基于Lux型群体感应系统干预的生物被膜调控在污水处理中的研究进展与前景
2017-11-03赵畅王宁王文昭徐期勇
赵畅,王宁,王文昭,2,徐期勇
1 北京大学深圳研究生院 环境与能源学院,广东 深圳 518055
2 福瑞莱环保科技(深圳)股份有限公司,广东 深圳 518055
基于Lux型群体感应系统干预的生物被膜调控在污水处理中的研究进展与前景
赵畅1,王宁1,王文昭1,2,徐期勇1
1 北京大学深圳研究生院 环境与能源学院,广东 深圳 518055
2 福瑞莱环保科技(深圳)股份有限公司,广东 深圳 518055
基于 Lux型群体感应系统的生物被膜调控在污水处理中的研究备受关注,群体感应系统的干预包括正向强化和负向削弱两类。群体感应系统的正向强化作用可提高生物膜法污水处理中的挂膜速度,提高污水处理效率,促进活性污泥中胞外聚合物(Extracellular polymeric substance,EPS)和可溶性微生物产物(Soluble microbial products,SMP)的生成,提高生物被膜的产量;群体感应的负向削弱作用可以降解生物被膜形成过程中所需要的信号分子,切断生物被膜形成的基因表达过程,有效抑制MBR膜表面生物被膜的形成,防止膜污染。对信号分子酰基高丝氨酸内酯(N-acyl homoserine lactone,AHLs)的结构和作用机理的进一步研究、群体感应淬灭菌的固定化技术与应用、多种防治膜污染方法的协同效果验证及群体感应干预在更多污水处理领域的应用可行性是该领域要研究的几个重要方向。
群体感应,群体感应淬灭,污水处理,生物被膜
1 引言
群体感应(Quorum sensing,QS)是细菌之间对周围环境变化作出响应并进行信号分子交流不断作出反应的调节机制[1],Lux型的QS理论始于20世纪70年代对海洋细菌费氏弧菌Vibrio fischeri和哈氏弧菌(夏威夷弧菌,Vibrio harveyi)生物发光现象的研究[2]:这两种细菌可产生一种在细胞之间进行扩散的自动诱导物(Autoinducer),随着研究的进一步深入,发现了费氏弧菌的LuxI和LuxR基因,基于此,提出了基于Lux类型基因调控的群体感应机制。在QS系统中,包括两个控制基因,即I基因和R基因。I基因指导合成自体诱导物合成酶——LuxI蛋白,该诱导物合成酶能够合成信号分子酰基高丝氨酸内酯(N-acyl homoserine lactone,AHLs);而R基因能够合成LuxR型蛋白。信号分子扩散转移到细胞外并进行累积,随着信号分子在环境中的浓度不断积累,当浓度达到启动阈值后,这些信号分子会再次进入细菌体内,与LuxR结合,结合后的复合物能激活相关基因的表达,从而合成生物被膜所需的功能性蛋白等物质,使细菌适应外界环境的变化(图1)。作为信号分子的自诱导物(Auto inducer,AI)小分子化学物质有酰基高丝氨酸内酯(N-acyl homoserine lactone,AHLs)[3]、寡肽类(Auto inducer peptides,AIPs)[4]、自然小分子(Natural small molecules,NSM)以及自诱导因子Ⅱ(Autoinducer-2,AI-2)[5]。多数AHL型群体感应是通过LuxI/R类型调控完成信号分子的传递过程。此外,QS控制还可调节生物发光、游动性等微生物群体行为[6-9]。
作为分子微生物学和环境资源保护与利用两个领域的交叉应用[10-11],群体感应(Quorum sensing,QS)对生物被膜生长进行调控干预,并应用于污水处理领域,受到越来越多的关注和研究,成为污水处理研究热点之一[12-15]。生物被膜(Biofilm)是微生物通过扩散、重力沉降等方法在附着物表面黏附、成熟而形成的黏度很高的水合凝胶层[16-17]。基于 Lux型的群体感应信号分子 AHLs在污水处理环境中广泛存在并对污水处理的效果产生影响[18-20]。本文首先对QS的基本背景理论进行系统的叙述,并介绍了群体感应系统正向强化和负向削弱作用在生物膜法污水处理、活性污泥污水处理和膜生物反应器(Membrane bioreactor,MBR)方面的研究进展,基于最新研究进展,对该方法在提高污水处理的高效可行性方面提出了相关应用前景和展望。

图1 Lux型群体感应系统示意图Fig.1 Lux type quorum sensing system diagram.
1.1 群体感应系统正向强化调控
Lux型群体感应调节生物被膜的产生、附着、脱落等过程。AHL类自诱导物作为细胞间交流最具有代表性的信号分子,是生物被膜形成过程中一种非常重要的信号分子[21]。在革兰氏阴性菌中,根据其碳链长度或酰基侧链取代基的差异,已鉴定出10余种AHL衍生物,常见的有C4-HSL、C6-HSL、C8-HSL、C10-HSL、C12-HSL等[22]。
群体感应系统的正向强化作用是指通过额外添加信号分子诱导物分子如AHLs,提高信号分子的浓度,激活目的基因的表达,生成大量微生物代谢产物,而这些初、次级代谢产物是构成生物被膜的主要组成成分,从而缩短生物被膜产生的时间,提高生物被膜的产量。具体应用在污水处理领域,则是通过额外添加 AHLs功能物质,实现生物被膜的较快生长和产量的提高。
1.2 群体感应系统负向削弱调控
群体感应系统的负向削弱调控是指通过干扰细菌的群体感应系统,阻止或破坏其参与细菌生物学功能的调控,又称为群体感应淬灭(Quorum quenching,QQ)[23]。群体感应淬灭技术是群体感应系统对生物被膜生长的负向干预调控,可减缓生物被膜的生长,目前已发现的抑制细菌的群体感应交流主要有3种途径[24]。
1)抑制信号分子的生物合成。如三氯生(Triclosan)是一种有效的烯酰基 ACP还原酶抑制剂,烯酰基 ACP还原酶参与酰基 ACP的合成,而后者是生成AHL的重要物质之一。通过加入三氯生来减少 AHL的产量,从而抑制 QS系统[25]。
2)通过合成一些AHL的结构类似物,与相应受体蛋白竞争性结合,减少实际的AHL与受体蛋白结合的可能性,并因此破坏其 QS行为[26-27]。
3)降解信号分子。通过添加AHL降解酶或能够产生该功能酶的细菌,降解AHL的浓度。AHL内脂酶(AHL-lactonase)和酰基转移酶(AHL-acylase)是目前研究较多且被证实能有效降解一系列AHLs的两种降解酶,内脂酶通过水解AHL的内脂键来破坏信号分子及其作用,酰基转移酶则通过作用于连在酰基高丝氨酸内脂上的氨基,生成脂肪酸和不具有任何生物活性的高丝氨酸内脂[28-31]。
上述3种群体感应淬灭技术均对QS进行负调控,即通过群体感应淬灭系统,使AHL浓度一直在阈值以下,不会激活目的基因的转录表达,使膜生长受到抑制,膜污染得以控制。已有研究发现城市污水厂活性污泥、处理合成污水的活性污泥及处理微污染源水的生物被膜中均存在群体感应所需信号分子自诱导物[10,32]。如果能抑制该过程中信号分子的产生,则QS机制和生物被膜形成过程将极大可能被阻断抑制。
2 群体感应系统干预在污水处理中的研究进展
2.1 群体感应正向强化干预在污水处理中的应用
生物被膜的产生及形成很大一部分是由Lux型的群体感应系统进行调控的,群体感应系统可以在不同水平上对影响生物被膜结构的因素进行调控,目前群体感应的正向强化作用在生物膜法、活性污泥法和MBR污水处理中均有应用,主要研究方向如下。
2.1.1 QS在生物膜法污水处理工艺中的应用
生物膜法技术实质上是生物固定化技术,它是将微生物菌剂固定在载体(即填料,一般为聚乙烯、聚氯乙烯等材料)上,通过人工强化技术将生物被膜引入到污水处理反应器中,便形成了生物膜反应器。在该技术中,生物被膜作为所有类型生物膜反应器中的关键部分,和出水水质等指标一样重要,其特性决定了整个工艺处理的效果和效率[33-34]。
群体感应理论和生物被膜的形成密切相关,是细菌群体行为活性的核心部分[15,35-37],已有研究发现 QS在最初生物被膜形成、生物被膜成分组成、生物膜法污水处理中具有重要作用[23,33,38-40]。De Clippeleir等[41]在氧限制自养硝化-反硝化(OLAND)生物转盘反应器中发现了C12-HSL的存在,通过添加额外的C12-HSL,显著提高了OLAND生物膜法的氨氧化速率;并得出厌氧氨氧化菌形成生物被膜的最小生物质浓度。孙颉等[42]在对生物被膜法处理养殖污水的研究中发现,添加两种不同种类的信号分子C6-HSL和N-3-oxo-C8-HSL的实验组附着基上的生物量明显多于未添加信号分子的对照组,且投加N-3-oxo-C8-HSL的实验组产生的生物量更多,约是对照组的6倍;通过数据因子SPSS分析,运用统计学打分方法研究,发现添加AHLs信号分子的两组污水环境的总体得分较高,水内环境较好。
目前基于Lux-QS在生物膜法污水处理方面的研究仍十分有限,然而,诸多研究已经发现在纯种菌培养体系内存在Lux型群体感应现象,如细菌团聚体的形成[21,43],由于细胞的运动性而形成的表层菌丝胶质化[44]、生物被膜厚度[45]等。细菌的QS理论对于生物被膜的形成具有作用,在实际的污水运行条件下,通过人为地提高QS的活性,能否显著地提高生物膜法污水处理的效率,有待进一步探究。
2.1.2 QS在活性污泥法污水处理工艺中的应用
活性污泥颗粒能从污水中去除溶解性的和胶体状态的可生化有机物,同时吸附水中的悬浮固体和其他一些物质,去除一部分磷素和氮素。该方法是污水处理中最广泛使用的方法,其中污泥的微生物活性是决定处理效果好坏的关键因素[46-47]。
在连续式活性污泥污水处理工艺中,活性污泥絮体是由无机物和高密度有机物的多孔聚集体,其中含有大量的胞外聚合物(Extracellular polymeric substances,EPS)矩阵交联体[48-51],高细胞密度的絮体很容易导致细胞和细胞之间的反应[52],产生更多的EPS等初、次级代谢产物,关于Lux型群体感应系统调控在活性污泥法污水处理中的应用研究仍然较少,Mrogan-Sagastume等[53]运用薄层色谱分析和生物检测法,证明了来自市政、医院和药物废水活性污泥中AHLs和AHLs类似诱导物的存在;Valle等[54]在降解苯酚活性污泥中分离出7株具有AHL类似生物活性的变形杆菌Proteussp.,进一步实验证明添加2–20μmol/L的AHL可使系统维持对苯酚的降解长达14 d,而不添加AHLs的对照组只能维持10 d的生物活性,且到14 d时苯酚降解能力已消失。Chong等[52]探究了 Lux类型调控的群体感应和胞外酶活性的关系,发现提高活性污泥中3-oxo-C6-HSL的浓度(10μmol/L),胞外几丁质酶的活性在60–90min内可提高10倍,并由此推测依靠AHL产生的胞外几丁质酶可保持气单胞菌Aeromonassp.总数在活性污泥体系中的优势种群作用,提高活性污泥对污水的处理效率。
在序批式活性污泥污水处理工艺中,已有研究运用生物显色检测法证明了颗粒状污泥比絮凝状污泥含有更多的AHL信号分子[55-58],在好氧活性污泥形成过程中,胞外聚合物(EPS)和微生物的聚集作用扮演着重要的角色[59-61]。Lux型群体感应系统通过促进疏水性 EPS的生成促进微生物的聚集和好氧污泥的形成和驯化[57],Tan等[62]通过额外添加40μL AHL显著提高了胞外聚合物(14%–36%)和蛋白质的生物量(7%–16%)。
AHLs在活性污泥和好氧颗粒污泥中普遍存在,群体感应在活性污泥处理过程中提高污泥性能方面有着重要作用,通过人为提高QS的作用效果,如补充AHLs或产生AHLs的细菌,能否提高连续式或提高序批式活性污泥法处理效率,是QS在活性污泥法污水处理领域的重要应用。
2.1.3 QS在MBR污水处理中的应用
胞外聚合物EPS和溶解性微生物产物SMP、好氧颗粒污泥的形成均是MBR中群体感应系统调节产生的膜污染主要成分[63-64]。于多[65]对不同运行时段、不同跨膜压力(TMP)条件下MBR中活性污泥及生物被膜的EPS和 SMP中蛋白质、多糖和DNA含量进行分析,发现可溶性污染物SMP在膜生物反应器发生膜污染的起始阶段发挥更大的污染作用,进一步发现蛋白质在EPS和SMP中含量均最多,在膜污染过程中起主要作用。生物被膜形成初期主要发挥作用的为C4-HSL、C6-HSL和3-o-C8-HSL,在生物被膜成熟稳定期中发挥主要作用的信号分子为C4-HSL、C6-HSL和3-o-C6-HSL,而膜污染后期发挥主要作用的信号分子为 C6-HSL和3-o-C8-HSL。余蓉等[66]在模拟生物污水运行的膜生物反应器MBR中,分离出一株能够产生短链C4-HSL的群体感应信号分子,并初步鉴定为嗜水气单胞菌Aeromonas hydrophila。
群体感应作用的存在会导致MBR膜组件表面生物被膜聚集生长,形成膜污染,使MBR运行效率降低,基于此,通过削弱群体感应调控过程、控制膜生长的群体感应淬灭理论在MBR膜污染防治方面的应用应运而生,众多学者在该方面开展了一系列研究。
2.2 群体感应系统负向削弱调控在MBR膜污染防治中的应用
基于干预群体感应过程的发生,通过削弱生物被膜形成过程的群体感应淬灭技术在污水处理领域的应用主要在膜生物反应器(Membrane bioreator,MBR)方面。MBR工艺处理污水具有占地面积小、处理效率高、出水浊度低、容积负荷高等诸多优势,在污水处理方面的应用得以迅速增长[67]。但膜污染成为限制其长久运行及大范围推广使用的主要问题,生物被膜在膜组件表面附着生长,导致滤膜的膜通量减小、膜压差增大,极大地阻碍了 MBR在污水处理中的应用[68]。研究者试图寻找可以有效减缓膜污染、提高膜组件使用寿命的方法,如膜表面属性修饰等物理法[69]、利用强酸强碱试剂清洗等化学法[70-71],虽在减缓膜污染方面均取得了一定的效果,但仍会带来诸多副作用,无法从根本上解决膜污染的问题,原因是对于生物被膜的形成过程而言,它是细菌等微生物自发地通过基因激活和表达的过程,而基于Lux型群体感应系统负向削弱调控理论,则可以从生物被膜形成的根源之处来进行干预,解决MBR膜污染,在污水处理方向更具有工程和实践操作的意义。目前采用群体感应淬灭(QQ)控制 MBR膜污染的物质主要 有3种:QQ功能酶控制膜污染[30,32,72-73],QQ功能菌控制膜污染[74-75],运用 Lux-type的信号分子类似物的干扰作用来控制膜污染[27,76-78]。
2.2.1 QQ酶控制膜污染
一些酰基转移酶和AHL内脂酶可以有效降解生物被膜形成过程中所需 AHLs信号分子的浓度,从而防治MBR膜污染,如Yeon等[72]首次试验并证明了猪肾酰基转移酶Ⅰ及AHL酰基转移酶通过淬灭AHL自诱导体而有效防止了膜生物反应器中的膜污染。Kim等[79]通过将酶形成酶壳聚糖-酰基转移酶矩阵,直接固定在纳滤膜上,有效减少了滤膜表面胞外聚合物(EPS)的分泌,从而减缓了生物被膜的形成,固定化酰化酶在20多天内可保持90%的活性,膜通量是空白对照组的1.5倍。Lee等[73]在此基础上对酶的固定化技术和活性的保持做了进一步改进,运用磁性纳米粒子——球形介孔二氧化硅制成了纳米级别酶反应物(Nanoscale enzyme reactors of acylase,NER-AC),使固定化QQ酶在1个月连续200 r/min转速下仍能保持90%的生物活性。
QQ酶由于其作用的高效性和直接性,在群体感应淬灭技术防治MBR膜污染方面具有重要的应用意义,但该方法也存在一定的不足:功能酶由于其本身的不稳定性及保存困难、易失活等特征,其使用范围和使用寿命大大受限。如何保持 QQ酶的高效活性及探究更多 QQ酶固定方法,是该领域下一步需克服的难题之一。
2.2.2 QQ菌控制膜污染
MBR污水处理系统中存在许多可分解AHLs的细菌,通过额外添加高效QQ菌可减缓MBR膜组件表面生物被膜的形成。Oh等[74]首次从活性污泥中分离出了能够产生 QQ分解酶的细菌红球菌属Rhodococcussp.BH4,并证实了运用群体猝灭酶可以延缓膜污染,又尝试了将能分解AHL的重组大肠杆菌封装入中空纤维膜的微孔中,并有效控制了生物淤积。然而该方法依然存在局限性,首先重组大肠杆菌保持需要抗生素环境,在没有抗生素存在下重组大肠杆菌会失活,再则实际运行环境中,重组大肠杆菌存活率低,难以存活。因此寻找实际生活污水本体中群体淬灭菌是解决这一问题的关键。Kim 等[80]将红球属菌Rhodococcussp.BH4通过制成细胞包埋珠(Cell entrapping beads,CEBs),通过细菌包埋珠对膜表面的物理冲刷和 QQ菌的生物作用,有效验证了其群体淬灭效应;进一步的研究[81]证明了BH4菌株生产了AHL降解酶,有效分解了所验证系统中的一系列AHLs。利用群体感应淬灭菌来延缓生物被膜生成,不但克服了酶的不稳定性,也解决了淬灭酶寿命及活性的问题。Cheong等[82]从小试阶段运行的MBR中提取到假单胞菌1A1(Pseudomonassp.1A1),经对比发现菌株1A1比菌株BH4表现出更强的群体感应淬灭能力和存活力。将假单胞菌1A1包埋后投入膜生物反应器中,结果显示其产生的AHL-acylase能降解长链信号分子,同时分泌的淬灭酶最终被传输到胞外,在胞外进行群体感应淬灭功能的作用,发生QQ效应,从而减缓了膜表面生物被膜的形成。
赵畅等[83]从多处实际污水处理厂活性污泥中分离纯化出一批群体淬灭功能菌株,并比较其对信号分子C6-HSL分解能力的不同,经分离测序,得到一株蜡样芽孢杆菌HG10[84-86],通过对菌株HG10进行包埋固定,验证了其群体感应淬灭功能在控制生物被膜形成方面的可行性。张海丰等[77]通过在MBR膜生物反应器中添加大蒜素制成的海藻酸钠包埋珠,使过膜压差TMP的增长速率减小了75%,并提高了污泥混合液的可滤性。
2.2.3 AHL结构类似物控制膜污染
前面所述两种方法都是通过降解信号分子来抑制生物被膜的形成,与前面两种方法不同,本方法是通过添加AHL结构类似物,占用R型蛋白上的结合位点,减少实际的AHLs信号分子与Lux-R型蛋白结合的概率,进而激活体系内原有 QQ功能菌的生物活性,使分解 AHL的基因高效表达,降低体系内 AHLs结合的有效性目的基因的激活,最终减缓生物被膜的生成[27,87-88]。
Yu等[27]通过添加AHL的结构类似物γ己内酯(Gamma-caprolactone,GCL),运用生物刺激作用验证了GCL富集活性污泥中的QQ细菌,防止MBR处理生活污水过程中生物被膜污染的可行性,并提出了一种“生物刺激”的QQ策略,即通过初始阶段加入 GCL富集活性污泥(GCL-consortia)和持续注入GCL方法。结果表明,经GCL富集后的活性污泥能有效降解高丝氨酸内酯,增加体系中QQ基因(qsdA)的浓度,控制胞外聚合物(EPS)的分泌,从而有效控制MBR中的生物淤积。这种生物刺激的QQ策略为MBR应用程序中的生物淤积控件提供了一个新的思路。Ponnusamy等[89]研究了一种环境友好型群体感应抑制剂香草醛(3-甲氧基-4-羟基苯甲醛)对生物被膜的抑制作用,发现香草醛对短链 AHLs有更好的抑制作用,并发现香草醛对RO膜的醋酸纤维膜抑制作用最显著。Kappachery等[90]用多种细菌模拟生物污染,并发现使用浓度为1.5 mg/mL的AHL结构类似物N-乙酰半胱氨酸(N-acetylcysteine,NAC)可以抑制RO膜上生物被膜的形成。
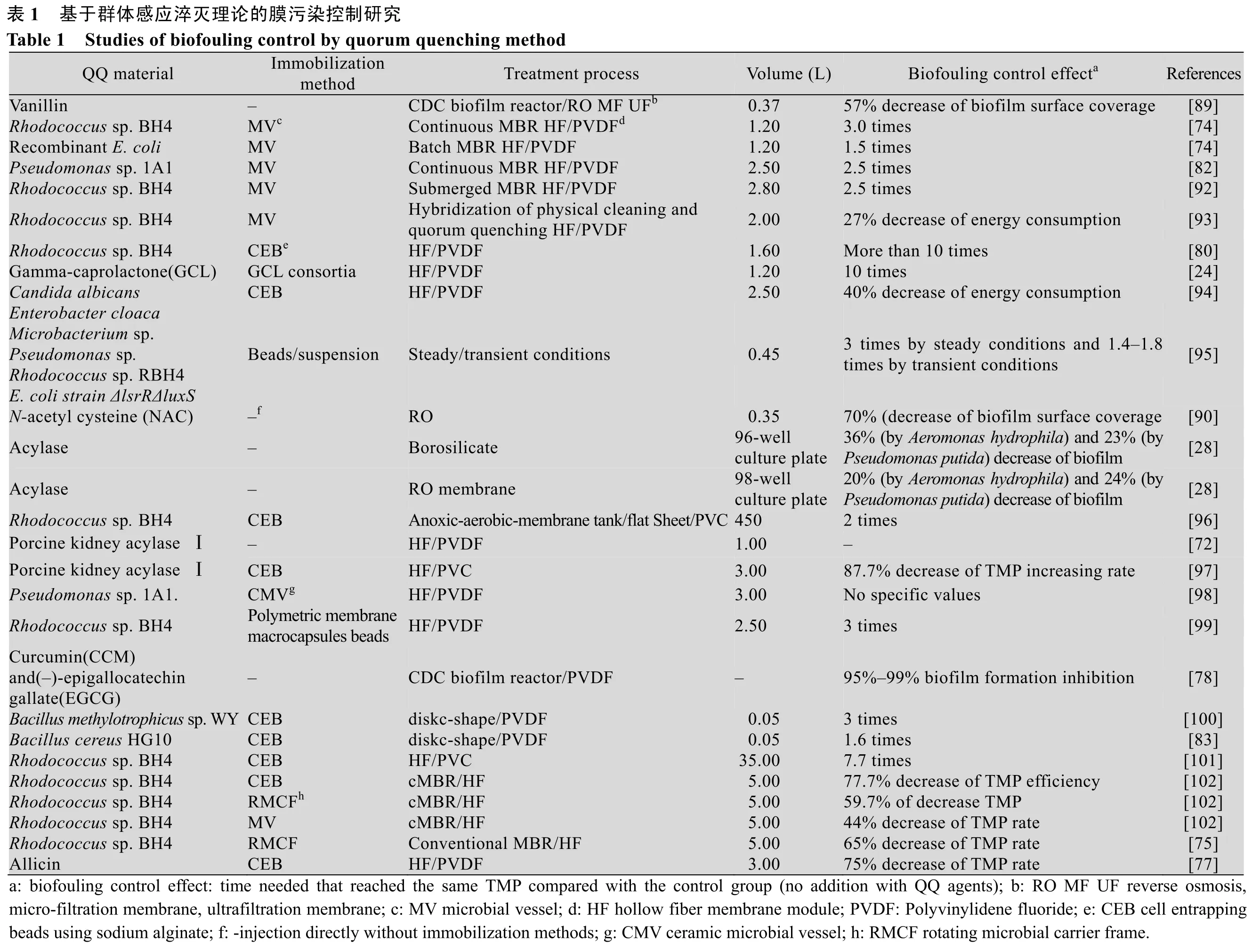
基于QQ对MBR膜污染防治的研究汇总见表1。上述3个研究方向均可以对MBR膜污染产生一定程度的效果,其中采用QQ酶是该领域最开始采取的方法,而存活率更高和保存更为容易的QQ菌进行膜污染防治成本低且效率更高,不会对原系统出水水质造成影响,是近几年膜污染生物防治采用的主要研究方法之一[91]。
3 总结与展望
近几年,基于Lux型的群体感应系统干预的生物被膜调控在污水处理中的研究得到了越来越广泛的关注。群体感应的正向强化作用可实现污水处理的快速挂膜和启动,但关于AHLs信号分子在挂膜材料表面或活性污泥表面的迁移运动及作用过程的探究仍处于相对空缺阶段。群体感应系统负向削弱作用有望从根本上解决 MBR膜污染问题,但目前应用于膜污染防治的群体感应淬灭菌分解信号分子AHLs的种类有限,在不同污水环境中,对膜污染的防治效果仍处于探索阶段[24,80,82,100]。
基于群体感应系统干预在污水处理中的相关问题已取得了一定的成绩,然而许多方向有待进一步探究,主要体现在如下几个方面。
1)AHL结构特征机理探究:生物被膜污水处理过程中参与生物被膜形成过程的AHLs信号分子种类繁多,不同AHLs之间的调控机制也不尽相同,更深入地了解AHL的结构特征,对AHLs定量和定性分析,从而更高效地提高污水处理效率,仍是群体感应机理在污水处理中应用的重要研究内容之一。
2)群体感应淬灭菌的固定化技术与应用:群体感应淬灭菌在防治膜污染方面效果显著,固定化微生物可以使 QQ菌在某一固定区域发挥其高效作用,提高处理过程的效率;但不同的固定化技术各有利弊,如利用海藻酸钠固定包埋法固定QQ菌,包埋珠内部细菌因缺少氧气,共聚焦激光扫描电镜(Confocal laser scanning microscopy,CLSM)图像显示存活率几乎为零[80],而中空纤维膜管式包埋方法对于中段的QQ菌而言,会因缺少与周围环境的物质交换,分解信号分子的效率很低[98,103]。如何在不破坏QQ菌生物活性的前提下设计出高效的微生物固定技术,以提高其防治膜污染的效果,是现阶段QQ技术在MBR膜污染防治方面需要研究的主要问题。
3)多种防治膜污染方法的协同效果验证:膜污染是生物污染和非生物污染协同作用的结果,群体感应干预系统只是从微生物的角度对膜污染进行干预和调控,在实际的污水处理工程运用中,应总结无机离子、有机分子、运行条件、操作方式等多种条件对膜污染的影响,如反冲洗的频率、出水方式的设置、膜通量大小的设置等[93,104],探讨如何应用物理方法和化学法等其他防治膜污染的方法与QS干预相结合,以实现污水处理成本最小化、效益最大化。
4)Lux型群体感应系统干预在更多污水处理领域的可行性验证:目前群体感应对生物被膜的负向削弱调控(群体感应淬灭)在污水处理方面的应用研究尚刚起步,大部分的研究仅限于MBR这一种污水处理模式,且大多为生活污水或人工自配污水,不同污水类型的处理,如高浓度有机废水(垃圾渗滤液)、高危废水(工业废水、医疗废水)等的适用性尚待研究和探讨,在不同污水环境中,对膜污染的防治效果仍处于探索阶段。后期可结合该方法在不同工艺、不同处理水质条件汇中的效果验证,扩展该技术在环保领域更多方面的应用。
[1]Siddiqui MF, Rzechowicz M, Harvey W, et al.Quorum sensing based membrane biofouling control for water treatment: a review.J Water Process Eng,2015,7:112–122.
[2]Nealson KH, Platt T, Hastings JW.Cellular controlof the synthesis and activity of the bacterial luminescent system.J Bacteriol,1970,104(1):313–322.
[3]Zhang HF, Sun MY, Yu HH.Research progress of the AHL-QS mitigation membrane fouling in membrane bioreactor.Chem Ind Eng Prog,2014,33(5):1300–1305(in Chinese).张海丰, 孙明媛, 于海欢.AHL-QS减缓膜生物反应器膜污染研究进展.化工进展,2014,33(5):1300–1305.
[4]Kalia VC.Quorum sensing inhibitors: an overview.Biotechnol Adv,2013,31(2):224–245.
[5]Xu F, Song XN, Cai PJ, et al.Quantitative determination of AI-2 quorum-sensing signal of bacteria using high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.J Environ Sci,2016,52:204–209.
[6]Papenfort K, Bassler BL.Quorum sensing signal-response systems in Gram-negative bacteria.Nat Rev Microbiol,2016,14(9):576–588.
[7]Wang TL, Guan W, Huang Q, et al.Quorum-sensing contributes to virulence, twitching motility, seed attachment and biofilm formation in the wild type strain Aac-5 ofAcidovorax citrulli.Microb Pathog,2016,100:133–140.
[8]Yang Q, Defoirdt T.Quorum sensing positively regulates flagellar motility in pathogenicVibrio harveyi.Environ Microbiol,2015,17(4):960–968.
[9]Rein M, Heinß N, Schmid F, et al.Collective behavior of quorum-sensing run-and-tumble particles under confinement.Phys Rev Lett,2016,116(5):058102.
[10]Yong YC, Wu XY, Sun JZ, et al.Engineering quorum sensing signaling ofPseudomonasfor enhanced wastewater treatment and electricity harvest: a review.Chemosphere,2015,140:18–25.
[11]Zhang W, Li C.Exploiting quorum sensing interfering strategies in gram-negative bacteria for the enhancement of environmental applications.Front Microbiol,2016,6:1535.
[12]Zhou NY.Effects of environments on bacterial quorum sensing.Microbiol China,2015,42(2):436(in Chinese).周宁一.环境因素对细菌群体感应的影响.微生物学通报,2015,42(2):436.
[13]Huang JH, Shi YH, Zeng GM, et al.Acyl-homoserine lactone-based quorum sensing and quorum quenching hold promise to determine the performance of biological wastewater treatments: an overview.Chemosphere,2016,157:137–151.
[14]Lade H, Paul D, Kweon JH.N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing with special reference to use of quorum quenching bacteria in membrane biofouling control.Biomed Res Int,2014,2014:162584.
[15]Lade H, Paul D, Kweon JH.Quorum quenching mediated approaches for control of membrane biofouling.Int J Biol Sci,2014,10(5):550–565.
[16]Wagner M, Horn H.Optical coherence tomography in biofilm research: a comprehensive review.Biotechnol Bioeng,2017,114(7):1386–1402.
[17]Suto R, Ishimoto C, Chikyu M, et al.Anammox biofilm in activated sludge swine wastewater treatment plants.Chemosphere,2017,167:300–307.
[18]Bakaraki N, Chormey DS, Bakirdere S, et al.Development of a sensitive liquid-liquid extraction method for the determination ofN-butyryl-L-homoserine lactone produced in a submerged membrane bioreactor by gas chromatography mass spectrometry and deuterated anthracene as the internal standard.Anal Methods,2016,8(12):2660–2665.
[19]Morohoshi T, Okutsu N, Xie XN, et al.Identification of quorum-sensing signal molecules and a biosynthetic gene inAlicycliphilussp.isolated from activated sludge.Sensors,2016,16(8):1218
[20]Wang JF, Ding LL, Li K, et al.Development of an extraction method and LC-MS analysis forN-acylated-L-homoserine lactones(AHLs)in wastewater treatment biofilms.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci,2017,1041–1042:37–44.
[21]Davies DG, Parsek MR, Pearson JP, et al.The involvement of cell-to-cell signals in the development of a bacterial biofilm.Science,1998,280(5361):295–298.
[22]Nam AN, Kweon JH, Ryu JH, et al.Reduction of biofouling using vanillin as a quorum sensing inhibitory agent in membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment.Membr Water Treat,2015,6(3):189–203.
[23]Oh HS, Tan CH, Low JH, et al.Quorum quenching bacteria can be used to inhibit the biofouling of reverse osmosis membranes.Water Res,2017,112:29–37.
[24]Ye JY, Tan X, Lü B, et al.Bacterial quorum sensing system and its applycation in controlling membrane biofouling.Environ Engn,2013,31(S1):196–199(in Chinese).叶姜瑜, 谭旋, 吕冰, 等.细菌群体感应现象及其在控制膜生物污染中的应用.环境工程,2013,31(S1):196–199.
[25]Janus MM, Krom BP, Crielaard W, et al.Inhibition of maturation of dental biofilm and cariogenic properties: WO,038065.2016-03-17.
[26]Morohoshi T, Tokita K, Ito S, et al.Inhibition of quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria by alkylamine-modified cyclodextrins. J Biosci Bioeng,2013,116(2):175–179.
[27]Yu HR, Liang H, Qu FS, et al.Biofouling control by biostimulation of quorum-quenching bacteria in a membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment.Biotechnol Bioeng,2016,113(12):2624–2632.
[28]Paul D, Kim YS, Ponnusamy K, et al.Application of quorum quenching to inhibit biofilm formation.Environ Eng Sci,2009,26(8):1319–1324.
[29]Nasuno E, Suzuki T, Suzuki R, et al.Novel quorum quenching enzymes identified from draft genome ofRoseomonassp.TAS13.Genom Data,2017,12:22–23.
[30]Yeon KM, Lee CH, Kim J.Magnetic enzyme carrier for effective biofouling control in the membrane bioreactor based on enzymatic quorum quenching.Environ Sci Technol,2009,43(19):7403–7409.
[31]Grover N, Plaks JG, Summers SR, et al.Acylase-containing polyurethane coatings with anti-biofilm activity.Biotechnol Bioeng,2016,113(12):2535–2543.
[32]Hu HZ, He JG, Liu J, et al.Biofilm activity and sludge characteristics affected by exogenousN-acyl homoserine lactones in biofilm reactors.Bioresour Technol,2016,211:339–347.
[33]Shrout JD, Nerenberg R.Monitoring bacterial twitter: does quorum sensing determine the behavior of water and wastewater treatment biofilms?Environ Sci Technol,2012,46(4):1995–2005.
[34]Feng L, Wu ZY, Yu X.Quorum sensing in water and wastewater treatment biofilms.J Environ Biol,2013,34(S2):437–444.
[35]Flemming HC, Wingender J.The biofilm matrix.Nat Rev Microbiol,2010,8(9):623–633.
[36]Bassler BL, Losick R.Bacterially speaking.Cell,2006,125(2):237–246.
[37]Mumford R, Friman VP.Bacterial competition and quorum-sensing signalling shape the eco-evolutionary outcomes of modelinvitrophage therapy.Evol Appl,2017,10(2):161–169.
[38]Parsek MR, Greenberg EP.Sociomicrobiology: the connections between quorum sensing and biofilms.Trends Microbiol,2005,13(1):27–33.
[39]Hancock LE, Perego M.TheEnterococcusfaecalisfsr two-component system controls biofilm development through production of gelatinase.J Bacteriol,2004,186(17):5629–5639.
[40]Davey ME, O’toole GA.Microbial biofilms: from ecology to molecular genetics.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev,2000,64(4):847–867.
[41]de Clippeleir H, Defoirdt T, Vanhaecke L, et al.Long-chain acylhomoserine lactones increase the anoxic ammonium oxidation rate in an OLAND biofilm.Appl Microbiol Biot,2011,90(4):1511–1519.
[42]Sun J.Study on quorum sensing of biofilm treatment in aquaculture wastewater[D].Qingdao:Ocean University of China,2012(in Chinese).孙颉.生物膜法养殖污水处理中群体感应现象的初步研究[D].青岛: 中国海洋大学,2012.
[43]Lynch MJ, Swift S, Kirke DF, et al.The regulation of biofilm development by quorum sensing inAeromonashydrophila.Environ Microbiol,2002,4(1):18–28.
[44]Steidle A, Allesen-Holm M, Riedel K, et al.Identification and characterization of ann-acyl homoserine lactone-dependent quorum-sensing system inPseudomonasputidastrain IsoF.Appl Environ Microb,2002,68(12):6371–6382.
[45]Labbate M, Queck SY, Koh KS, et al.Quorum sensing-controlled biofilm development inSerratia liquefaciensMG1.J Bacteriol,2004,186(3):692–698.
[46]Mayhew M, Stephenson T.Low biomass yield activated sludge: a review.Environ Technol,1997,18(9):883–892.
[47]Liu Y, Fang HHP.Influences of extracellular polymeric substances(EPS)on flocculation,settling, and dewatering of activated sludge.Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol,2003,33(3):237–273.
[48]Ding ZJ, Bourven I, Guibaud G, et al.Role of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)production in bioaggregation: application to wastewater treatment.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,2015,99(23):9883–9905.
[49]Chen R, Nie YL, Hu YS, et al.Fouling behaviour of soluble microbial products and extracellular polymeric substances in a submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor treating low-strength wastewater at room temperature.J Membr Sci,2017,531:1–9.
[50]Shi YH, Huang JH, Zeng GM, et al.Exploiting extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)controlling strategies for performance enhancement of biological wastewater treatments: an overview.Chemosphere,2017,180:396–411.
[51]Wang ZW, Wu ZC, Tang SJ, et al.Role of EPS in membrane fouling of a submerged anaerobic-anoxic-oxic (A-A-O) membrane bioreactor for municipal wastewater treatment.Desalin Water Treat,2011,34(1/3):88–93.
[52]Chong G, Kimyon O, Rice SA, et al.The presence and role of bacterial quorum sensing in activated sludge.Microb Biotechnol,2012,5(5):621–633.
[53]Morgan-Sagastume F, Boon N, Dobbelaere S, et al.Production of acylated homoserine lactones byAeromonasandPseudomonasstrains isolated from municipal activated sludge.Can J Microbiol,2005,51(11):924–933.
[54]Valle A, Bailey MJ, Whiteley AS, et al.N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones (AHLs) affect microbial community composition and function in activated sludge.Environ Microbiol,2004,6(4):424–433.
[55]Liu JR, Nguyen D, Paice M.Aerobic granule formation in a sequencing batch reactor treating newsprint effluent under low phosphate conditions.Water Sci Technol,2010,62(11):2571–2578.
[56]Li YC, Lü JP, Zhong C, et al.Performance and role ofN-acyl-homoserine lactone(AHL)-based quorum sensing(QS)in aerobic granules.J Environ Sci,2014,26(8):1615–1621.
[57]Lv JP, Wang YQ, Zhong C, et al.The effect of quorum sensing and extracellular proteins on the microbial attachment of aerobic granular activated sludge.Bioresour Technol,2014,152:53–58.
[58]Xiong XQ, Liao HD, Ma JS, et al.Isolation of a rice endophytic bacterium,Pantoeasp.Sd-1, with ligninolytic activity and characterization of its rice straw degradation ability.Lett Appl Microbiol,2014,58(2):123–129.
[59]Ni SQ, Sun N, Yang HL, et al.Distribution of extracellular polymeric substances in anammox granules and their important roles during anammox granulation.Biochem Eng J,2015,101:126–133.
[60]Xing C, Liu YJ, Yang YQ, et al.Spatial distribution characteristics of different EPS components in granular sludge under the strengthening granulation condition.Environ Sci Technol,2016,39(7):23–27(in Chinese).邢超, 刘永军, 杨月乔, 等.强化造粒条件下颗粒污泥中EPS不同组分的空间分布特征.环境科学与技术,2016,39(7):23–27.
[61]Lü JP, Wang YQ, Zhong C, et al.The microbial attachment potential and quorum sensing measurement of aerobic granular activated sludge and flocculent activated sludge.Bioresour Technol,2014,151:291–296.
[62]Tan CH, Koh KS, Xie C, et al.The role of quorum sensing signalling in EPS production and theassembly of a sludge community into aerobic granules.ISME J,2014,8(6):1186–1197.
[63]Xi LJ, Lü N, Zhang HF, et al.Analysis of formation and degradation mechanism of soluble microbial product and its effect on membrane filterability for membrane bioreactor.J Chem Ind Eng,2013,64(8):3003–3008(in Chinese).郗丽娟, 吕娜, 张海丰, 等.SMP形成与降解机制分析及其对MBR膜过滤的影响.化工学报,2013,64(8):3003–3008.
[64]Defrance L, Jaffrin MY, Gupta B, et al.Contribution of various constituents of activated sludge to membrane bioreactor fouling.Bioresour Technol,2000,73(2):105–112.
[65]Yu D.Impact analysis of quorum sensing(QS)on membrane fouling of MBR[D].Shenyang: Liaoning University,2016(in Chinese).于多.群体感应(QS)对MBR膜污染影响分析[D].沈阳: 辽宁大学,2016.
[66]Yu R, Feng L, Song P, et al.Isolation and identification of a dominant strain from membrane fouling layer and its characteristics of quorum sensing.J Beihua Univ: Nat Sci,2015,16(6):803–808(in Chinese).余蓉, 封磊, 宋萍, 等.一株具有群体感应的膜污染层优势菌分离鉴定.北华大学学报: 自然科学版,2015,16(6):803–808.
[67]Meng FG, Chae SR, Shin HS, et al.Recent advances in membrane bioreactors: configuration development, pollutant elimination, and sludge reduction.Environ Eng Sci,2012,29(3):139–160.
[68]Jo SJ, Kwon H, Jeong SY, et al.Effects of quorum quenching on the microbial community of biofilm in an anoxic/oxic mbr for wastewater treatment.J Microbiol Biotechnol,2016,26(9):1593–1604.
[69]Karkhanechi H, Takagi R, Matsuyama H.Biofouling resistance of reverse osmosis membrane modified with polydopamine.Desalination,2014,336:87–96.
[70]Sun YM, Fang YY, Liang P, et al.Effects of online chemical cleaning on removing biofouling and resilient microbes in a pilot membrane bioreactor.Int Biodeter Biodegr,2016,112:119–127.
[71]Cai WW, Liu Y.Enhanced membrane biofouling potential by on-line chemical cleaning in membrane bioreactor.J Membr Sci,2016,511:84–91.
[72]Yeon KM, Cheong WS, Oh HS, et al.Quorum sensing: a new biofouling control paradigm in a membrane bioreactor for advanced wastewater treatment.Environ Sci Technol,2009,43(2):380–385.
[73]Lee B, Yeon KM, Shim J, et al.Effective antifouling using quorum-quenching acylase stabilized in magnetically-separable mesoporous silica.Biomacromolecules,2014,15(4):1153–1159.
[74]Oh HS, Yeon KM, Yang CS, et al.Control of membrane biofouling in MBR for wastewater treatment by quorum quenching bacteria encapsulated in microporous membrane.Environ Sci Technol,2012,46(9):4877–4884.
[75]Ergön-Can T, Köse-Mutlu B, Koyuncu İ, et al.Biofouling control based on bacterial quorum quenching with a new application: rotary microbial carrier frame.J Membr Sci,2017,525:116–124.
[76]Zhang JM, Rui X, Wang L, et al.Polyphenolic extract fromRosarugosatea inhibits bacterial quorum sensing and biofilm formation.Food Control,2014,42:125–131.
[77]Zhang HF, Yu HH, Sun MY.Influences of allicin entrapping beads on mixed liquor filterability in membrane bioreactor.Chemistry,2016,79(2):170–174(in Chinese).张海丰, 于海欢, 孙明媛.大蒜素包埋球对膜生物反应器混合液可滤性影响解析.化学通报,2016,79(2):170–174.
[78]Lade H, Paul D, Kweon JH.Combined effects of curcumin and(-)-epigallocatechin gallate on inhibition ofN-acylhomoserine lactone-mediated biofilm formation in wastewater bacteria from membrane bioreactor.J Microbiol Biotechnol,2015,25(11):1908–1919.
[79]Kim JH, Choi DC, Yeon KM, et al.Enzyme-immobilized nanofiltration membrane to mitigate biofouling based on quorum quenching.Environ Sci Technol,2011,45(4):1601–1607.
[80]Kim SR, Oh HS, Jo SJ, et al.Biofouling controlwith bead-entrapped quorum quenching bacteria in membrane bioreactors: physical and biological effects.Environ Sci Technol,2013,47(2):836–842.
[81]Oh HS, Kim SR, Cheong WS, et al.Biofouling inhibition in MBR byRhodococcussp.BH4 isolated from real MBR plant.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,2013,97(23):10223–10231.
[82]Cheong WS, Lee CH, Moon YH, et al.Isolation and identification of indigenous quorum quenching bacteria,Pseudomonassp.1A1, for biofouling control in MBR.Ind Eng Chem Res,2013,52(31):10554–10560.
[83]Zhao C, Wang WZ, Xu QY.Isolation of quorum quenching bacteria and their function for controlling membrane biofouling.Environ Sci,2016,37(12):4720–4726(in Chinese).赵畅, 王文昭, 徐期勇.群体感应淬灭菌的分离及其膜污染控制性能.环境科学,2016,37(12):4720–4726.
[84]Wahman S, Emara M, Shawky RM, et al.Inhibition of quorum sensing-mediated biofilm formation inPseudomonasaeruginosaby a locally isolatedBacilluscereus.J Basic Microb,2015,55(12):1406–1416.
[85]Jia SF, Yang YX, Huang ZY, et al.Study on multiple functional mixed microbes for treating municipal sewage.Environ Sci,2000,21(3):81–84(in Chinese).贾省芬, 杨彦希, 黄志勇, 等.处理城市污水的多功能混合菌研究.环境科学,2000,21(3):81–84.
[86]Xie B, Xiong SZ, Liang SB, et al.Performance and bacterial compositions of aged refuse reactors treating mature landfill leachate.Bioresour Technol,2012,103(1):71–77.
[87]Kalia VC, Purohit HJ.Quenching the quorum sensing system: potential antibacterial drug targets.Crit Rev Microbiol,2011,37(2):121–140.
[88]Ponnusamy K, Paul D, Jihyang K.Inhibition of quorum sensing mechanism andAeromonas hydrophilabiofilm formation by Vanillin.Environ Eng Sci,2009,26(8):1359–1363.
[89]Ponnusamy K, Kappachery S, Thekeettle M, et al.Anti-biofouling property of vanillin onAeromonashydrophilainitial biofilm on various membrane surfaces.World J Microbiol Biotechnol,2013,29(9):1695–1703.
[90]Kappachery S, Paul D, Kweon JH.Effect ofN-acetylcysteine against biofouling of reverse osmosis membrane.Desalination,2012,285:184–187.
[91]Kim AL, Park SY, Lee CH, et al.Quorum quenching bacteria isolated from the sludge of a wastewater treatment plant and their application for controlling biofilm formation. J Microbiol Biotechnol,2014,24(11):1574–1582.
[92]Jahangir D, Oh HS, Kim SR, et al.Specific location of encapsulated quorum quenching bacteria for biofouling control in an external submerged membrane bioreactor.J Membr Sci,2012,411–412:130–136.
[93]Weerasekara NA, Choo KH, Lee CH.Hybridization of physical cleaning and quorum quenching tominimize membrane biofouling and energy consumption in a membrane bioreactor.Water Res,2014,67:1–10.
[94]Lee K, Lee S, Lee SH, et al.Fungal Quorum Quenching: A paradigm shift for energy savings in membrane bioreactor(MBR)for wastewater treatment.Environ Sci Technol,2016.50:10914–10922.
[95]Waheed H, Xiao Y, Hashmi I, et al.Insights into quorum quenching mechanisms to control membrane biofouling under changing organic loading rates.Chemosphere,2017.182:40–47.
[96]Lee S, Park SK, Kwon H, et al.Crossing the border between laboratory and field: bacterial quorum quenching for anti-biofouling strategy in an MBR.Environ Sci Technol,2016,50(4):1788–1795.
[97]Jiang W, Xia SQ, Liang J, et al.Effect of quorum quenching on the reactor performance, biofouling and biomass characteristics in membrane bioreactors.Water Res,2013,47(1):187–196.
[98]Cheong WS, Kim SR, Oh HS, et al.Design of quorum quenching microbial vessel to enhance cell viability for biofouling control in membrane bioreactor.J Microbiol Biotechnol,2014,24(1):97–105.
[99]Kim SR, Lee KB, Kim JE, et al.Macroencapsulation of quorum quenching bacteria by polymeric membrane layer and its application to MBR for biofouling control.J Membr Sci,2015,473:109–117.
[100]Khan R, Shen F, Khan K, et al.Biofouling control in a membrane filtration system by a newly isolated novel quorum quenching bacterium,Bacillus methylotrophicussp.WY.RSC Adv,2016,6(34):28895–28903.
[101]Maqbool T, Khan SJ, Waheed H, et al.Membrane biofouling retardation and improved sludge characteristics using quorum quenching bacteria in submerged membrane bioreactor.J Membr Sci,2015,483:75–83.
[102]Köse-Mutlu B, Ergön-Can T, Koyuncu I, et al.Quorum quenching MBR operations for biofouling control under different operation conditions and using different immobilization media.Desalin Water Treat,2016,57(38):17696–17706.
[103]Christiaen SEA, Brackman G, Nelis HJ, et al.Isolation and identification of quorum quenching bacteria from environmental samples.J Microbiol Meth,2011,87(2):213–219.
[104]Nahm CH, Choi DC, Kwon H, et al.Application of quorum quenching bacteria entrapping sheets to enhance biofouling control in a membrane bioreactor with a hollow fiber module.J Membr Sci,2017,526:264–271.
(本文责编 郝丽芳)
Wastewater treatment based on biofilm regulation by Lux type quorum sensing system–a review
Chang Zhao1, Ning Wang1, Wenzhao Wang1,2, and Qiyong Xu1
1School of Environment and Energy,Shenzhen Graduate School,Peking University,Shenzhen518055,Guangdong,China
2Fairylands Environmental Sci-Tech.(Shenzhen)Go.,Ltd.,Shenzhen518055,Guangdong,China
Studies on biofilm regulation based on Lux type quorum sensing system in wastewater treatment have attractedmuch attention.The intervention of quorum sensing system includes both mechanisms of positive and negative control.The positive invigorating effect improves the efficiency of biofilm wastewater treatment, promotes the production of extracellular polymeric substance(EPS)and soluble microbial products(SMP), and increases the yield of biofilm.The negative weakening effect of quorum sensing can decompose the signal molecules needed in the process of biofilm formation, interrupts the gene expression process of biofilm formation, and inhibits the formation of biofilm on MBR membrane surface effectively.The further study of the structure and mechanism ofN-acyl homoserine lactone(AHLs), the immobilization technology and application of quorum quenching bacteria, the synergistic effect verification of different biofouling control methods and the application feasibility of quorum sensing system based technology in more wastewater treatment fields are the next important researches to explore.
quorum sensing, quorum quenching, wastewater treatment, biofilm
April18,2017;Accepted:June20,2017
Wenzhao Wang.Tel: +86-755-26033226; E-mail: wangwz@pkusz.edu.cn

赵畅, 王宁, 王文昭, 等.基于Lux型群体感应系统干预的生物被膜调控在污水处理中的研究进展与前景.生物工程学报,2017,33(9):1596–1610.
Zhao C, Wang N, Wang WZ, et al.Wastewater treatment based on biofilm regulation by Lux type quorum sensing system–a review.Chin J Biotech,2017,33(9):1596–1610.
Supported by:Science and Technology Project of Shenzhen(Nos.JCYJ20150626110817181, CXZZ20151117141320317).
深圳市科技计划项目(Nos.JCYJ20150626110817181, CXZZ20151117141320317)资助。
时间:2017-08-10
http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1998.Q.20170810.0959.001.html
王文昭 日本宇都宫大学环境微生物学博士,美国宾夕法尼亚州立大学博士后,现在北京大学深圳研究生院环境与能源学院博士后流动站工作。主持多项国家、省级科研项目。长期从事生物膜及细菌群体感应和群体感应淬灭等方面相关研究,在国际期刊发表高水平学术文章10余篇,被引逾百次;受邀赴日本、美国、欧洲等国家和地区参加著名国际会议12次。解析了群体感应系统对绿针假单胞菌抗生素生产调控的机制,发现并鉴定了AiiM和AidC两种新型群体感应信号分子分解酶。
