RPIP—HPLC—ICP—MS测定饮用水中铬形态
2018-02-03祝银刘琴杨承虎王范盛李子孟宋凯
祝银+刘琴+杨承虎+王范盛+李子孟+宋凯

摘要 本文建立一种改进的高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定淡水中铬形态的方法。通过样品加标回收验证本方法的准确度,本方法Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(Ⅵ)的回收率均在93%~115%之间。通过制备7个浓度水平确定得到铬元素的校准曲线范围,Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(Ⅵ)的相关系数接近1(r=0.999 9),Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(Ⅵ)的LOD分别为0.094、0.100 μg/L,Cr(Ⅲ)的LOQ为0.28 μg/L,Cr(Ⅵ)为0.30 μg/L。综上所述,方法的定量限、重现性和准确度满足淡水中Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(Ⅵ)的定量分析,可以有效应用于其预期的使用。
关键词 形态分析;铬形态;饮用水;高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法
中图分类号 O657.7+2;O657.63 文献标识码 A 文章编號 1007-5739(2018)01-0174-02
Determination of Chromium Speciation in Drinking Water by RPIP-HPLC-ICP-MS
ZHU Yin 1,2 LIU Qin 1,2 YANG Cheng-hu 1,2 WANG Fan-sheng 1,2 LI Zi-meng 1,2 SONG Kai 1,2
(1 Marine Fisheries Research Institute of Zhejiang Province,Zhoushan Zhejiang 316021; 2 Key Lab of Sustainable Utilization of Technology Research for Fishery Resource of Zhejiang Province)
Abstract The approach presented in this paper refered to the modification of a method for the detection and quantitative determination of chromium species in water by high-performance liquid chromatography inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. The accuracy of the method was verified by sample adding recovery estimation. The recovery rates of both determined analytes were between 93% and 115%.Calibration curve was obtained by preparing seven concentration levels of each chromium species. In both cases,the correlation coefficient was close to 1(r=0.999 9)for Cr(Ⅲ)and Cr(Ⅵ). Using the HPLC-ICP-MS method,LOD was 0.094 μg/L and 0.100 μg/L for Cr(Ⅲ)and Cr(Ⅵ),respectively. According to the modified blank determination method,LOQ for Cr(Ⅲ)was 0.28 μg/L and for Cr(Ⅵ)was 0.30 μg/L.As a result of the method validation experiment,the obtained limit of quantification,repeatability and intermediate precision were satisfied for the quantification of Cr(Ⅲ)and Cr(Ⅵ)in water matrices. The method can be applied effectively for its intended use.
Key words speciation analysis;chromium speciation;drinking water;HPLC-ICP-MS
铬是硬度最大的金属元素,化学符号Cr,广泛分布于环境中,并且在工业中有许多应用,例如电镀与钢铁业[1]。在铬的几种存在形式中,Cr(Ⅲ)是人体必需的营养物质,但Cr(Ⅵ)是剧毒,具强氧化性,并且极易渗透生物膜[2]。目前,欧盟饮用水中允许的总铬含量是50 μg/L。国内现行地表水的Cr(Ⅵ)根据不同的水域对应不同限量值,Ⅴ类水质限量为100 μg/L,Ⅱ类、Ⅲ类和Ⅳ类水质限量均为50 μg/L,Ⅰ类限量为10 μg/L。
高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱技术(HPLC-ICP-MS)是测定水样中铬元素形态的良好分析手段。ICP-MS作为最灵敏的检测器之一,具有元素特异性、宽线性动态范围和极低检测限等优点[3]。ICP-MS的动态反应池技术(DRC)极大地降低了40Ar12C+和35Cl16OH+的光谱干扰,从而提高了铬元素分析的灵敏度[4]。铬形态分析的色谱方法可能包括离子色谱(IC),离子对反相色谱(RPIPC)。RPIP-HPLC是广泛使用的一种简单、灵活、灵敏的分离铬化合物的方法。尽管在这一领域拥有大量文献,但尚未建立充分有效的方法,尤其是关于形态分析的可追溯性和不确定度测量的论证。本研究的目的是使用RPIP-HPLC-ICP-MS测定饮用水中Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(Ⅵ),并对分析程序进行详细的验证。
1 材料与方法
1.1 仪器设备
ICP-MS:7900a型(USA,Agilent);HPLC:1220型(USA,Agilent)。色谱柱:Perkin Elmer C8(3.3 mm,3 μm);柱温25 ℃;进样体积50 μL;流速1.2 mL/min;流动相0.8 mmol/L TBAH,0.6 mmol/L EDTA,pH=6.9;洗脱程序为等度洗脱;总进样时间3 min。质谱条件RF 功率1 050 W;采样深度7.8 mm;冷却气流量(Ar)13 L/min;等离子体气流量(Ar)15 L/min;雾化气流量(Ar)0.88 L/min;辅助气流量(Ar)1.2 L/min;样品提升速率0.8 mL/min;采集时间750 s;积分时间1 s;监测质量数(m/z+)为52Cr+;采样锥和截取锥为Ni。
1.2 試剂材料
Cr(Ⅵ)标准储备溶液1 000 mg/L,NSI;Cr(Ⅲ)标准储备溶液1 000 mg/L,NSI;四丁基氢氧化铵(TBAH,美国Sigma-Aldrich 公司);乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA),分析纯;硝酸,优级纯;甲醇,优级纯。
1.3 样品处理
样品收集在100 mL聚乙烯瓶中,并立即冻结,在分析前除霜。样品经0.2 μm再生纤维素滤膜过滤。样品与流动相按体积比3∶1稀释,保存在玻璃瓶中,室温下1 h左右,形成(CrEDTA)-复合物。
2 结果与分析
2.1 线性范围
用10 μg/L的标准溶液配置工作曲线(n=7),确定Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(Ⅵ)的保留时间。通过分析极端浓度分析物的方差,确定工作曲线范围,并根据文献计算F值[5]。在本研究中,F值估计铬元素校准曲线的浓度限值为0.3、10.0 μg/L。可以得出结论,计算结果的方差在统计学上无显著差异。因此,校准曲线的选择是正确的。制备7个浓度水平(0.3、1.0、2.0、3.0、5.0、7.5、10.0 μg/L)的点分别得到铬元素的校准曲线,Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(Ⅵ)的相关系数接近1(r=0.999 9)。Cr(Ⅵ)的灵敏度高于Cr(Ⅲ)。
2.2 检出限和定量限
检出限(LOD)定义为可以可靠测量的最低浓度。这个值是由空白样品-空白测定方法信号的标准偏差的3倍计算出来的[6-8]。在本研究中,使用了以下3种方法测定LOD:①改进的空白测定方法。基于对可定量分析的空白样本的测定:LOD=3 S。其中S表示铬元素浓度为的0.5 μg/L时10个独立测量值的标准偏差(n=3)[5,9]。②图解法。基于3个标准溶液的标准偏差得到,根据公式LOD=3 S0(S0表示截距)计算Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(VI)(n=6)浓度为0.3、0.4、0.5 μg/L时的标准偏差。③线性回归方法。基于信号的标准偏差和校准曲线的斜率(标准偏差/斜率比)计算:LOD=3.3 S/b。其中,S表示表示信号的标准偏差(根据校准曲线估计),b为校准曲线的斜率[5,10]。定量限(LOQ)是分析物定量测定的最低浓度,可用精度和准确度的可接受水平确定。在本研究中,计算为3倍LOD。采用HPLC-ICP-MS法,根据改进的空白测定方法Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(Ⅵ)的LOD分别为0.094、0.100 μg/L[Cr(Ⅲ)的LOQ为0.28 μg/L,Cr(Ⅵ)为0.30 μg/L]。因为在m/z+为52时,铬元素的LOD值为背景标准偏差的3倍(表1)。因此,得到的结果易于与其他比较。
2.3 精密度
精密度在重现性和中间精密度条件下确定,并通过分析加入了2 μg/L铬元素标准溶液的饮用水进行评估。重现性和中间精密度表示为变异系数(CV)。同一操作者在短时间内使用相同的方法和设备测定重现性,在同一天重复测量上述水样10次。对于Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(Ⅵ),得到的结果分别为1.5%和1.6%。所得结果对应于先前提出的值。
同一操作者在较长时间内用相同方法获得的结果评估中间精密度,连续3 d从相同的加标饮用水样品中进行测定。得到变异系数Cr(Ⅲ)为3.4%、Cr(Ⅵ)为3.5%,表明中间精密度良好。
2.4 准确度
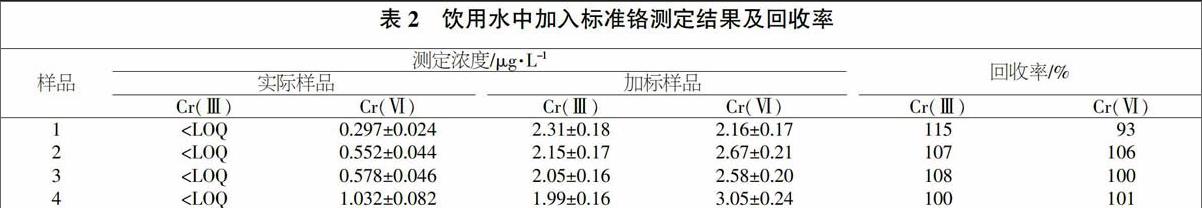
评价方法准确度最常用的方式是使用特定标准物质。本研究中,因为缺少适用于铬形态分析的标准物质[13,18-19],方法通过确定每个分析物的回收率来验证优化分析过程的效率。将2种铬元素添加到浓度为2.0 μg/L的4种不同水体基质中,在饮用水加标溶液中进行的回收率结果见表2。可以看出,提出的方法可以检测水中存在的Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(Ⅵ),并且低于WHO提出的水中总铬含量。采集的样品中检测出铬元素的回收率在93%~115%之间。结果表明,Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(Ⅵ)的回收率在±10%之内。加标样品回收率在加标值±25%以内,则认为可接受。该标准由美国EPA方法6020A推荐用于ICP-MS的元素分析,并在本研究中得到确认。
3 结论
目前,铬的形态分析主要是在环境样品中进行。HPLC-ICP-MS法使饮用水中Cr(Ⅲ)和Cr(Ⅵ)的检测和量化快速、准确。采用改良的空白测定法测定LOD,并将所得结果与其他研究人员所得的值进行比较。在大部分铬形态研究文献中,LOD通常用最简单的方法计算,即背景的3倍标准偏差。每个元素的回归系数为0.999 9,从而证明了该方法的线性和重现性。对加标样品的定量分析表明,2种铬元素的回收率在93%~115%之间。
4 参考文献
[1] KOTAS′ J,STASICKA Z.Chromium occurrence in the environment and methods of its speciation[J].Environ Pollut,2000(107):263-283.
[2] METZE D,JAKUBOWSKI N,KLOCKOW D.Speciation of chromium[M]//CORNELIS R,CREWS H,CARUSO J,et al.Handbook of elemental spe-ciation II:Species in the environment,food,medicine and occupational health. New York:Wiley,2005.
[3] WROBEL K,CARUSO JA.Elemental and isotope ratio mass spectrometry [M]//GROSS M L,CAPRIOLI R M.The encyclopedia of mass spectrometry,Volume 5:elemental and isotope ratio mass spectrometry.Oxford:Elsevier,2010.
[4] EIDEN G,BARINAGA C J,KOPPENAAL D W[M]//GROSS ML,CAPRI-OLI RM.The encyclopedia of mass spectrometry,Volume 5:elemental and isotope ratio mass spectrometry. Oxford:Elsevier,2010.
[5] KONIECZKA P,NAMIES′NIK J.Quality assurance and quality control in the analytical chemical laboratory[M]//A practical approach. Boca Raton:Taylor & Francis Group,2009.
[6] KUO CY,JIANG SJ,SAHAYAM AC.Speciation of chromium and vanad-ium in environmental samples using HPLC-DRC-ICP-MS[J].J Anal At Spectrom,2007(22):636-641.
[7] CHANG Y L,JIANG S J.Determination of chromium species in water samples by liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma-dynamic reaction cell-mass spectrometry[J].J Anal At Spectrom,2001(16):858-862.
[8] NEUBAUER K,REUTER W,PERRONE P.Chromium speciation in water by HPLC/ICP-MS:Application Note[Z].Norwalk:Perkin Elmer,2003.
[9] EURACHEM GUIDE.The fitness for purpose of analytical methods:a laboratory guide to method validation and related topics[Z].Teddington:LGC,1998.
[10] GU¨RLEYU¨KH,WALLSCHLA¨GERD.Determination of chromium(III)and chromium(VI)using suppressed ion chromatography inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].J Anal At Spectrom,2001(16):926-930.
[11] XING L,BEAUCHEMIN D.Chromium speciation at trace level in potable water using hyphenated ion exchange chromatography and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with collision/reaction interface[J].J Anal At Spectrom,2010(25):1046-1055.
[12] International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. ICH Guideline Q2(R1):validation of analytical procedures:text and methodology[EB/OL].[2013-02-12].http://www.ich.org/.
[13] CHEN Z L,MEGHARAJ M,NAIDU R.Removal of interferences in the speciation of chromium using an octopole reaction system in ion chromatography with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Talanta,2007(73):948-952.
[14] WOLF R E,MORRISON J M,GOLDHABER M B.Simultaneous determi-nation of Cr(III)and Cr(VI)using reversed-phased ionpairing liquid chromatography with dynamic reaction cell inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].J Anal At Spectrom,2007(22):1051-1060.
[15] WANG HJ,DU XM,WANG M,et al.Using ion-pair reversed-phase HPLC ICP-MS to simultaneously determine Cr(III)and Cr(VI)in urine of chromate workers[J].Talanta,2010(81):1856-1860.
[16] VANHAECKE F,SAVERWYNS S,DE WANNEMACKER G,et al.Comparison of the application of higher mass resolution and cool plasma conditions to avoid spectral interferences in Cr(III)/Cr(VI)speciation by means of high-performance liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Anal Chim Acta,2000(419):55-64.
[17] SE′BY F,CHARLES S,GAGEAN M,et al.Chromium speciation by hy-phenation of high-performance liquid chromatography to inductively coupled plasma-massspectrometry:study of the influence of interfering ions[J].J Anal At Spectrom,2003(18):1386-1390.
[18] XIE Q,KERRICH R,IRVING E,et al.Determination of five arsenic sp-ecies in aqueous samples by HPLC coupled with a hexapole collision cell ICP-MS[J].J Anal At Spectrom,2002(17):1037-1041.
[19] CASTILLO A,ROIG-NAVARRO A F,POZO O J.Capabilities of microbore columns coupled to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in speciation of arsenic and selenium[J].J Chromatogr A,2008(1202):132-137.
