AMSTAR使用过程中存在的问题及建议
2018-03-26张方圆沈傲梅强万敏
张方圆,沈傲梅,强万敏
系统评价作为循证医学重要的研究方法和最佳证据的重要来源,被公认为是评价临床疗效、制定临床实践指南和规范的基石[1]。尽管作为循证医学中高质量证据的来源,但只是针对高质量的系统评价,低质量的系统评价则会降低研究结果的价值,从而可能对决策者产生误导[2]。因此,确保系统评价结果的真实性非常必要。
系统评价的质量评价包括方法学质量评价和报告质量评价。AMSTAR作为目前最常用的系统评价方法学质量评价工具[3],由Shea等[4]专家在综合OQAQ(Overview Quality Assessment Checklist)和SQAC(Sack’s Quality Assessment Checklist)等基础上编制而成,具有较好的信效度[5-7]。但有很多研究者指出AMSTAR在使用过程中存在一些问题,包括某些条目很难理解或解释不清楚,影响系统评价方法学质量评价的准确性、有些条目偏向于报告质量评价,而不是针对方法学质量评价等,并针对这些问题提出了指导性建议[8-13]。因此,本研究旨在对AMSTAR存在的问题及其相应的建议进行总结,以期提高其实用性和确保方法学质量评价过程的准确性。
1 AMSTAR评价清单
AMSTAR共11个条目,每个条目的评价选项有“是”、“否”、“不清楚”和“不适用”,具体的条目内容和说明见表1[4,14]。
2 AMSTAR使用过程中存在的问题及建议
很多使用者指出AMSTAR在使用过程中存在问题,一些条目及其说明不够明确;如条目7中“研究的科学性”表述不清,就单个研究而言,评价偏倚风险比研究的质量更重要;此外,科学性评价是针对单个研究还是整体研究也不清楚;还有一些条目偏向于报告质量,而不是方法学质量评价;关于评价选项也存在一些问题,如当信息不足时,评价“否”或“不能回答”难以区分。为了确保AMSTAR评价结果的科学性和准确性,本研究对各条目存在的问题及相应的建议进行了总结[1,15-22],具体内容如表2~3所示。
有研究者[15]建议补充新的条目:在系统评价的方法、分析和结论部分是否考虑到亚组情况?即在确定系统评价研究范围和关键问题时,以及在检索、数据提取、分析和结论部分时应考虑相关人群亚组和特征;评价选项包括“是”、“否”和“不能回答”;在系统评价过程中考虑了相关主要的亚组人群和特征,评价为“是”。
3 R-AMSTAR简介
R-AMSTAR量表是2010年由Kung等[23]在AMSTAR量表的基础上对各个条目的评分标准进
行完善而成;R-AMSTAR共11个条目,每个条目下面都有具体的标准,具体的条目描述及说明见表4;各条目根据满足标准的情况评为1~4分,总分最高为44分,最低为11分。目前,R-AMSTAR同样被较多的研究者所使用[24-27];此外,研究显示R-AMSTAR较AMSTAR具有更好的信度和实用性[28]。本文还根据以上AMSTAR量表使用过程中总结的建议对R-AMSTAR原条目2、3和4的顺序进行了调整。

表1 AMSTAR评价清单及说明
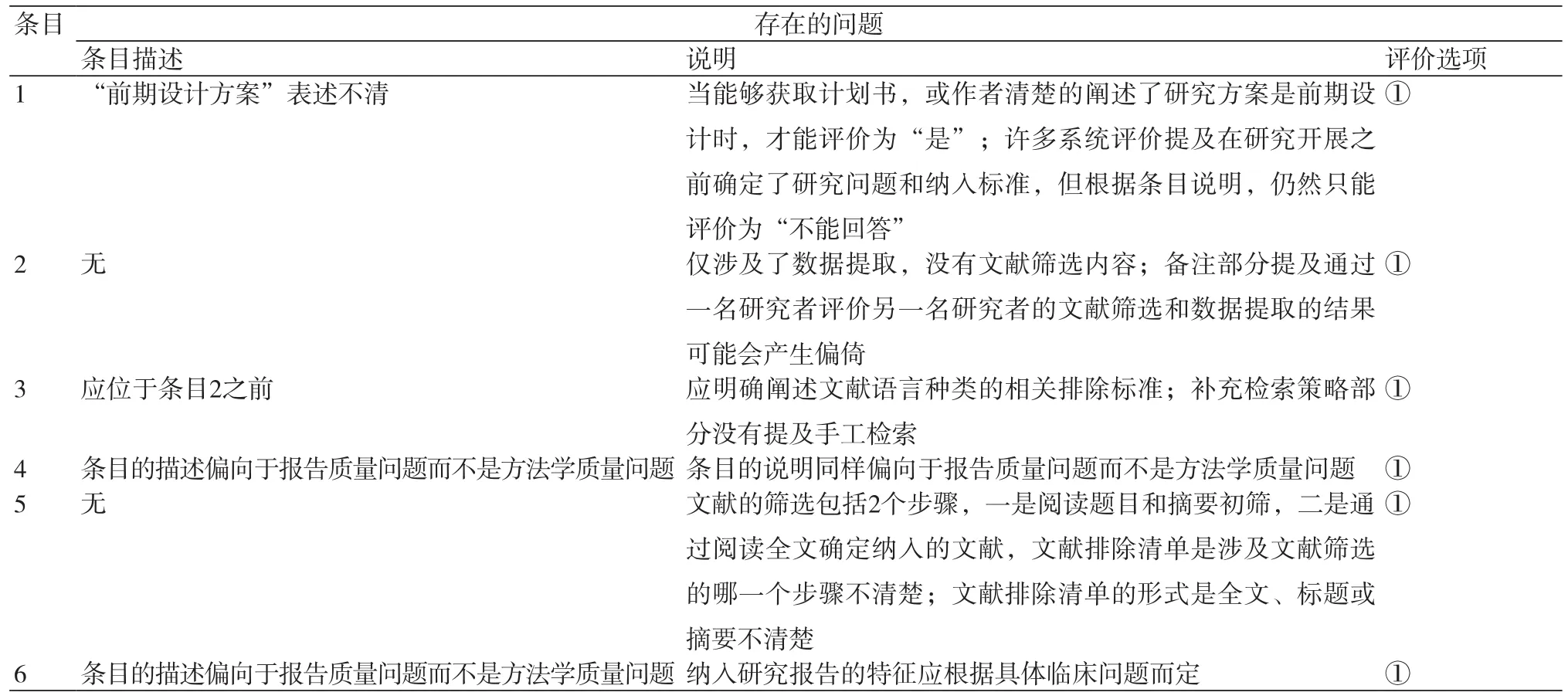
表2 AMSTAR使用过程中存在的问题

注:“①”表示“不适用”评价选项不合适
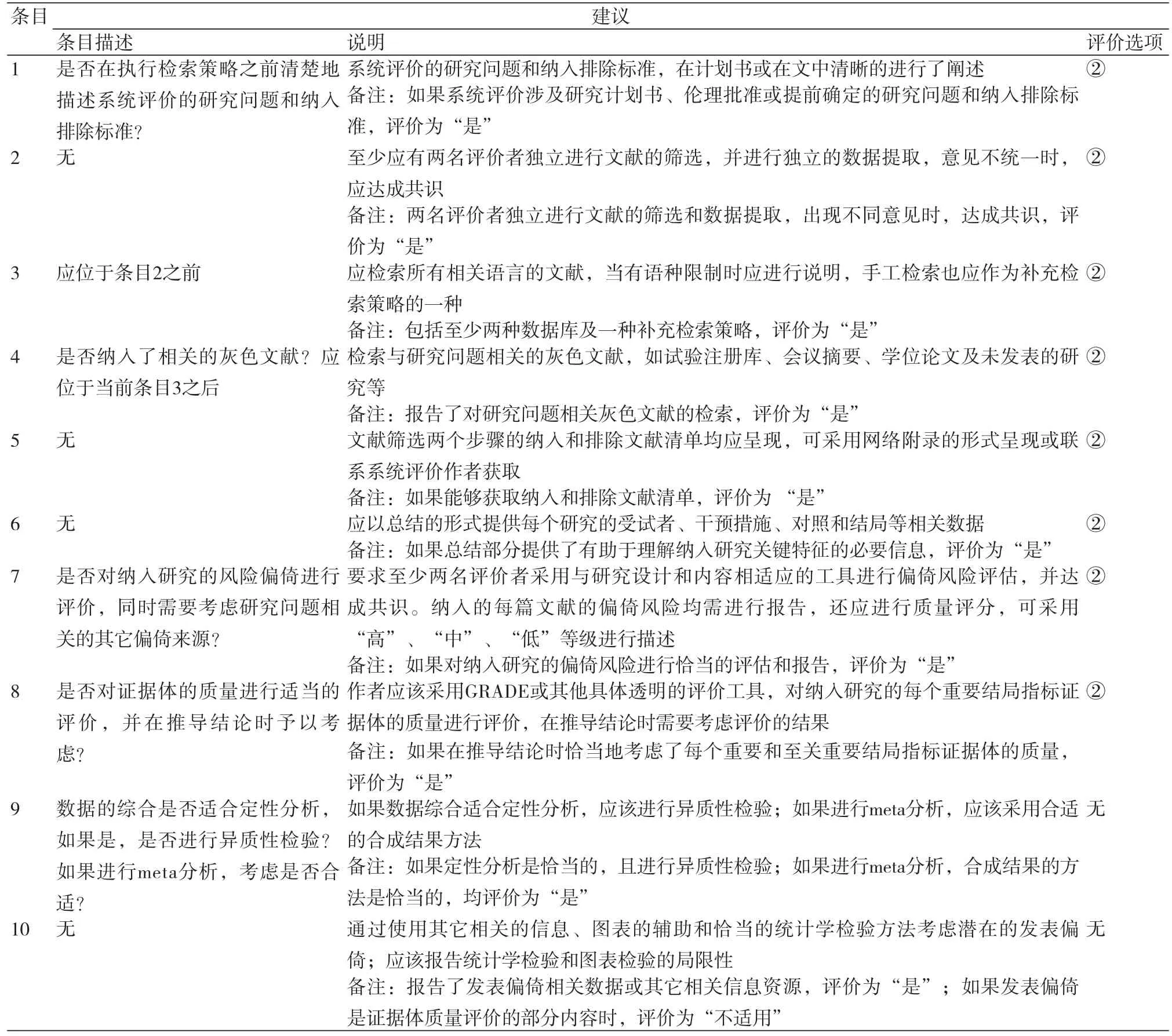
表3 AMSTAR使用过程中的建议

注:“②”表示删除“不适用”评价选项

表4 R-AMSTAR评价清单及说明
4 小结
AMSTAR是通过严格的编制和考验程序而形成的,是一种值得推荐的系统评价方法学质量评价工具[14]。然而,AMSTAR也存在一些不足,需要在实践中不断完善提升。本文对AMSTAR使用过程中存在的问题及建议进行了总结,以期为AMSTAR发展更新提供参考。此外,R-AMSTAR具有较好的信效度和实用性,同样推荐用于系统评价的方法学质量评价。
[1] Jr CMF. Critical appraisal of AMSTAR:challenges, limitations,and potential solutions from the perspective of an assessor[J]. Bmc Medical Research Methodology,2015,15(1):63.
[2] Jadad AR,Cook DJ,Jones A,et al. Methodology and reports of systematic reviews and meta-analyses:a comparison of Cochrane reviews with articles published in paper-based journals[J].JAMA,1998,280(3):278-80
[3] Pussegoda K,Turner L,Garritty C,et al. Systematic review adherence to methodological or reporting quality[J]. Systematic Reviews,2017,6(1):131.
[4] Shea BJ,Grimshaw JM,Wells GA,et al. Development of AMSTAR:a measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews[J]. Bmc Medical Research Methodology,2007,7(2):1-7.
[5] Shea BJ,Hamel C,Wells GA,et al. AMSTAR is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews[J]. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology,2009,62(10):1013-20.
[6] Shea BJ,Bouter LM,Peterson J,et al. External Validation of a Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews (AMSTAR)[J]. Plos One,2007,2(12):e1350.
[7] Pieper D,Buechter RB,Li L,et al. Systematic review found AMSTAR,but not R(evised)-AMSTAR,to have good measurement properties[J]. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology,2015,68(5):574-83.
[8] Aziz T,Compton S,Nassar U,et al. Methodological quality and descriptive characteristics of prosthodontic-related systematic reviews[J]. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation,2013,40(4):263-78.
[9] Lang LA,Teich ST. A critical appraisal of the systematic review process:systematic reviews of zirconia single crowns[J]. Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 2014,111(6):476-84.
[10] Johnson BT,Macdonald HV,Jr BM,et al. Methodological quality of meta-analyses on the blood pressure response to exercise:a review[J].Journal of Hypertension,2014,32(4):706-23.
[11] Kelley GA,Kelley KS. Effects of exercise on depressive symptoms in adults with arthritis and other rheumatic disease:a systematic review of meta-analyses[J]. Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders,2014,15(1):121.
[12] Sardanelli F,Bashir H,Berzaczy D,et al. The role of imaging specialists as authors of systematic reviews on diagnostic and interventional imaging and its impact on scientific quality: report from the EuroAIM Evidence-based Radiology Working Group[J]. Radiology,2014,272(2):533-40.
[13] Pieper D,Mathes T,Eikermann M. Can AMSTAR also be applied to systematic reviews of non-randomized studies?[J]. BMC Research Notes,2014,7(1):1-6.
[14]熊俊,陈日新. 系统评价/Meta分析方法学质量的评价工具AMSTAR[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2011,11(9):1084-9.
[15] Burda BU,Holmer HK,Norris SL. Limitations of A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews (AMSTAR) and suggestions for improvement[J]. Systematic Reviews,2016,5(1):58.
[16] Wegewitz U,Weikert B,Fishta A,et al. Resuming the discussion of AMSTAR: What can (should) be made better?[J]. Bmc Medical Research Methodology,2016,16(1):111.
[17] Kirkham JJ,Altman DG,Williamson PR. Bias Due to Changes in Specified Outcomes during the Systematic Review Process[J]. Plos One,2010,5(3):e9810.
[18] Page MJ,Mckenzie JE,Kirkham J,et al. Bias due to selective inclusion and reporting of outcomes and analyses in systematic reviews of randomised trials of healthcare interventions[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2014(10):R35.
[19] Moher D,Shamseer L,Clarke M,et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement[J]. Systematic Reviews,2015,4(1):1.
[20] Buscemi N,Hartling L,Vandermeer B,et al. Single data extraction generated more errors than double data extraction in systematic reviews[J]. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology,2006,59(7):697-703.
[21] Morrison A,Polisena J,Husereau D,et al. The effect of Englishlanguage restriction on systematic review-based meta-analyses:a systematic review of empirical studies[J]. Int J Technol Assess Health Care,2012,28(2):138-44.
[22] Guyatt G,Oxman AD,Akl EA,et al. GRADE guidelines:Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables[J]. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology,2011,64(4):383-94.
[23] Kung J,Chiappelli F,Cajulis OO,et al. From Systematic Reviews to Clinical Recommendations for Evidence-Based Health Care:Validation of Revised Assessment of Multiple Systematic Reviews(R-AMSTAR) for Grading of Clinical Relevance[J]. Open Dent J,2010,4: 84-91.
[24] Conley J,O'Brien C W,Leff B A,et al. Alternative Strategies to Inpatient Hospitalization for Acute Medical Conditions:A Systematic Review[J]. Jama Internal Medicine,2016,176(11):1693.
[25] Pinnock H,Parke HL,Panagioti M,et al. Systematic meta-review of supported self-management for asthma:a healthcare perspective[J].Bmc Medicine,2017,15(1):64.
[26] 刘舒丹,刘琴,贺安然. 国内免疫接种领域系统评价/Meta分析的质量评价[J]. 中国免疫学杂志,2014(6):797-801,813.
[27] 罗燕,刘琴,杜成凤,等. 国内杂志发表的冠心病防治领域Meta分析的质量评价[J]. 中国循环杂志,2014(12):979-82.
[28] Popovich I,Windsor B,Jordan V,et al. Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews in Subfertility:A Comparison of Two Different Approaches[J]. Plos One,2012,7(12):e50403.
