北京浅山区香山特色小镇规划设计探索
2018-04-17黄剑
黄剑

1 军庄生态小镇区位关系Junzhuang Eco-town location
从北京市区向西60km左右,就来到了京郊传统度假地之一的军庄镇(图1)。根据《北京城市总体规划2016——2035》中提出的“一核一主一副,两轴多点一区”的城市空间结构,其中“一区”是指包含门头沟在内的浅山生态涵养区,是首都重要的生态屏障和水源保护地,也是保障首都可持续发展的关键区域,承载着接受平原发展辐射和带动山区城镇化的双重职能。北京浅山区指高程在100~300m之间的浅山丘陵地区,其中军庄镇紧邻永定河,三面环山,在北京水系生态走廊和浅山生态屏障上占据了重要的地位,并且是区域生态廊道上的一块“踏脚石”(steppingstone)。旅游和经济发展的压力与脆弱生态环境的保育,是军庄镇面临的突出课题。
通过生态、经济和社会要素的平衡互动来实现可持续的社区发展是设计的重要策略 (图2)。我们将浅山区视为一个生命系统,通过构建区域生态基础设施来引导和约束城区发展,构建安全的浅山生态格局,强调对生态环境和自然空间的保护,并且从设计上加强林相修复和生物栖息地的复建,逐步提升生物多样性,使这个生命系统更健康,更具韧性。
人与自然的长期互相塑造,成就了军庄小镇的特色风貌,也造成了水土流失、植被群落单一和生物品种不断减少的脆弱生态环境(图3)。设计团队在对160hm2的军庄文旅休闲特色小镇进行景观规划设计的同时,也同步展开针对全镇3 000多hm2的生态环境的综合评估和保护规划,在“生态优先”的理念下因地制宜地制定了林地修复、栖息地重建、水资源与水生态综合管理等6个生态环境修复策略和20个具体措施。其中,水资源管理,林地和栖息地复育是可持续环境保育的核心策略。
水资源管理方面,设计团队着重通过蓄滞、净滤和节水3个层面,对水资源进行合理规划和管理,构建军庄小镇的海绵系统(图4,表1)。为了保证辖域内防洪安全,项目组一方面建议河道修复、疏挖沟渠等措施,并根据水流勘测的数据进行各类排洪渠的合理布置,以达到快速排洪的效果;另一方面,在水量和流速较小的上游地区则设计缓坡、石笼等更为友好的生态驳岸,改善自然亲水的山地水环境。在规划的小镇中心区域,场地顺应地势分成5个标高区域,通过巧妙设置季节性的水景、生态草沟、雨水花园和干塘,既保留了原有冲沟的场地记忆,又实现了场地地表径流的有效收集与回用。
此外,根据地形的塑造和径流关系的分析在全区布置的干塘、雨水花园和生态草沟等,就像一个个海绵细胞,能够蓄滞和净化地表径流,滋养土壤和植被,回补地下水,也缓解了市政排水及排洪的压力,更好地实现水净化和水安全。
浅山区的地貌十分复杂,而且普遍面临退化、侵蚀、污染等问题。在对镇域的生态分析中,设计团队以国土林地斑块为基础(主要为林场保护区边界及镇村落边界),在GIS技术支持下以根据林地修复条件相关的因子,主要包括海拔高度、地形坡度、土层深度、现有林地条件以及景观可视性等,将镇域内的主要林地划分为五大林地修复类型:退化林地修复、城镇景观林营造、陡坡地和容易被侵蚀的地区林地修复、废弃矿山周边绿化、林地栖息地修复(图5)。
整个镇域现状林业用地面积为1 889.35hm2,其中可实施修复林地的面积为2 150.89hm2。规划考虑10年的中长期林地修复计划,逐步形成约64.5%以上的浅山特色林地区域。针对目前浅山区以次生林为主的树种单一、群落结构简单等问题,采用局部疏伐、逐步更新等方式,以形成生物多样性更丰富的混交林(图6)。
退化的林相问题也带来过去百年间浅山地区物种数量的大幅下降。为此,景观设计师与生态专家紧密协作,根据当地特色动物资源设立目标先锋种群,配置合理的植物群落以提供多样化的筑巢、繁衍环境,吸引区域小型哺乳动物、林鸟、昆虫等,重建生态友好的浅山特色栖息地(图7)。根据陡坡、平地等不同场地类型和坡向关系,设计团队制定了土壤、植被与生物的同步分级恢复策略,布置适宜的乡土树种和先锋物种,通过长期的生态保育计划促进自然的正向演替,逐步修复退化的林地,提高土地的生态服务功能,并形成多样化的混交林。

2 可持续社会发展示意图Social sustainable development diagram

3 区域生态适宜性分析Analysis of regional ecological suitability

4 区域干塘调蓄设施规划及分区图Planning and zoning of regional dry pond storage facilities
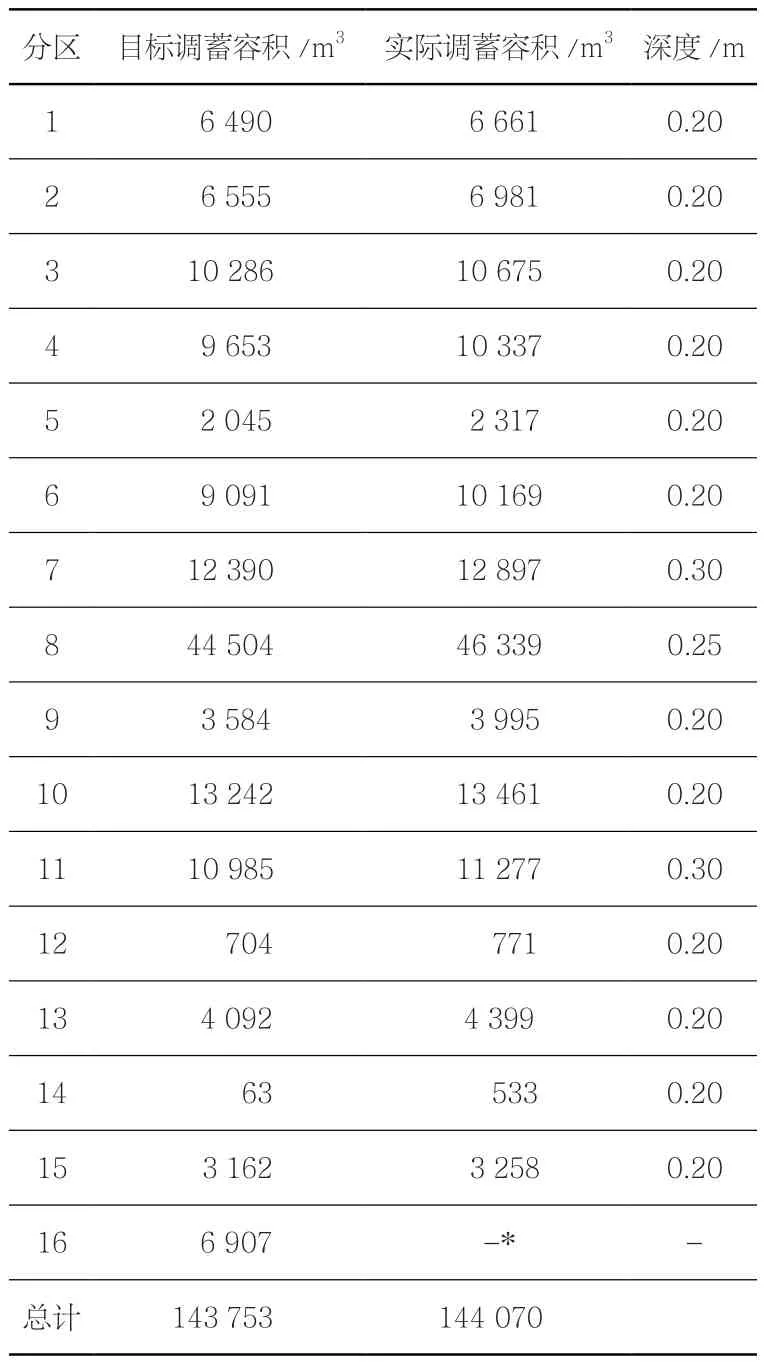
表1 区域干塘调蓄设施规划及分区表Tab. 1 Regional dry pond planning and chart
山地景观设计对现状和自然要素高度敏感,十分需要因地制宜,巧于因借。设计团队秉持“生态优先,修复基于保护”的理念,通过对资源的重组和空间的重构,增加丰富的策划内容,让小镇更优美、更生态(图8)。
结合分区策划和生态环境规划策略,设计团队在小镇农场附近设置了一片以“大自然的秘密”为主题的亲子互动区域,配合专业的自然教育课程让人们在休闲玩乐的过程中接触、感知和探索大自然,亲身感受人与树木、鸟类、昆虫等自然环境亲密共生的关系。自然生境的重塑不仅是单纯的景观修复,更是鲜活可见的生态教育过程。
军庄镇是京西古道上的节点,历史人文景观和旅游资源十分丰富。北京特产京白梨就产自军庄镇,这里有从清代延续至今具有400年历史的贡梨园。春天开遍山野的洁白梨花,夏秋之交甘甜绵软的京白梨,不仅是老北京的美好记忆,更是当地人的骄傲和生存之本。
设计中保留了所有的果园,并提出了土壤的生态优化措施,停用化肥,改传统的井水灌溉为滴灌、喷灌结合。建议原本的单一梨树种植改为四季套种、种植——养殖结合等复合式种植。这不仅能够显著节水,还能改良土壤,提高土地生产效率,改善微气候并促进自然资源的良性循环和动态平衡,也让梨园呈现出更丰富的季节性景观 (图9)。
基于综合环境敏感度评估确定适宜的开发强度和场地的可承载力,利用本土资源和农业相关知识,建立生态、农业和旅游相结合的系统,推行“朴门农业”和“绿色旅游Green Globe”可持续旅游标准,以保护环境、维护生态平衡为前提,鼓励社区参与和体验式的旅游。
“陇驾庄,会编筐,男的打底,女的上邦”,一句当地流传的民谚,道出了京西荆编的好口碑。京西山区盛产荆条,荆编就地取材,可以编出背篓、箩筐,也可以搭棚、铺顶,而且能够变换出丰富的纹理效果。这本是家家户户流传的手工艺,不过随着现代化生活的普及,荆编也在逐渐退出村民的生活舞台,直到与我们的景观设计团队相遇。荆编被定义为一种重要的景观元素在场地内广泛应用,比如梨园的围栏、篱笆,甚至入口的墙面、小镇客厅的凉亭,并且通过这个元素的发掘,大力鼓励村民的广泛参与和创造性的发挥,最终让荆编工艺的展现和应用成为项目中一个精彩的亮点,也让村民从中体会到手工艺带来的自豪(图10~12)。

5 林地修复过程示意Forestry restoration process
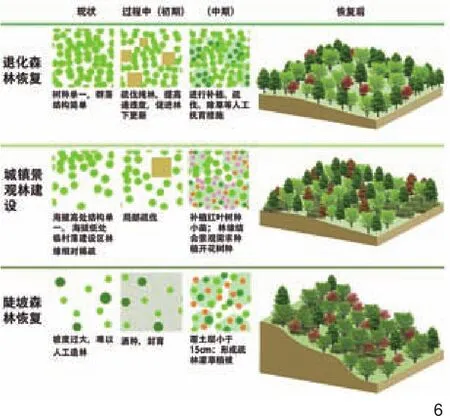
6 区域林地修复类型Regional forestry restoration zoning plan

7 林地栖息地复建示意图Forest habitat restoration diagram

9季相综合管理示意图Quarterly integrated management diagram
原本主要是生产性质的贡梨园在入口区改造后呈现出现代和开放的面貌。入口旁边的保留建筑被改成小镇客厅及生态展示中心。室外的空场地上,我们结合休息区域增加了可供休息和停留的绿岛形成对景,并作为场地海绵设施的一部分。原有的场地边界通过传统工艺和材料,在原址上用毛石手工砌筑成传统的城墙样式,保留着这里的场地记忆,傍晚在这里远眺夕阳可以欣赏西山优美的天际线。场地周边的梨树和其他大树全部被保留,在展示中心外面的小径还特意下挖了1m多以避让现场的老树。层层的梨园台地之间增加了雨水花园,台地间设置休息平台,上面的休息凉亭是村民和设计师共同创作的荆编作品。所有的材料和工艺都来自当地,梨园的传统生产过程通过铜浮雕墙展现。建成后这里不仅成为小镇的生态展示中心,更是属于村民的小镇客厅(图13~15)。
通过景观、生态、林业、水利、岩土,旅游及经济策划等多专业的跨界合作,设计团队从多元角度的分析发现议题,制定适合军庄的规划设计策略,并且一直深入到工程执行层面,保障现场的施工成效。军庄生态小镇的规划设计还未结束,作为北京浅山区生态保护与开发的一次尝试,希望探索出一条“修复基于保护的生态规划,策划结合现状的景观设计”的浅山区特色小镇的可持续之路。
(编辑/王一兰)
项目地址:北京门头沟军庄镇
生态规划和景观设计公司:AECOM
设计团队:沈同生,David Gallacher,黄剑,罗志坚,王福龙,赵星,李露曦,李琦,鲍艾艾,陆瑶,杨宁婧,江丹
项目时间:2017年
项目面积:160hm2
图片来源:AECOM

8 场地景观剖面Landscape long section

10 民间工艺荆编的设计与应用Design and application of folk craftsmanship vitex weaving
60 kilometres from Beijing, Junzhuang Town is a traditional tourist destination due to its natural beauty and pear orchard. In the Beijing Masterplan it is defined as part of the low mountain ecoconservation area, which is not only an ecological buffer of Beijing, but a radial influence on the developed plain area. Highly sensitive, valuable and fragile, Junzhuang is an important stepping stone in the Beijing eco-corridor.
Hillside areas are a living system. We are looking to a sustainable social development of hillside area based on ecological restoration, local engagement and integrated design. Our ecological planning provides guidelines to limit urban development, build safe landscapes, and nurture the protection of natural public spaces and still grow economically. By strengthening the forest and habitat restoration through design, biodiversity can be improved and the eco-system can be more healthy and resilient.

11 当地居民参与建造荆编凉亭Local residents engaged in the construction of vitex woven pavilion.
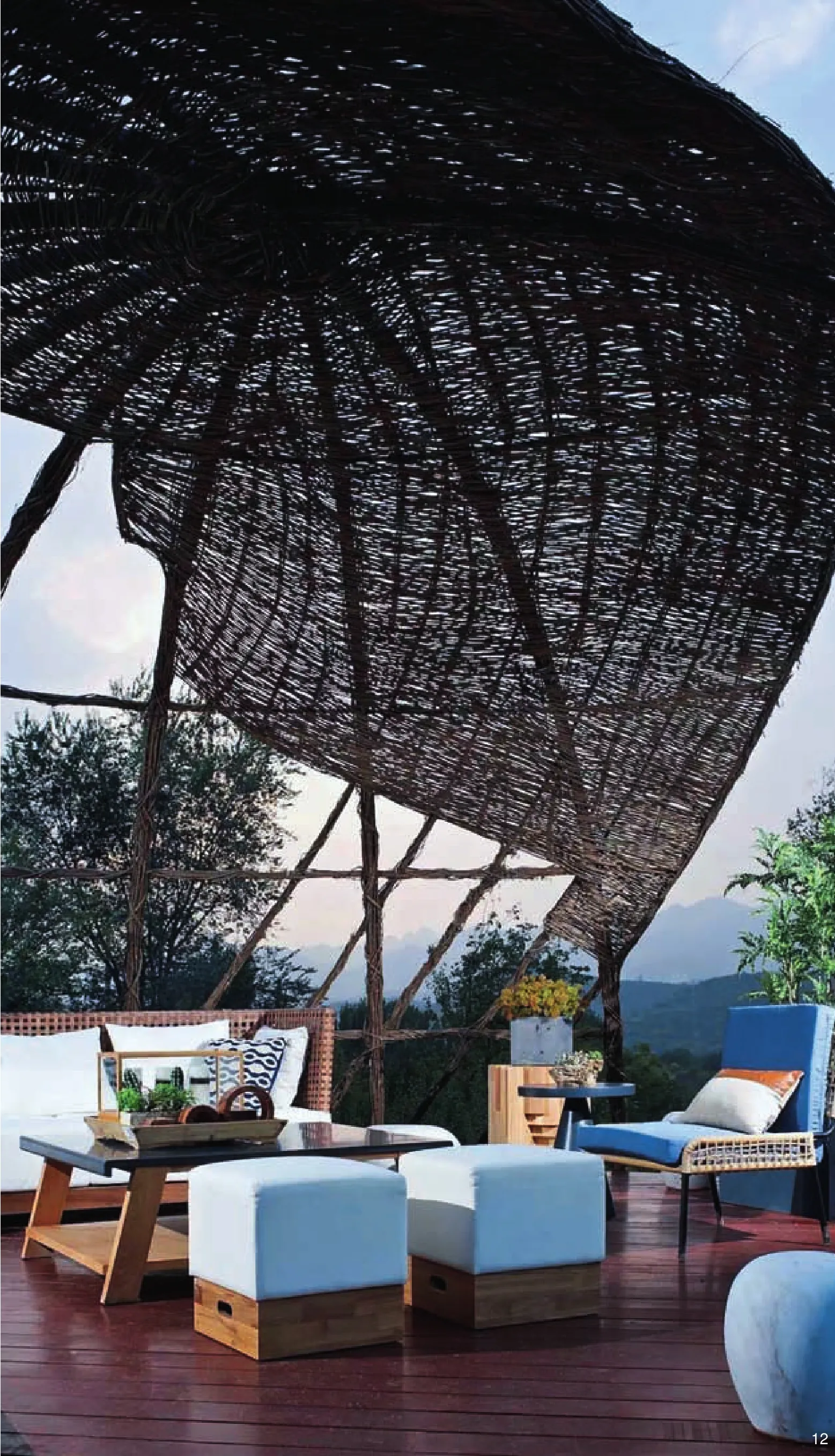

12 荆编凉亭建成实景Photo of vitex woven pavilion

13 贡梨园入口序列长剖面Long section of entrance sequence of Royal Pear Orchard

14 贡梨园入口实景Build photo of Royal Pear Orchard entrance
On the site, the gate of the orchard is renovated to be a friendly exhibition center, and a “living room”for local community. Surrounded by preserved pear trees, a modern and sculptural chaste-weaving pavilion is created by the collaborative effort of landscape designers and local villagers, linking the new landscape with the local traditional craftsmanship. A copper embossed screen wall describes the traditional pear producing process. Through the landscape, culture,ecology and economy can be integrated smoothly.
For flood control, varies methods of river restoration, dredging and ditching are suggested.Drainage channels, dry ponds, rain gardens, and bio-swales are arranged based on water flow survey data and terrain and runoff analysis. Eco-friendly embankment methods e.g. gentle slope and gabion wall are used in the upstream areas where flow rate are low.
Following the original contours and a natural gulch on site, the layout of town center is integrated with storm water management design.Seasonal water features are designed with dry ponds and rain gardens, bringing the memory of site into its modern life.
The design team developed a hierarchically recovery strategy in which soil, vegetation and biological will be improved simultaneously for varies terrain types and slopes. The design can promote positive forest succession by making longterm ecological conservation plan and planting appropriate native tree species and pioneer species.Through natural restoration of degraded forest land, the site’s ecological service function will be improved gradually, and eventually forms diverse mixed forests.
Set up target pioneer species and communities based on native biological resources. Create diversified nesting and breeding environments which shall attract regional small mammals, forest birds, insects and etc. by planting appropriate vegetation communities, and ecologically friendly low mountain habitats will be restored.
Beijing White Pear is a special local product from Junzhuang Town, especially the ones from “Royal Pear Orchard” with over 400 years history. All pear orchards are well protected in the planning. Permaculture measurements are proposed - previous underground-water irrigation and chemical fertilizer are replaced by dripping irrigation and community participated bio-farming,more energy saving and productive.
It is suggested that the original single pear tree planting to be changed to composite planting model in four seasons, conserving more and improve soil quality, land production efficiency, and microclimate.
Not only more effective agriculture production and management, but also better interactive green tourism programs are proposed, such as nature school and camping, bird watching, eco-sightseeing and organic farming. All programs are based on the local natural resources, and involved with local communities, to reduce the disturbance of the site,and improve the long time economic benefit to the communities.
“Good baskets from folks in Longjia Village,man works on the frame and woman on the detail.”
The folk song tells the long history and reputation of chastetree weaving in this area.Western Beijing mountainous area abounds in chastetree, so the villagers uses the local material to make plates, baskets, fences, and roof tops.This is a simple technology with countless rich patterns created by villagers’ imagination and interest. Chastetree weaving was a popular handicraft for every household, but in modern life, it has gradually fading out from the everyday life of the villagers until it meets our landscape design team.
The construction started from the entry area of the Royal Pear Orchard which has over 400 year’s history. The entrance of the Royal Pear Orchard is an important connection of public open space with production area, and is a place for people to meet and talk. A few steps up along the main axis of Royal Pear Orchard through the renovated modern gate, guest will meet with a copper embossed screen wall telling the story of traditional pear production process. The design follows the topography and retains existing trees and the rough walls which outlined the site. The existing building is transformed into an eco-display center. A green island is added on the plaza to provide rest area, also form the view and helps“sponge” function of the site. The original rough stone wall and the pear trees remains on site, to keep the memory of the place. From the platform looking west on the sunset, the silhouette of west mountain is stunning.

15 小镇客厅建成实景Photo of town living room
Pass through the exhibition center towards the terrace garden, a path is dropped 1 meter to bow to the existing big, old verdant tree, as a salute to the history. A few rain gardens are created among terraces to guide the water flow. A modern and sculptural chaste weaving pavilion on the terrace garden becomes the focal point; this is a creative art by the collaboration of villagers and landscape designers, using traditional local material and technique, linking the new landscape with the local traditional craftsmanship.
The entry area then becomes not only a welcoming and exhibition center, but also the favorite gathering place that local villagers are proud of, a place where people join and see the contrast of before and after, experiencing the new lifestyle in an old village. It transforms an old culture into a new one, and then becomes a modern vision of an eco-village celebrating its unique tradition.
The cross line corporation from landscape,environment, forestry, water utility, geotechnical engineer, tourism and economic planning brings a multi-benefit perspectives. The strategy of long term social sustainable development implements from planning to construction. This is still an ongoing process and experiment for “eco-planning of renovation based on protection, landscape design integrated with programming” for hillside area.
Location: Mentougou Junzhuang Town, Beijing
Design Firm: AECOM
Design Team: Stone Shen, David Gallacher, Jane Huang,Oliver Luo, Fulong Wang, Smile Zhao,Heather Li, Lizzie Li, Aiai Bao, Yao Lu,Ningjing Yang, Lotus Jiang
Construction: 2017
Site Area: 160hm2
Photo and Image: AECOM
