无线传感器网络中基于“k−覆盖问题”的多项式时间算法
2018-01-08王骐肖正安王怀兴
王骐,肖正安,王怀兴
无线传感器网络中基于“−覆盖问题”的多项式时间算法
王骐,肖正安,王怀兴
(湖北第二师范学院物理与机电工程学院,湖北 武汉 430205)

无线传感器网络;−覆盖问题;扩展圆盘;相邻分界线;多项式时间算法
1 引言

2 基于UDG的几何图形
2.1 问题的描述


图1 −违反值和−支持值示意
2.2 圆盘的扩展
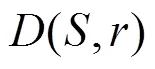

图2 大于的“2−违反”路径
同理可得定理2。
3 解决方案——多项式时间算法
3.1 子区域及其分界线
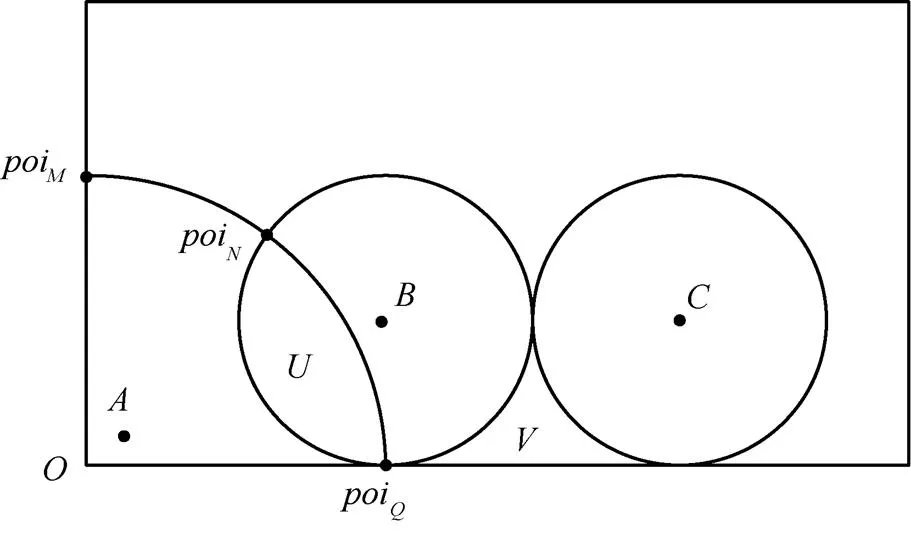
图3 子区域及其分界线


由于这段弧是由两个相邻子区域相交的公共部分,分属的两个子区域的覆盖度可能不相同,所以根据定义5来计算这段弧的覆盖度就会产生矛盾[11]。为此特做以下定义。

图4 内弧和外弧
定义7 (相邻分界线)如果两段分界线(内弧、外弧或边界线)具有公共点,那么称这两段分界线为相邻分界线。
根据定义7,由于同一段弧的内弧和外弧具有无限多个共同点,因此它们互为相邻弧。当且仅当两段分界线具有相同交点或切点时,它们互为相邻分界线,如图3所示。由于子区域可看成是由若干相邻分界线形成的,因此,这些分界线具有和子区域相同的覆盖度。
Procedure:/*计算所有的分界线,并且判定两段分界线是否为相邻分界线
input: 传感器节点集{1,2,…, s},圆半径
output: 分界线集{1,2,…, bor}
for1 to
计算disk和所有其他圆或边界线的交点或切点
for 圆周线上的每对相邻交点或切点
定义分界线bor
划分bor为内弧和外弧
for 平面边界线上的每对相邻交点或切点
定义分界线bor
/*计算每段分界线的覆盖度
for 每段分界线bor
switch(分界线类型)
casebor为边界线的一部分
选取点poi∈bor
计算点poi的范围内传感器节点数量
casebor为一段外弧
选取点poi∈bor
计算点poi的范围内传感器节点数量,不包括poi所属圆的中心节点
casebor为一段内弧
选取点poi∈bor
计算点poi的范围内传感器节点数量,包括poi所属圆的中心节点
/*判定两段分界线是否互为相邻分界线
set 所有分界线为非相邻分界线
for 每个交点或切点poi
ifpoi为bor和bor的端点
setbor和bor为相邻分界线
end
3.2 最差k−覆盖问题


input: 边界线集合{1,2,…,},∈,∈
output: 布尔变量结果值
if()≥或() ≥
= 0
return
取消所有分界线的标记
标记/*起始于
list=
tree=
while(非空)
从链表头选取分界线
从链表删除分界线
for相邻的每段分界线
if()
标记
在树上将作为的孩子
在链表尾增加
if被标记
= 1
return
else
= 0
return
end
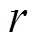
set/*设定搜索空间的上限值
set/*设定搜索空间的下限值
set/*设定迭代次数
for= 1 to
= (+)2
{1,2,…,}=() /*调用函数(,)计算所有的分界线

if= 1
=
else
end
上限值和下限值可根据平面维度以及传感器节点的密度来设定。每次迭代将使搜索空间减半,例如,如果搜索空间(||)的值为1 000,经过10次迭代可得到结果,且误差小于1。一般情况下,10~20次迭代可足以确保结果的准确性[15]。
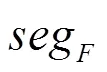
3.3 最佳k−覆盖问题
4 仿真结果

图5 k−违反的最大值
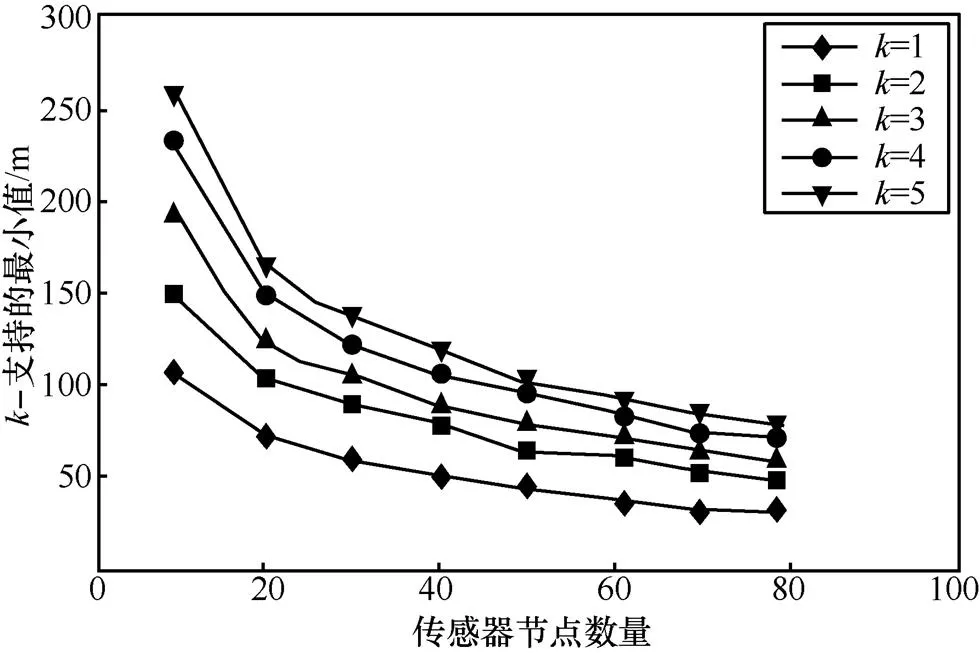
图6 k−支持的最小值
对比图5和图6,可得到以下结论。
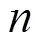
• 当传感器节点数量相同时,−支持的最小值要远大于−违反的最大值。可以证明,任何情况下,−支持的最小值均不会小于−违反的最大值。
5 结束语
本文分别阐述了最差和最佳−覆盖问题,并基于扩展圆盘的几何图形提出了一系列的定义和定理,将−覆盖问题转化成了寻找相邻分界线的问题,提出了解决此问题的多项式时间算法。

[1] MEGERIAN S, KOUSHANFAR F, POTKONJAK M, et al. Worst and best-case coverage in sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transaction on Mobile Computing, 2005, 4(1):84-92.
[2] 杨海雳, 赵静. 基于Voronoi图的无线传感器网络覆盖算法研究[J]. 信息通信, 2015(7):28-31.
YANG H L, ZHAO J. Research of coverage algorithm with Voronoi diagram for wireless sensor network [J]. Information & Communications, 2015(7):28-31.
[3] 王成, 樊建席, 王仁喜, 等. 基于Voronoi图的无线传感器网络K覆盖算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2012, 38(4):84-87.
WANG C, FAN J X, WANG R X, et al. K coverage algorithm in wireless sensor network based on Voronoi diagram[J]. Computer Engineering, 2012, 38(4):84-87.
[4] 丁旭, 吴晓蓓, 黄成. 基于改进粒子群算法和特征点集的无线传感器网络覆盖问题研究[J]. 电子学报, 2016, 44(4): 967-973.
DING X, WU X P, HUANG C. Area coverage problem based on improved PSO algorithm and feature point set in wireless sensor networks[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2016, 44(4) : 967-973.
[5] 孙泽宇, 伍卫国, 王换招, 等. 无线传感器网络基于参数可调增强型覆盖控制算法[J]. 电子学报, 2015, 43 (3):466-474.
SUN Z Y, WU W G, WANG H Z, et al. An enhanced coverage control algorithm for wireless sensor networks based on adjustable parameters[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2015, 43 (3): 466-474.
[6] 刘志强, 沈廼桐, 毛强, 等. 无线传感器网络动态覆盖的CVT算法[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2015(6):115-118.
LIU Z Q, SHEN N T, MAO Q, et al. A dynamic coverage algorithm for wireless sensor networks based on CVT[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2015(6):115-118.
[7] 高洁, 吴延红, 白建侠, 等. 无线传感器网络最小覆盖能量优化算法[J]. 传感技术学报, 2016, 29(9):1435-1440.
GAO J, WU Y H, BAI J X, et al. The minimum coverage energy optimization algorithms in wireless sensor network[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors And Actuators, 2016, 29(9):1435-1440.
[8] LIU X Y, WU K L, ZHU Y, et al. Mobility increases the surface coverage of distributed sensor networks[J]. Computer Networks the International Journal of Computer & Telecommunications Networking, 2013, 57(11):2348-2363.
[9] TAN L, CHENG Y C, YANG M H, et al. Priority coverage algorithm and performance simulation for node deployment in directional sensor networks[J]. Sensor Letters, 2014, 12(2): 275-280.
[10] 鲁晓波, 阮福, 王立中. 无线传感器网络覆盖优化策略[J]. 内蒙古师大学报(自然汉文版), 2016, 45(4):480-483.
LU X B, RUAN F, WANG L Z. Coverage optimization strategy of wireless sensor networks based on improved artificial fish swarm algorithm[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 45(4):480-483.
[11] 王兴伟, 蔡凌, 黄敏, 等. 基于空间镶嵌的三维无线传感器网络覆盖机制[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2014, 35(3): 433-436.
WANG X W, CAI L, HUANG M, et al. Spatial tessellation basedcoverage scheme for 3D wireless sensor network[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2014, 35(3):433-436.
[12] MINI S, UDGATA S K, SABAT S L. Sensor deployment and scheduling for target coverage problem in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2014, 14(3):636-644.
[13] MAHBOUBI H, MOEZZI K, AGHDAM A G, et al. Distributed deployment algorithms for improved coverage in a network of wireless mobile sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 10(1):163-174.
[14] ZHANG Y, SUN X, WANG B. Efficient algorithm for-barrier coverage based on integer linear programming[J]. China Communications, 2016, 13(7):16-23.
[15] BAN D S, WEN J, JIANG J, et al. Constructing-barrier coverage in mobile wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Software, 2011, 22(9):2089-2103.
Polynomial time algorithm for solving-coverageproblem in wireless sensor networks
WANG Qi, XIAO Zheng’an, WANG Huaixing
School of Physics and Electromechanical Engineering, Hubei University of Education, Wuhan 430205, China
How to solve the-coverage problem, which was divided into worst-case and best-case, inside the two-dimensional target area in wireless sensor networks was explored, and a polynomial time algorithm for solving this problem was put forward. In this algorithm, a series of definitions and theorems were proposed based on the geometric graph of growing disks, and the-coverage problem was transformed into one of finding a series of adjacent borders. The simulation results show that the algorithm could compute the optimal-breach path and-support path in polynomial time, so as to avoid or select the network coverage reasonably.
wireless sensor network,-coverage problem, growing disk, adjacent border, polynomial time algorithm
TN918.91
A
10.11959/j.issn.1000−0801.2017287
2017−07−20;
2017−09−30
湖北省高等学校优秀中青年科技创新团队计划项目(No.T201417)
Hubei Provincial Department of Education Research Program (No.T201417)
王骐(1970−),男,博士,湖北第二师范学院物理与机电工程学院副教授,主要研究方向为无线传感器网络安全、嵌入式系统应用。

肖正安(1974−),男,湖北第二师范学院物理与机电工程学院讲师,主要研究方向为图像数字信号处理。
王怀兴(1977−),男,湖北第二师范学院物理与机电工程学院副教授,主要研究方向为嵌入系统应用。
