SHOULDERING RESPONSIBILITY
2017-10-22ByXuHongcai
By+Xu+Hongcai

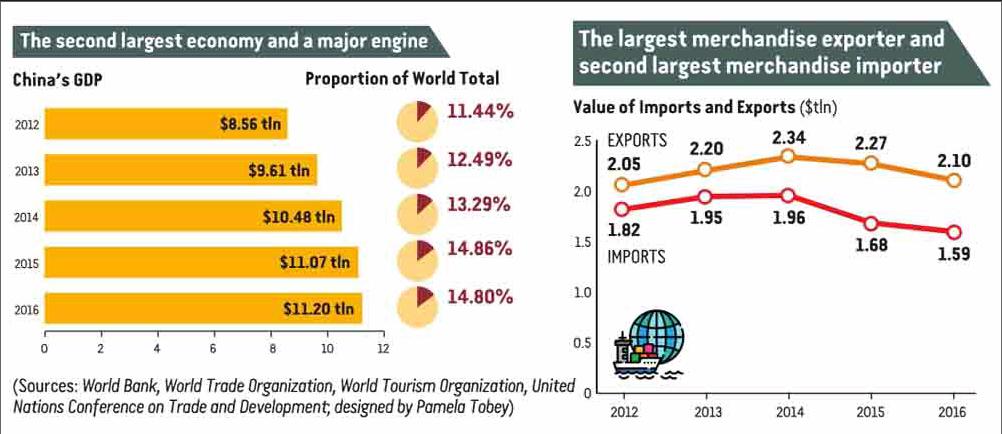
From the macro perspective of economic size and growth speed, China is the worlds second largest economy, with its GDP growing 6.7 percent and reaching $11 trillion last year. It contributed more than 34 percent to the worlds gross value added in 2016.
Specifi cally, Chinas ongoing poverty reduction campaign contributes greatly to the world. During the 13th Five-Year Plan (2016-20) period, China has pledged to lift 70 million people out of poverty. With the governments various targeted policies, the poor will be employed, with increased income and improved welfare. As China is an important part of the global community, addressing Chinas challenges, most notably poverty, means solving a large part of the worlds problems and contributing to humanity.
Chinas goal is to double its 2010 GDP and per-capita income of residents and achieve a moderately prosperous society in all aspects by 2020. This means poverty should be eliminated. No one can be left behind.
Despite a slight deceleration in GDP growth in recent years, the income of Chinese is increasing and their welfare is improving. As President Xi Jinping has said, reform should strengthen peoples sense of gain. Thats the philosophy of Xis governance.
Economic progress
Economic transformation and the new type of urbanization since the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China(CPC) in 2012 has increased and will continue to increase residents income. Their diversified consumption demands have led to an expansion in imports from other countries. During the past five years, China has seen average annual imports of nearly $2 trillion.
As income rises, Chinas consumption pattern is transitioning from a traditional focus on housing and cars to tourism, cultural activities, information, health services, etc. More than 100 million overseas trips have been made by Chinese tourists annually during the past five years and their spending, ranked fi rst in the world, has contributed to the world economic growth.
Chinas urbanization aims to transform several hundred million farmers into urban residents. Such a huge social transformation will lead to income growth as well as a boom in infrastructure construction and consumption. By 2020, China will have a middle class of 600 million people, which means a huge consumption market and a surge in imports.
China has also become a large investing country, with its non-fi nancial outbound direct investment exceeding $170 billion in 2016, which has helped the host countries create jobs, improve infrastructure and increase tax revenue.endprint
Facing a slowdown in economic growth in recent years, Chinas leadership has made a rational judgment on the trend. It calls it an economic “new normal,” which features a slowing growth rate, improving economic structure and a shift of growth engines from production and investment to services and innovation.
This judgment is based on the fact that the old growth model led by investment and exports, which relies mainly on an increase in the supply of factors of production, is no longer sustainable. Therefore, China must change its growth engines to consumption and innovation. By cultivating new growth drivers through mass entrepreneurship and innovation, this form of development has become a national strategy.
The Third Plenary Session of the 18th CPC Central Committee held in November 2013 issued a blueprint for economic reform, making it clear that the market will play a decisive role in resource allocation and the government should transform its functions. All the ensuing reforms are sticking to this principle.
Therefore, although economic growth has decelerated in recent years, the efficiency and quality of economic growth have been improving. This is a result of the ongoing supply-side structural reform, which focuses on improving the quality and efficiency of the supply side. Economic structure has also been improved. The service industrys contribution to Chinas GDP has reached 55 percent. Consumption has contributed more than 60 percent to GDP growth. Meanwhile, energy consumption per unit of GDP has been dropping and China is moving up the global value chain.
“Making progress while maintaining stability” is not only a principle of Chinas economic work, but has also become a methodology in governing the countrys economy.
Enhanced quality of economic growth also means the efforts in coping with climate change, reducing resources consumption and carbon dioxide emissions, and protecting the environment have paid off, which are also contributions China has made to the international community.
China is still a developing country. It has a long way to go to realize its industrialization, informatization, urbanization and agricultural modernization. Meanwhile, its population is aging, the old growth engines are losing steam and the new engines are still in the early stages of formation. China must push forward various reforms to bring the most benefits to the people.endprint
Role in global governance
Chinas major contribution to global governance during the past five years is the Silk Road Economic Belt and 21st-Century Maritime Silk Road (Belt and Road) Initiative proposed by Xi in 2013. Against the backdrop of rising trade and investment protectionism and declining growth momentum in the world, Xi put forward the initiative, which is Chinas solution to economic globalization. It is based on the principles of extensive consultation, joint contributions and shared benefits.
When participating in global governance, China always works within the framework of the UN and seeks a synergy between its own development policies and those of other countries. This provides an open, inclusive solution that makes the pie of the global economy bigger.
Chinas contribution to global governance has two aspects:
Theoretically, it has proposed the concept of a human community with shared destiny, the Silk Road Spirit of peace and cooperation, openness and inclusiveness, mutual learning and mutual benefits, and the Belt and Road Initiative.
In practice, it has been participating in different levels of international cooperation to improve global governance. China has ratified and pledged to strictly implement the Paris Agreement on climate change. Chinas development targets in its 13th FiveYear Plan voluntarily accord with the goals of the UNs 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. As the host country of the G20 Summit in 2016, China defended globalization, insisted on fighting protectionism, and urged G20 members to start implementing the UNs sustainable development goals.
This years Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation and BRICS Summit, held in May and September respectively, focused on the major concerns of developing countries, such as poverty reduction in African countries, industrialization and urbanization of less developed countries and South-South cooperation. All these are among the UN goals. China is sparing no effort in strengthening South-South cooperation and fighting protectionist activities in order to promote the creation of a more fair and inclusive global governance system.
At the G20 platform, China is strengthening policy coordination with other members, promoting trade and investment facilitation, and developing a new economy in order to promote the sustainable growth of the global economy.
Whereas in the past China only participated in global governance, it has now become a leader in some aspects. It has provided solutions, put forward proposals and interacted with the international community. Thats the responsible role of a major economy.
As Xi said during his speech at the opening of the Belt and Road Forum on May 14, “Deficit in peace, development and governance poses a daunting challenge to mankind.” China is responsible in making up for these deficits.
China has moved to the center of the world stage, attracting the worlds attention, and it will not shun its responsibilities.
While hoping to have a peaceful environment, China is further opening its market to the world. It has set up free trade zones and continued shortening its “negative list”—a list of sectors in which foreign investment is not permitted—to expand access to the Chinese market for foreign investors.endprint
