中国新疆地区和塔吉克斯坦黄地老虎发生世代与种群动态的比较研究
2017-07-19王盼盼AbdusattorSaidovAnvarJalilov阿迪力吾彼尔哈里提哈山刘兆海马英杰吕昭智
王盼盼,Abdusattor Saidov,Anvar Jalilov,阿迪力·吾彼尔,哈里提·哈山,刘兆海,马英杰,吕昭智,5
(1.中国科学院新疆生态与地理研究所,乌鲁木齐830011;2.中国科学院大学,北京100049; 3.塔吉克斯坦科学院动物学与寄生物学研究所,塔吉克斯坦; 4.石河子148团农业技术推广站,新疆石河子832048;5.中科院中亚生态与环境研究中心,乌鲁木齐830011)
中国新疆地区和塔吉克斯坦黄地老虎发生世代与种群动态的比较研究
王盼盼1,2,Abdusattor Saidov3,Anvar Jalilov3,阿迪力·吾彼尔1,哈里提·哈山1,刘兆海4,马英杰1,吕昭智1,5
(1.中国科学院新疆生态与地理研究所,乌鲁木齐830011;2.中国科学院大学,北京100049; 3.塔吉克斯坦科学院动物学与寄生物学研究所,塔吉克斯坦; 4.石河子148团农业技术推广站,新疆石河子832048;5.中科院中亚生态与环境研究中心,乌鲁木齐830011)
【目的】对黄地老虎(Agrotis segetum Schiff)在我国新疆,塔吉克斯坦的发生世代及种群动态进行比较,研究我国新疆黄地老虎种群演替原因,为塔吉克斯坦黄地老虎防治提供技术服务。【方法】应用测报灯对我国新疆石河子(2006、2009~2011),塔吉克斯坦(2014)农田黄地老虎进行监测,分析我国新疆,塔吉克斯坦黄地老虎的发生世代及种群动态。【结果】在塔吉克斯坦,黄地老虎一年发生3~4代,高峰期单灯诱蛾量达到90头;黄地老虎在我国新疆大部分地区1年发生3代,南疆个别地区发生3~4代,北疆少数地区发生1~2代,高峰期单灯诱蛾量<40头/灯,已不再作为防治对象。【结论】黄地老虎在塔吉克斯坦平均每年比我国新疆多发生1~2代,塔吉克斯坦一年发生3~4代,我国新疆大部分地区1年发生3代。在塔吉克斯坦,黄地老虎成虫高峰期诱蛾量远大于我国新疆地区。
黄地老虎;种群动态;发生世代
0 引言
【研究意义】黄地老虎Agrotis segetum Schiff,俗名切根虫、夜盗虫,属鳞翅目,夜蛾科,为杂食性害虫,主要危害棉花、小麦、玉米、瓜、菜、马铃薯和苜蓿等作物[1-2],在欧洲、中亚、俄罗斯及中国等地均有分布[3]。20世纪50~70年代,黄地老虎是我国新疆棉花和小麦等农作物主要害虫,80年代危害逐年减轻,90年代以后黄地老虎在农田为次要害虫,已不作为防治对象[4]。塔吉克斯坦与我国新疆维吾尔自治区接壤,均为植棉大区,两地有着相似的气候条件,黄地老虎一直是塔吉克斯坦棉田的主要害虫[5],严重影响棉花生产,对塔吉克斯坦黄地老虎的研究和防治刻不容缓。【前人研究基础】黄地老虎在我国新疆不同地区发生代数和发生高峰不同。在新疆和田、墨玉、莎车地区,黄地老虎一年发生3~4代,3月下旬为化蛹盛期,4月下旬为越冬代成虫羽化盛期[6]。在新疆南部阿拉尔垦区,黄地老虎一年发生完整的3代,全年成虫发生高峰在5月上中旬、6月下旬~7月上旬、8月下旬~9月上旬[7]。在新疆小海子垦区,1年发生3代,全年成虫发生高峰在4月中下旬、7月上旬和8月下旬[8],而石河子地区黄地老虎发生规律尚未见报道。在塔吉克斯坦,黄地老虎一年发生3~4代,越冬代高峰在4月中下旬[5,9]。【本研究切入点】目前,我国新疆石河子地区黄地老虎的种群动态尚未报道;塔吉克斯坦黄地老虎的全年种群动态特征尚不明确。通过对我国新疆石河子和塔吉克斯坦田间黄地老虎监测数据进行分析比较,明确两地的发生世代及种群动态。【拟解决的关键问题】研究我国新疆和塔吉克斯坦黄地老虎发生世代及种群动态,我国新疆黄地老虎种群演替原因,为塔吉克斯坦黄地老虎的防治提供技术服务。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
采集我国新疆石河子148团(44°43'N;86°06' E)黄地老虎数据,塔吉克斯坦杜尚别(38°38'N; 68°51'E)和库尔干秋别(37°50'N;68°46'E)诱蛾数据。“佳多”牌PS15II型频振式杀虫灯(河南省汤阴县佳多科工贸有限责任公司,功率30 w)。
1.2 方法
2006、2009~2011年,每年4月初在我国新疆石河子148团植保站安装测报灯,8月下旬拆除,每天日落后开灯,日出前关灯,收集诱集的黄地老虎并记录其数量。
2014年6月1日在塔吉克斯坦杜尚别和库尔干秋别安装测报灯,9月10日拆除,每天日落后开灯,日出前关灯,收集诱集的黄地老虎并记录其数量。
1.3 数据处理
利用Microsoft Excel、origin 8.0软件,对我国新疆石河子和塔吉克斯坦诱集的黄地老虎数量进行处理、统计分析并作图,分析和比较黄地老虎在两地的种群动态和世代发生情况。
2 结果与分析
2.1 黄地老虎发生世代
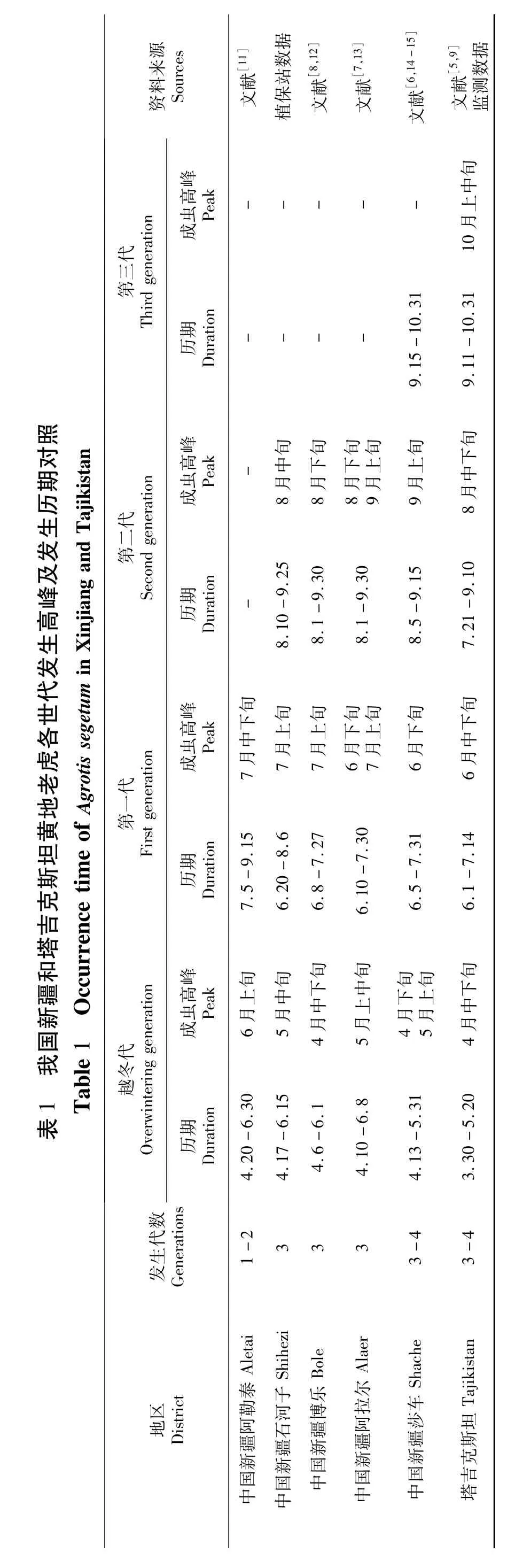
对我国新疆石河子和塔吉克斯坦采集的诱蛾数据及参考相关资料分析表明,黄地老虎在我国新疆大部分地区1年发生3代,南疆个别地区发生3~4代,北疆少数地区发生1~2代,在塔吉克斯坦一年发生3~4代;塔吉克斯坦成虫始见期早于我国新疆约7~17 d,成虫各代高峰出现时间比我国新疆早10 d左右;黄地老虎在塔吉克斯坦发生时期长于在我国新疆的发生时期,为3月30~10月10日,第2代发生时期明显长于其他世代的发生期。表1
2.2 黄地老虎发生与棉花生育期的关系
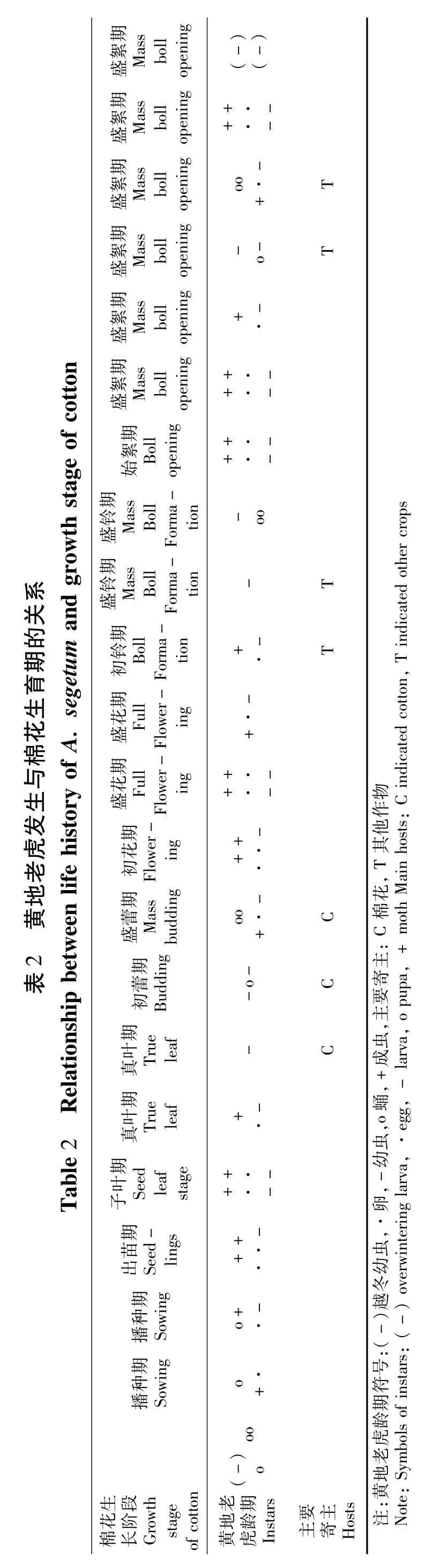
黄地老虎属于苗期害虫,其发生危害与棉花播期有密切关系[10]。其以第一代为害严重,在棉花苗期、蕾期发生较重。除棉花以外,第二代对夏播作物也有一定危害,第三代对秋播作物危害较重,如冬麦等。表2
2.3 我国新疆和塔吉克斯坦黄地老虎成虫种群消长动态
从监测的成虫数量分析发现,塔吉克斯坦监测地黄地老虎的种群数量明显大于我国新疆监测点的靶标害虫成虫数量。在我国新疆石河子地区,黄地老虎一年发生3代,各代高峰分别为5月中旬、7月上旬、8月上旬;高峰期蛾量<40头/灯。黄地老虎在塔吉克斯坦一年发生3~4代,其第一代和第二代高峰为6月中下旬、8月中下旬,塔吉克斯坦第二代高峰期持续时间较长;高峰期蛾量达到90头/灯。图1,图2在塔吉克斯坦杜尚别和库尔干秋别地区第一代、
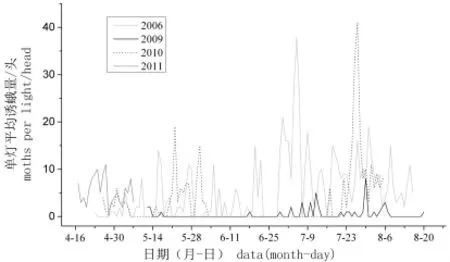
图1 我国新疆石河子148团2006,2009~2011年黄地老虎种群消长动态Fig.1 The population dynamics of Agrotis segetum in 148th Agricultural Regimental Farm,Xinjiang,China
第二代黄地老虎的生育期及高峰期相差不大。但库尔干秋别在6月第一代黄地老虎种群数量最大,而杜尚别为8月第二代黄地老虎种群数量最大。在塔吉克斯坦,各月份、各代均是雌蛾的数量远大于雄蛾的数量,雌蛾数量占总蛾量的60%以上。在我国新疆地区尚未发现这种情况。图2,图3,图4
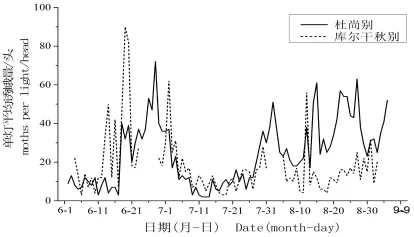
图2 塔吉克斯坦杜尚别和库尔干秋别黄地老虎种群动态Fig.2 The population dynamics of Agrotis segetum in Dushanbe and Kurgan-tube,Tajikistan
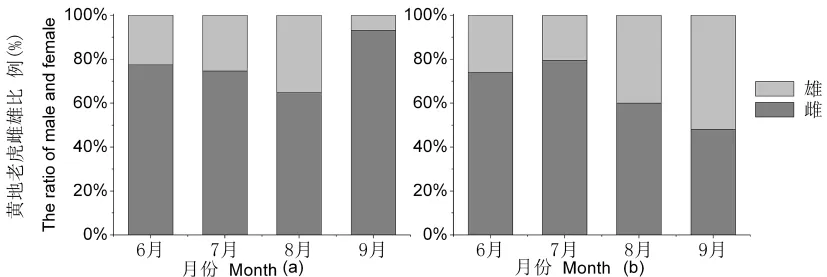
图3 库尔干秋别(a)和杜尚别(b)6~9月黄地老虎雌雄比例Fig.3 Female and male proportion of Agrotis segetum from April to September in Kurgan-tube(a)and Dushanbe(b)
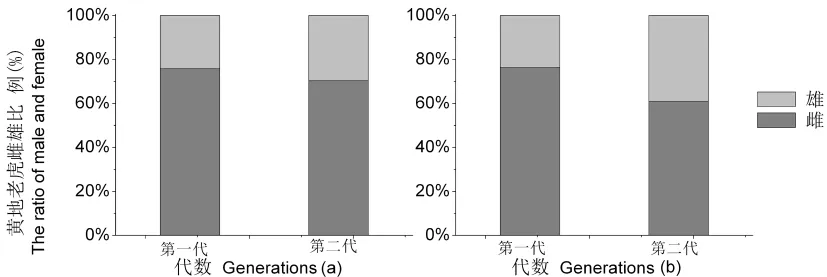
图4 库尔干秋别(a)和杜尚别(b)第一代、第二代黄地老虎雌雄比例Fig.4 Female and male proportion of the first and second generation of Agrotis segetum in Kurgan-tube(a)and Dushanbe(b)
3 讨论
3.1 塔吉克斯坦黄地老虎发生世代
根据Mukhitdinova[9]的研究发现,黄地老虎在塔吉克斯坦一年发生3~4代,研究从6月1日开始监测,到9月10日结束,错过了越冬代和第三代的部分信息,只有两代完整的种群动态数据,对塔吉克斯坦黄地老虎的种群动态监测仍需继续。
在塔吉克斯坦地区黄地老虎1年发生3~4代,其在我国新疆北疆发生2~3代,南疆发生3~4代。在塔吉克斯坦黄地老虎平均每年比我国新疆多发生1~2代,这与塔吉克斯坦光热资源丰富有关,如塔吉克斯坦哈特隆州有效积温5 800~6 000℃,而且没有我国新疆春季的倒春寒、大风、沙尘暴,秋季急速降温、霜冻等恶劣天气,棉花播种从3月上旬开始,可一直持续到6月[16],这为黄地老虎的发生提供了食物来源。
3.2 塔吉克斯坦监测点黄地老虎种群数量大于我国新疆监测点的诱虫数量
塔吉克斯坦种植面积最大的作物是小麦和棉花,两作物播种面积之和占塔国总播种面积的65%左右。塔吉克斯坦以冬小麦和棉花为主的种植结构,为黄地老虎的发生提供了有利条件。据王敬儒等[6]对我国新疆莎车地区1958~1961年黄地老虎越冬代调查表明,黄地老虎在冬麦田占绝对优势(占85.7%~100%)。黄地老虎在冬麦田越冬,在春天刚好以第一代幼虫危害棉花[1]。
塔吉克斯坦肥力投入较低、灌溉设施差、农田管理粗放[17]、农田杂草数量大等原因也为黄地老虎的发生提供了条件。
我国新疆地区地老虎的种群数量逐年下降,有两个关键因子。我国新疆各地冬小麦种植面积呈减少趋势,1996~2000年平均种植面积比1986~1990年减少了10%~30%。棉花面积呈现出增加趋势,1996~2000年棉花平均种植面积比1986~1990年增加了43%~70.8倍[18]。我国新疆种植结构的变化减少了黄地老虎的越冬场所,从而影响了黄地老虎的种群数量。地膜棉的种植有效减少了黄地老虎的种群数量,降低黄地老虎的危害。地膜覆盖不利于黄地老虎产卵,黄地老虎喜在杂草上产卵[19-20],地膜的使用使得田间杂草数量减少,黄地老虎产卵可选择寄主减少,产卵量降低;其次,应用地膜植棉,棉花播种期有所提前,出苗早且生长快,茎秆迅速木质化,黄地老虎第一代幼虫错过棉花出苗期,取食受到影响,从而影响其种群数量[21];再次,地膜覆盖会影响黄地老虎的生长环境,地膜覆盖会改变土壤的温度、湿度[22],从而影响黄地老虎的生长发育及其有效出土羽化。
3.4 塔吉克斯坦黄地老虎雌蛾数量大于雄蛾
在塔吉克斯坦,各月份、各代均是雌蛾的数量远大于雄蛾的数量。这可能与幼虫取食的食料有关。根据王敬儒[23]的研究,不同食料对警纹地老虎成虫性比有一定影响,警纹地老虎幼虫取食灰藜和玉米雌虫数量略大于雄虫(53.8%~56%);取食甜菜、苜蓿,雌蛾占70%,雄蛾仅占30%;取食马铃薯雄虫多于雌虫,雄蛾占62.5%,雌蛾占37.5%。黄地老虎亦可能存在这种情况。
4 结论
黄地老虎在塔吉克斯坦一年发生3~4代,平均每年比我国新疆多发生1~2代,其第一代和第二代高峰为6月中下旬、8月中下旬,高峰期单灯诱蛾量达到90头。黄地老虎在我国新疆大部分地区1年发生3代,南疆个别地区发生3~4代,北疆少数地区发生1~2代,高峰期单灯诱蛾量<40头/灯。黄地老虎属于苗期害虫,以第一代为害严重,在棉花苗期、蕾期发生较重。除棉花以外,第二代对夏播作物也有一定危害,第三代对秋播作物危害较重,如冬麦等。在塔吉克斯坦,各月份、各代别均是雌蛾的数量远大于雄蛾的数量,雌蛾数量占总蛾量60%以上,这可能与幼虫取食的食料有关。
References)
[1]王敬儒,戴淑慧,禹如龙,等.黄地老虎越冬及春季发生规律[J].新疆农业科学,1962,(3):105-107.
WANG Jing-ru,DAI Shu-hui,YU Ru-long,et al.(1962).The overwintering and occurrence regularity in spring of Agrotis segetum[J].Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences,(3):105-107.(in Chinese)
[2]仵均祥.农业昆虫学(北方本)[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2003.
WU Jun-xiang.(2003).Agricultural Entomology[M].Beijing: China Agriculture Press.(in Chinese)
[3]何玫,刘壮俊.黄地老虎颗粒体病毒基因组全测序[J].生物化学与生物物理学报,2000,(1):32.
HE Mei,LIU Zhuang-jun.(2000).Genome sequencing of Agrotis segetum granulosis virus[J].Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica,(1):32.(in Chinese)
[4]吕昭智,王玲,张秋红,等.黄地老虎种群动态与积雪的关系[J].生态学杂志,2006,25(12):1 532-1 534.
LZhao-zhi,WANG Ling,ZHANG Qiu-hong,et al.(2006).Relationships between overwintering Agrotis Segetum population and snow[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,25(12):1,532-1,534.(in Chinese)
[5]Mukhitdinov,S.M.,Vreysen,M.J.B.,Robinson,A.S.,&Hendrichs,J.(2006).Management of cotton insect pests in Tajikistan.Area-Wide Control of Insect Pests.Springer Netherlands.
[6]王敬儒.地老虎及其防治[J].新疆农业科学,1959,(4):158-160.
WANG Jing-ru.(1959).Agrotis Segetum and its control[J].Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences,(4):158-160.(in Chinese)
[7]陈婧,罗树凯,刘蓉,等.新疆南部阿拉尔垦区棉田黄地老虎成虫种群动态分析[J].中国棉花,2013,40(4):28-30.
CHEN Jing,LUO Shu-kai,LIU Rong,et al.(2013).Analysis on population dynamics of Agrotis Segetum in Alaer Reclamation Area,Southern Xinjiang[J].China Cotton,40(4):28-30.(in Chinese)
[8]蔡志平,张栋海,李克福,等.新疆小海子垦区果棉间作田黄地老虎、警纹地老虎和八字地老虎成虫种群动态[J].中国棉花,2012,39(3):22-24.
CAI Zhi-ping,ZHANG Dong-hai,LI Ke-fu,et al.(2012)A-nalysis on population dynamics of Agrotis Segetum(Schiffermiiller),Agrotis exclamationis Linnaeus andXestiac-nigrum Linnaeus in Xiaohaizi Reclamation Area,Xinjiang[J].China Cotton,39 (3):22-24.(in Chinese)
[9]Mukhitdinova,S.M.(1971).The phenology,population dynamics and survival rates of agrotis segetum schiff.in southern tadzhikistan.Trudy Vsesoyuznogo Nauchno-issledovatel'skogo Instituta Zashchity Rastenii:123-137.
[10]杨海峰.黄地老虎为害与作物播期的关系[J].新疆农业科学,1964,(8):304-306.
YANG Hai-feng.(1964).The relationships between harm ofA-grotis Segetum and crop sowing date[J].Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences,(8):304-306.(in Chinese)
[11]许国身.黑光灯下黄地老虎成虫消长情况[J].新疆农业科技,1975,(4):23-24.
XU Guo-shen.(1975).Population dynamics of cutworm(Agrotis segetum)by black-light trapping[J].Xinjiang Agricultural Science and Technology,(4):23-24.(in Chinese)
[12]喻小松.地老虎成虫发生规律及影响因素[J].农业科技与信息,2009,(2):17-18.
YU Xiao-song.(2009).Occurrence regularity and influencing factors of Agrotis segetum[J].Agricultural Science and Technology and Information,(2):17-18.(in Chinese)
[13]杜秉仁.新疆黄地老虎的习性调查及防治方法[J].中国农业科学,1957,(8):453-454.
DU Bing-ren.(1957).Behavior investigation and control ofAgrotis segetum in Xinjiang[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,(8):453-454.(in Chinese)
[14]禹如龙.黑光灯诱集地老虎的观察[J].新疆农业科学,1979,(10):18-20.
YU Ru-long.(1979).The observation of cutworms by blacklight trapping[J].Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences,(10):18-20.(in Chinese)
[15]王敬儒,戴淑德,禹如龙,等.黄地老虎生物学特性的研究[J].新疆八一农学院学报,1983,(1):43-49.
WANG Jing-ru,DAI Shu-de,YU Ru-long,et al.(1983).Studies on the biological characteristic ofAgrotis segetum[J].Xinjiang Bayi Agronomy Journal,(1):43-49.(in Chinese)
[16]师维军.塔吉克斯坦棉花科研与生产概况[C]//.中国棉花学会2013年年会论文汇编:69-72.
SHI Wei-jun.(2013).Tajikistan's cotton research and production profile[C]//.2013 Annual Meeting Proceeding of China Cotton Society:69-72.(in Chinese)
[17]师维军.对塔吉克斯坦棉花生产与科研的考察报告[J].江西棉花,2011,33(5):64-66.
SHI Wei-jun.(2013).The report on Tajikistan's cotton research and production[J].Jiangxi Cotton,33(5):64-66.(in Chinese)
[18]刘德祥,董安祥,梁东升,等.气候变暖对西北干旱区农作物种植结构的影响[J].中国沙漠,2007,27(5):831-836.
LIU De-xiang,DONG An-xiang,LIANG Dong-sheng,et al.(2007).Affect of climate warming on crops planting structure in Arid Zone of Northwestern China[J].Journal of Desert Research,27(5):831-836.(in Chinese)
[19]朱宝清.黄地老虎产卵的指示植物-龙葵[J].中国棉花,1979,(2):47.
ZHU Bao-qing.(1979).Indicator plant for cutworms spawningnightshade[J].China Cotton,(2):47.(in Chinese)
[20]汤建国.地膜棉苗期害虫发生的特点[J].江西农业科学,1985,(1):15.TANG Jian-guo.(1985).The occurrence of seedling pests in cotton fields with plastic film mulching[J].Jiangxi Agricultural Science&Technology,(1):15.(in Chinese)
[21]刘绍友.地膜棉害虫发生特点及防治对策[J].中国棉花,1984,(2):40-41.LIU Shao-you.(1984).Pests occurrence and control in cotton fields with plastic film mulching[J].China Cotton,(2):47.(in Chinese)
[22]刘小青.地膜棉田温、湿度的变化特点[J].西南科技大学学报(哲学社会科学版),1986,(2):77-79.
LIU Xiao-qing.(1986).The change characteristics of temperature and humidity in cotton field with plastic film mulching[J].Journal of Southwest University of Science and Technology,(2): 77-79.(in Chinese)
[23]王敬儒,戴淑慧.警纹地老虎Euxoa exclamationis(Linnaeus)的初步研究[J].昆虫学报,1966,(2):120-130.
WANG Jing-ru,DAI Shu-hui.(1966).Studies on the bionomic of Euxoa exclamationis(L.)(Lepidoptera,Noctuidae)[J].Acta Entomologica Sinica,(2):120-130.(in Chinese)
Occurrence Generation and Preliminary Comparison of Population Dynamics of Cutworm(Agrotis segetum)in Xinjiang of China and in Tajikistan
WANG Pan-pan1,2,Abdusattor Saidov3,Anvar Jalilov3,Adili Wubier1,Haliti Hashan1,LIU Zhao-hai4,MA Ying-jie1,LZhao-zhi1,5
(1.Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Urumqi 830011,China; 2.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Tajikistan;3.Institute of Zoology and Parasitology,Tajikistan Academy of Sciences,Dushanbe,Tajikistan;4.Agricultural Technology Extension Station of Shihezi 148thRegimental Farm,Shihezi Xinjiang 832048,China;5.CAS Research Center for Ecology and Environment of Central Asia,Urumqi 830011)
【Objective】In order to provide the effective control of Agrotis segetum in Tajikistan,the occurrence and population dynamics of A.segetum in Xinjiang and Tajikistan were compared and the potential reasons were discussed for the population succession and declination in Xinjiang,China.【Method】A.segetum moths were monitored by light traps in Shihezi(from 1980-2011)and Tajikistan(2014).The occurrence and population variation were analyzed according to the monitoring data.【Result】In Tajikistan,A.segetum developed 3-4 generations in a year and could be caught up to 90 individuals per light per night at the peak time.In most places of Xinjiang,A.segetum developed 3 generations yearly,in some parts of southern Xinjiang,it could develop 3-4 generations and while in few areas of northern Xinjiang it could develop 1-2 generations.At the peak timing,A.segetum could be caught less than 40 individuals per light per night,which indicated that A.segetum,were no longer the major insect pests in Xinjiang.【Conclusion】A.segetum can develop 1-2 generations more in Tajikstan than in Xinjiang.A.segetum can develop 3-4 generations per year in Tajikistan,while 3 generations yearly in most places of Xinjiang.A.segetum trapping moths in Tajikistan are far more than in Xinjiang region of China at the fastigium.
Agrotis segetum;population dynamics;generation
LZhao-zhi(1968-),male,native place:Qishan,Shanxi.Researcher,research field:Entomology.(E-mail):zhaozhi@ ms.xjb.ac.cn
S433.8+2
A
1001-4330(2017)05-0918-07
10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2017.05.016
2017-02-09
自治区国际科技合作项目“中塔棉花有害生物综合治理及其示范”(20136015);中国科学院特色研究所项目“塔吉克斯坦农业害虫生态防控技术与示范”(TSS-2015-014-FW-1-4)
王盼盼(1990-),女,河北人,硕士研究生,研究方向为昆虫生态学,(E-mail)wpan_pan@sina.com
吕昭智(1968-),男,陕西人,研究员,研究方向为昆虫生态学,(E-mail)zhaozhi@ms.xjb.ac.cn
Supported by:Autonomous Region of International Science&Technology Cooperation Projects"The IPM to cotton pests in China and demonstration in Tajikistan"(20136015);Characteristic Institute Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences"Ecological prevention and control for agricultural pests in Tajikistan"(TSS-2015-014-FW-1-4)
