中国僵尸企业的识别及预警研究
2017-11-04孙莹崔静
孙 莹 崔 静
(中国海洋大学管理学院,山东青岛 266100)
10.3876/j.issn.1671-4970.2017.05.014
2017-04-11
国家社会科学基金青年项目(17CJY004、16CJY007);山东省社会科学规划研究项目青年项目(15DGLJ06)
孙莹(1983—),女,山东莱芜人,讲师,博士,从事营运资金管理研究。
中国僵尸企业的识别及预警研究
孙 莹 崔 静
(中国海洋大学管理学院,山东青岛 266100)
僵尸企业近年来成为各界关注的焦点,学术界关于僵尸企业的认定并无共识。识别出僵尸企业是处理僵尸企业问题的第一步,提早预警、防止僵尸企业出现是解决这一问题的根本之策。结合中国国情,将银行补贴和政府补助同时考虑在内,并基于僵尸企业长时间逐步演化的特点,提出符合中国现实的僵尸企业识别方法,在此基础上从财务视角建立了僵尸企业的预警模型。通过3年的预警模型可以看出,现金负债总额比、现金流动负债比、总资产净利润率、流动资产净利润率、扣除非经常性损益后的每股净利润指标具有稳定的预测效果,能够有效实现僵尸企业的预警,为企业提前发现危机,及时采取措施提供了理论依据。
僵尸企业;识别方法;财务预警
一、引 言
当前,中国经济步入新常态,传统经济体制遗留的问题在转轨时期凸显出来,僵尸企业大量涌现。据统计,2012—2015年,A股所有上市公司中有265家上市公司连续3年扣除非经常损益后归属母公司的净利润为负。需要关注的是,2014年末,上述265家上市公司仅利息净支出达446.79亿元,较去年同期427.01亿元继续增长。这些企业只有依赖银行贷款和政府补助才能继续存活。僵尸企业拉低了资源配置效率、挤占了正常企业的发展机会,容易引发系统性金融风险,已成为影响经济发展的痼疾,中央多次召开会议郑重提出要清理僵尸企业,清理僵尸企业成为供给侧改革的首要任务。
僵尸企业最早由Kane提出,他借用了恐怖电影中行尸走肉、处于濒死状态且传染性强的僵尸形象用于解析日本20世纪80年代和90年代金融危机[1]。Ridzak给出的定义是:如果企业没有获得银行的继续贷款就会违约,这种企业就是僵尸企业[2]。近几年,国内对僵尸企业的研究日益增多,但就其界定并不存在统一认识。朱鹤等认为僵尸企业是指那些负债累累、生产效率低下、利润率低,但由于获得银行或政府的补贴而没有破产的企业[3];朱舜楠认为,僵尸企业是那些丧失竞争能力和盈利能力,只能依靠政府补助和银行贷款存活,持续亏损3年以上且不符合结构性调整的企业[4];邹蕴涵认为,僵尸企业是指那些由于效率低下而依赖金融机构或政府资助而存活的企业,其最突出的特点是企业形式还存在,却不能产生效益[5];张栋等认为,僵尸企业是指那些无望恢复生气[6],但由于获得放贷者或政府的支持而免于倒闭的负债企业[7]。僵尸企业的识别方法主要是定性识别,量化识别方法仍处于研究阶段。常用的CHK量化识别方法未考虑政府因素,存在很多局限,因此,建立一个适用我国僵尸企业识别方法是摆在当前的迫切任务。虽然僵尸企业问题成为学术界的热门话题,但当前关于僵尸企业的研究仅限于僵尸企业的界定、成因、影响与对策。如刘奎甫等对“僵尸企业”内涵界定、识别方法、形成原因、影响效应等相关问题进行了梳理,发现对“僵尸企业”的界定需要满足“陷入财务危机”和“债权人继续提供借贷”两个标准[8];栾甫贵等认为僵尸企业浪费了社会资源,加剧了产能过剩,阻碍了产业发展,恶化了信用环境,诱发了系统性风险[9];熊兵认为“僵尸企业”的形成主要有3方面的原因[10];程虹等从微观角度出发,对僵尸企业形成的自身微观因素进行实证研究,认为要从根本上清理僵尸企业还要激发产品质量创新的内生动力,加大技术创新,利用市场机制实现企业家精神的优胜劣汰[11];孙丽借鉴了日本僵尸企业的处置经验,并提出了适应于我国的僵尸企业处置方法[12]。而僵尸企业的识别只是第一步,如何从事后处理僵尸企业转为事前预防僵尸企业的出现及恶化是解决这一问题的根本。最早开始研究财务预警模型的是吴世农等,其运用判定分析方法建立企业破产预测模型[13]。吴世农等选取了70家ST公司和70家非ST公司,利用3种不同方法,分别建立了Fisher线性判定模型、多元线性回归模型和Logit模型[14]。在识别僵尸企业的基础上,分析僵尸企业的特征、研究其预警体系才是解决这一问题的根源与重点。笔者沿着“识别僵尸企业--分析僵尸企业的特征--建立僵尸企业预警体系”这一思路展开研究。
本文的创新之处在于:第一,立足于中国国情,从财务管理的视角出发,提出利用财务指标来定量识别僵尸企业的方法;第二,尝试将财务预警模型运用于僵尸企业,将僵尸企业与财务预警相结合,建立了Logistic僵尸企业预警模型,从根源防治僵尸企业的形成。
二、僵尸企业的界定与识别
1.僵尸企业界定
学术界关于僵尸企业的界定并未达成统一认识,各位学者从不同角度表达对僵尸企业的认识。陈静将经济学中的僵尸企业定义为资不抵债、到期无法偿还债务,靠金融机构的贷款存活的企业[15];Peek等认为僵尸企业是那些经济效率低下,无盈利能力,债台高筑、丧失活力、利润率小于零的企业[16];何帆等将僵尸企业定义为那些负债累累、生产效率低下、利润率低,但由于获得银行或政府补贴而没有破产的企业[17]。
综观可知,僵尸企业的界定紧紧围绕两个特征:一是生产经营困难,企业资不抵债或即将资不抵债、无法偿还到期债务,以致陷入财务危机;二是尽管生产经营困难、陷入财务危机,但由于获得银行或政府的资金支持并没有破产,而得以继续存活、僵而不死,这两个特征缺一不可。第一,陷入财务危机。僵尸企业与一般财务危机企业有根本不同,两者虽然都出现财务危机,但是僵尸企业能够获得利益相关者的补给、从外部获得持续资金支持维持经营,而且僵尸企业具有明显的长期性和依赖性,而一般出现经营困难的企业会通过调整实现财务状况的好转,或在经历亏损之后直接破产退出市场。第二,持续获得外部资金支持。外部资金来源是指银行贷款和政府补助,掩盖不良资产是银行心甘情愿向僵尸企业持续放款的动机。僵尸企业生产经营无法产生足够的现金流来偿还本息,存在破产风险,银行的不良贷款势必会增加,导致银行核心资本充足率无法满足《巴塞尔协议》规定的4%的标准,银行只能继续放款,不让僵尸企业破产,由此陷入恶性循环。在经济下行的压力下,政府面临就业率、GDP等压力,不允许僵尸企业破产,反而会激励银行给企业贷款,甚至直接给予企业政府补助、税收返还,源源不断地给企业输血。
基于上述分析,笔者将僵尸企业定义为因生产经营困难,导致资不抵债、陷入财务危机,依靠自身能力难以扭亏为盈,但能够持续获得外部资金来源而免于破产的企业。
2.僵尸企业识别
国内外关于僵尸企业的识别方法有显著差异。国外以日本为代表,秉持CHK方法为代表的“利息观”,此后又有学者在CHK方法基础上进行改进,加入盈利标准,但都是围绕银行给企业的优惠,并没有涉及政府因素。而我国国情与国外有很大差异,政府的干预是一个重要影响因素,僵尸企业可能只获得政府补助或银行补贴,也可能两者兼有,但同时满足两个条件的僵尸企业容易遗漏。“持续亏损观”也仅仅考虑了政府补助因素,未考虑银行补贴。
基于僵尸企业两个典型特征,对其的识别也紧紧围绕这两个特征。获得外部资金支持有两种途径:政府补助、持续获得银行借款。因此,僵尸企业的现状就存在3种模式:陷入财务危机+获得政府补助、陷入财务危机+持续获得银行借款、政府补助和银行借款同时获得。
其一,“陷入财务危机+获得政府补助”。衡量“陷入财务危机”用到的指标是扣除非经常性损益后的净利润,即扣除非经常性损益后的净利润小于0认为陷入了财务危机。为了从一个较长时间跨度上来审视僵尸企业,运用连续3年扣除非经常性损益后的净利润即连续3年扣除非经常性损益后的净利润小于0,就认定为其是僵尸企业。非经常性损益包括政府补助,因此不需单独界定。其二,“陷入财务危机+持续获得银行借款”。衡量银行补助用“当年借款余额大于去年”;来自银行借款则表现为负债的增加,采取“当年的借款余额大于去年”。但是仅仅用这一个条件容易将正处于发展上升期、需要大量融资的优秀企业包括在内,因此“陷入财务危机”这一条件就显得尤为重要,僵尸企业还必须满足“当年扣除非经常性损益后的净利润小于0”,这样可以将处于发展期、需要大量借款的优秀企业排除在外。

表1 僵尸企业识别方法

表2 僵尸企业结果统计表
详细计算方法见表1。笔者提出的识别僵尸企业的方法(简称综合法)满足连续3年扣除非经常性损益后净利润小于0,或者满足“当年借款余额大于去年,且当年扣除非经常性损益后的净利润小于0”的企业都被认定为僵尸企业。与现有文献相比,综合法有两个优势:第一,从一个长时间跨度来审视僵尸企业,将“一次性僵尸企业”排除在外;第二,国外学术界在研究僵尸企业时并没有考虑政府这一因素,而反观中国,政府在僵尸企业的形成中产生深刻影响,直接政府补助、税收返还等都是企业外部资金来源,基于中国国情应将政府因素考虑在内。
(1)数量分析
选取2007—2015年间非金融行业上市公司,全部数据来源于国泰安数据库。经处理后,2007—2015年上市公司样本数量(家)分别为1 617、1 671、1 817、2 167、2 398、2 525、2 683、2 868。
结果发现,2009—2015年运用综合法①综合法采用连续3年数据,因此综合法下僵尸企业数据从2009年开始。识别出来的僵尸企业数量分别为448家、339家、349家、254家、260家、236家和268家,并且发现用连续3年亏损方法识别出来的僵尸企业和有持续借贷方法识别出来的僵尸企业有近50%是重合的。为了对比结果,将3年连续亏损和持续借贷法的结果占比也列出,具体情况如表2和图1所示。

图1 僵尸企业数量趋势图
由表2和图1可以看出,无论是用亏损1年、连续3年亏损还是综合方法,识别出来的僵尸企业数量总体呈上升趋势,并且与宏观经济走势相吻合。笔者采用综合方法识别僵尸企业,2009年占比为14.75%、2010年减少为10.89%,随后又开始上涨,到2015年达到15.62%。可能原因是2008年金融危机爆发,僵尸企业数量增加,而2009年国家采取了一揽子刺激政策之后经济开始好转。但是,由于政策效果有延迟效应,在2012年呈现一个小低潮,僵尸企业数量占比最低为10.06%。2012年之后,随着经济步入新常态、经济增长放缓、国内需求不足,出口又受到2013年欧债危机等国际环境的影响而外需不振,僵尸企业数量又呈现增加趋势。
(2)行业分析
根据证监会2012年行业分类标准,对2015年非金融类上市公司中僵尸企业的数量按行业进行分类排序。为了对比分析结果,同时呈现出运用连续3年亏损法的行业排序结果(表3)。
由表3可知,僵尸企业行业分布有3点特征:第一,钢铁、有色金属大型设备制造业等产能过剩行业是僵尸企业的重灾区。综合法和连续3年亏损识别出的僵尸企业中,排名前4位的都是化学原料及化学制品制造业、计算机、通信和其他电子设备制造业、通用设备制造业、专用设备制造业。综合法识别出来的僵尸企业中有色金属冶炼及压延加工业、是金属矿物制品、黑色金属冶炼及压延加工业、煤炭开采和洗选业等产能过剩行业合计占比14.82%,超过排名第1位的化学原料及化学制品制造业。第二,传统的劳动密集型行业,如纺织、造纸、大型制造业等僵尸企业数量也很多,这些劳动密集型企业提供了大量的就业机会、承担着缓解就业矛盾的压力,但这也从侧面佐证了政府保就业是造成僵尸企业的重要原因。第三,僵尸企业涉及行业范围广、结构复杂,不仅传统行业出现僵尸企业,有些朝阳行业如计算机、通信和其他电子设备制造业、房地产业等也出现不少僵尸企业。

表3 2015年僵尸企业排名前16的行业

表4 变量定义表
三、僵尸企业的财务预警模型研究
1.研究样本选取
通过识别发现,2015年共448家僵尸企业,由于僵尸企业形成有一个过程,因此基于僵尸企业t-1年、t-2年、t-3年的财务数据建立3个财务预警模型。在僵尸企业配对样本的选择上,采用随机选取法。非僵尸企业是既不满足连续3年亏损,也不满足当年外部融资跟去年比有所增加且当年扣除非经常性损益之后的净利润小于零的企业。结果表明,共669家企业符合上述条件,作为配对组的候选样本。
剔除缺失值和财务异常值后,共选取324对共648家企业,并把324对僵尸企业和配对的非僵尸企业分为两组,274对共548家用于模型的建立,另外50对共100家用作检验样本,检验模型的预测效果。
2.预警变量选取与检验
僵尸企业出现的根本原因在于其自身不能产生足够的现金流,因此笔者从现金流视角选取全面反映偿债能力、盈利能力、营运能力、发展能力4个方面的财务指标。但与财务危机企业选取的现金流量指标稍有不同,考虑到政府补助和扣除非经常性损益后的净利润,因此在财务指标计算时要扣除这两个因素。按照上述方法,为全面反映僵尸企业的财务特征,从偿债能力、盈利能力、获现能力、营运能力、发展能力5个方面选取了14个指标(表4)。
对自变量的正态分布检验采用Kolmogorov-Smirnov检验(以下简称为K-S 检验),来验证变量是否符合正态分布。僵尸企业前3年样本数据正态分布检验结果显示,2014年、2013年和2012年14个解释变量的P值均小于0.05,拒绝原假设,即14个财务分析指标均不服从正态分布,这与大多数学者的研究结果一致。因此,使用非参数检验的方法。选取独立样本的Mann-Whitney U(曼-惠特尼U检验),僵尸企业前3年的U检验结果显示,2014年14个解释变量概率P值均小于0.05,拒绝原假设,两组指标存在显著性差异,通过检验;2013年14个解释变量概率P值均小于0.05,拒绝原假设,两组指标存在显著性差异,通过检验;2012年解释变量X1现金流利息保障倍数和X12营运指数的概率P值分别为0.143和0.238,大于0.05,接受原假设,说明X1(现金流利息保障倍数)和X12(营运指数)两个指标不存在显著性差异,在回归分析时剔除,其他解释变量概率P值均小于0.05,拒绝原假设,两组指标存在显著性差异,通过检验。
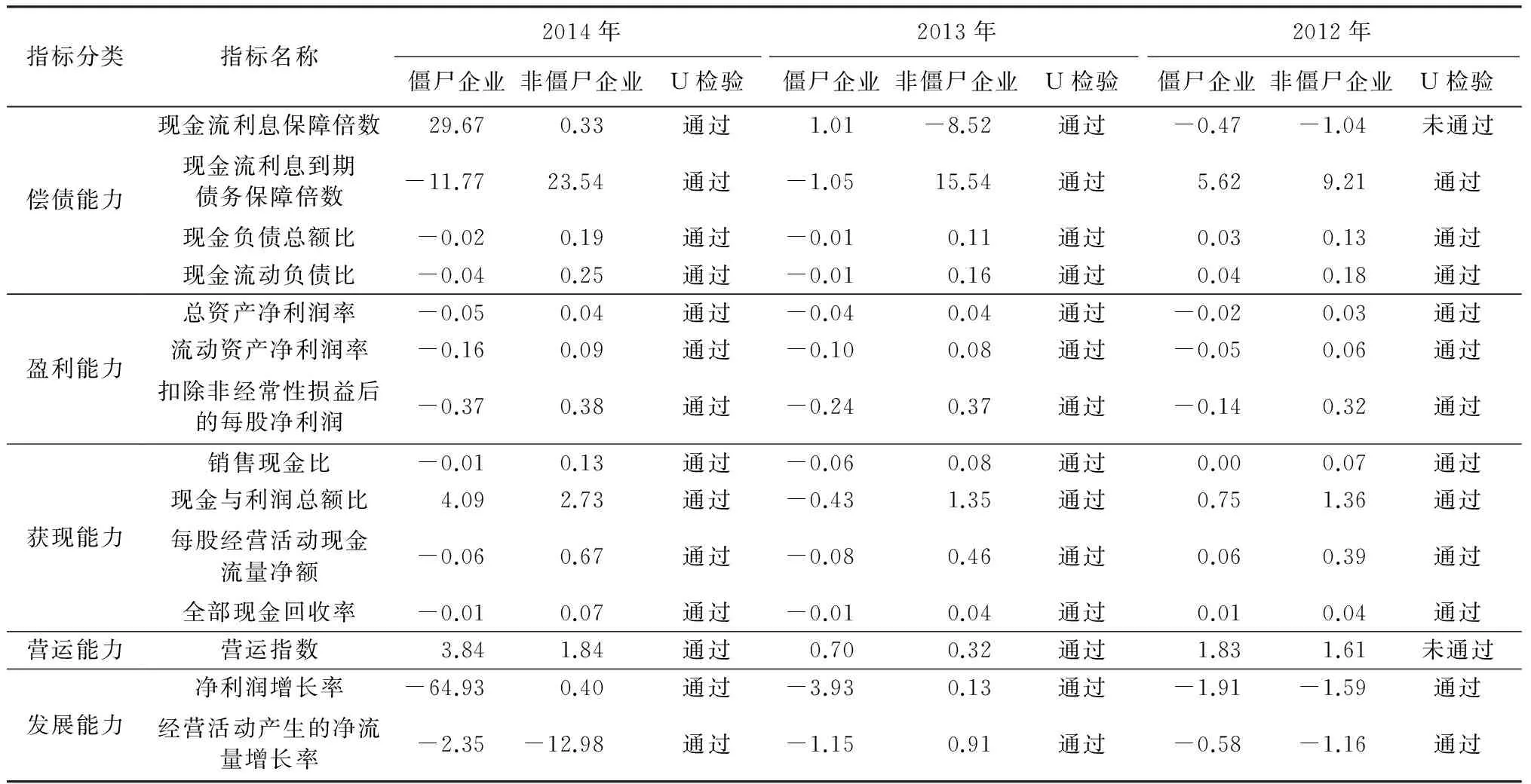
表5 均值比较表
3.僵尸企业财务特征分析
根据僵尸企业样本和非僵尸企业样本,分别计算构建预警模型中14个财务指标的均值和衡量均值显著性差异的U检验,来研究僵尸企业的财务特征。对僵尸企业的财务特征进行分析能深入剖析僵尸企业的财务现状。详细财务指标均值比较见表5。
(1)偿债能力特征
由表5可知,现金流利息保障倍数和营运能力指标在2012年未通过显著性检验,均值比较结果也没有规律性,因此这两个指标不具有代表性。从偿债能力看,除了现金流利息保障倍数外,其他反映偿债能力的3个指标均值均显著低于非僵尸企业。具体来看,2012—2014年僵尸企业现金流利息到期债务保障倍数分别为5.62、-1.05、-11.77,非僵尸企业分别为9.21、15.45、23.54,3年均明显低于非僵尸企业;2012—2014年僵尸企业现金负债总额比分别为0.03、0.01、-0.02,非僵尸企业现金负债总额比分别为0.13、0.11、0.19,3年均明显低于非僵尸企业;2012—2014僵尸企业现金流动负债比分别为0.04、-0.01、-0.04,非僵尸企业现金流动负债比分别为0.18、0.16、0.25,3年均明显低于非僵尸企业。由此可知,僵尸企业的偿债能力比非僵尸企业的偿债能力差。
(2)盈利能力特征
从盈利能力来看,2012—2014年僵尸企业反映盈利能力的3个指标均值均为负数,非僵尸企业均值均为正数,僵尸企业处于亏损状态。具体来看,2012—2014年僵尸企业总资产净利润率分别为-0.02、-0.04、-0.05,非僵尸企业总资产净利润率分别为0.03、0.04、0.04,均明显小于非僵尸企业;2012—2014年僵尸企业流动资产净利润率分别为-0.05、-0.10、-0.16,非僵尸企业流动资产净利润率分别为0.06、0.08、0.09,均明显小于非僵尸企业;2012—2014年僵尸企业扣除非经常性损益后的每股净利润分别为-0.14、-0.24、-0.37,非僵尸企业扣除非经常性损益后的每股净利润分别为0.32、0.37、0.38,均明显小于非僵尸企业。僵尸企业盈利能力明显比非僵尸企业差,僵尸企业处于亏损状态。
(3)获现能力特征
从获现能力来看,2012—2014年僵尸企业销售现金比分别为0.00、-0.06、-0.01,非僵尸企业分别为0.07、0.08、0.13,均小于非僵尸企业;2014僵尸企业现金与利润总额比为4.09,大于非僵尸企业2.73,但是2013和2012年僵尸企业现金与利润总额比均小于非僵尸企业;2012—2014年僵尸企业的每股经营活动现金流量净额和全部现金回收率指标也均小于非僵尸企业。僵尸企业的获现能力比较差,总体来看不如非僵尸企业。
(4)发展能力特征
从发展能力来看,僵尸企业的净利润增长率小于非僵尸企业,具体来看,2012—2014年僵尸企业利润增长率分别为-1.91、-3.93、-64.93,非僵尸企业利润增长率分别为-1.59、0.13、0.40,均小于非僵尸企业;2013年僵尸企业经营活动产生的净流量增长率为-1.15,小于非僵尸企业的0.91,但2012年和2014年僵尸企业经营活动产生的净流量增长率大于非僵尸企业经营活动产生的净流量增长率,这可能是由于行业差异。总体来看,僵尸企业的发展能力还是要比非僵尸企业差。
通过以上分析发现,僵尸企业在盈利能力和偿债能力指标方面明显比非僵尸企业差,僵尸企业处于亏损境地、无法偿还到期债务,为此财务预警中应重点关注盈利能力和偿债能力方面指标;其他方面,虽有个别指标在个别年份出现反向趋势,但总体上看僵尸企业的获现能力和发展能力较差。
4.僵尸企业的Logistic预警模型的构建
僵尸企业的形成不是一蹴而就的,有着较长的形成过程,因此选取僵尸企业前3年的数据分别建立僵尸企业形成前3年的Logistic预警模型,以从较长时间跨度来研究僵尸企业预警。选取0.5作为判别僵尸企业的临界点,概率P大于0.5是僵尸企业,小于0.5是健康企业。
(1)因子分析
通过显著性检验,2012年12个解释变量通过了显著性检验,2013年和2014年14个指标均通过显著性检验。通过相关检验可知,14个变量之间存在很高线性相关性,由于Logistic回归模型假设变量之间不能存在共线性,因此采用因子分析法。因子分析不仅能够解决变量之间的线性相关性,并且能够降维,将原来的14个解释变量抽象出其共同特征,综合成少数几个因子,代替原有变量参与模型的建立,大幅度减少运算分析过程。KMO 检验和 Bartlett 球形检验结果得出:KMO 值为 0.713,Bartlett 球形检验显著性为0.000,非常显著。通过主成分分析提取了7个因子,累计贡献率为83.867%。
因子载荷矩阵结果显示:因子1在全部现金回收率、现金负债总额比、现金流动负债比和每股经营活动产生的现金流量净额的载荷远远高于其他指标,现金负债总额比、现金流动负债比代表了企业的偿债能力,全部现金回收率、每股经营活动产生的现金流量净额代表企业的获现能力。因子2在总资产净利润率、流动资产净利润率、扣除非经常性损益后的每股净利润3个指标载荷最高,因子2代表企业的盈利能力。因子3在现金流利息保障倍数、现金流利息到期债务保障倍数上载荷远高于其他指标,因子3也代表企业的偿债能力。因子4在净利润增长率指标高达.957,因子4代表企业的发展能力。因子5在营运指数上的载荷高达.951,因子5代表企业营运能力。因子6在现金与利润总额比载荷达0.999,与因子1中全部现金回收率、每股经营活动产生的现金流量净额指标一样代表企业的获现能力。因子7在经营活动现金净流量增长率指标上的载荷高达0.998,代表企业发展能力。
根据因子得分系数矩阵(表6)可以得到主成分(用F表示)的线性表达式。
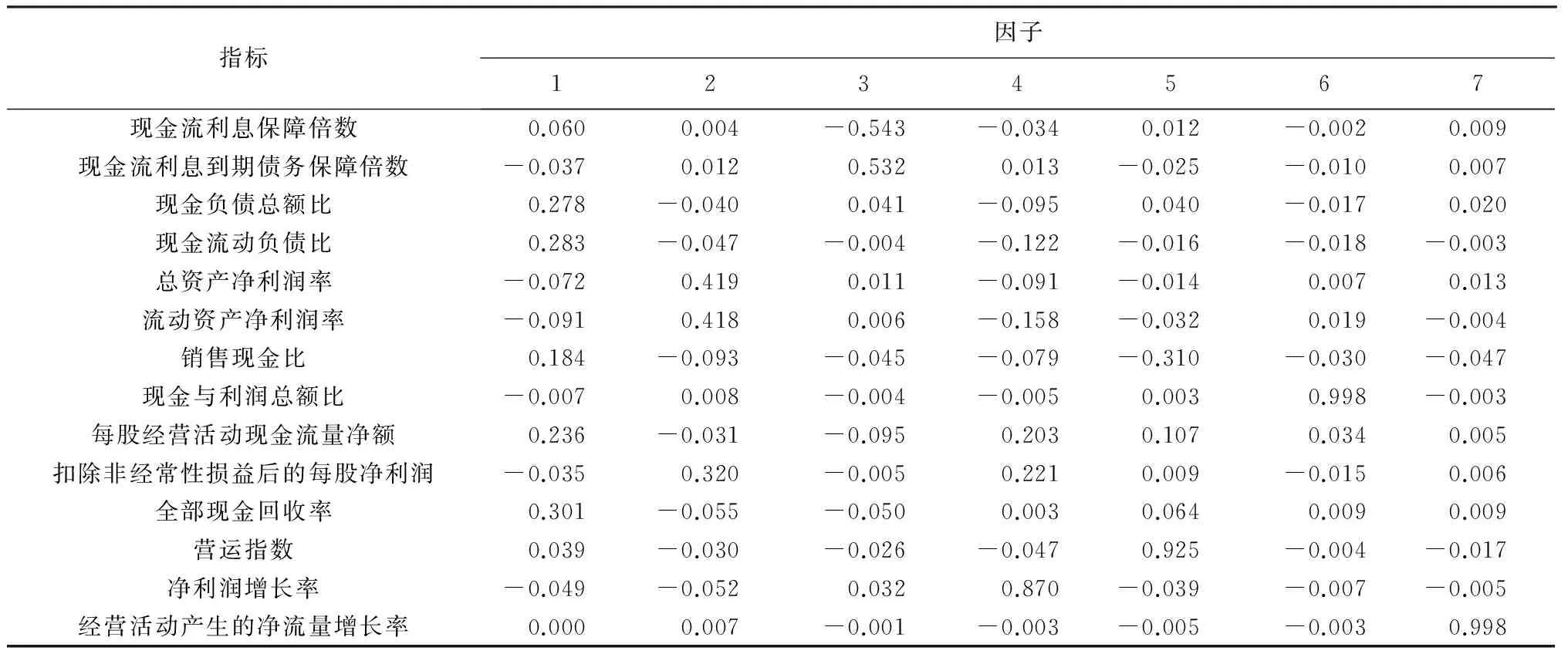
表6 t-1年因子得分系数矩
F1=0.06X1-0.037X2+0.278X3+0.283X4-0.072X5-0.091X6+0.184X8-0.007X9+0.236X10-0.035X7+0.301X11+0.039X12-0.49X13+0.000X14;
F2=-0.004X1+0.012X2-0.04X3-0.047X4+0.419X5+0.418X6-0.093X8+0.008X9-0.031X10+0.32X7-0.055X11-0.03X12-0.052X13+0.007X14
F3=-0.543X1+0.532X2+0.041X3-0.004X4+0.011X5+0.006X6-0.045X8-0.004X9-0.095X10-0.005X7-0.05X11-0.026X12+0.032X13-0.001X14
F4=-0.034X1+0.013X2-0.095X3-0.112X4-0.091X5-0.158X6-0.079X8-0.005X9+0.023X10+0.221X7+0.003X11-0.047X12+0.87X13-0.003X14
F5=0.012X1-0.025X2=0.04X3-0.016X4-0.014X5-0.032X6-0.31X8+0.003X9+0.107X10+0.009X7+0.064X11+0.925X12-0.039X13-0.005X14
F6=-0.002X1-0.01X2-0.017X3-0.018X4+0.007X5+0.019X6-0.03X8+0.0998X9+0.034X10-0.015X7+0.009X11-0.004X12-0.007X13-0.003X14
F7=0.009X1+0.007X2+0.02X3-0.003X4+0.013X5-0.004X6-0.047X8-0.003X9+0.05X10+0.006X7+0.009X11-0.017X12-0.005X13+0.998X14
(2)t-1年Logistic回归模型及效果检验
通过前文因子分析确定的7个因子作为自变量,采用Enter方法强制所有因子进入回归方程,回归结果如表7所示。

表7 t-1年Logistic 回归系数估计值及显著性检验结果
从表7可知,因子1、因子2、因子7在0.01的显著性水平下通过检验,因子3在0.05的显著水平下通过检验。由此可见,僵尸企业和非僵尸企业在偿债能力、盈利能力、获现能力和发展能力上与僵尸企业有明显区别,可通过这几个指标实现僵尸企业的预警。得到2014年的Logistic 回归方程:
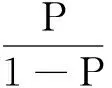
0.452F3+2.732F7
(1)
推出:

(2)
表8中Hosmer 和 Lemeshow 是拟合统计量,原假设方程对数据拟合良好。本次拟合优度测试结果P指为0.999,显著大于0.05,接受原假设,表明Logistic 回归方程是合适的。

表8 H-L拟合优度检验
将之前挑选出的50对检验样本带入2014年Logistic 回归方程,得到回判结果如表9所示。

表9 Logistic 回归模型在僵尸企业t-1年的判定结果
通过表9看出,50对检验样本中,50家非僵尸企业有3家被判错为僵尸企业,正确率为94%;50家僵尸企业中有4家被判错为非僵尸企业,正确率为92%。总体正确率为93%,因此模型检验结果正确率较高,模型是适合的。
采用上述同样的方法得到T-2年和T-3的Logistic预警模型。
t-2年的Logistic回归方程为:
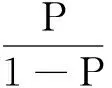
(3)
推出:

(4)
t-3年的Logistic回归方程为:
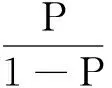
(5)

(6)
t-2年、t-3模型检验效果较好,且两个模型的预测准确率分别为91.4%和88.6%,低于t-1年的预测准确率。
5.模型应用
通过预警模型看出,反映偿债能力的现金流指标和反映盈利能力的现金流指标在僵尸企业预警中发挥重要作用。僵尸企业是一个逐渐演化的过程,通过建立僵尸企业的预警模型,进行财务预警研究是防止僵尸企业形成的有效方法。
在具体应用中,通过现金流指标构建的预警模型,可以计算出企业的预警值(0-1范围内),根据得到的预警值判断企业所处的财务危机阶段和相应的财务状态,进而有针对性的采取措施。从企业自身角度,预警模型可以帮助企业发现自身存在的财务问题,及时转变财务战略和经营方针,如改变融资结构等,积极应对问题;从政府角度来看,可以通过预警模型及时掌握企业经营状态,为政府预算提供信息,也是政府干预经济的晴雨表;从投资者角度来看,可以通过预警模型及时发现被投资企业的财务状况和盈利能力,及时调整投资方向,降低投资风险,维护投资者的利益;从债权人来看,可以通过预警模型来准确判断企业的偿债能力,以此判断债权投资的风险程度,为其是否提供融资提供决策依据。
四、结论与建议
基于僵尸企业文献分析提出僵尸企业的定义,并深入结合国情提出僵尸企业的定量识别方法,为解决僵尸企业问题奠定基础。在识别方法的设计上,将“政府补助”和“银行补贴”两个因素同时考虑在内,并基于僵尸企业的演变过程,扩大时间跨度。同时,在2015年僵尸企业名单的基础上详细分析其行业分布和财务特征。笔者以识别出的僵尸企业和配对非僵尸企业为样本,建立了僵尸企业形成前3年的预警模型,以实现僵尸企业预警,提早发现财务危机。具体而言,通过3年的预警模型可以看出:现金负债总额比、现金流动负债比、总资产净利润率、流动资产净利润率、扣除非经常性损益后的每股净利润指标具有稳定的预测效果,能实现僵尸企业的预警,应重点关注这几个指标;反映获现能力和发展能力的指标预测效果并不是很稳定;僵尸企业在偿债能力、盈利能力方面与非僵尸企业存在很大差异。
基于此,企业应从以下3个方面预防僵尸企业的形成:第一,企业建立自身的现金流指标财务预警机制。现金流指标能更好地反映企业的偿债能力、更为真实地反映企业的财务状况,通过预警模型可以发现企业潜在的财务危机,企业应及时采取措施,走出困境。第二,提高企业自身创新能力,如转变经营策略,寻找其他的发展机会和商机;转型升级,而不是一味“等要靠”,依赖外部的援助等。企业必须提高创新能力,通过自身寻求转变,才能获得持续发展。第三,应加快混合所有制改革。僵尸企业中国有企业占很大比例,其中钢铁煤炭行业尤为严重,国有企业效率低下、内部管理体质僵化,甚至存在多头管理,应考虑改变国企的管理体系,加快混合所有制改革步伐,借鉴民营企业的管理模式,优化内部管理,减少任人唯亲的管理理念,采用市场化经理人制度,改善内部管理机制等,以加快推动中国经济增长新动力机制的形成[18]。同时,积极探索新常态下的商业发展新模式,如网络商业、平台商业、服务商业、素质商业、多元化商业等[19]。
[ 1 ] KANEE J. Dangers of capital forbearance: the case of the FSLIC and“zombie”S&Ls[J]. Contemporary Economic Policy,1987, 5(1): 77-83.
[ 2 ] RIDZAK T. Lending activity and credit supply to firms during the crisis-evidence from the croatian micro level data[M]. Croatian: Croatian National Bank, 2011.
[ 3 ] 朱鹤,何帆. 中国僵尸企业的数量测度及特征分析[J]. 北京工商大学学报(社会科学版),2016, 31(4):116-126.
[ 4 ] 朱舜楠,陈琛.“僵尸企业”诱因与处置方略[J]. 改革,2016(3):110-119.
[ 5 ] 邹蕴涵. 我国僵尸企业的判别、影响及对策建议[J]. 中国物价,2016(7):80-82.
[ 6 ] 张栋,谢志华,王靖雯. 中国僵尸企业及其认定——基于钢铁业上市公司的探索性研究[J]. 中国工业经济,2016(11):90-107.
[ 7 ] 黄少卿,陈彦.中国僵尸企业的分布特征与分类处置[J].中国工业经济,2017(3):24-43.
[ 8 ] 刘奎甫,茅宁.“僵尸企业”国外研究述评[J]. 外国经济与管理,2016,38(10):3-19.
[ 9 ] 栾甫贵,李方玉. 僵尸企业的文献回顾与评价[J]. 会计之友,2017(14):70-75.
[10] 熊兵.“僵尸企业”治理的他国经验[J]. 改革,2016(3):120-127.
[11] 程虹,胡德状.“僵尸企业”存在之谜:基于企业微观因素的实证解释——来自2015年“中国企业—员工匹配调查”(CEES)的经验证据[J]. 宏观质量研究,2016,4(1):7-25.
[12] 孙丽.日本处理僵尸企业问题的经验教训研究[J].日本学刊,2017(3):46-58.
[13] 吴世农,黄世忠. 企业破产的分析指标和预测模型[J]. 中国经济问题,1987(6):8-15.
[14] 吴世农,卢贤义. 我国上市公司财务困境的预测模型研究[J].经济研究,2001(6):46-55.
[15] 陈静. 上市公司财务恶化预测的实证分析[J]. 会计研究,1999(4):32-39.
[16] PEEK J,ERIC S R.Unnatural selection: perverse incentives and themisallo cation of credit in Japan[J].American Economic Review,2005,95(4):1144-1166.
[17] 何帆,朱鹤.僵尸企业的识别与应对[J].中国金融,2016(5):20-22.
[18] 张杰,金岳.供给侧结构性改革下中国经新动力形成机制、障碍与突破途径——基于生产率形成的逻辑视角[J].郑州大学学报(哲学社会科学版),2016,49(6):65-71.
[19] 黄国雄.试论新常态下商业发展模式[J].浙江工商大学学报,2015(6):82-85.
ResearchintoMultidimensionalPovertyGovernancefromthePerspectiveofTargetedPovertyAlleviationConcerning“FiveWaysofAlleviatingPoverty”
/HUANG Chengwei, et al
(The State Council Leading Group Office of Poverty Alleviation and Development, Beijing 100028,China)
The multidimensional property of poverty determines that the main body and means for poverty governance should be diverse. Based on the five ways of alleviating poverty, the idea of targeted poverty alleviation realizes the requirement of project arrangements and verifies the multidimensional poverty governance theory. Literature analysis demonstrates that the idea of “five ways of alleviating poverty” is on the basis of multidimensional poverty theory, environmental determinism, governance theory and endogenous development theory, which embodies the accuracy and targetable feature of public strategies. Such idea also has high theory value and conforms to the requirements of “Four-Comprehensiveness“ and the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation. In terms of Lankao, the idea of “five ways of alleviating poverty” and micro situation variable are effectively combined with each other, which results in maximum output of public strategies. Finally, Lankao is alleviated from poverty.
five ways of alleviating poverty; targeted poverty alleviation; multidimensional poverty governance; Lankao
InnovationDimensionsofAnti-PovertyGovernanceSysteminCurrentChina’sPovertyAlleviationCampaign
/ZUO Ting, et al
(College of Humanities and Development Studies, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100089, China)
Abstract: The innovation of anti-poverty governance system is not only for the livelihood improvement of the underprivileged, but also for the innovation of the national governance system. China’s anti-poverty governance changes from temporary, project-oriented governance to institutional governance. In order to improve the performance of anti-poverty, Chinese government has made numerous innovations in the governance of anti-poverty system. Four innovations are of great significance to the national governance system. The first one is the moving-down governance center. The second one is the formation of collaborative governance framework. The third one is the involvement of different stakeholders, including the underprivileged, community organizations, cooperatives, the third party organizations and business entities. The last one is the diversification of governance instruments, measures and tools. Diversified governance instruments are implemented and are combined with time and space. At the same time, there are still some potentials to be explored and improved, such as the improvement of autonomous ability of administrative village, the sustainability and replicability of the innovation system, the improvement of endogenous power,the balance between commercial interests and the effectiveness of poverty alleviation and the perfection of policy implement.
Keywords: anti-poverty governance system; downward governance; collaborative governance; participatory governance; diversification of governance instruments
“Fracture”and“Reconstruction”:AStudyofReservoirMigrants’WayofTargetedPovertyAlleviationfromthePerspectiveofCapitalTransfer
/LI Xiaoming
(School of Public Administration, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China)
Abstract: The paper takes the common SW village in the South-to-North Water Diversion Project’s external migrant resettlement area for example to explore the way of targeted poverty alleviation in reservoir region migrants, the results show that the key to poverty alleviation is the capital transfer. First, it is embodied in that the migrants’ secondary poverty and interventional poverty problems cannot be solved at the beginning of the movement because of coexistence of living exchange subsystem vulnerability and livelihood fracture caused by the blocked transfer way of capital. Second, the key to SW new village’s targeted poverty alleviation for eight years is the reconstruction of the capital transfer path due to efforts made by many sides. That is, breaking the traditional agricultural path dependence by natural exchange upgrading, providing market conversion conditions by the government to make human capital and natural capital transfer to material capital available, excavating the advantage culture capital of migrants’ traditional culture, breaking the segregation system by well-running capital transfer activity and forming a virtuous circle of micro and macro interaction.
Keywords: reservoir region migrants; targeted poverty alleviation; capital transfer; fracture and reconstruction
PovertyExit:PolicyImplication,MechanismDeconstructionandDevelopmentSupportPolicyContinuation
/ZHENG Ruiqiang
(Economy and Management College, Jiangxi Agricultural University, Nanchang 330045, China)
Abstract: The improvement of poverty exit mechanism may help reconstruct poverty alleviation and development business process, improve living capacity of poverty alleviation subjects and optimize poverty alleviation governance. The paper comprehensively studies the operation characteristics of poverty exit mechanism, such as focusing on poverty alleviation and development system to improve the efficiency of poverty alleviation resources, highlighting the diversity of the main subjetcs involved in poverty alleviation and the creation of governance mechanisms and emphasizing the use of modern information technology and new management model innovation in poverty exit mechanism. Then it analyzes the practical difficulties in poverty exit as follows: The standard of poverty exit is rigid and fails to measure in a scientific way; The understanding divergence makes the idea of “procedure legitimacy is reasonable” be available; The positive incentives in poverty alleviation is ineffective. Finally, it makes the following suggestions: taking strict targeted measures in poverty alleviation, improving index system of poverty exit, focusing on strict exit procedures of poor household and poor villages, paying attention to the appraisal of poverty exit work, enhancing publicity education on poverty exit, combing spiritual poverty alleviation with material poverty alleviation, relating positive stimulation with negative stimulation, providing support guarantee for poverty exit work, innovating support polity and developing sustainable ability of the living of the subjects.
Keywords: poverty exit; policy implication; operational characteristics; practical dilemma; improving strategy
TheRealityTranscendenceofMarx'sCommunityThought
/HUANG Ju, et al
(School of Marxism, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310028, China)
Abstract: People have the dual attributes of nature and society. The extension and externalization of human social dimension is manifested in the form of community. The community has become the focal point of philosophy due to its close connection with people. Based on ethics, faith, a priori multi-dimensional degree of discussion, it is possible for Western philosophy to form the city community, the community of beliefs, the contract community, a priori rational community, the community of love and other major community thinking. The common feature of the traditional community is to understand the community in an abstract and intuitive way and the understanding of the community is introduced to the abstract field. Through criticizing the abstract limitations of the traditional community thought, Marx holds that social relations are the fundamental link to maintain the common life and the union of the free people is the development direction of the community. Thus, it is possible to bring about the revolutionary change on the core issues related with the premise of the community and the foundation, the relationship among internal members and the development direction.
Keywords: Marx;community thought;practice;abstract
TheRevolutionaryChangeofMarxismPhilosophyandItsContemporaryInspiration
/SHAN Lianchun, et al
(School of Marxism, Hohai Universtity, Nanjing 211100, China)
Abstract: The revolutionary change of Marxism philosophy is developed in the practice of constant struggle. The issue of “material interests” is the harassing problem to Marx because his early idealism thought keeps conflict with objective reality. It is the period of 1844 Economic Philosophy Manuscript (called Manuscript) that Marx’ philosophical thought undergoes a revolutionary change on the basis of the study of economics. In the Manuscript, Marx introduces human practice to philosophical criticism and realizes the transformation of philosophy from conceptual ontology to practical ontology. Marx holds that material production plays decisive role in and thus makes revolutionary transformation on historical idealism by means of historical materialism. Based on the new interpretation of alienated labor, Marx scientifically predicts the inevitability of the realization of the proletariat’s communism ideals. Therefore, in the new era, to keep on developing Marxism, it is necessary to understand the internal logic of the transformation of Marx’s philosophical thought.
Keywords: Marxism philosophy; revolutionary change; material interests
ThreeCognitiveElementsof“ChinaExperience”
/YU Dahuai, et al
(Research Base of Socialism Theoretical System with Chinese Characteristics, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China)
Abstract: Based on the follow-up studies of “China experience”, the paper discusses three important cognitive elements, namely, decisive elements, descriptive elements and evaluative elements. In general, the follow-up studies of “Chinese experience” should find the decisive factors in economic and social development, realize the descriptive elements in humanistic concern and complete the evaluation factors in the history of social development. At the same time, the interaction and impact of the three elements determine the research aspect and research quality of the “Chinese experience”.
Keywords: China experience; values; capital; happiness
OntheIdeaofSharedDevelopmentandItsHistoricalImplication
/PAN Gege, et al
(School of Marxism, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China)
Abstract: The idea of shared development is an important part of the theory of socialism with Chinese characteristics. It is the latest theoretical achievements arising from the exploration of the socialist road with Chinese characteristics since the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China. The idea of shared development fits into the demands of the times of social development, scientifically interprets the purpose, the subjects and the benefits of the development achievements. The idea of shared development is people-oriented and further stresses the people-oriented nature of shared development. Such idea is of great theoretical significance to build a well-off society. It helps to improve the social equity mechanism, provides system for building a well-off society and makes the ultimate realization of the free and comprehensive development of human beings available.
Keywords: sharing;development idea; historical implication
TheHarmoniousAllocationFrameworkofInitialCarbonDioxideEmissionsBasedonThreePairsofEquilibrium
/WANG Jigan, et al
(Business School, Hohai University, Nanjing 211100, China)
Abstract: The confirmation and allocation of initial carbon dioxide emissions are the preconditions of carbon emissions trading market. Based on the harmony theory,three pairs of equilibriums namely supply-demand equilibrium, regional-industry equilibrium and equity-efficiency equilibrium are considered. The connotation and thinking of harmonious allocation for initial carbon dioxide emissions are analyzed. The harmonious allocation methods and theoretical frame of initial carbon dioxide are put forward. Firstly,Based on carbon emissions control target, scenario analysis theory and interval mathematics theory, the pre-allocation model of initial carbon dioxide emissions is set up to get preconfigured plan. Secondly, to evaluate the harmonious degree of the preconfigured plan, the harmonious evaluation model is established. Thirdly, on the basis of improving preconfigured plan failed to pass the harmonious evaluation, the harmonious evolution model is obtained.
Keywords: initial carbon dioxide emissions; supply-demand;regional-industry; equity-efficiency;harmonious allocation
ResearchintoSynergyStrategyofInnovativeDevelopmentofIndustriesthroughFinanceintheYangtzeEconomicZone
/LIU Liang
(Shanghai Academy of Social Sciences, Shanghai 200433, China)
Abstract: Finance is the core of modern economy and promoting the industry innovation through finance is one of the important contents of the strategy of China’s“developing the country through science and education”. This paper discusses the theory and mechanism of promoting industry innovation development through finance from the perspective of cross-regional capital investment effect, resource allocation discrimination effect, growth span effect and industrial innovation development effect. Based on a comprehensive analysis of the present situation of the Yangtze economic zone including cross-regional industry development through finance, hierarchical development of regional financial center construction and cross-regional industry coordination development, this paper puts forward the strategic idea of promoting the coordination development of industrial innovation in the Yangtze economic zone on the basis of coordination development of financial center construction.
Keywords: the Yangtze Economic Zone; finance; industry; coordination development
ResearchintotheInfluentialFactorsofAirPollutioninChina:AnAnalysisofDynamicSpatialPanelModelofChineseCities
/LIU Jun, et al
(China Institute of Manufacturing Development, Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, Nanjing 210044, China)
Abstract: Identifying the key factors that have impact on air pollution can provide a scientific basis for the rational formulation and effective implementation of air pollution policies in China. This paper uses panel data of 119 prefecture-level cities from 2012-2015 to study the influential factors of air pollution with the spatial dynamic panel data model. The results show that there are significant spatial spillovers and dynamic effects in the spatial dimension and time dimension of urban air pollution in China. There is a significant inverted “U” relationship between air pollution and economic development, which verifies the existence of Environmental Kuznets Curve. The industrial structure measured by the second industry of GDP and the increasing density of the population significantly aggravates the urban air pollution. Technological advances and urban greening may improve the pollution, while the investment of governing air pollution in urban environment is not significant. According to the above findings, this paper makes the corresponding policy suggestions for improving urban air pollution at last.
Keywords: air pollution; influential factors; AQI
AnAnalysisofCustomerCommunity-BasedInnovationModel:ACaseStudyofCspace
/TANG Zhen,et al
(Business School, Hohai University, Nanjing 211100, China)
Abstract: Based on the value co-creation theory, the paper makes intensive study of using customer community to co-innovate between firms and customers. On the basis of value chain model and value co-creation theory, this paper firstly constructs conceptual framework for innovative customer community. Then, it proposes theoretical propositions of developing innovative customer community by analyzing existing literatures. Thirdly, it verifies the propositions by taking Cspaces and its customer community as research subjects. Finally, it reconstructs value chain model for innovative pattern of customer community.
Keywords: customer community; value co-creation theory; value chain model; innovation mode
TheRuralCommunityCapacityandtheWell-BeingofRuralResidents
/QI Xiaoming, et al
(College of Humanities and Social Development, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing 210095, China)
Abstract: The traditional rural community is mainly dominated by government, adopting top-down and exogenous development, and often ignores the community's internal capacity construction. In fact, community capacity construction may have an impact on community development and the well-being of rural residents. The paper takes the southwest of Anhui rural areas for example and analyzes the relationship between rural community and rural residents’ well-being on the basis of factor analysis and ordinal regression model. It is found that at the present stage in Southwest Anhui the well-being of rural residents in general is at the middle level. Rural community ability factors include rural community organization ability, rural community autonomy ability and the ability of rural community to cultivate internal social capital and external social capital. Rural community autonomy has the most positive impact on the well-being of rural residents, the ability of the community to cultivate internal social capital follows and the impact of community organizational capacity is the minimal. Therefore, in the future, it is necessary to vigorously promote the villagers’ autonomy, cultivate the social capital of rural communities, especially good interpersonal trust and neighborhood mutual assistance and further improve the organization and management capabilities of existing organizations in rural communities.
Keywords: community capacity; rural area; well-being; rural residents; community
ResearchintotheRecognitionandEarlyWarningofChineseZombieCompany
/SUN Ying,et al
(School of Management,Ocean University of China,Qingdao 266100, China)
F279.2;F426
A
1671-4970(2017)05-0081-08
(责任编辑:高 虹)
Abstract: Zombie company problem has become a hot topic in recent years,but there is no consensus on the identification of zombies in academic circles. Identify zombie company is the first step to solve zombie company problems and early warning is the fundamental solution to avoiding the emergence of zombie company. Based on the long-term evolution characteristics of zombie enterprises, the paper proposes zombie enterprises’ identification method that conforms to China’s reality, combining with China’s national conditions and taking bank subsidies and government subsidies into consideration. Then it establishes early warning model of zombie enterprises from the perspective of finance. Built on the analysis of three-year early warning model, it is found that the ratio of total cash liabilities, cash flow liabilities, net profit margin of total assets, net profit margin of current assets, net profit per share after deducting non-recurring gains and losses have stable forecasting effect, which can realize the warning of zombie enterprises. It provides theoretical basis for enterprises to detect crises in advance and take measures on time.
Keywords: zombie company;recognition methods;financial warning
