SOX9在膀胱癌中的表达和分析
2017-08-24曾昭昌刘远灵周宇林江福能万跃平
万 颂,习 明,华 伟,曾昭昌,刘远灵,周宇林,江福能,万跃平
·临床医学·
·论著·
SOX9在膀胱癌中的表达和分析
万 颂,习 明,华 伟,曾昭昌,刘远灵,周宇林,江福能,万跃平
目的 检测在膀胱癌中SOX9的表达情况,探讨其在膀胱癌中发生、发展可能起的作用。方法 选取近5年在广州市花都区人民医院泌尿外科住院行膀胱癌手术的80例患者的病理标本,以60例膀胱癌组织作为研究组,20例膀胱癌旁组织作为对照组,采用免疫组织化学染色及Western blot方法测定各组研究对象中SOX9蛋白的表达水平。结果 SOX9在膀胱癌组织中阳性表达区域主要出现在细胞核,在膀胱癌旁组织中阳性表达区域主要在细胞质和细胞核。SOX9在膀胱癌中的表达比在膀胱癌旁中的高,SOX9在膀胱癌中是癌与非癌的表达为差异有统计学意义(P<0.001),而与年龄、性别和临床病理分期无关(P>0.05)。结论 SOX9在膀胱癌中表达升高,且在癌与非癌中表达有差异,可能成为膀胱癌新的诊断标志物。
SOX9;膀胱癌;免疫组化;癌与非癌;诊断标志物
膀胱癌是泌尿系统中最常见的恶性肿瘤,也是全身十大常见肿瘤之一,居我国泌尿生殖系肿瘤发病率第1位,而在西方其发病率仅次于前列腺癌,居第2位[1]。目前癌症预测和治疗大部分是根据医生的经验来决定的,存在着判断错误风险,且膀胱癌在临床检测中还没有一个比较精准的标志物。SOX9属于性别决定基因簇SOX[SRY(sex-determining region Y) box],其影响着男性的性别决定、软骨形成、神经发生和神经嵴的发展[2-5]。先前的研究也曾报道,在前列腺癌(prosate cancer, PCa)患者中SOX9血清水平的增加可能提示PCa侵略性肿瘤进展和预后不良,建议将其潜在作为PCa的血清学肿瘤标记[6]。然而SOX9表达的临床意义和功能特征还未见报道,因此本课题重点观察SOX9蛋白在膀胱癌组织及癌旁组织中的表达差异,探讨其在膀胱癌中发生、发展中可能起的作用。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料 所有膀胱癌标本来自广州市花都区人民医院泌尿外科近5年住院的膀胱癌手术患者。所有患者手术前未经过放疗 、化疗等针对肿瘤的任何治疗, 并有患者手术前后完整的病案资料。所选取的60例膀胱癌标本,均通过病理检查证实为膀胱癌, 作为研究组。同时选取20例膀胱癌旁组织标本,作为对照组。所获取标本均经医院伦理委员会批准并征得患者本人或家属的同意,入选患者均签署知情同意书。
1.2 试剂 兔抗人SOX9多克隆抗体购自abcam公司,兔抗人β-catenin多克隆抗体购自武汉博士德公司,组织总蛋白抽提试剂盒、West blot试剂盒购自上海康成生物工程公司。
1.3 方法 (1)免疫组化SP法。手术标本均经4%多聚甲醛固定,常规石蜡包埋,4 μm厚连续切片,切片染色前常规脱蜡、水化,高温修复抗原,全部操作按照SP试剂盒说明完成。用已知的阳性切片作为阳性对照,用磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)代替一抗作为阴性对照,每次试验均设置阴性对照。(2)Western blot方法。手术标本至-80℃冰箱保存,提取组织总蛋白,加入蛋白裂解液,用匀浆器裂解组织蛋白。每25μg等份变性蛋白经SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳,然后将蛋白电转至PVDF 膜, 5%的脱脂牛奶封闭,摇床摇动封闭2 h,将对应的蛋白一抗和内参进行4℃孵育过夜。将一抗回收,用TBST洗脱液漂洗,将目的PVDF膜装入配制好的二抗进行常温孵育1 h,使用HRP-ECL发光法,最后进行曝光处理。
1.4 统计学处理 采用SPSS 13.0统计软件处理,所有实验数据均用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,计量资料分别采用重复测量数据的方差分析或两独立样本t检验。P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 免疫组化结果 SOX9在20例膀胱癌旁组织中阳性表达区域主要出现在细胞质和细胞核,免疫组化评分为(5.15±4.17)分;SOX9在60例膀胱癌中阳性表达区域主要在细胞核,免疫组化评分为(8.10±2.64)分。2组间差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。见图1。60例膀胱癌患者病理样本年龄、性别、临床病理分期差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表1。

注:A、B:膀胱癌旁组织中SOX9的表达,C、D:膀胱癌组织中SOX9的表达图1 SOX9在膀胱癌组织及癌旁组织中的表达
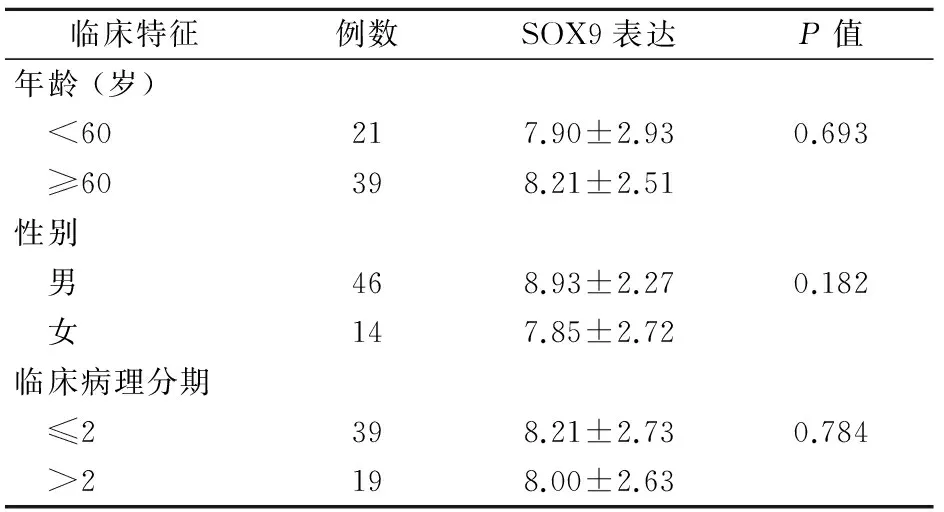
临床特征例数SOX9表达P值年龄(岁) <60217.90±2.930.693 ≥60398.21±2.51性别 男468.93±2.270.182 女147.85±2.72临床病理分期 ≤2398.21±2.730.784 >2198.00±2.63
2.2 Western blot结果 SOX9蛋白在膀胱癌及癌旁组织中的表达分别是9.34±2.68和6.66±1.90,2组间差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见图2。
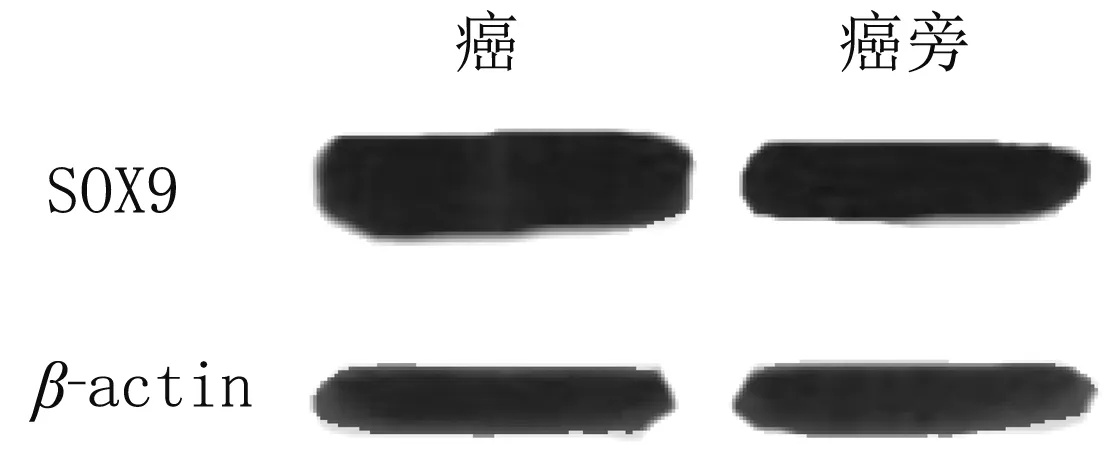
图2 SOX9蛋白在膀胱癌及癌旁中的表达
3 讨论
在关于各种癌症中SOX9的表达研究中,高表达SOX9往往与病人的不良预后相关。2013年Zhu H等[7]发现在骨肉瘤患者中SOX9过表达影响总体存活率和复发率,这表明SOX9可以成为骨肉瘤患者肿瘤进展和预后的标志物。2014年Qin等[8]进一步证实SOX9和前列腺癌发生发展相关,这符合笔者先前的研究发现,笔者发现上调SOX9与PCa的进展和不良预后明显相关。2015年Xia等[9]发现在胰腺导管腺癌中SOX9的过表达同远端转移和不良预后相关,表明SOX9在胰腺导管腺癌的发生发展中起了重要作用。
新的标志物对于癌症的诊断与治疗都是非常有意义的。SOX9蛋白表达在肿瘤组织中高于相邻的良性组织,而SOX9染色差异存在于各种肿瘤组织中。在乳腺癌和肺癌细胞中,SOX9蛋白表达在细胞质和细胞核。在PCa、胃癌和结直肠癌组织中,SOX9在细胞核染色是局部的,适度的细胞质和细胞核染色可以发现前列腺癌相邻的良性前列腺细胞。本研究显示了类似的结果,观察染色在膀胱癌组织中的细胞核,而在相邻的良性组织,SOX9抗体染色在细胞质和细胞核。
笔者通过对60例膀胱癌组织和20例膀胱癌旁组织的研究,发现SOX9在膀胱癌组织中表达升高,与年龄、性别和临床分期无关。因此SOX9可以作为膀胱癌的新的诊断标志物。
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(1): 7-30. DOI:10.3322/caac.21332.
[2] Kent J, Wheatley SC, Andrews JE, et al. A male-specific role for SOX9 in vertebrate sex determination[J]. Development, 1996, 122(9): 2813-2822.
[3] Lefebvre V, Huang W, Harley VR, et al. SOX9 is a potent activator of the chondrocyte-specific enhancer of the pro alpha1(II) collagen gene[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 1997, 17(4): 2336-2346. DOI:10.1128/mcb.17.4.2336.
[4] Stolt CC, Lommes P, Sock E, et al. The SOX9 transcription factor determines glial fate choice in the developing spinal cord[J]. Genes Dev, 2003, 17(13): 1677-1689. DOI:10.1101/gad.259003.
[5] Perez-Alcala S, Nieto MA, Barbas JA. LSOX5 regulates RhoB expression in the neural tube and promotes generation of the neural crest[J]. Development, 2004, 131(18): 4455-4465. DOI:10.1242/dev.01329.
[6] Zhong WD, Qin GQ, Dai QS, et al. SOXs in human prostate cancer: implication as progression and prognosis factors[J]. BMC Cancer, 2012, 12: 248. DOI:10.1186/1471-2407-12-248.
[7] Zhu H, Tang J, Tang M, et al. Upregulation of SOX9 in osteosarcoma and its association with tumor progression and patients' prognosis[J]. Diagn Pathol, 2013, 8: 183. DOI:10.1186/1746-1596-8-183.
[8] Zhong W, Qin GQ, He HC, et al. Combined overexpression of HIVEP3 and SOX9 predicts unfavorable biochemical recurrence- free survival in patients with prostate cancer[J]. OncoTargets and Therapy, 2014: 137. DOI:10.2147/ott.s55432.
[9] Xia S, Feng Z, Qi X, et al. Clinical implication of Sox9 and activated Akt expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Med Oncol, 2015, 32(1): 358. DOI:10.1007/s12032-014-0358-0.
(本文编辑:甘辉亮、边冬冬)
Expression and analysis of SOX9 in urinary bladder carcinoma
WanSong,XiMing,HuaWei,ZengZhaochang,LiuYuanling,ZhouYulin,JiangFuneng,WanYiaoping
(UrinarySurgeryDepartment,HuadouPeople′sHospitalAffiliatedtotheSouthMedicalUniversity,Guangzhou510800,China)
Objective To detect the expression of SOX9 in urinary bladder carcinoma and explore its possible role in the occurrence and development of urinary bladder carcinoma.Methods Pathological samples of 80 patients who
surgery due to urinary bladder carcinoma in the Urinary Surgery Department of Huadou People's Hospital were collected for the study. Carcinoma tissues from 60 cases were used as the research group, and benign tissues from another 20 cases were used as the control group. The expressions level of SOX9 were detected in the research subjects of the 2 groups by using immunohistochemistry(IHC)and Western blot(WB).Results Positive immunostainings of SOX9 were observed in the nucleus of carcinoma cells, while the SOX9 positive immunostainings in benign tissues could be noticed in the cytoplasm and nucleus of the surrounding gland epithelial cells. The expression level of SOX9 in bladder carcinoma was higher as compared with that of the benign tissue surrounding carcinoma, and the expression level of SOX9 in bladder carcinoma was higher than that of the benign tissues surrounding carcinoma. Statistical significance could be seen in the expression level of SOX9, when comparisons were made between carcinoma tissue and non-carcinoma tissue(P< 0.001). However, clinical pathological grading seemed to have no association with age and gender(P>0.05).Conclusion The expression level of SOX9 elevated in bladder carcinoma, and significant differences could be seen in the expressed levels of carcinoma and benign tissues, which might be a potential biomarker in the diagnosis of bladder carcinoma.
SOX9; Urinary bladder carcinoma; Immunohistochemistry; Cancer and non-cancer; Diagnostic marker
广东省科技计划项目(2014A020212471);花都区科技计划项目(HD15CXY005,15-HDWS-068)
510800 广东 广州,南方医科大学附属花都区人民医院泌尿外科(万颂、习明、华伟、曾昭昌、刘远灵、周宇林、万跃平);广东省临床分子医学及分子诊断重点实验室(江福能)
万跃平,电子信箱:songyouxiang@163.com
R373.14
A
10.3969/j.issn.1009-0754.2017.04.010
2017-03-22)
