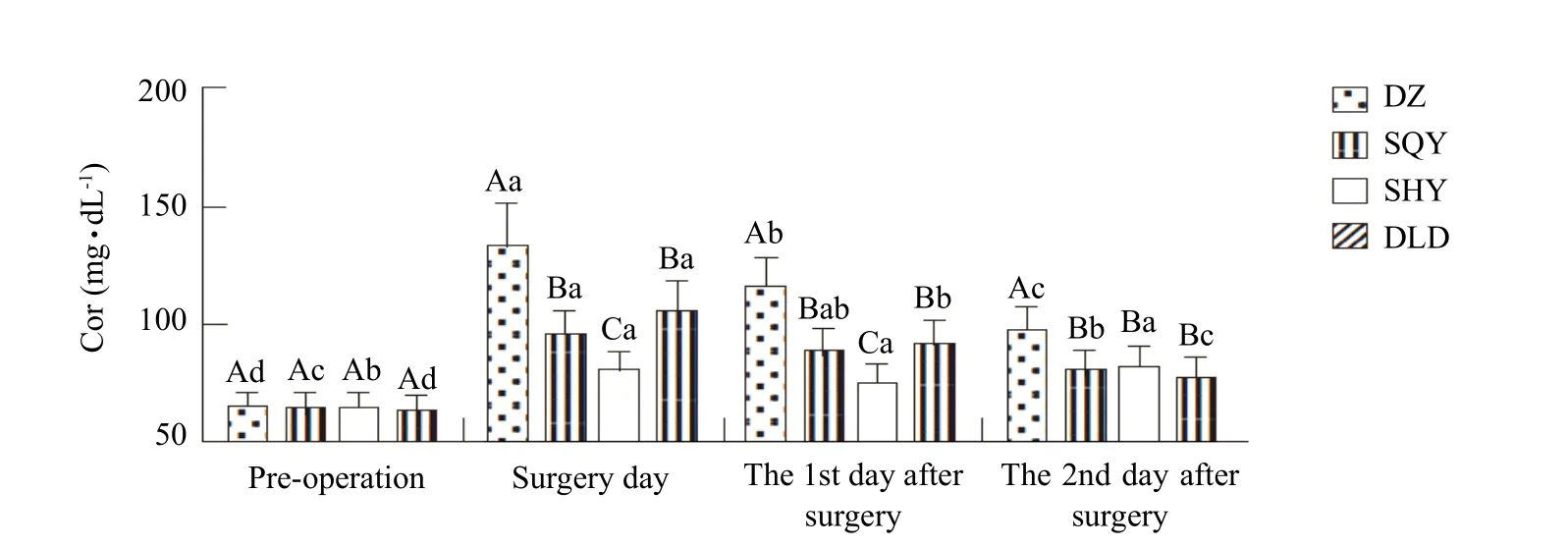
Fig. 2 Content of Cor in serum of different groups (mg · dL-1, n=8)
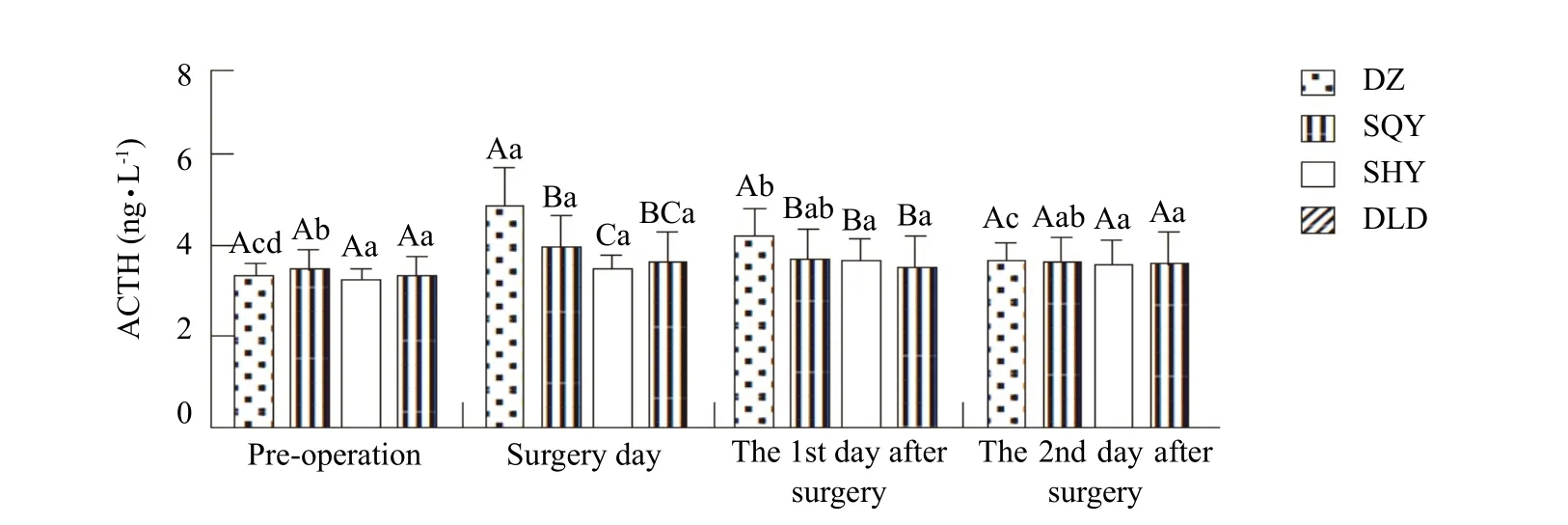
Fig. 3 Content of ACTH in serum of different groups (mg · dL-1, n=8)
Discussion
The most important feature of postoperative high metabolic stress response is hyperglycemia, which is called stress diabetes or surgical diabetes by some scholars (Siracusaet al., 2010; Freemanet al., 2010).The stress hyperglycemia existed in the early time is"benign situation" of body's own protection. In this period, the state of hyperglycemia might provide energy for tissue repair and ensure the normal physical activities of bodies. Besides, it was conducive to improve anti-infection and the condition (Mcalisteret al., 2003). However, an intense and persistent stress response might cause neurohumoral response and the release of a variety of cytokines, and lead to glucose metabolism disorders and a rapid long-term increase in blood glucose, which was not conducive to wound healing and body rehabilitation (Kimet al.,2016; Kotagalet al., 2015; Palermoet al., 2016). The experiment showed that the level of blood glucose of dogs in both the control group and experiment groups increased obviously on the day of operation,but dropped gradually on the 2nd day and the 3rd day. The level of blood glucose dropped effectively,when administered low dose of dexmedetomidine and tilidine. No significant differences were found among the three groups.
The release of Cor might be caused by preoperative preparation, anesthesia, operation and pain. Besides,the level of Cor increased owing to stress response at the early stage of surgical trauma with an antiinflammatory and resolutive effect on the body conducive to tissue repair, which belonged to normal physiological defensive reaction of body. Because Cor could inhibit the chemotaxis of hemameba, persistent and high levels of Cor was not conducive to exertion of the anti-infective effects of body, which might result in increasing the possibility of secondary infection and problems on tissue repair (Iwasakiet al., 2015).Cor was a sensitive indicator of the stress response of bodies. When surgical injury might be not effectively alleviated and eliminated, the level of Cor in serum would increase rapidly. If the stress response persisted,Cor would be maintained at a corresponding high level and transformed from the initial beneficial effects into a deleterious effect in bodies (Peckinset al., 2016).The results of test showed that the level of Cor would increase to the highest value on the surgical day and then dropped when no implementation of anti-stress and analgesic measures had been adopted. Besides,the result of the test was still significantly higher than the preoperative level (p<0.05). The level of Cor was decreased effectively when administered with a low dose of dexmedetomidine and tilidine which had different degrees of anti-stress effects. And, 10 min after administration of intramuscular injection of 20 μg · kg-1dexmedetomidine was the most effective way against the surgical wound stress in the experiment under statistical analysis.
When stress response existed, pituitary would secrete ACTH, which could promote adrenal cortex secreting GCS, and then improve the ability of stress of bodies by enhancing the secretion of peripheral corticosteroids. When bodies were stimulated by stress of the perioperative period, a series of neuroendocrine responses would be produced by the stimulation of the marginal system-hypothalamicpituitary-adrenal axis (LHPA axis) releasing a variety of hormones, which was the adaptive response to animal organisms (Luoet al., 2016). However, if the stress response remained intense and lasted for a long time, the physiological effects of ACTH would have a variety of adverse influences on bodies (Asteriouet al., 2016).
The test of ACTH showed that the content of ACTH increased obviously on the day of operation in DZ group (p<0.05) and then dropped. The level basically restored to preoperative level at the end of the test.It could been found that dexmedetomidine administered before anesthesia could not reduce ACTH level efficiently, but postoperative administration of dexmedetomidine and tilidine had a significant influence on remaining ACTH content stable with an anti-stress effect.
Conclusions
Intramuscular injection of 20 μg · kg-1dexmedetomidine 10 min after administration could reduce the level of blood glucose and Cor and ACTH in serum,which had an effect better than tilidine on anti-surgical traumatic stress response. And the overall effects were better than tilidine.
Asteriou C, Lazopoulos A, Rallis T,et al. 2016. Video-assisted thoracic surgery reduces early postoperative stress: a single-institutional prospective randomized study.Therapeutics & Clinical Risk Management, 12(1): 59-65.
Canfrán S, Bustamante R, González P,et al.2016. Comparison of sedation scores and propofol induction doses in dogs after intramuscular administration of dexmedetomidine alone or in combination with methadone, midazolam, or methadone plus midazolam.Veterinary Journal, 210: 56-60.
Iwasaki M, Edmondson M, Sakamoto A,et al.2015. Anesthesia,surgical stress, and "long-term" outcomes.Acta Anaesthesiologica Taiwanica Official Journal of the Taiwan Society of Anesthesiologists, 53(3): 99-104.
Khenissi L, Nikolayenkova-Topie O, Broussaud S,et al.2016.Comparison of intramuscular alfaxalone and ketamine combined with dexmedetomidine and butorphanol for castration in cats.Journal of Feline Medicine & Surgery, 19(8): 791-797.
Kim S P, Broussard J L, Kolka C M. 2016. Isoflurane and sevoflurane induce severe hepatic insulin resistance in a canine model.Plos One,11(11): e0163275.
Kotagal M, Symons R G, Hirsch I B,et al.2015. Perioperative hyperglycemia and risk of adverse events among patients with and without diabetes.Annals of Surgery, 261(1): 97-103.
Luo W, Fang M, Xu H,et al.2016. Comparison of mirna expression profiles in pituitary-adrenal axis between beagle and Chinese field dogs after chronic stress exposure.Peerj, 4(2): e1682.
Freeman L J, Rahmani E Y, Al-Haddad M,et al.2010. Comparison of pain and postoperative stress in dogs undergoing natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery, laparoscopic, and open oophorectomy.Gastrointest Endosc, 72(2): 373-380.
Mcalister F A, Man J, Bistritz L,et al.2003. Diabetes and coronary artery bypass surgery: an examination of perioperative glycemic control and outcomes.Diabetes Care, 26(5): 1518-1524.
Palermo N E, Gianchandani R Y, Mcdonnell M E,et al.2016. Stress hyperglycemia during surgery and anesthesia: pathogenesis and clinical implications.Current Diabetes Reports, 16(3): 1-7.
Parashchanka A, Schelfout S, Coppens M. 2014. Role of novel drugs in sedation outside the operating room: dexmedetomidine, ketamine and remifentanil.Current Opinion in Anaesthesiology, 27(4): 442-447.
Peckins M K, Susman E J, Negriff S,et al.2016. Cortisol profiles: a test for adaptive calibration of the stress response system in maltreated and nonmaltreated youth-corrigendum.Development &Psychopathology, 27(2): 1563-1564.
Romano M, Portela D A, Breghi G,et al.2015. Stress-related biomarkers in dogs administered regional anaesthesia or fentanyl for analgesia during stifle surgery.Veterinary Anaesthesia & Analgesia,43(1): 44-54.
Siracusa C, Manteca X, Cuenca R,et al.2010. Effect of a synthetic appeasing pheromone on behavioral, neuroendocrine, immune, and acute-phase perioperative stress responses in dogs.Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association, 237(6): 673-681.
Srithunyarat T, Hagman R, Höglund O V,et al.2017. Catestatin,vasostatin, cortisol, and pain assessments in dogs suffering from traumatic bone fractures.Bmc Research Notes, 10(1): 129-132.
杂志排行
Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Research on Market Risk Assessment of Dairy Farms: Taking 75 Dairy Farms in Heilongjiang Province as Examples
- Agricultural Exports Competitiveness of Pakistan in Global Market
- New Islanding Detection Method with Better Performance in Presence of Non-resistive Load
- Design of Greenhouse Environment Control System Based on Internet of Things
- Identification and Genetic Diversity Analysis of Chinese Mitten Crab(Eriocheir sinensis) in the Liao River Area
- Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus as a Dietary Supplement on Nonspecific Immune Response and Disease Resistance in Juvenile Common carp, Cyprinos carpio
