湖北十堰市核桃优株选择
2018-01-15陈春芳赵雪姣张琳姚圣典林玉良刘乐平吴楚
陈春芳 赵雪姣 张琳 姚圣典 林玉良 刘乐平 吴楚
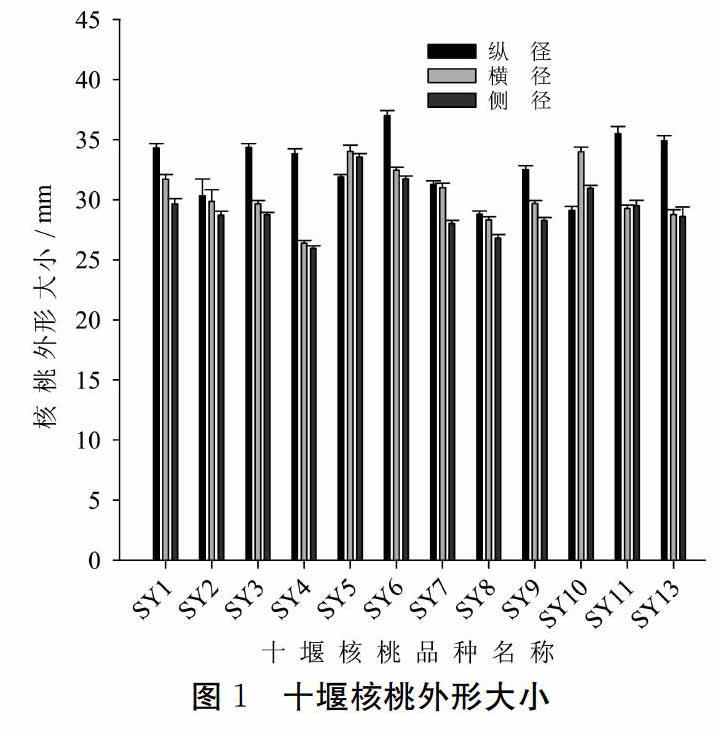
摘 要: 为综合评判湖北省十堰市核桃坚果品质的优劣,为十堰核桃育种筛选打下基础。在野外调查的基础上,收集了12个十堰核桃品种,对其坚果外形特征(纵径、横径和侧径)、单果重以及主要营养成分进行了分析。结果表明,十堰3号外形一致性程度较差,十堰1号的给人们感觉良好。十堰10号的平均单果重最大,达到11.82 g;十堰7号出仁率最高,高达58.01%,与其它十堰核桃的出仁率差异显著;十堰5号可溶性糖含量最高达到4.04%;十堰3号的可溶性蛋白含量最高达到97.05 mg/g;十堰13号总蛋白含量最高达到232.67 g/kg;十堰3号粗脂肪含量最高达到77.76%。根据这些分析结果,可以得出初步结论:十堰3号可以用于核桃油的加工;十堰7号可以用于核仁加工;十堰10号可以用于干果生产。
关键词: 核桃;品质分析;优株选择;十堰市
中图分类号: S794.9 文献标识码: A 文章编号: 1004-3020(2018)05-0015-06
Analyses on Morphological Traits and Main Nutrients of Walnut Fruits in Shiyan, Hubei
Chen Chunfang (1) Zhao Xuejiao (2) Zhang lin (3) Yao Sendian (4) Lin Yuliang (5) Liu Leping (6) Wu Chu (2)
(1.Hubei Academy of Forestry Wuhan 430075;
2.Yangtze University Jingzhou 434023;
[JP3]3.Institute of Forestry Research of Shiyan Shiyan 442000;
4.Institute of Forestry Research of Xingsan Yichang 443700;
5.Forestry Bureau of Danjiangkou Shiyan 442700 ; 6. Pengchang Forest Farm Jingmen 434000)
Abstract: In order to select the best local walnut varieties in Shiyan, Hubei province andincreasing the incomes of local walnut producers and improving market completion ability, twelve walnut varieties were collected based on the field investigation in Shiyan and their morphological traits and main nutrients were analyzed. These results showed that the single fruit weight of Shiyan No. 10 was the greatest (11.82 g), and Shiyan No. 7 had the highest kernel ratio of 58.01%, and Shiyan No. 5 had the highest level of soluble sugars (4.04%). Shiyan No.3 had the highest content of soluble proteins (97.05 mg/g), and the highest level of total proteins occurred in Shiyan No. 13 (232.67 g/kg), and Shiyan No. 3 had the greatest content of crude lipids (77.76%). It was concluded that the fruits of Shiyan No. 3 could be used for walnut oil production, and the fruits of Shiyan No. 7 could be used for kernel production, and the fruits of Shiyan No. 10 could be sold as nuts.
Key words: Juglans regia ; quality analysis;optimal plant; selection; Shiyan
1 前言
核桃 (Juglans regia)為胡桃科 (Juglandaceae)胡桃属 (Juglans) 落叶乔木。因其种仁营养丰富、风味独特和用途多样,为世界四大干果(核桃、扁桃、腰果、榛子)之首。核桃种仁营养价值高,含大量脂肪、蛋白质、多种维生素和微量元素,可生食,可榨油,其核仁含油量65.1%~ 68.4%、油味清香,是高级食用油和高级工业用油,能有效防治人体胆固醇过高、高血压、糖尿病、肥胖症等疾病,具有很强的保健功能。正因为如此,世界各地大力发展核桃产业,同时对核桃的生理生态 [1-2]、品质 [3]、遗传 [4-7]以及核桃消费对人体健康状况的影响 [8-11]等方面进行深入的 研究。
自两千多年前核桃被引入中国,核桃受到人们的极大欢迎,亚热带和温带地区均有栽培。各地的气候和地理条件的差异使得中国核桃的种群结构和遗传特性发生了很大的变化 [12]。正基于此,在各种气候和土壤条件下,选择品质最优且抗性最强的核桃品种对于一个地区的核桃产业的发展具有至关重要的意义。
近十年来,湖北十堰市大力发展核桃产业。该地区所栽培的核桃品种均来自外地,因而出现了一些问题,如抗病性和授粉差。鉴于此,选择当地优良品种进行推广栽培,对于当地的核桃产业的良性发展具有重要意义。在走访调查的基础上,选择了12个核桃品种,对其果实的外在形态和核仁品质进行了分析,以期筛选出最优良的品种在当地进行推广栽培。
2 试验材料与方法
2.1 试验材料
经过数年的野外调查,在十堰市初步确定了12个核桃优株。于2015年9月获得各个优株的果实,取其中2 kg作为实验样品。
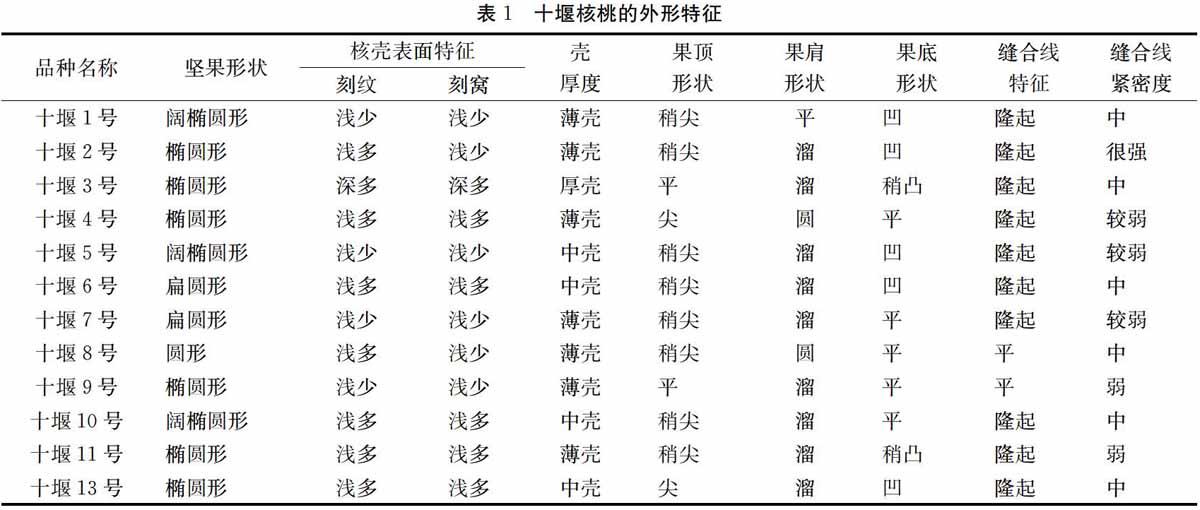
2.2 坚果外形特征及标准
坚果形状:椭圆形、阔椭圆形、圆形、异形。核仁皮色:黄白色、黄、白色。种仁饱满度:饱满、较饱满、不饱满。果顶形状:尖、稍尖、平。果尖形状:溜、圆、平、耸。果底形状:凸、稍凸、平、凹。缝合线特征:隆起、平、凹。核壳厚度:露仁、纸皮(0.1~ 0.9 mm)、薄壳(1.0~1.5 mm)、中壳 (1.6~2.0 mm)、厚壳(>2.0 mm)。内褶壁:退化、革质、骨质。隔膜:膜质、革质、骨质。种仁味感:香、甜、涩。
2.3 坚果主要物理指标及测定方法
单果重测定:随机抽取30个样果,用感量为1/1000的电子天平单个称重,取平均值。果径:随机抽取30个样果,用数显游标卡尺(广陆,GLA13S)测定其纵径、横径、侧径。出仁率:随机取40个样果进行编号,分别取仁,称重,计算出仁率,取平均值。取仁难易度:随机抽取30个样果,将核桃砸开取仁,若内褶壁退化,能取整仁的为取仁极易;若内褶壁不发达,能取半仁的为取仁容易;若内褶壁发达、能取1/4的为取仁较难。
2.4 核仁主要成分的测定
核仁脂肪含量测定:用索氏抽提法测定,采用国家标准(GB/T 14772-2008)。核仁蛋白质含量测定:用凯氏定氮法测定,采用国家标准 (GB 5009.5-2010)。核仁可溶性糖的测定:采用蒽酮法比色法,核仁可溶性蛋白质含量测定 [13]。
2.5 数据處理
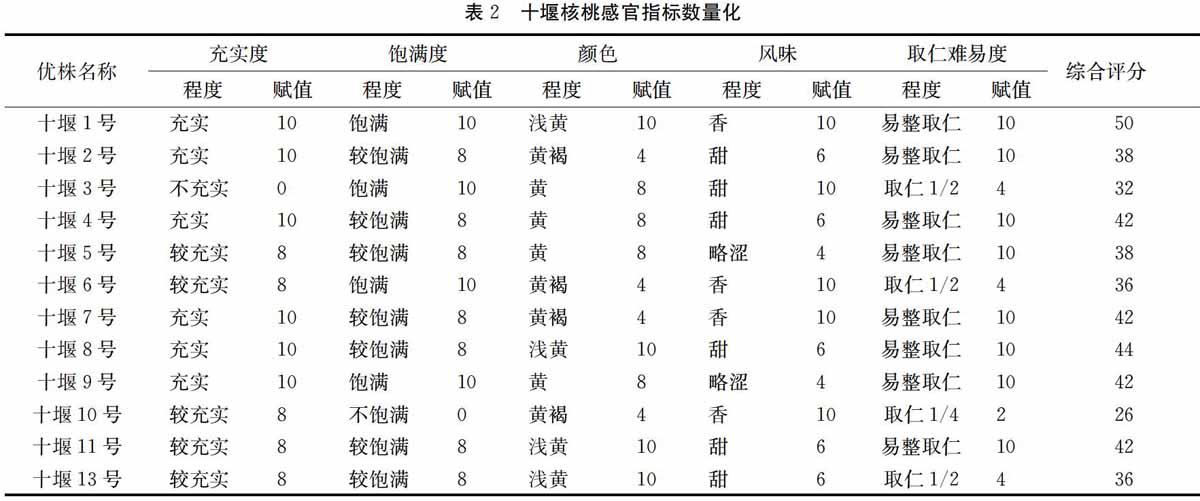
采用赋值法,将核仁充实度等感官指标数量化(见表2),采用SPSS 17.0统计软件,对坚果横径、纵径等9个数量指标进行统计分析,分析各核桃品种之间各个参数的差异显著性( P <0.05)。
参 考 文 献
[1]Ameglio T, Cochard H, Ewers FW. Stem diameter variations and cold hardiness in walnut trees. J Exp Bot[J],2001(52):3135-2142.
[2]Solar A, Colaric M, Usenik V, Stampar F. 2006. Seasonal variations of selected flavonoids, phenolic acids and quinones in annual shoots of common walnut ( Juglans regia L.). Plant Science, 170:453-461.
[3]Cag larir mak N. Biochemical and physical properties of some walnut genotypes ( Juglans regia L.). Food[J], 2003(47):28-32.
[4]Karimi R, Ershadi A, Vahdati K, Woeste K. Molecular characterization of Persian walnut populations in Iran with microsatellites markers. J Am Soc Hortic Sci[J], 2010(45):1403-1406.
[5]Ma Q, Zhang J, Pei D. Genetic analysis of walnut cultivars in China using fluorescent amplified fragment length polymorphism. J Amer Soc Hort Sci[J], 2011,136(6):422-428.
[6]Pollegioni P, Woeste K, Olimpieri I, Marandola D, Cannata F, Malvolti ME. Long term human impacts on genetic structure of Italian walnut inferred by SSR markers. Tree Genetics Genomes[J], 2011(7):707-723.
[7]Pollegioni P, Woeste KE, Chiocchini F, Olimpieri I, Tortolano V, Clark J, Hemery GE, Mapelli S, Malvolti ME. Landscape genetics of Persian walnut ( L.) across its Asian range. Tree Genetics & Genomes[J],2014(2):14-16.
[8]Feldman EB. The scientific evidence for a beneficial health relationship between walnuts and coronary heart disease. J Nutr[J], 2002(132):1062-1101.
[9]Spaccarotella KJ, Kris-Etherton PM, Stone WL, et al. The effect of walnut intake on factors related to prostate and vascular health in older men. Nutr J[J], 2008(7):13.
[10]Banel D, Hu FB. Effects of walnut consumption on blood lipids and other cardiovascular risk factors: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr[J], 2009(90):56-63.
[11]Ma Y, Njik VY, Millet J, Dutta S, Doughty K, Treu JA, Katz DL. . Effects of walnut Consumption on endothelial function in type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care[J],2010 (33):227-232.
[12]Wang H, Pei D, Gu R,Wang B.Genetic diversity and structure of walnut populations in central and southwestern China revealed by microsatellite markers. J Hortic Sci[J], 2008 (133):197-203.
[13]王學奎.植物生理生化实验原理和技术(第二版)[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社,2011:190-192, 202-204.
