老年心脏介入术后肺部感染相关危险因素分析及护理对策
2017-08-01张灵芝
张灵芝
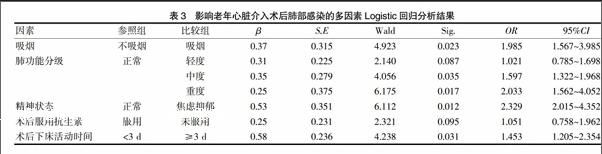
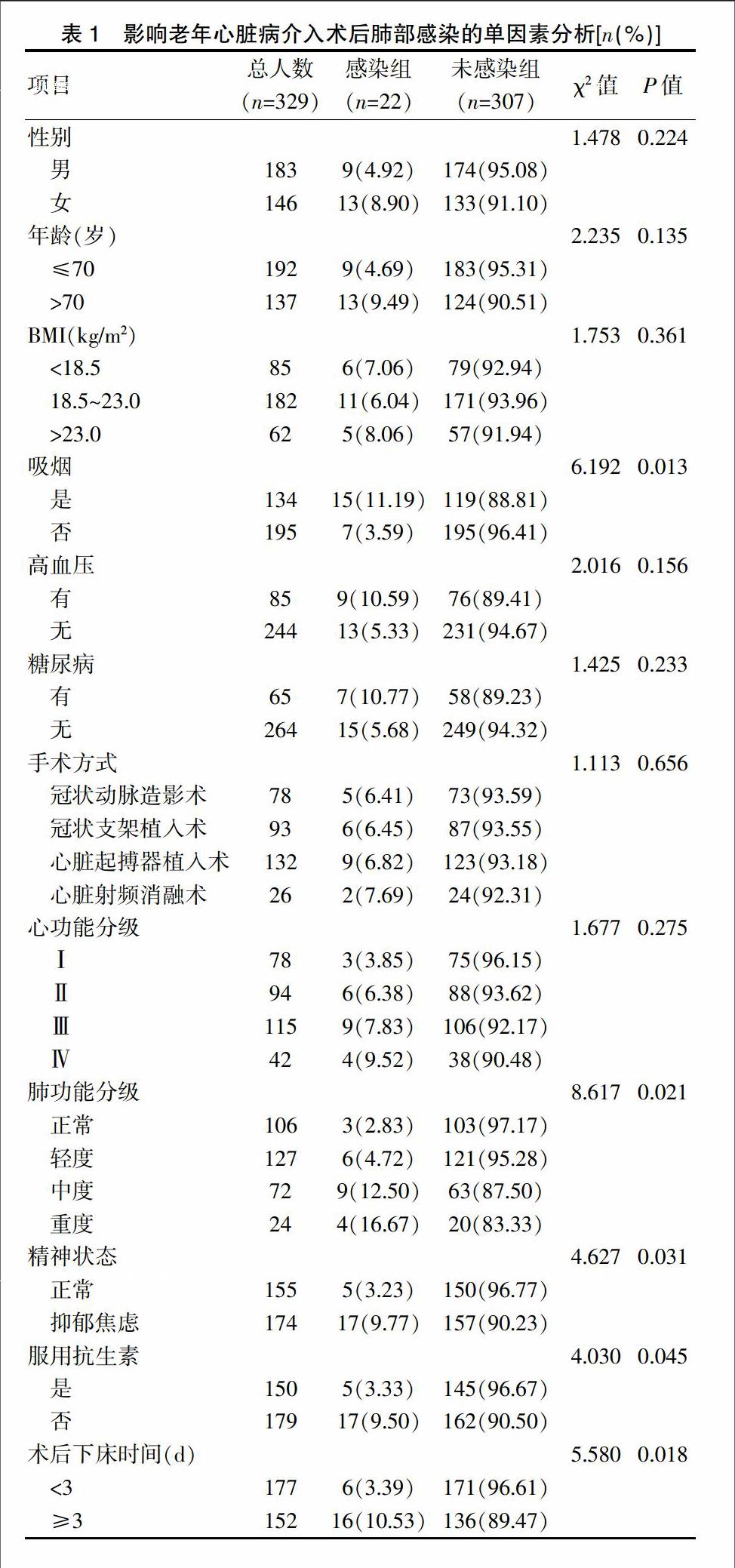
[摘要]目的 探讨老年心脏介入术后肺部感染的危险因素及护理对策。方法 选取2014年1月~2016年10月在本院行心脏介入治疗的老年患者329例作为研究对象,根据患者术后是否发生肺部感染分为感染组(n=22)和未感染组(n=307),对两组患者的临床资料进行回顾分析,并采用Logistic回归分析法分析造成肺部感染的危险因素。结果 329例患者中发生肺部感染22例,感染率为6.69%。感染组与肺感染组患者在吸烟、肺功能分级、精神状态、术后下床活动时间及术后服用抗生素方面差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),而在年龄、性别、体质量、高血压、糖尿病、手术方式及心功能分级方面均无统计学差异(P>0.05);Logistic回归分析,结果显示吸烟、肺功能分级、精神状态、术后下床活动时间均是心脏介入术后肺部感染的主要影響因素(P<0.05)。结论 老年患者心脏介入治疗后并发肺部感染的影响因素较多,长期吸烟、肺功能差、抑郁焦虑及长期卧床均与肺部感染有关,应采取相应护理措施,降低肺部感染的发生风险。
[关键词]老年;心脏介入术;肺部感染;危险因素;护理对策
[中图分类号] R473 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-4721(2017)06(a)-0149-04
[Abstract]Objective To explore the risk factors and nursing strategies of pulmonary infection in elderly patients after cardiac intervention.Methods A total of 329 elderly patients were enrolled in our hospital from January 2014 to October 2016 and were divided into infection group (n=22) and non infection group (n=307) according to whether the patients had pulmonary infection after cardiac intervention.The clinical data were retrospective analyzed and logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the risk factors of pulmonary infection.Results There were 22 cases of pulmonary infection in 329 patients,the infection rate was 6.69%.There were significant differences in smoking,pulmonary function classification,mental status,time of bed movement and intake of antibiotics after operation between the infection group and non infection group group (P<0.05),whereas there was no significant difference in age,gender,body weight,hypertension,diabetes mellitus,operation mode and cardiac function grade in two grops (P>0.05).Logistic regression analysis showed that smoking,pulmonary function classification,mental state,postoperative time of bed movement were the main influencing factors of pulmonary infection after cardiac intervention (P<0.05).Conclusion Long-term smoking,poor lung function,depression and anxiety and long-term bed rest are related to pulmonary infection,and corresponding nursing measures should be taken to reduce the risk of pulmonary infection in elderly patients after cardiac intervention.
[Key words]Elderly;Cardiac intervention;Pulmonary infection;Risk factors;Nursing strategies
心脏介入治疗是一种近年来新兴发展起来的心脏手术,该手术具有诊断明确、创伤性小、疗效显著的优点,已成为及药物治疗和外科手术后广泛应用于临床的治疗手段[1]。随着我国人均寿命的增长,人口老龄化的加重,心血管疾病的发生率日益增多,心脏介入术的实施量亦随之增多,据临床统计显示我国年均介入手术实施量可达50万例,同时其带来的不良反应及术后严重并发症引起较高重视[2]。由于老年患者术前存在较多基础疾病加之自身功能退化,抵抗力相对较差,术中创伤及术后合并症的存在使患者术后易产生感染,其中肺部感染是老年患者术后较为严重的并发症,会导致患者预后较差,甚至增加死亡的发生率[3-4]。因此,本研究对我院2014年以来实施心脏介入治疗的老年患者的临床资料进行回顾分析,探讨影响术后肺部感染的危险因素,以期为临床护理提供参考,具体结果报道如下。
