联合检测血清CYFRA21-1和SCC-Ag水平在诊断食管癌中的应用价值
2017-09-15贺旭东
贺旭东
·论著·
联合检测血清CYFRA21-1和SCC-Ag水平在诊断食管癌中的应用价值
贺旭东
目的分析联合检测血清CYFRA21-1、SCC-Ag水平在诊断食管癌中的应用价值。方法随机选取2014年7月至2016年7月肿瘤内科和消化内科就诊的食管癌患者874例为研究对象(试验组),同时期健康体检者874例为对照组,分别采集试验患者空腹5.0 ml静脉血,检测血清中细胞角蛋白19片段抗原(CYRRA21-1)和鱗状细胞癌相关抗原(SCC-Ag)的含量水平,应用SPSS 20.0统计软件进行分析。结果(1)试验组CYRRA21-1高于对照组(38.19±49.75,4.86±2.79),试验组SCC-Ag高于对照组(28.77±52.26,2.05±1.83),2组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。(2)CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag在不同分化程度之间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。(3)CYRRA21-1在试验组中的阳性率为79.75%,SCC-Ag在试验组中的阳性率为74.83%。(4)ROC曲线分析显示,CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag的联合检测对诊断食管癌具有一定的指导意义,可以提高诊断的阳性率,特异性为100%。结论细胞分化程度与血清CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag含量水平无必然联系,联合诊断血清CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag含量水平,有助于提高食管癌的诊断率,具有一定的应用价值。
细胞角蛋白19片段抗原;鱗状细胞癌相关抗原;食管癌
食管腺癌是食管腺体发生的恶性肿瘤,其危险因素有吸烟、胃食管反流、肥胖、遗传易感性等[1]。我国大概超过95%属于鳞状细胞癌,欧美国家大多数是腺癌[2]。根据社会调查结果显示,在农村存在食管癌的人数要比城市多,并且男性占大多数[3]。食管癌早期没有很明显的症状所以导致一般检查到食管癌的时候已经发展到中后期,这时再进行手术之后只有13%~22%能够多生存6年[4]。临床上检测癌症主要通过肿瘤标志物,使用方便、快速、经济,并且某些肿瘤标志物的灵敏度非常高,在疾病开始的时候就能够被检测到,而且整个发病到结束都能通过其进行监测。鳞状细胞癌相关抗原(squamous cell carcinoma antigen,SCC-Ag)属于抗原,Kato等[5]在子宫癌的活检组织进行研究找到了一种鳞状细胞组织抗原TA-4。而且在其他发生在身体不同位置的鳞状细胞癌患者血液中都存在这种抗原[6]。细胞角蛋白19片段抗原(cytokeratin 192 fragments,CYFRA21-1)存在上皮细胞胞浆中的细胞角蛋白,在发生细胞癌变的过程中这种蛋白会死亡然后进入血液中,主要存在的是食管上皮和肺癌等的细胞胞浆中[7]。本文主要对联合检测血清CYFRA21-1、SCC-Ag水平在诊断食管癌中的应用价值进行研究,为临床治疗提供参考。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 随机选取2014年7月至2016年7月在我院肿瘤内科和消化内科就诊的食管癌患者874例研究对象为试验组,男562例,女312例;平均年龄(66.9±8.4)岁;按临床分期Ⅲ~Ⅳ期,其中Ⅲ期532例,Ⅳ期342例,按病理结果可分为高分化280例,中分化392例,低分化202例,选取同时期健康体检者874例为对照组,男527例,347例;平均年龄(62.5±14.7)岁;2组性别比、年龄比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。
1.1.1 纳入标准:试验组:经电子胃镜及病理学诊断明确为食管鳞癌患者,年龄>18周岁,根据临床分期为Ⅲ~Ⅳ期,患者且均为初治未进行手术、放化疗及其他抗肿瘤治疗;对照组:年龄>18周岁,体质健康者,经过筛查已排除恶性肿瘤。
1.1.2 剔除标淮:食管组年龄<18周岁,既往行手术、放化疗或其他抗肿瘤治疗者,合并有严重心、脑、肺脏疾病,肝、肾功能不全及感染性疾病;对照姐年龄<18周岁,体质虚弱的老年人,妊娠或哺乳期女性。
1.2 研究方法 分别采集试验患者空腹5.0 ml静脉血,检测血清中CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag的含量水平。
1.3 观察指标 血清中CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag的含量水平。
1.4 质量控制 所有试验患者的血清样品均重复检测3次,取平均值,肿瘤标志物阳性界定值:CYRRA21-1:0~7 ng/ml,SCC-Ag:0~2.5 ng/ml。

2 结果
2.1 2组患者血清中CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag含量水平分析 通过对2组患者血清中CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag的含量水平进行比较分析,试验组CYRRA21-1高于对照组,试验组SCC-Ag高于对照组,2组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。见表1。

组别CYRRA21⁃1SCC⁃Ag试验组38.19±49.7528.77±52.26对照组4.86±2.792.05±1.83t值26.34724.951P值0.0020.001
2.2 试验组患者不同分化程度中CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag的含量水平分析 通过对试验组患者不同分化程度中CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag的含量水平进行比较分析,CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag在不同分化程度之间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表2。

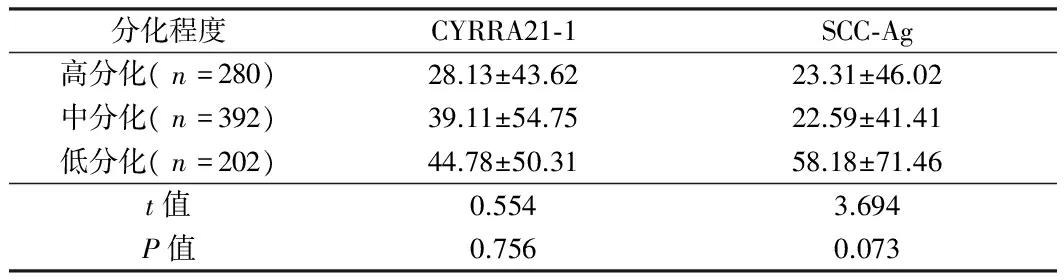
分化程度CYRRA21⁃1SCC⁃Ag高分化(n=280)28.13±43.6223.31±46.02中分化(n=392)39.11±54.7522.59±41.41低分化(n=202)44.78±50.3158.18±71.46t值0.5543.694P值0.7560.073
2.3 血清中CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag在试验组中阳性率分析 通过对血清中CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag在试验组的阳性率进行比较分析,CYRRA21-1在试验组中的阳性率为79.75%,SCC-Ag在试验组中的阳性率为74.83%。见表3。

表3 血清中CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag试验组中的阳性率比较 n=874
2.4 联合检测血清CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag水平在食管癌中的价值分析 通过建立ROC曲线对联合检测血清CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag水平在食管癌中的价值进行比较分析,CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag的联合检测对诊断食管癌具有一定的指导意义,可以提高诊断的阳性率,特异性为100%。见图1。

图1 联合检测血清CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag水平在食管癌中的价值
3 讨论
肿瘤是以细胞异常增生为特点的一类疾病,其发生并非单个分子事件,而是一个多因素参与、多途径、多步骤的复杂过程,是环境和遗传因素共同作用的结果[8]。肿瘤因为遗传因素的只有小部分,大部分的肿瘤患者发生细胞癌变主要还是因为生活习惯和生活环境导致的,比如缺乏微量元素、发生感染、生活不规律等[9,10]。利用肿瘤标志物进行监测不仅能在疾病从发生到结束实现动态监测,同时操作方便,费用较低,使其被广泛的用在临床,肿瘤标志物的种类有很多,包括酶、胚胎蛋A、癌基因蛋白等,起到监测食管癌的肿瘤标志物有CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag等。
Kato等[11,12]是鳞状上皮细胞抗原的最早发现者,他们是在宫颈鳞癌患者身上找到的,是现在首选的宫颈癌诊断标志物。鳞状上皮细胞抗原的含量直接关系着肿瘤TNM分期以及手术之后的恢复。在进行检测未进行治疗的时候,其表达越强烈患者越接近末期,也就是生命时长越短,它属于独立的高风险宫颈癌肿瘤标志物[13]。逐渐发现在其他如肺、食管等发生鳞状细胞癌变的地方也有SCC-Ag的表达,并且直接决定肿瘤的属性[14]。Jeffrey等[15]研究中检测到SCC-Ag存在的食管癌患者有73.8%,还有其他多名医者都对该标志物进行阳性率检测分析,国内外都没有一个统一的概率值,并且该值的波动很大,还有待进一步研究统一。研究显示食管鳞癌患者SCC-Ag的敏感度是26.7%。Ni等[16]研究发现肿瘤分期和SCC-Ag肿瘤标志物的分化程度有很大关系。肿瘤细胞分化越差,SCC-Ag表达就会越强烈,肿瘤的恶性程度就更深,所以我们认为在SCC-Ag的水平对反应肿瘤恶化程度以及分期有直接的指导作用。并且有在手术之后检测是否发生复发的价值。Lu等[17]研究发现,肿瘤的大小、是否发生转移等情况都和SCC-Ag的含量有正相关关系,可以作为食管鳞癌的诊断因子。
单克隆抗体(KS19.1)和(BM19.21)共同构成了能够判断出细胞角蛋白19(cyotkeratin19,CK19)片段的CYRRA21-1,它是首选的非小细胞肺癌的标志物。Ievleva[18]研究发现它在血清中的表达水平直接关系到非小细胞肺癌的分期以及预后。在早期对非小细胞肺癌进行诊断治疗有很重要的地位,并且它在整个非小细胞肺癌发生发展手术之后是否复发都有检测参考的价值。Senekjian等[19]在食管鳞癌的治疗中利用CYRRA21-1作为标志物,发现它能够将治疗反应很快的显示出来,因为它只有大概4 d的半衰期。Maniar等[20]研究发现49.2%的准确率存在食管癌患者中。本文研究结果显示,试验组CYRRA21-1高于对照组(38.19±49.75,4.86±2.79),试验组SCC-Ag高于对照组(28.77±52.26,2.05±1.83),2组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag在不同分化程度之间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),CYRRA21-1在试验组中的阳性率为79.75%,SCC-Ag在试验组中的阳性率为74.83%,ROC曲线分析显示,CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag的联合检测对诊断食管癌具有一定的指导意义,可以提高诊断的阳性率,特异性为100%。这说明CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag的联合检测对食管癌有一定诊断价值,多种肿瘤标志物联合对肿瘤情况进行检测会更加的快捷准确,能够避免出现单项标志物不敏感导致漏诊的风险,为早期诊断出食管癌进行及时的控制延长生命有一定的应用价值。
细胞分化程度与血清CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag含量水平无必然联系,联合诊断血清CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag含量水平,有助于提高食管癌的诊断率,具有一定的应用价值。
1 Kang DL,Hyoung SL,Sung WK,et al.Clinical significance of melanoma-associated antigen A1-6 expression in sputum of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx and hypopharynx.Head Neck,2016,5:38-44.
2 Heng W,Ning W,Yao Z,et al.Clinical significance of Wnt-11 and squamous cell carcinoma antigen expression in cervical cancer.Medical Oncology,2014,13:315-321.
3 Sun A,Chiang CP.Levamisole and/or Chinese medicinal herbs can modulate the serum level of squamous cell carcinoma associated antigen in patients with erosive oral lichen planus.J of Oral Pathol Med,2001,30:542-548.
4 Ohara K,Tanaka Y,Tsunoda H,et al.Assessment of cervical cancer radioresponse by serum squamous cell carcinoma antigen and magnetic resonance imaging.Obstet Gynecol,2002,100:781.
5 Kong Y,Gu C,Zhong D,et al.Celecoxib antagonizes the cytotoxicity of oxaliplatin in human esophageal cancer cells by impairing the drug influx.Eur J Pharm Sci,2016,81:137-148.
6 Shi H,Zhou S,Liu J,et al.miR-34a inhibits the in vitro cell proliferation and migration in human esophageal cancer.Pathol Res Prac,2016,212:444-449.
7 Andreas A,Matthias B,Mehran D,et al.Anastomotic Leak Predicts Diminished Long-Term Survival after Resection for Gastric and Esophageal Cancer.Surgery,2016,14:537-542.
8 Ge JS,Yang Jh,Chen CP,et al.Dermoscopic Characterization and Image Study of a Sister Mary Joseph Nodule in a Patient with Esophageal Cancer.Dermatologica Sinica,2016,17:217-224.
9 Xu YJ,Cheng CH,Lee JM,et al.Management of Malnutrition in Esophageal Cancer Patients.Journal of Cancer Research and Practice,2014,11:3264-3271.
10 Salvatici M,Achilarre MT,Sandri MT,et al.Squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCC-Ag) during follow-up of cervical cancer patients:Role in the early diagnosis of recurrence.Gynecologic Oncology,2016,142:115-119.
11 Hemmatzadeh K,Mohammadi H,Karimi M,et al.Differential role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis and treatment of Esophageal cancer.Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2016,4:375-382.
12 Torigoe M,Wu L,Song XX,et al.Ultrasensitive and visual detection of squamous cell carcinoma antigen based on a silver-enhanced sandwich immunoassay using nanocomposites.Sensors Actuators:Chemical,2016,9:836-841.
13 Shi H,Shi S,Wu Y,et al.Qigesan inhibits migration and invasion of esophageal cancer cells via inducing connexin expression and enhancing gap junction function.Cancer Letters,2016,18:4216-4223.
14 Wu L,Hu Y,Sha Y,et al.An “in-electrode”-type immunosensing strategy for the detection of squamous cell carcinoma antigen based on electrochemiluminescent AuNPs/g-C 3 N 4 nanocomposites.Talanta,2016,22:763-769.
15 Jeffrey V,Chen S,Bassetti MF,et al.Radiation Dose Escalation in Esophageal Cancer Revisited:Contemporary Analysis of the National Cancer Data Base,2004-2012.International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics,2016,42:2874-2883.
16 Ni S,Riedl KM,Schwartz SJ,et al.Efficacy comparison of lyophilized black raspberries and combination of celecoxib and PBIT in prevention of carcinogen-induced esophageal cancer in rats.Journal of Functional Foods,2016,25:1837-1842.
17 Lu J,Sun XD,Yang X,et al.Impact of PET/CT on radiation treatment in patients with esophageal cancer:A systematic review.Critical Reviews in Oncology Hematology,2016,24:107-114.
18 Ievleva ES,Ermoshina NV,Ageenko AI.Immunomorphological identification of an antigen associated with squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix uteri.Eksp Onkol,1988,10:33-35.
19 Senekjian EK,Young JM,Weiser PA,et al.An evaluation of squamous cell carcinoma antigen in patients with cervical squamous cell carcinoma.Gynecology,2014,17:1572-1580.
20 Maniar HS,Desai SA,Chiplunkar SV,et al.Modulation of tumour associated antigen expressed on human squamous cell carcinoma cell lines by recombinant interferon-alpha.European journal of cancer,1993,29:57-61.
ApplicationvalueofcombineddetectionofserumlevelsofCYFRA21-1withSCC-Agindiagnosisofesophagealcancer
HEXudong.
ClinicalLaboratoryCenter,AffiliatedHospitalofLiaoningTCMUniversity,Shenyang110032,China
ObjectiveTo analyze the application value of combined detection of serum levels of cell keratin 19 fragment antigen (CYRRA21-1) with squamous cell carcinoma associated antigen (SCC-Ag) in diagnosis of esophageal cancer.MethodsA total of 874 patients with esophageal cancer who were treated in our hospital from July 2014 to July 2016 were enrolled as trial group,at the same time, 874 healthy subjects were enrolled as control group.The serum levels of cytokeratin 19 fragment antigen (CYRRA21-1) and squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCC-Ag) were detected and compared between two groups.ResultsThe levels of CYRRA21-1 in trial group were higher than those in control group (38.19± 49.75 vs 4.86±2.79),and the levels of SCC-Ag in trial group were higher than those in control group (28.77±52.26 vs 2.05±1.83),there were significant differences between two groups (P<0.01). However there were no significant differences in CYRRA21-1和SCC-Ag among different differentiation degrees of tumor (P>0.05).The positive rate of CYRRA21-1 in trial group was 79.75%,and the positive rate of SCC-Ag in trial group was 74.83%.ROC curve analysis showed that the combined detection of CYRRA21-1 with SCC-Ag had a certain guidance significance in diagnosis of esophageal cancer,which could increase positive rate of diagnosis,with specificity being 100%.ConclusionThe cell differentiation degree is not necessarily correlated to serum levels of CYRRA21-1 and SCC-Ag,but combined detection of serum levels of CYRRA21-1 with SCC-Ag is helpful to improve diagnosis rate of esophageal cancer and has certain application value.
cell keratin 19 fragment antigen; squamous cell carcinoma associated antigen; esophageal cancer
110032 沈阳市,辽宁中医药大学附属医院临床检验中心
10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2017.19.002
R 735.1
A
1002-7386(2017)19-2890-04
2017-04-18)
