基于MLNNI法的正交各向异性复合材料参数识别的逆算法
2017-08-28杨小娟田万鹏熊勇刚
杨小娟+田万鹏+熊勇刚
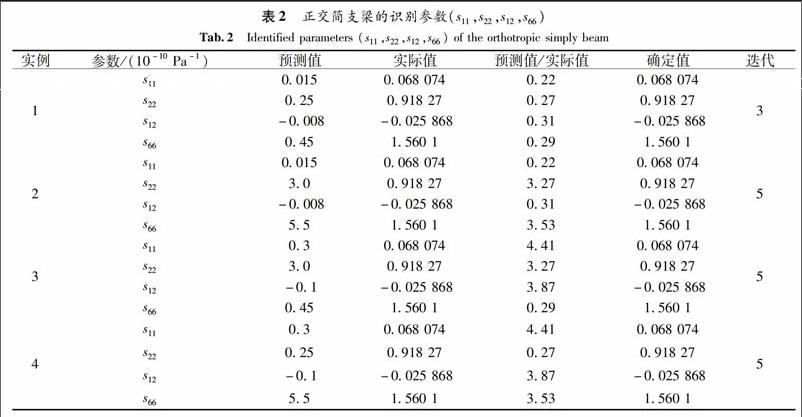


摘 要 为有效确定二维各向异性材料的材料参数,提出一种基于无网格局部自然邻近插值法(MLNNI)的识别方法.该方法只需在目标域上构建节点数组.而其逆问题即求解以模拟数值和实测数据之间偏差为目标函数的最小值,并采用复变函数微分法(CVDM)计算用于获取新的参数的灵敏度系数.区别于有限差分法,复变函数微分法对步长大小不敏感,而且若步长足够小,灵敏度系数的精度可以非常精确.数值算例表明所提出的方法有效.
关键词 无网格法;参数识别;各向异性;复变函数微分法
中图分类号 TU313.3文献标识码 A文章编号 1000-2537(2017)04-0062-06
Abstract To determine material parameters of two-dimensional orthotropic materials, a new identification approach is proposed in this work based on the meshless local natural neighbor interpolation (MLNNI) method. It is only necessary to construct an array of nodes in the targeted domain. The identification inverse problem is formulated as the minimization of an objective function representing the difference between numerical simulation displacements and measured data. Sensitivity coefficients used to obtain parameter updates are calculated by the complex variable differentiation method (CVDM). Unlike the finite difference method, CVDM has the advantage of step size insensitivity and sufficiently small steps. The accuracy of the sensitivity coefficients can approach the computer precision. Based on the investigation of numerical example, high accuracy results have been obtained, which demonstrates the potential of our proposed approach.
Key words meshless method; parameter identification; orthotropic; complex variable differentiation method
由于強度和刚度的特性,正交各向异性复合材料在工程结构中得到了广泛应用.对于结构设计和维护,其材料参数非常重要[1-3].然而,从实验室里试验样品得到的数据与从工程实际结构元件上得到的数据有很大区别[2].而且,在某些情况下从一个更大的结构中取出一个测试样本非常困难,因为这会破坏材料的内部一致性[4].因此,寻求材料参数的识别方法[1-6],可以得到可靠的正交各向异性介质的材料参数.但是,到目前为止,大部分的材料参数识别方法基于网格数值方法得到的,如有限元法和边界元法.
本文基于无网格局部自然邻近插值法提出了一种新的逆算法来确定二维各向异性材料的弹性本构参数.广义局部彼得洛夫-伽辽金无网格法是该方法的一种特殊情况.近年来无网格方法[7-12]的发展和应用受到越来越多的关注.这些方法的主要特点是,变量是在一个集群的分散节点上构建的,这不仅可以为生成网格减轻负担,还可以更准确地描述不规则的几何形状.局部彼得洛夫-伽辽金无网格法由Atluri和Zhu创立,它是一种真正意义上的无网格法,因为它不需要任何元素或背景网格用作插值或整合.这种方法不同于其他无网格方法,区别在于它的控制方程满足局部子域逐点使加权残值为零.其弱形式主要适合于几何形状简单的局部区域,因此,它被成功地广泛应用于工程问题,如弹性静力学问题[7-8]、断裂力学问题[9]和不可压缩流体流动问题[10].但是,彼得洛夫-伽辽金法本身不满足位移边界条件的移动最小二乘法(MLS).为了克服这个缺点,基于自然邻点插值(NNI)[11]和当地弱形式的局部Petrov-Galerkin方法(称为无网格局部自然邻近插值(MLNNI)方法 [12]) 被用来分析固体的压力.这种方法显示了巨大的优势,因为它不仅可以保持彼得洛夫-伽辽金无网格法的突出特点,还具有易于收敛的自然邻近插值的本质边界条件的优点 [11-12].
对于本文所考虑的逆问题,采用Levenberg-Marquardt(LM)方法来迭代求解目标函数的最小值,并确定二维正交各向异性介质中的未知材料参数.作为一种基于梯度的方法,LM方法需要计算灵敏度系数,例如,参数的目标函数的导数.虽然有限差分法(FDM)是计算灵敏度系数的最简单方法,但它的扰动步长的选择必须有实验依据.目前,复变函数微分法(CVDM),作为一种数值微分法吸引了更多研究者[6,13-14]的关注.该复变函数微分法的主要优点在于,它避免了相近数值之间的减法,因此不涉及与小步长相关联的精度问题.本文中,用复变函数微分法结合上述LM方法精确计算灵敏度系数.两个数值例子验证了该方法的有效性和准确性.
1 无网格局部自然邻近插值方法
如上所述,无网格局部自然邻近插值是用来分析工程问题.Cai和Zhu[12]首次提出了线性弹性分析方法,以减少计算成本,简化了基本边界条件的施加.
1.1 自然邻近插值
自然邻近插值是基于著名的Voronoi图和Delaunay三角剖分建立起来的.在二维欧氏空间R2考虑一组节点N={x1,x2,x3,…,xM},Voronoi图是一个分区的空间被分解成子区域TI,在每个区域TI与节点xI相关联.用数学术语表示,Voronoi多边形TI被定义为[11]:
参考文献:
[1] 孙秀山,黄立新,刘应华,等. 二维正交各向异性结构弹塑性问题的边界元分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2005,22(3):156-161.
[2] HUANG L X, SUN X S, LIU Y H, et al. Parameter identification for two-dimensional orthotropic material bodies by the boundary element method[J]. Engi Anal Bound Elements, 2004,28(3):109-121.
[3] 黄立新,向志海,孙秀山,等.正交各向异性复合材料孔板性能参数识别测点的最优布置[J]. 工程力学, 2006,38(10):201-209.
[4] MEUWISSEN M H, OMENS C W, BAAIJENS F P, et al. Determination of the elasto-plastic properties of aluminium using a mixed numerical-experimental method[J]. J Mater Proc Tech, 1998,75(8):204-211.
[5] LIU G R, HAN X. Computational inverse techniques for nondestructive evaluation [M]. Florida: CRC Press, 2003.
[6] GAO X W, HE M C. A new inverse analysis approach for multi-region heat conduction BEM using complex-variable-differentiation method[J]. Engi Anal Bound Elements, 2005,29(10):788-795.
[7] HU D A, LONG S Y, LIU K Y, et al. A modified meshless local Petrov-Galerkin method to elasticity problems in computer modeling and simulation[J]. Engi Anal Bound Elements, 2006,30(10):399-404.
[8] ARBDOLLAHIFA A, NAMI M R, SHAFIEI A R. A new MLPG method for elastostatic problems [J]. Engi Anal Bound Elements, 2012,36(12):451-457.
[9] CHING H K, BATRA R C. Determination of crack tip fields in linear elastostatics by the meshless local Petrov-Galerkin (MLPG) method[J]. Comp Model Engi Sci, 2001,2(5):273-289.
[10] WU X H, TAO W Q, SHEN S P, et al. A stabilized MLPG method for steady state incompressible fluid flow simulation[J]. J Comput Phy, 2010,229(12):8564-8577.
[11] SUKUMAR N, MORAN B, BELYTSCHKO T. The natural element method in solid mechanics[J]. Int J Numer Meth Engi, 1998,43(11):839-887.
[12] CAI Y C, ZHU H H. A meshless local natural neighbour interpolation method for stress analysis of solids [J]. Engi Anal Bound Elements, 2004,28(8):607-613.
[13] LYNESS J N, MOLER C B. Numerical differentiation of analytic functions [J]. Siam J Numer Anal, 1967,4(10):202-210.
[14] VATSA V N. Computation of sensitivity derivatives of navier-stokes equations using complex variables [J]. Adv Engi Softw, 2000,31(6):655-659.
[15] 袁亞湘,孙文瑜. 最优化理论与方法[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2001.
