Artificial intelligence in Internet of things
2018-03-25✉
✉
Machine Intelligence Unit,Indian Statistical Institute,203 B.T.Road,Kolkata 700108,West Bengal,India
Abstract:Functioning of the Internet is persistently transforming from the Internet of computers(IoC)to the‘Internet of things(IoT)’.Furthermore,massively interconnected systems,also known as cyber-physical systems(CPSs),are emerging from the assimilation of many facets like infrastructure,embedded devices,smart objects,humans,and physical environments.What the authors are heading to is a huge‘Internet of Everything in a Smart Cyber Physical Earth’.IoT and CPS conjugated with ‘data science’may emerge as the next‘smart revolution’.The concern that arises then is to handle the huge data generated with the much weaker existing computation power.The research in data science and artificial intelligence(AI)has been striving to give an answer to this problem.Thus,IoT with AI can become a huge breakthrough.This is not just about saving money,smart things,reducing human effort,or any trending hype.This is much more than that-easing human life.There are,however,some serious issues like the security concerns and ethical issues which will go on plaguing IoT.The big picture is not how fascinating IoT with AI seems,but how the common people perceive it-a boon,a burden,or a threat.
1 Introduction
We are quite fascinated by the word ‘smart’.However,what we have today is still far from being smart like a human.Let us consider the example of a smartphone,although it is ‘smart’,it cannot do much automatically.For example,it is not able to put notifications or message alerts in ‘silent mode’automatically when the owner is driving.It would be smarter if it could at least reduce distractions caused by the alerts when the owner is driving.This requires some kind of wireless connection between the person,his/her smartphone,and the car.In another situation,if the owner falls sick,the smart phone should make an emergency call to a family member or a hospital nearby.It will again need certain connections and information(about the family members and hospitals)to facilitate this.If we go on giving examples like this,we will see nearly everything present in the physical world need to be connected to everything else to meet some requirements or the other.To make these things ‘smart’,we will need artificial intelligence(AI).
AI is a technology that targets at making computers do human-like reasoning. This development will accelerate the digital transformation of industries.Be it humans,animals,plants,machines,appliances,soil,stones,lakes,buildings,or anything one can think of,connecting them together and making‘smart decisions’can make the world an autonomous place.To make the world and its physical objects actually autonomous,we need a machine learning(ML)[1]emulating human learning as well as a data analysis(DA)[2]module in the system.ML would create techniques to facilitate learning in various components/devices of the network to make them automatic and self-standing,whereas DA would evaluate/analyse all the data that is generated over time to find out the past trends and be more efficient/effective in future.This trend has been growing and now efforts are being made to incorporate ML and DA into sensors[3]and embedded systems[4]of the smart systems.The technology behind AI is really intriguing and what it will turn into forces us to rethink everything we know about the meaning and purpose of life and work.The pace at which ML and DA are driving AI calls for a good need to discuss trends,challenges,and threats that will grow gradually.
One of the greatest ideas behind this trend is the Internet of things(IoT)[5]which anticipates a world saturated with installed intelligent gadgets,frequently called ‘smart objects’(SOs)[6],interconnected through the Internet or other communication mediums like Bluetooth,infrared etc.These connections will be human–human,human–physical things,and physical things–physical things.Internet of everything(IoE)[7]is also a similar idea that suggests that every living,non-living,or virtual object is connected to each other through some communication medium.When these concepts are deployed to the physical world,what we get is a cyber-physical system(CPS)[8].Such a world would be data wealthy,using which knowledge could be extracted.Various disciplines like database management system(DBMS)[9],pattern recognition(PR)[10],data mining(DM)[2],ML[1],and big data analytics(BDA)[11]will need improvised methods to deal with the data,overlapping largely in their scope.This article mainly revolves around intuitions,challenges,and applications of AI in the concepts of IoT,CPS,and IoE.
2 Artificial intelligence
AI is the science of instilling intelligence in machines so that they are capable of doing tasks that traditionally required the human mind.AI-based systems are evolving rapidly in terms of application,adaptation,processing speed,and capabilities.Machines are increasingly becoming capable of taking on less-routine tasks.While humans intelligence is actually ‘taking’a perfect decision at the appropriate time,AI is merely about ‘choosing’a right decision at the appropriate time.To put it plainly,the creativity in decision that humans can take is lacking in AI.It may be argued that human ingenuity will always change the role of productive work,but AI-based systems have quite elegantly reduced repetition of human efforts and could give results in comparatively low time.Most of the ongoing works in AI can be termed as‘Narrow AI’.This means that only certain tasks are enhanced by technology.However,we are aiming for something much more than that.Hence,many fields have conjugated to drive the AI development.
Various domains like philosophy,computer science,mathematics,statistics,biology,physics,sociology,psychology,and many more have come up together to boost the interdisciplinary nature of AI.Intelligence comes from all the data generated in each of these domains.Analysis of this data is important to bring out the principles behind it.The human brain is capable of doing it easily,but it takes a long time.This is because,the data in the real world has some unwelcome properties:
·huge volume,
·unstructured nature,
·varied data sources,
·needs real-time processing,
·changes continuously.
There are other properties too like volatility,virility etc.AI can be regarded as a technique to use the data in an efficient manner so that it is understandable to the people who provide it,modifiable(in the case of errors),holds usefulness in the present scenario,and is meaningful.
AI,therefore,relies heavily on data science techniques.To state in a broader way,data science is the science of developing tools and methods to analyse large volumes of data and gain information from it.The discipline is,therefore,an amalgamation of many other research areas.For developing tools,the ideas mainly come from computer science which are primarily concerned with algorithmic efficiency and storage scalability.For analysis,the ideas come from much more varied sources.Methodologies are borrowed from both the basic sciences(like physics,statistics,graph theory)and the social sciences(like economics,sociology,political science).Specific techniques which are naturally interdisciplinary are also very popular in data science,such as PR[10],ML[2],data mining[12],DBMSs[9],and BDA[13,14].
One of the main tools to achieve AI is ML.The human brain can solve certain types of learning problems.For example,there are plenty of optical neurons in the visual system which make object recognition easy for humans.Learning is not only restricted to humans,it is diversified to animals,plants etc.A bird learns to fly,a child learns to speak,plants learn to adapt to the environment,and so on.Our very survival depends on the ability to learn and adjust to the environment.Machines can be equivalently made to learn and modify itself for better performance imitating the natural process of learning,to be termed as ‘ML’.Learning(including ML) mainly takes place in three ways:supervised [2],reinforcement,and unsupervised[15].Other methods[1]like semi-supervised learning[16],active learning [17],inductive learning[18],deductive learning[1],transfer learning[19]etc.also exist.Some are even inspired by the biological sciences to mimic the evolution process of living beings[20].The goal of ML is not just instilling consciousness in a machine,but to design algorithms that allow the machine to learn.
Learning can be defined as the act of acquiring or improving behaviours,skills,values,preferences,thereby increasing the knowledge.It may also include synthesising various types of information.Basically,learning is the mechanism by which a system modifies its parameters such that its future performance can be improved.This process of learning can be imitated by machines with the help of ‘ML’[2].ML is an emerging field in computer science research which gives inanimate systems an ability to learn[21]without actually having to programme them explicitly.In contrast to more traditional uses of computers,the IoT scenario where the volume,variety,velocity,and complexity of the data are overwhelming,it is impossible for a human programmer to provide an explicit, fine detailed specifications to execute the task.Thus,the concept of ML is made to be concerned with implicit learning skills,which would make a computer/system eventually teach themselves to adapt to the current environment and make independent decisions.This is how ML makes up for the smart concept in CPS or IoT[22].

Table 1 Smart animal to smart machine analogy
ML is an approach to achieve AI[23]which is based around the concept that machines should be given access to data so that they can learn for themselves.The way that we will eventually create human-like AI has frequently been talked about as a certainty by researchers.Surely,we are moving towards that objective with expanding speed.A significant part of the advancement that we have found in recent years is all because of the fundamental changes in how we view AI working,which have been brought about mainly by ML.Therefore,it would not be inappropriate to give ML the credit of instilling smartness in machines.
2.1 Smartness or intelligence
‘Smartness’or intelligence is at both microscopic and macroscopic levels of IoT.These sentences may sound like a far-futuristic wave of talking refrigerators and self-driving taxis,but it means much more than that.Now,SOs are mostly concerned about data,devices,and connectivity.The data needs to be analysed to bring out the hidden insights;this can be done with the help of BDA.Eventually,it is the analysis of this big data with ML that makes the whole system smart.
Table 1 makes the idea clear about the extent ML has spread into the idea of ‘smartness’.It shows few examples of animals whose smartness have been replicated by several man-made AI machines.Such machines are or will be capable of performing certain functions like the corresponding animal or will have some similar characteristics.Although complete replication of all the characteristics of the living being has not been achieved,but research is progressing gradually towards making these AI machines behave more like its living counterpart.
It is seen that certain characteristics and behaviour are yet to be instilled into machines to make them somewhat ‘intelligent’.The philosophy that drives ML is to automate the analytical models and enable algorithms to continuously learn from the available data.This data should be stored or tracked,in order to be processed on time.There may be a lot of available data generated each moment,but all of it may not be useful.The key idea is to collect relevant data and analyse it efficiently.
3 Internet of things
Even a few decades back,nobody could have imagined having a video chat with their families in a different continent.Nowadays,it is a common thing.All of these is due to technology getting cheaper,and devices emerging with new and improved capabilities.People can get things done with a click on their smartphone,be it sending emails,paying bills,transferring money,or booking a cab.
What we had since 1991 was ‘Internet of computers(IoC)’and it gradually grew in size as more and more people started using it.With the advent of pocket phones and connected devices,the Internet of devices started and eventually grew larger as mobile phones,computers,laptops,and tablets became cheaper and more accessible to the common man.Gartner,Inc.forecasted that 6.4 billion connected things will be in use worldwide in 2016,up to 30%from 2015,and will reach 20.8 billion by 2020[24].In 2016,>5.5 million new things got connected every day,thus,emerging the huge scope for IoT.Since various things are continuously connecting to form an IoT,there are various disciplines that get associated with IoT.Therefore,IoT can also be thought of as a combination of various domains.Fig.1 gives a representative list of some domains(most of these overlap with each other in terms of concepts and techniques)constituting the IoT.IoT is just a connected system of physical things(like appliances,crop fields,plants,animals etc.)and humans.Humans are connected to these devices using some SOs attached to both which are capable of sending,receiving,and analysing data.These SOs represent the entity(a human or a physical thing),it is attached to,in the network.
3.1 Internet of everything
Usually,people get confused about the concepts of IoT and IoE.According to Cisco[7],‘the Internet of Everything is the intelligent connection of people,process,data and things’.The IoE connects up the physical things to the cyber things into one cohesive whole.It is not just about allowing devices to talk to each other;it is about allowing everything(living,non-living,or any virtual object)to talk about each other.This virtual object part is missing in IoT.IoT may have SOs(attached to physical things and humans)and an Internet infrastructure,but does not include a smart non-physical entity(PE)(kind of a ‘cyber thing’analogous to any physical thing).In IoE,connections can be human–human,physical thing–physical thing,cyber thing–cyber thing,human–physical thing,physical thing–cyber thing,human–cyber thing.The concepts IoT and IoE are very overlapping.To get a better view of the concepts,we illustrate a venn diagram in Fig.2.
We will describe Fig.2 in terms of sets.The following relations hold:
Things∩Intelligence=Smart Objects(Devices).
Network∩Intelligence=Smart Network.
Things∩Network=Networked Devices.
Services∩Intelligence=Smart Services.
Services∩Network=Internet Services.
Things∩Intelligence∩Network=Internet of Things(IoT).
Internet Services∩Intelligence=Internet of Services(IoS).
Internet of Things∪Internet of Services=Internet of Everything(IoE).
IoE has turned into a catchphrase to depict the integration of connectivity and intelligence to pretty much everything(physical or virtual)with a specific end goal to give them special functionalities.For example,a smart website that may have some embedded intelligence to identify when a person is getting annoyed by an unnecessary advertisement or getting excited by an offer flashed on the screen.Let us imagine a user-specific website;different users see different layout/representation of the same website.In future,we might also be able to develop web-based facilities so that even the disabled could use the Internet for their benefits.Then only the true purpose of the Internet would be served.Internet is for everyone and everything.Thus,comes the need to understand the key concepts that build these IoE and IoT.

Fig.1 Different fields merging into IoT

Fig.2 Venn diagram for the concept of IoT,IoS,and IoE
3.2 Things and everything
When we are talking about IoT and IoE,we must be very clear about the concept of ‘things’and ‘everything’.One straightforward concept that may come to mind is anything that can be connected may be the ‘thing’in IoT.However,we define it other way round.There can be more features in making a physical object a ‘thing’.The ‘thing’(living or non-living)should have:
(i)a way to generate or collect data,
(ii)a way to process data,
(iii)a way to send or receive data,
(iv)a way to identify itself.
The main concept to consider,when thinking of IoT,is that‘Things’are physical objects,i.e.anything that has a real-life presence.The Internet as we know it is not just made of physical devices.For instance,a website cannot be thought to be a PE;it exists somewhere virtually.This is true for services that we might use every day,such as online shopping sites,social media sites etc.These ‘intelligent services’along with the ‘things’make the‘everything’.Thus,inter-connections as well as intra-connections between ‘things’from physical world and ‘intelligent services’from the cyber world make the IoE.
3.3 AI enabled IoT
IoT is a vast concept encompassing too many sensors,actuators,data storage,and data processing capabilities interconnected by the Internet.Thus,any IoT-enabled device can sense its surroundings,transmit,store,and process the data gathered and act accordingly.The last step of acting accordingly is entirely dependent on the processing step.The true smartness of an IoT service is determined by the level of processing or acting that it can perform.A non-smart IoT system will have limited capability and will be unable to evolve with the data.However,a smarter IoT system will have AI and may serve the actual goal of automation and adaptation.In this context,few examples of existing IoT services with the working of AI behind them are discussed here.
3.3.1 Voice assistants:These are cloud-based voice services which act as table-top personal assistants for users.They perform various tasks through third-party applications and other smart devices in their proximity.They are capable of answering queries,calling cabs,making restaurant reservations,playing music,switching smart lights on/off,and many more tasks based on the user’s voice commands.Few of the well-known voice assistants are:
·Alexa is the voice assistant from Amazon,which is used in products like Amazon Echo,Amazon Tap etc.There is a specific set of skills known as the Alexa Skills Kit(ASK)that can be modified and updated to personalise or improve certain skills.
·Siri from Apple Inc.is used in Apple Homepod which serves a similar purpose.
·Google Assistant used in Google Home has additional features where it can recognise up to six different users and pull their respective details to converse with them.
These voice assistants are capable of performing multiple tasks mostly due to the application of various subfields of AI.Automatic far- field voice recognition,wake word detection,speech to text conversion,natural language processing and understanding,contextual reasoning,dialogue management,question answering,conversational AI etc.are performed continuously to make the voice assistants perform functions real time.
3.3.2 Robots:Recent advancements in this field of robotics have led to the creation of robots who have increased human likeness and are able to interact with humans while understanding,reciprocating,and expressing certain human emotions.Robots are IoTs in themselves since they contain multiple sensors and actuators along with AI that helps them continuously learn and adapt themselves over time.
·Pepper from SoftBank Robotics is a human-shaped robot which is termed as a humanoid companion which can interact with humans.It is able to understand a human’s emotion through his/her facial expression,body movement,tone of voice,words used etc.It can identify four human emotions,namely joy,sadness,anger,and surprise,and reciprocates appropriately through movement,touch,words,and display on its screen.It is able to move around and interact with humans and other devices in its vicinity.Pepper is commercially used in various stores to interact with customers.
·Sophia from Hanson Robotics is a social humanoid robot which is incredibly human-like and can express emotions through>50 facial expressions.During a conversation,it is able to maintain eye contact with the human while conversing.Sophia is the world’s first robot to get a country’s full citizenship.She has even given multiple interviews and sang in a concert.
·Robotic Kitchen from Moley Robotics is an advanced fully functional robot integrated into a kitchen.It has robotic arms,oven,hob,and a touchscreen unit for human interaction and is able to prepare food of expert quality from its recipe library.
Application of natural language processing,computer vision,shape recognition,object recognition,detection and tracking,block-chain technology to analyse inputs and responses,facial recognition,voice recognition,speech-to-text technology,obstacle recognition,haptics etc.have been widely used in these robots to enable them function effectively.
3.3.3 Smart devices:In an IoT apart from the voice assistants and robots,there are SOs/devices that are present which make the task simpler for humans.SOs that are AI enabled use applications of object identification,facial recognition,voice recognition,speech and expression identification,deep neural networks,transfer learning,computer vision etc.
·Smart Oven by June aims to cook food perfectly everytime.It has an HD camera and food thermometer which helps to automatically monitor the food being cooked inside the oven,and can switch cooking modes if necessary.This oven can be operated through Alexa and can recommend and configure automatic cook programme by analysing the likings of the user.
·SkyBell is an HD Wi-Fi doorbell from Honeywell that allows the user to answer the door through a smartphone or a voice assistant.The video camera at the doorbell sends an alert and live feed to the home owner’s phone to alert him/her about the person at the door.The owner can converse with the person through SkyBell even from a remote location.This has helped keep trespassers and burglars at bay.
·Smart Lights by Deako can be controlled remotely through smartphones and Alexa or Google Assistant.They are connected via the Internet and can receive software upgrades from time to time.·Automotive AI by Affectiva is an in-cabin sensing AI that can be used in robo taxis and highly automated vehicles.It detects emotional and cognitive state of the occupants in the vehicle from their face and voice through in-cabin cameras and microphones.
3.3.4 Industrial IoT:Apart from being used inside smart homes,IoT has a huge application area in the various industrial sectors.These solutions perform statistical and financial analysis of a company as a whole and finally provide predictions using some AI and ML algorithms.
·Primer is a product from Alluvium which provides industrial solutions.Primer creates a real-time stability score analysis based on the data collected,the sensors in the system,and assets.It aims to detect potential issues well beforehand and helps operators identify the anomalies and make necessary changes from something as small as a sensor to the entire facility.
·Plutoshift is another industrial IoT-based solution.It enables industrial companies to continuously track the performance of their assets,measures financial impact,and provides support for informed decision-making.
Thus,the opportunities and potential of both AI and IoT can advance when they are combined.As IoT generates data,ML and BDA carry the potential to find insights of huge value in the data.Without the AI,the data that the IoT generates remains useless.IoT needs to depend on AI as it is impossible for any human to find information in the data that IoT generates.Moreover,if a new pattern in data is detected,the machine will be capable enough to learn by itself which will be impossible for a non-AI IoT system to do.
4 Cyber-physical systems
The term ‘CPSs’emerged around 2006,when it was coined by Helen Gill at the National Science Foundation(NSF)in the USA[8].CPS according to NSF are‘engineered systems that are built from,and depend upon,the seamless integration of computational algorithms and physical components’.Today,it is thought of as a system that works on and is monitored by computer-based mechanisms(built inside each component as well as in the complete system),strongly connected via the Internet and is easily accessible to its users.
During World War II,Wiener established a technology in anti-aircraft guns that can automatically aim and fire.In spite of the fact that the components he utilised did not include advanced computers,his control logic was effectively a computation,but one did with analogue circuits and mechanical parts.This thought has emerged as a necessity-driven concept.Few decades back,people only imagined automatic cars;today,people are already creating automated cars with advanced abilities to help reduce accident rates.To enhance this plan further,future road networks may also be connected with the cars via the Internet and communicate the information to help reduce traffic congestion,accidents etc.These may also be connected to police station,hospitals,and so on.
In today’s context,CPSs are emerging from the integration of infrastructure,SOs,embedded computational devices,humans and physical environments, which are normally tied by a communication framework.These incorporate frameworks like smart cities,smart grids,smart factories,smart buildings,smart homes,and smart cars where everything is associated with each other protest.They are expected to give a resilient, flexible,proficient,and cost-effective scenario.Let us imagine that a road-accident patient is rushed to a hospital only to be asked to make a police complaint first or wait for the police to arrive.If somehow these systems could be interconnected,the information about the accident would be immediately sent to the police.All the necessary actions would be taken instantly and the chances of delay in the treatment would be reduced.However,such connections between objects should manifest as a valid relationship in the physical world too.For example,a traffic monitoring system should be connected to police stations and hospitals,but in no way it should be linked to person’s home security system.Connecting these two may lead to security issues,and also overburden the data store as well as the network.So,the connections made between devices and systems should be carefully planned,keeping in mind all the pros and cons of each connection.To make these connections and systems work perfectly and efficiently in harmony,an independent platform needs to be created which work for the individual objects as well as the system on the whole.
4.1 CPS:a combination of disciplines
The CPS technology is prevalently from the industrial sector and serves as the engine of innovation for a new era of end user products.The infrastructure of CPS is,therefore,a combination of numerous disciplines(most of which overlap).
(i)ML:It is a platform to learn the trends of the system from data generated in the past,to make an informed decision in future,without manual monitoring.
(ii)BDA(data science):All the data that is generated in the huge interconnected system will constitute a massive content that will be processed and analysed over time to make the system better.Usually,ML algorithms are modified and adapted to handle the ‘Big Data’scenario.
(iii)Design:The overall system needs a robust,tolerant,and efficient design,which connects all the components as required.
(iv)Process science:Different industrial manufacturing processes are demanding the use of automation in their production lines.
(v)Wireless sensor networks(communication):The whole system would depend on communication;wireless connections between each component of the system would help pass information from one object/system to another.
(vi)Software:All the working devices and system need a software to work.These softwares would be system and task-specific.
(vii)Embedded systems:The gadgets/devices that constitute a CPS would contain embedded systems,like camera,temperature measure etc.Each device would have different embedded systems or sensors as per their requirements.
(viii)Cybernetics:It is relevant to mechanical,physical,biological,cognitive,and social systems.To enable any device attached to an entity for storing,processing,sending/receiving data,this field is highly in demand.
(ix)Mechatronics and robotics:These are fields which seek human-like actions for different tasks.These will not be manually handled or given some fixed instructions,rather they will be intelligent enough to know what needs to be done at the right time.
(x)High performance/cloud computing:Typically,the issues considered cannot be solved on a single commodity computer within a sensible amount of time(excessively complex operations are required)or the execution is incomprehensible,because of restricted accessible assets(a lot of training data is required).High performance/cloud computing is the way to beat these impediments by utilising specialised or high-end hardware or by accumulating computational power from several units.The corresponding data distribution and operations across several units simultaneously requires the concept of parallelism.(xi)Cognitive science: Cognitive science predominantly involves concepts from psychology,philosophy,neuroscience,anthropology,computer science,and linguistics.It is the study of mind and the level of intelligence.The goal is to understand the nature of knowledge in various living beings and how that knowledge is acquired,processed,and used.
This is not an exhaustive list of the various domains that may merge up to make CPS.Owing to the interdisciplinary nature of the research,most of the concepts overlap.Moreover,other domains may also collaborate in future to improve the CPS scenario in some form.
5 Components of IoT-CPS
Now that we have established a clear relationship between IoT,CPS,and the related terms around it,the ecosystem of these technologies matter most.Since CPS is a combination of subsystems,we can concentrate on the structure and components of IoT initially.If we dismantle the various parts of IoT,we would be left with something as shown in Fig.3.
From Fig.3,we can see that there are various components in an IoT system.Apart from network infrastructure and security,a major portion of IoT requires data storage and processing on a macroscopic(i.e.in the overall system)as well as on a microscopic level(i.e.in each SO locally).The SOs themselves should have some data processing, intelligence, and decision-making capability in them.For this,they need to have built-in data processing tools to analyse the sensor data and make some smart decision.ML and data analytics[12]are the best candidates for such smart DA.On a macroscopic level too,more than billions of things will generate data independently and it would be transmitted over the network to some remote data storage locations for further DA and all this in real time.It sounds like a big data task.A lot of data will be generated,stored,and processed continuously.So,BDA and ML together will weave out the intelligence in IoT.
Any SO can also have a limited data storage capability and limited data processing capability as well.For example,a smart watch signals to walk whenever the user is detected stationary(sitting or lying down)for a long period of time.However,it does not alert when the user is sleeping.It can clearly differentiate when the user is sleeping and sitting.To do so,it does not need to transmit the data to any server and perform a remote processing.It collects data and does some small analysis inside itself to actuate the alarm.These short-term decision-making capabilities are embedded in a smart device.For long-term decision-making or for finding insights,remote storage and processing may be needed.
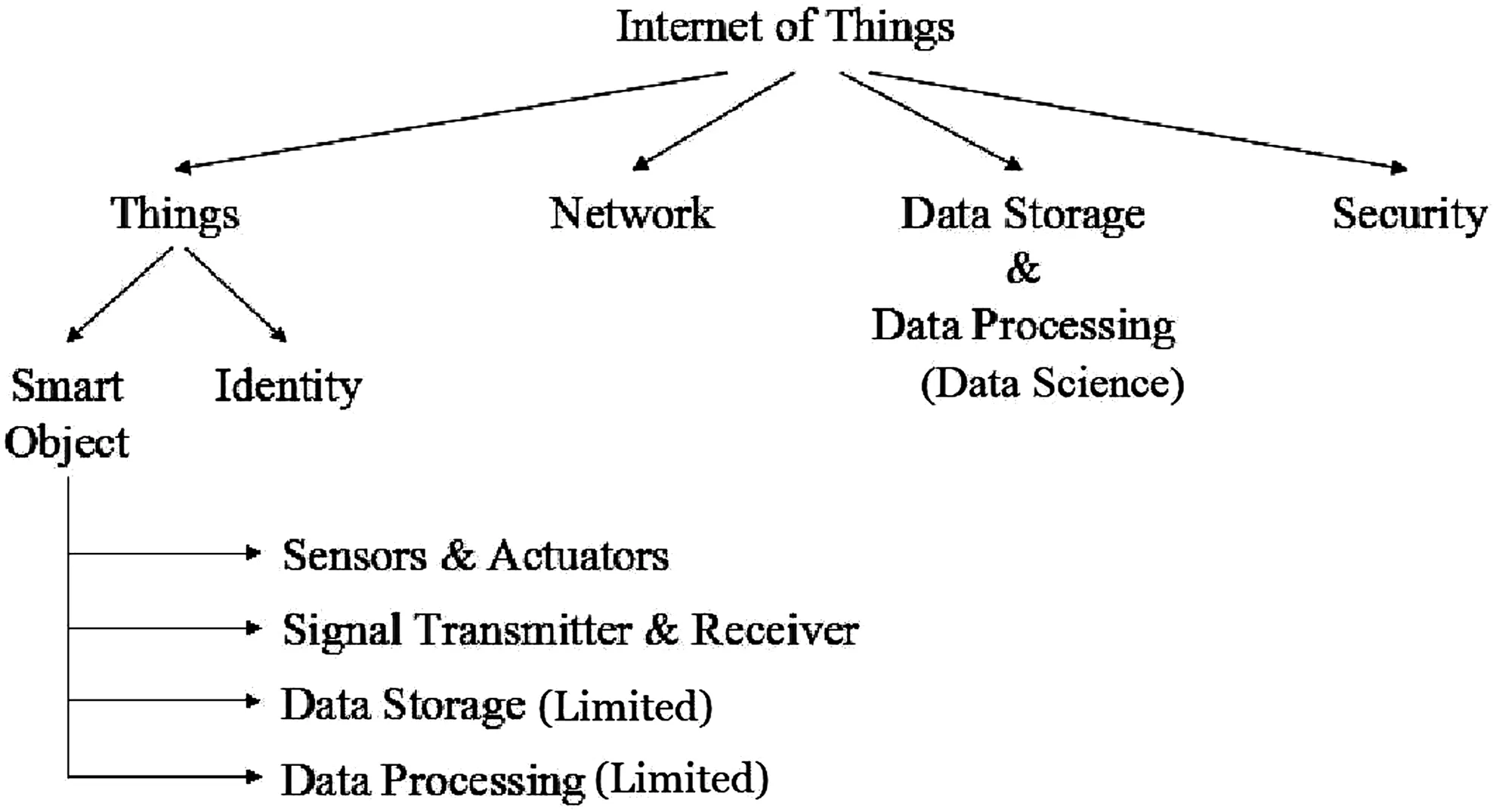
Fig.3 IoT architecture tree
IoT will mean too many connected devices.When such‘everything to everything’connection is established,physical world will be full of sensors/actuators and the virtual world will be full of data.The network will be highly complicated,and data would be generated throughout the CPS all the time.Different analysing systems will be handling different parts of the IoT–CPS.All of the data is not needed to be handled at one place or at one time.So,smaller relevant portions of the data are extracted and dealt with as and when needed.The data should be analysed reasonably in real time in order to make useful decisions.The data that is generated and handled by IoT is essentially done by the individual parts of IoT which together form a whole system.These parts of IoT are discussed in the following sections.
5.1 Smart objects
To catch up with such a substantial concept,we will require at least millions(or more)of data generating SOs.These will act like the building blocks of such a major system.We have two elements to consider in the physical world:a PE and SO.
A PE can be anything from people,creatures,and plants which may not be able to directly interface with the IoT but is an integral part of the system.Such physical entities will have SOs attached to them.These SOs are the AI elements that have the ability to communicate via network.They can be anything like implanted chips,wearables,or smartphone that is somehow attached to the PE.So,an SO becomes that device which helps a PE connect to the ‘Internet’of things.The Internet however is virtual and both the PE and SO are physical objects.Hence,they must need a digital representation.The digital representation of the PE by the SO is the digital entity(DE).For example,if we are the PE,our smartphone becomes the SO and our social media app becomes the DE.Sometimes,the PE itself maybe integrated to an SO,like an automated car.SOs are physical world portrayal of DEs in digital world,having the capability to sense,store,process(locally),and communicate via networking.SOs may act as intelligent agents with some level of self-rule,cooperate with other entities,and exchange information with human clients and other computing devices within the interconnected CPS.DEs are virtual programming elements which have autonomous objectives.They can be either services or simple coherent data entries.
A PE or thing can be represented in the cyber world by a DE by its digital proxy(DP).DPs can be viewed as users in cyber world,just like our social media profiles(our DP)are viewed as being us(where we are the PE).Every PE has a DP,which is used to represent it in the digital world.There are numerous sorts of digital portraits(which are known as DE)of PE that we can imagine:avatars,three-dimensional(3D)models,objects(or instances of a class in an object-oriented programming language),and even a social network account could be viewed as such.However,in the IoT context,DPs have two fundamental properties:
(i)Each DP must have just a single ID that distinguishes it from others.The association between the DP and the PE must be established automatically.
(ii)Relevant digital parameters pertaining to the characteristics of the PE can be refreshed upon any difference in the former.Similarly,changes that influence the DP ‘might’be shown on the PE in the physical world through actuators.
Data generated by these SOs need to be transmitted through wireless technologies,and the objects themselves should be clearly identifiable.All transmitted data can be collected in a distributed database and then monitored,analysed,and processed.The IoT will push the advancement in digital storage too.The collection,transmission,and processing this massive data to mine out valuable insights in real time bring us back to the topic of data analytics and ML again(Fig.4).
5.2 Data storage and data processing

Fig.4 Example of real world to virtual world mapping
As we understand,the main motive of IoT and CPS is to create an autonomous system that can handle different situations across the globe,which would eventually assist humans to lead a better life.The basic IoT–CPS framework consists of SOs(which seem like the nodes in a graph)and the connections between them.Assuming all the nodes and connections are made,the data is being generated and communicated from one node to another every moment.However,the SOs do not know what to do with it.Neither can they store it,nor do they know how to process it;this would make the whole system useless.The objective of being autonomous,making decisions,and taking actions would never be fulfilled without having proper data storage and processing units.This is an essential feature,needed both locally in SOs and also globally in the complete system.The SOs will handle small sets of data continuously flowing into the system;this can be stored temporarily in the SO till a task is done,and then it can be moved to the global data store.The data store of the whole system may not receive streaming data,but will mostly get large chunks of collected data from time to time.To handle both these types of data in real time,and utilise them effectively,the role of BDA is crucial.
All these data are to be stored,but what exactly needs to be done in the processing phase is unknown.We expect a smart system,IoT–CPS,to work autonomously,i.e.observe its surroundings(through different parameters),learn from experience,understand the need of the hour,and make a useful decision/action.For an object/system to imitate humans,it needs the ability to learn from the data.Since human intervention may not be available or desired most of the time,the system needs to learn independently.All these can be effectively done with the help of AI.
5.3 Communication networks
Continuous analysis of big data over these platforms demands an efficient and reliable network structure.Virtualisation of nearly every physical thing imposes big challenges on the network service providers.There should be advanced wireless technologies that can handle such enormous eruption of devices.Smart devices need a smart network infrastructure.Connecting machines and devices to telecommunication networks is not new.What makes IoT an innovation is the incorporation of smartness in the devices as well as the network.This will ensure networks which will automatically detect the necessity of connections between two objects and thereby increasing or decreasing the connection strength.Moreover,smart networks may also be smartly secure.They will easily identify the intrusion or theft situations and take necessary steps for that.There are numerous such capabilities that are still waiting to be harnessed.
Some people believe that for long-distance operations,5G networks can meet all the requirements of IoT devices.These 5G networks will be faster and smarter,but,sometimes it is hard to imagine why we would need such high bandwidth of data.For example,a smart water-heater with 5G connection will seem unnecessary.That is because,much of the technology that will connect to the network during this IoT surge are not yet invented.For example,our personal assistants might not be inside our phones.They can be holographic projections roaming with us and also connected to the Internet.5G is projected to be deployed by 2020.However,it is yet to be witnessed whether a 5G network can also handle the IoT or we need some more Gs.
Connection through the Internet may not always be necessary.For short-range communication services,we might use Bluetooth technology.The new Bluetooth low-energy(BLE)has been designed to operate on very low power consumption.The devices may be connected to the smartphone via BLE and may be used to send/receive small chunks of data only.For smaller devices that are not being moved around too far and which may not need to be connected throughout the day,Bluetooth connection seems to be a good choice.However,BLE may not be suitable for transferring bigger files or to hold a good connection at a large distance.In those cases,Wi-Fi connectivity is often an obvious choice for people who want wireless connectivity in a local area.Typically,it has a data transfer rate of 150–200 Mbps and can be maximum up to 600 Mbps.It can therefore be beneficial for file transfers,but is too power consuming under the scenario of IoT.
There are several other communication protocols that may become the skeleton for IoT.Zigbee[25],Z-Wave[26],6LowPAN[27],near- field communication[28],Sigfox[29],LoRaWAN[30]etc.are used for various use cases.
5.4 Security
All these things may sound fascinating,but as Jeong has pointed out in her book[31],IoT means ‘Internet of Garbage’.It says that‘if the Internet was a city,its streets would be piled so high with garbage that driving to the grocery store would be almost impossible’.The Internet contains garbage like harassment and intimidation,crimes,copyright abuse,malwares,spams etc.However,we can develop better interactions and better discourse,through insightful architecture,strict moderation,and efficient community management.We just need to filter the useful content from the garbage first and then attempt to find value in it.
As IoT will be rapidly adopted across the globe,it will generate new demands.The biggest concern,after putting together everything in IoT like the SOs,BDA,and communication capabilities,is to ensure the security in such a large-scale scenario.Securing the IoT devices means much more than just securing the devices themselves.The software applications and network connections that link to those devices should also be secure.Users of SOs and IoT will be highly vulnerable since their data is available on a network.There are three key issues of IoT devices and services–data confidentiality,privacy,and trust.In IoT,the user along with the authorised SOs may access the data.The IoT device needs to be able to verify that the entity(person or other device) is authorised to access the service. Therefore,authentication and identity management is needed.
The act of protecting the interconnected systems and their components has come to be known as ‘cyber security’.Cyber security is of utmost importance while dealing with smart devices,IoT,and CPS to avoid hackers from accessing users data.Cyber security aims to
(i)protect both IoT devices and services of unauthorised access from within the devices and externally;
(ii)protect the services,hardware resources,information and data,both in transition and storage.
There are various technologies for cyber security like cryptographic systems, firewall,intrusion detection systems,anti-malware softwares and scanners,secure socket layers.
Moreover,there are always some ethical issues.Suppose a small wearable gadget records the health and fitness information of a user.This information is available to the gadget service providers,since the gadget is connected to their global database.Now,the service providers may sell this user data to other companies without the user’s consent.Depending on the fitness tracker information of the user,he/she may start receiving offers or advertisement via messages/emails about some new fitness gear.In this case,the IoT is anticipating what might interest the user might buy.Some users may not want their personal information sold in this way,while others do not mind promotional offers.In another case,the user’s personal information may be used against him/her leading to some unwanted situation.Most of the time,selling of these user data without user consent are not beneficial to the user.Data sharing should be an option for the user to choose.Selling or distribution of user’s personal data should be done only with user’s consent.
6 AI and IoT-CPS
The first industrial revolution during 1760–1840 gave rise to a rapid growth of machines.With the advent of the second industrial revolutions (1870–1914),people became richer and urban.Currently,a ‘smart’or ‘cyber’revolution is under way.A number of interdisciplinary technologies and sciences are converging and giving rise to smarter softwares,new materials,dexterous robots,ground-breaking inventions(like 3D printers),and a whole range of personalised web services.When compared with the previous two industrial revolution phases,this smart revolution is evolving at an exponential pace.Growing interest in the study and development of AI[23]are pushing the product vendors to introduce AI into almost every strategy they make.Almost every organisation has plenty of data at hand,and therefore needs AI to use it efficiently for their own benefit.
6.1 AI enabled IoT-CPS
Talking of data,we have plenty of that in the IoT–CPS scenario.Data–big or small–is an invariably integral part of the IoT world of connected devices.The SOs should themselves be able to do a small-scale local processing and have some inherent intelligence.However,for a data-dependent decision,more data should be utilised.Storing these data for analytics inside an SO may not always be feasible.Here,the macroscopic version comes to play;the data are sent to remote locations in a distributed fashion and are analysed.The analysis results are then integrated and finally the decision,in some necessary cases,may be sent back to the SO where the actuator can then perform its task.The time between sending the data and actuating the decision should be practically less or else it would not be meaningful.Traditional analytic tools are not capable of capturing the entire essence of this massive data in real-time.On the one hand,the volume,velocity,and variety is too large for comprehensive analysis;whereas on the other hand,the range of possible relationships and correlations between different data sources are very vast for any analyst to manually comprehend.A good ML system,in order to deal such big data,requires
(i)data preparation capabilities,
(ii)learning algorithms–basic and advanced,
(iii)automation and adaptive processes,
(iv)scalability,
(v)ensemble modelling,and
(vi)real-time decision-making.
This means the system should be able to make most of the decisions and take required actions quickly.ML already has some good capability[1]of letting computers do some thinking for us.However,we are striving for more when we are trying to deal with big data.That is why we need to adapt the ML methods to handle big data and also build some new ideas.
The emergence of CPS and IoT are inspired totally by the idea of social,economic,and human benefit.Therefore,CPS and IoT can be thought to be almost anything like personalised healthcare,smart grids,smart industries,smart transportation etc.For example,a smart industry can improve its manufacturing processes by sharing real-time information among the various industrial equipments,supply chains,distributors,business systems,and customers.A healthcare CPS like a smart hospital may monitor the physical conditions of patients remotely to serve the far to reach areas.Whenever a road accident occurs,the nearest hospital,police station,and family member may be notified.An ambulance is immediately sent to the accident location,the on-duty doctor is alerted,and the police arrives at the spot without wasting any time doing things manually.Similar emergency situations should benefit the most from these interconnected autonomous systems.This ‘smartness’is what AI will bring to such IoT–CPS infrastructure.
The IoT–CPS applications involve components that interact through a complex physical environment.Such a connected environment is therefore a challenging innovation that can possibly change existing ventures.For example,manufacturing industries,energy systems,healthcare,transportation facilities,buildings,critical infrastructure,emergency response systems,defence,agriculture etc.will undergo an upgradation to their smarter and interconnected versions.Such organisations should have systemaware assets which would automatically asses the forthcoming faults or failures in the system.By being system-aware,we mean that a device implanted in any part of a machine should be able to sense itself along with its environment.The advances in AI applied to such connected IoT–CPS scenario will help us understand the vision of not only a smarter but a ‘brilliant planet’.
6.2 Cognitive AI and IoT-CPS
IoT not only means a combination of wireless sensor networks,data storage,embedded systems,or security issues,it means much more than that.It is a vision of a world connected by intelligence.This seems to be science fiction,but this is what makes IoT the buzz word today.The conventional way to deal with programmable computing is to filter the information through a progression of a fixed set of rules and then arrive at an outcome.However,it will not be that efficient to fulfil all that IoT promises to deliver.This is because in flexibility restrains their convenience in tending to numerous parts of a mind boggling,quick paced world,where the information processing capability declines exponentially and it goes unused.Psychological figuring has no such constraints.Instead of having a set of rules,psychological frameworks learn from the hidden relations within the connections with people,things,environment,and their encounters with each other.So,instead of being deterministic,they are probabilistic.This empowers them to keep pace with the volume,variety,variability,and unusualness of data produced by the IoT.
These psychological frameworks are called cognitive computation models in formal terms.These frameworks form an essential part of the AI in IoT–CPS.They are capable of comprehending the 80%of the world’s information that researchers call ‘unstructured’.Examples of such unstructured data include recordings,sound,even online journals,images,mails,and tweets.This implies that almost all the organisations are presently ready to light up parts of the IoT that were already imperceptible.At the point when such cognitive understanding is connected to the IoT,the outcome is what we call cognitive IoT,which we characterise as frameworks that mix knowledge into,and gain from,the physical world.
‘Cognition’ is the process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thoughts,experience,and senses.So,intuitively,cognitive IoT can be thought of as an extension of IoT which is capable of understanding,reasoning,and learning.These three aspects of cognition vary in meaning while comparing human cognition and cognitive IoT.For IoT,to ‘understand’would mean to be able to collect large volumes of data from the network and find the underlying meaning of the data.It would be able to create concepts,identify various entities,and define relationships between them.To have the ability to ‘reason’for an IoT means it should be capable of finding appropriate answers to queries or solve relevant problems without being explicitly programmed.Lastly,a cognitive IoT should be able to ‘learn’,i.e.independently infer new information from the data at hand using the past knowledge it has obtained.
6.3 Example cases of AI enabled IoT-CPS
Although machines are not made to completely replace humans,they are just there to help humans reduce the task load.Obviously,humans need to maintain supremacy over machines.AI is most effective when it is conjoined with human intelligence,rather than replacing it.It highlights the idea that computers and humans have different strengths in the vast field of excellence:computers are much more efficient at doing arithmetic jobs and counting,while humans show a remarkable performance in logic and reasoning.These differing forms of intelligence are complimentary,not diametrically opposites.Thus,AI is the technology that can fulfil our dream to have ‘things’that can ‘think’[32].Some examples of cases where AI have been incorporated and used in IoT–CPS scenario are as follows.
Energy utilisation:Algorithms have been developed on a small scale,to reduce energy consumption in a coffee machine(ARIIMA).It can be modified and implemented in other scenarios to reduce energy consumption;for example,in temperature control systems of houses,which can make them efficient and reduce wastage.Different houses will have different temperature settings adjusted according to the residents,and the system will learn that efficiently.
Routing/traffic:Traffic management or routing is a field of application in ML.Depending on different parameters like traffic,road condition,weather etc.,best routes are suggested.
Cost savings:Predictive abilities are amazingly helpful in an industrial setting.By drawing information from different sensors in or on machines,ML calculations can learn the usual running conditions of the machines.So,when some irregularities occur,it can identify the machine and raise an alarm.This would save cost as well as avoid accidents.An organisation called Augury does precisely this with vibration and ultrasonic sensors installed on their equipments[33]and saves money by predicting any malfunction before it happens.
In plain words,we want an ‘Internet of Things’where both the‘Internet’and the ‘Things’have the power to think[32].That inculcation of thought is where the ‘intelligence’ flavour of IoT lies.This may seem too over-rated,but this is what research on current AI all about.
7 Challenges
After all the idea has been developed,the gap between an idea and a working prototype is huge.Even if the working prototype is set,one may need resources to develop the prototype.Even if one is able to strive past all of this,the question that stands now is how do we know if this hot new technology will succeed or fail.Most of us,even experts in that particular domain,get it wrong most of the time.Recent IoT trends indicate that data is coming at a faster speed,from various sources in various forms.It obviously exceeds the abilities of an information system to imbibe,store,analyse,and process it.It is not hard to find databases with some petabytes of data,but the main objective is to not let all of these data go to waste.Therefore,efforts are being made to recognise and extract meaningful information(patterns,structure,underlying relationships etc.)from them.This task is quite complicated and it needs advanced storage and processing techniques due to the unimaginable volumes of data.In this scenario,new algorithms are being devised and well-known techniques are being revisited and tailored in the fields of PR,ML,data mining etc.to handle the new challenges posed by these data.There are other concerns too regarding such a union of technologies.The field of AI needs more development with the advent of such IoT–CPS infrastructure.As example cases,we can discuss some issues.Complex adaptive AI systems may lead to self-sustaining malicious evolution of systems that can mimic a cancerous growth in the human body.We would therefore need more research to combat such systems using superior evolving AI systems.Cyber security will also be a major concern as in this age of technology,there will be cyber wars.Any autonomous system will be used for malicious reasons if hacked.Such vulnerabilities of AI systems should be checked so that they stay safeguarded against such attacks.Mock attacking AI systems should be developed that would immunise the existing safeguarding AI system.There should also be systems that would predict the new type of attacks that can arise.Any organisation must develop systems to quickly recover from cyber events that disrupt usual business operations.Critical information that may be maliciously used against an individual should be automatically identified and should be kept private even if people share it publicly.AI systems can be used to ensure such privacy as well.
7.1 Challenges of CPS
CPS can be thought of as a reality to virtual mapping where the physical world is connected to the virtual world of information processing via some actuators and sensors.Thus,there is a need for IoT infrastructure inside every CPS.Now,we also need the IoT infrastructure to connect various CPSs with one another.The sensors inside a CPS will continuously spew real-time data.Many CPSs around the world would therefore be a massive generator of big data and will demand real-time processing.In this scenario,a number of specific challenges are raised due to the large-scale nature of CPS.
The physical world is governed by the elementary laws of physics.The changes made here are static.Therefore,the interaction between objects in the real physical world is well known.Whereas,the cyber world is governed mainly by basic laws of data.The data is either volatile or continuously changing.Any physical system may be predicted partially by simulation,but for a cyber process,it is difficult to predict the behaviour.When the two worlds come together in a CPS,they need to operate in synchronicity.It poses a big challenge for global system control. Moreover, the interconnectedness and data sharing features demand for well-defined platforms and control interfaces.There eventually builds up a need of an even tighter cyber security in such a large-scale platform.
There are even bigger challenges with the ‘big data’that the CPS creates.The data should be efficiently stored,cleaned,processed,and analysed in real time.After all these steps,it is essential to explore the heterogenous nature of CPS models.This can be done by the compositional verification and testing methods.There is an urgent need of standardised architectures and abstractions that enables efficient design and development of CPSs.Even after all these challenges,people are striving to fight all odds and make this work for the promising future that it holds.
7.2 Challenges of IoT
IoT may seem fascinating to talk about.We argue that most of the technical challenges have been addressed like having the ultra-low-power microcontrollers,advanced sensors,wireless technologies etc.,but still we are speculating about the IoT rocket to take off.There are still some major issues which have held the world to be encompassed by this IoT yet.
7.2.1 Connectivity:Though the world has advanced its scope and use of the Internet,it is still not available in many small villages and remote locations around the world.Though companies like Google has invested in ideas like‘balloon powered Internet’,it is still a challenge to bring the whole earth within the coverage of the Internet.The whole idea of IoT is built on the assumption that there will be constantly reliable and fast network connectivity.This is one of the biggest roadblocks IoT is facing presently.
7.2.2 Security and trust:Trust and security in the world of connected devices are the two key problems to mass adoption of IoT.Users are quite concerned about IoT being a safe option to share their data.Once every information and device is interconnected and is available on a network,it can be accessed by hackers and can be used for various fraud.For example,an IoT connected home might increase the security risk of a burglar intrusion.Or a company’s privacy may get breached when the competitors get access to its production data.Even if all the security measures are taken,there will still be trustability issue.
7.2.3Interoperability:It is hard to make meaningful connections between many random devices.IoT requires standards to enable platforms that are connected,communicable,operable from distant locations,programmable across devices,and should be independent of the model,manufacturer,or industry it is coming from.In other words,the IoT should be platform independent and should work even if the devices have different OSs(operating systems),different OEMs(original equipment manufacturers),different types of connectors,different versions,and different protocol standards.
7.2.4 Scale:IoT means millions of connected devices.This will call for two major trends:data integration and ‘big little data’.The former means that all types of data will be generated from this system,and they need to be combined as and when analysis is needed.The latter however indicates the tremendous multiplication of small data sets across the web.The blending of small data sets with small data sets,small data sets with big data sets,and big data sets with big data sets will require different approaches.Moreover,as new innovations will be made,newer types of devices will emerge.IoT will have to keep up the pace with these too.The scale of devices will also grow and will impose a heavy burden on the connectivity aspect.The initial system should be able to handle changes in the structure of the system.It should have scope for change in future without much modification in the original structure.
7.2.5 Energy and environment:Most of the devices that we currently use operate on battery power and have a very limited shelf life.As IoT gains popularity,the number of devices and the size of the network will grow quite fast.Based on the current energy availability,it would be impossible to power these billions of tiny devices along with the full- fledged network across the globe.We would eventually have to shift to more unconventional sources of energy for prolonged use.
If the future devices also have a very short shelf life like the devices now,that would generate a huge amount of e-waste.It would then be impossible for the environment to keep balance in nature and be a hazard.Thus,for future development of IoT,the individual devices as well as the total system should be eco-friendly in nature.Development in IoT will demand research in the field of unconventional or renewable energy resources,research to make devices that will have a long shelf life,and in the field of reusability and recycling of resources.
7.3 Challenges of DA
With the advent of IoT,practically everything will have a virtual existence in the cyber world.All of these entities will generate data like nobody has imagined before.Analysing these massive and fast- flowing data requires advanced technologies (like virtualisation softwares),adaptable cloud computing etc.It also needs very powerful high-performance computing devices that can provide the mechanism to discover the underlying insights in big data.
The IoT connected devices will produce data at such a staggering rate that in future the data volume from this first era of big data will seem to be a dwarf.ML can likewise help machines,humans,devices etc. collectively called ‘things’, get together to comprehend what important information individuals may need from the data.Additionally,ML assumes a basic part in IoT aspect to handle the immense volume of data produced by those‘things’.It gives IoT and those ‘things’a cerebrum to think,which is called ‘embedded intelligence’by a few researchers[34].
Indeed,something to remember is that if someone is determined to search for a pattern in a given data,he/she will eventually discover one.This inclination to discover patterns might be the reason for human knowledge,i.e.having the capacity to identify conveniently meaningful patterns out of things we have watched.However,maybe the key issue with this sort of pattern discovering, both with humans and artificially intelligent computers,is judging whether the patterns we unavoidably find are at all significant,genuine,and valuable.
In conjunction with proper AI structures and upgraded ML models,this may in the long run prompt an exact impersonation of the human brain on a significantly greater scale.Under the attire of IoT,we may begin making complex systems that are sufficiently canny to begin understanding things as mystifying as human irrationality,crimes,and even human’s dependence on machines.Once these characteristics get assimilated in them,that renders them smart,there is no reason why people would not be threatened and inevitably subjugated by such machines.
8 Conclusion
In future,people will be wearing intelligent gadgets,eating intelligent capsules that judge the impact of the medicine on the body,living inside intelligent homes,and so on.This sounds like a science fiction,but this is what all the present research is about.Everything will be smart and will be connected to the Internet.All branches of science will collaborate to create something of a big value.We will have a ‘smart cyber revolution’.However,there is still a debate on whether we are heading towards a creative destruction or not.
For instance,machines are now able to take on less-routine tasks,and this transition is occurring during an era in which many workers are already struggling.Nonetheless,with the right policies we can get the best of both worlds:automation without rampant unemployment.Eventually,human ingenuity changes the role of productive work.Educational opportunities will be promoted and there will be more skilled labour with re-skilling and up-skilling.
As we will continuously deploy AI models in the wild,we will be forced to re-examine the effects of such automation on the conditions of human life.Although these systems bring myriad benefits,they also contain inherent risks,such as privacy breach,codifying and entrenching biases,reducing accountability and hindering due process,and increasing the information asymmetry between data producers and data holders.The IoT–CPS is a diverse and complex network.Keeping track of every unethical or security breach incident will be difficult.Any failure or bugs in the software or hardware will have serious consequences.Even power failure can cause a lot of inconvenience.So,we may need another AI system on top of such AI enabled IoT to monitor its whereabouts each instant.Someday,we may need a democracy of such systems which will prevent themselves from not doing irrational things.Our lives will go on to be increasingly controlled by technology,and we will depend on them for everything.Whatever be the case,humans should still have supremacy over all the man-made smartness.Only then we can control this revolution without getting enslaved by it.
9 References
[1] Michalski,R.S.,Carbonell,J.G.,Mitchell,T.M.:‘Machine learning:an artificial intelligence approach’(Springer Science&Business Media,Berlin,Germany,2013)
[2] Witten,I.H.,Frank,E.:‘Data mining:practical machine learning tools and techniques’(Morgan Kaufmann,Burlington,Massachusetts,2016)
[3] Monostori,L.,Kádár,B.,Bauernhansl,T.,et al.: ‘Cyber-physical systems in manufacturing’,CIRP Ann.,2016,65,(2),pp.621–641
[4] Lee,E.A.,Seshia,S.A.:‘Introduction to embedded systems:a cyber-physical systems approach’(MIT Press,Cambridge,Massachusetts,2016)
[5] Hassan,Q.F.,Khan,A.R.,Madani,S.A.:‘Internet of things:challenges,advances,and applications.Chapman&Hall/CRC computer and information science series’(CRC Press,Boca Raton,Florida,2017)
[6] Fortino,G.,Trunfio,P.:‘Internet of things based on smart objects:technology,middleware and applications’(Springer,New York,USA,2014)
[7] Yang,L.T.,Di Martino,B.,Zhang,Q.:‘Internet of everything’,Mobile Inf.Syst.,2017,2017,pp.1–3
[8] Baheti,R.,Gill,H.:‘Cyber-physical systems’,Impact ControlTechnol.,2011,12,pp.161–166
[9]Gorman,M.M.:‘Database management systems:understanding and applying database technology’(Elsevier Science,USA,2014)
[10] Theodoridis,S.,Koutroumbas,K.:‘Pattern recognition’(Elsevier Science,USA,2008)
[11] Marz,N.,Warren,J.:‘Big data:principles and best practices of scalable real-time data systems’(Manning,New York,USA,2015)
[12] Leskovec,J.,Rajaraman,A.,Ullman,J.D.: ‘Mining of massive datasets’(Cambridge University Press,Cambridge,UK,2014)
[13] Fan,J.,Han,F.,Liu,H.:‘Challenges of big data analysis’,Natl Sci.Rev.,2014,1,(2),pp.293–314
[14] Zikopoulos,P.,Eaton,C.:‘Understanding big data:analytics for enterprise class hadoop and streaming data’(McGraw-Hill Osborne Media,New York,USA,2011)
[15] Ghosh,A.,Mishra,N.S.,Ghosh,S.:‘Fuzzy clustering algorithms for unsupervised change detection in remote sensing images’,Inf.Sci.,2011,181,(4),pp.699–715
[16] Halder,A.,Ghosh,S.,Ghosh,A.:‘Aggregation pheromone metaphor for semi-supervised classification’,Pattern Recognit.,2013,46,(8),pp.2239–2248
[17] Cohn,D.:‘Active Learning’,in Sammut,C.,Webb,G.I.(Eds.):‘Encyclopedia of Machine Learning and Data Mining(Springer,New York,USA,2017),pp.9–14
[18] Jha,S.,Seshia,S.A.:‘A theory of formal synthesis via inductive learning’,Acta Inform.,2017,54,(7),pp.693–726
[19] Pan,S.J.,Yang,Q.:‘A survey on transfer learning’,IEEE Trans.Knowl.Data Eng.,2010,22,(10),pp.1345–1359
[20] Ghosh,A.,Jain,L.C.:‘Evolutionary computation in data mining’,in Ghosh,A.,Jain,L.C.(Eds.): ‘Studies in fuzziness and soft computing’(Springer,Berlin,Heidelberg,2006)
[21] Hastie,T.,Tibshirani,R.,Friedman,J.:‘The elements of statistical learning:data mining,inference,and prediction’,in Diggle,P.,Gather,U.,Zeger,S.(Eds.):‘Springer series in statistics’(Springer,New York,2013)
[22] Holler,J.,Tsiatsis,V.,Mulligan,C.,et al.:‘From machine-to-machine to the internet of things:introduction to a new age of intelligence’(Academic Press,Cambridge,UK,2014)
[23] Kaplan,J.:‘Artificial intelligence:what everyone needs to know.What everyone needs to know’(Oxford University Press,Oxford,UK,2016)
[24] Câmara,D.,Nikaein,N.: ‘Wireless public safety networks 2:a systematic approach’(Elsevier Science,USA,2016)
[25] Appadurai,A.S.,Kumar,D.:‘Performance analysis of ZigBee and OWC in wireless body area network’,Small,2016,5,(3),pp.564–567
[26] Gomez,C.,Paradells,J.:‘Wireless home automation networks:a survey of architectures and technologies’,IEEE Commun.Mag.,2010,48,(6),pp.92–101
[27] Shelby,Z.,Bormann,C.:‘6LoWPAN:the wireless embedded internet,vol.43’(John Wiley&Sons,New Jersey,USA,2011)
[28] Coskun,V.,Ozdenizci,B.,Ok,K.:‘A survey on near field communication(NFC)technology’,Wirel.Pers.Commun.,2013,71,(3),pp.2259–2294
[29] Edwards,C.:‘Over the hills&far away[sensors and IoT]’,Eng.Technol.,2016,11,(6),pp.60–63
[30] Bor,M.,Vidler,J.E.,Roedig,U.:‘Lora for the internet of things’.Proc.2016 Int.Conf.Embedded Wireless Systems and Networks,EWSN‘16,Graz,Austria,2016,pp.361–366
[31] Jeong,S.:‘The internet of garbage’(Forbes Media,New York,USA,2015)
[32] Gershenfeld,N.:‘When things start to think:integrating digital technology into the fabric of our lives’(Henry Holt and Company,Augury Systems,Haifa,Israel,2014)
[33] Yoskovitz,S.,Gal,S.: ‘Automatic mechanical system diagnosis’,22 October 2012.US Patent App.13/657,037
[34] Guo,B.,Zhang,D.,Yu,Z.,et al.:‘From the internet of things to embedded intelligence’,World Wide Web,2013,16,(4),pp.399–420
