滴灌毛管首部射流脉冲三通水力特性试验研究
2017-07-18王新坤肖思强樊二东徐胜荣
王新坤,肖思强,樊二东,徐胜荣
滴灌毛管首部射流脉冲三通水力特性试验研究
王新坤,肖思强,樊二东,徐胜荣
(江苏大学流体机械工程技术研究中心,镇江212013)
该文研究毛管射流脉冲三通水力特性并提出毛管脉冲三通水力设计方法。在脉冲三通2个出口端,安装6组不同长度的毛管(30、40、50、60、70、80 m),在5种压力条件下(5、6、8、10、12 m水头),分别测试6组不同长度毛管的脉冲水力特性,建立描述射流脉冲三通的脉冲水力特性和水头损失的非线性方程,以及脉冲特性和灌水均匀系数的非线性方程,经验证,拟合公式计算值与试验值相对误差不大于1.5%,表明得到的非线性方程可反映脉冲三通的水力特性与水头损失及灌水均匀系数的变化规律。以此为基础,提出设计情况下脉冲三通进口压力计算步骤,通过设计实例表明,基于水头振幅和脉冲频率获得的灌水均匀系数分别为98.13%和98%,绝对误差仅0.13%,可以简便快速地确定不同需水作物条件下毛管脉冲三通的进口压力,预测毛管的灌水均匀系数。该研究结果为射流脉冲三通滴灌系统水力设计提供计算方法。
压力;流量;灌溉;射流脉冲三通;水力特性;滴灌
0 引 言
滴灌具有灌水均匀、高效节水节肥、改善作物品质、增产增收等优点,是中国大面积推广应用的高效节水灌溉方式之一[1-5]。随着水资源的日趋紧张,作为能够节能节水的灌溉技术,低压滴灌与地下滴灌将是今后滴灌技术发展的一个重要方向[6-8]。然而低压滴灌与地下滴灌的毛管及灌水器内流速较小,灌水器易堵塞,灌水均匀度易受到影响。因此,灌水均匀性与堵塞是低压滴灌与地下滴灌技术的难点问题,也是影响其发展的瓶颈问题[9-14]。脉冲滴灌可在低压工况下工作,毛管可铺设地下和地表,且具有抗堵塞性能好、灌水均匀度高的特点[15-17],受到各国的广泛关注与应用。
王庆安[18]设计了一种主要由脉冲发生器及定量灌水管组成的脉冲滴灌系统,其核心部件脉冲发生器由型芯、脉冲胶囊、壳体组成,通过脉冲胶囊储水与脉冲的循环实现连续脉冲流。高胜国等[19]提出一种用单片机、变频调速技术形成脉冲水流冲洗地下滴灌系统,提高抗堵塞能力的技术方案。王聪等[20-21]基于可编程控制器和变频器提出一种波动水压灌溉系统,并对波动水压条件下灌水器的水力性能与抗堵塞性能进行了研究。这些脉冲发 生器一般通过电子脉冲、变频装置或橡胶、塑料膜、弹簧等弹性材料产生脉冲水流,造价较高,安装、使用、维护较复杂,弹性材料易于疲劳损坏,可靠性、灵敏性及持久性难以保证。毛管射流脉冲三通能够使流道内的水流产生强烈紊动和涡流,并且结构简单,稳定性好,造价低,低抗堵塞性能好、灌水均匀度高[22]。许鹏等[23]对毛管射流脉冲三通的结构参数、内部的流动机理、脉冲特性进行了研究。杨玉超[24]考察了射流三通的几何尺寸和进口压力的影响,研究了几种因素对振荡频率、出口压力、影响程度和可振性的影响,但未深入分析其射流三通的水头损失、出口水头等水力特性。本文对不同压力下的毛管射流脉冲三通进行水力特征试验,研究毛管射流脉冲三通的进口流量、脉冲频率及水头振幅与水头损失间的关系,建立脉冲特性和灌水均匀系数的关系式,并提出毛管脉冲三通水力设计方法。
1 材料与方法
1.1 供试毛管射流脉冲三通
毛管射流脉冲三通是基于射流附壁与切换理论设计的一种脉冲发生器。脉冲三通的壁面限制射流卷吸的范围,导致射流与壁面之间发生干涉。同时射流自身几何结构存在着微小不对称性和水流紊乱,因而两侧壁面和射流之间产生的干涉效果存在不对称,这将引起射流两侧产生压力差,进而推动射流附壁与偏转[25-27]。脉冲三通的主要结构包括喷嘴、控制道、分流劈和输出道等(图1a)。杨玉超基于大棚草莓滴灌系统流量(滴头流量2.2 L/h)及普通三通结构(外径16 mm正三通,莱芜丰田节水器材股份有限公司),通过数值模拟和正交试验,确定了能够产生最佳脉冲水流的脉冲三通基本尺寸[24]。本研究对文献[24]确定的尺寸进行加工,获得脉冲三通成型产品(图1b),其喷嘴宽度为4 mm;位差为2 mm;侧壁倾角为10°;劈距为35 mm;控制管宽度为2.5 mm;控制管长度为 54 mm;分流劈半径为3.5 mm;输出道内宽度为7 mm。
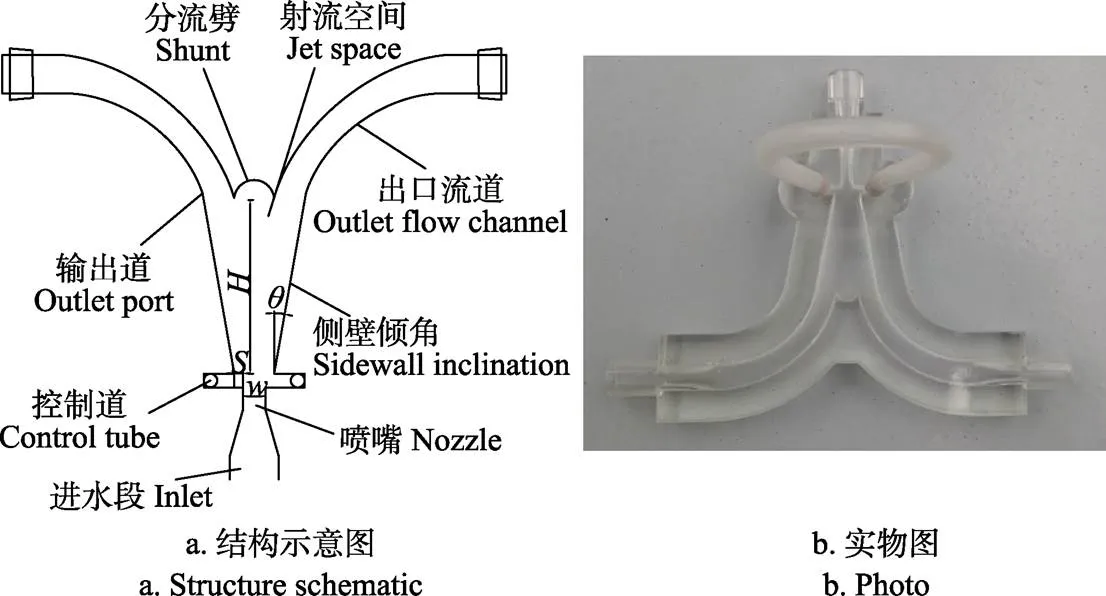
注:θ、S、W、H分别为侧壁倾角(°)、位差长度、喷嘴宽度、劈距长度,mm。
1.2 水力特性试验
2016年5月,试验在江苏大学喷灌试验厅进行。试验系统组成如图2所示,主要由毛管射流脉冲三通、水箱、水泵、阀门、压力表、涡轮流量计等组成。
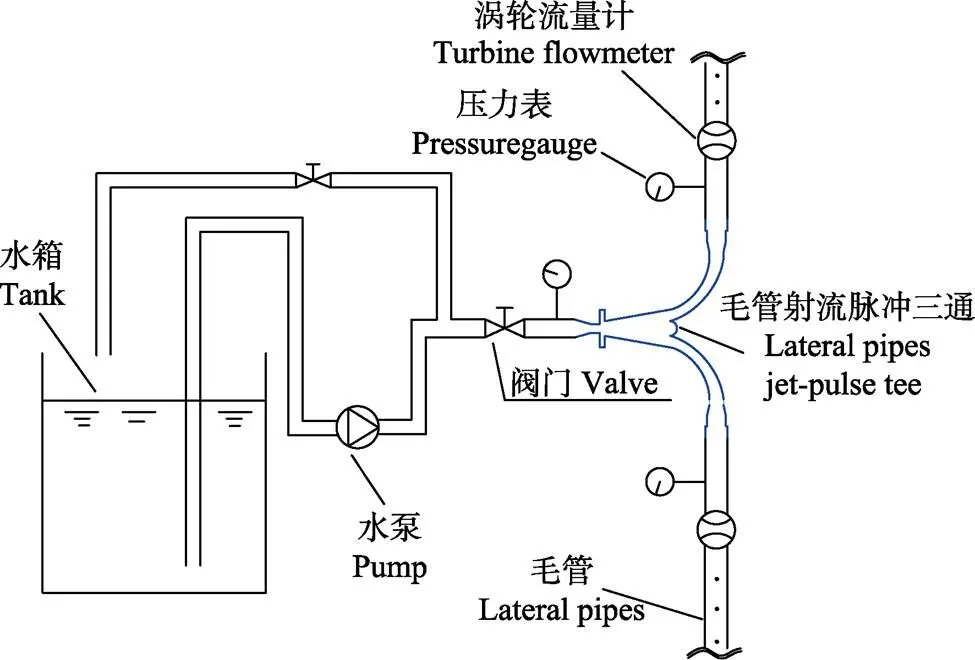
图2 试验系统示意图
毛管射流脉冲三通接入试验系统,调整进口阀门开度控制脉冲三通进口的压力和流量,使脉冲三通在低压条件下正常工作,为保证射流脉冲三通2个出口脉冲水流的对称性和出口流动状态的对称性,采用6组不同长度的毛管代替阀门。本试验采用内镶片式滴灌带(莱芜丰田节水器材股份有限公司),滴头间距30 cm,内径16 mm。进行6组试验,2个脉冲三通出口连接的毛管长度相同,单侧毛管铺设长度分别为30、40、50、60、70、80 m。前期试验表明,射流三通结构能使滴灌带内产生脉冲水流,对灌水器有间歇性的冲洗作用,试验中射流三通在50~120 kPa下会产生脉冲水流,故每组试验进口压力分别设定为5、6、8、10、12 m水头5个水平,并监测记录每组试验5个压力条件下的水力特性指标和毛管灌水均匀度。拟采用毛管铺设长度为30、40、50、60、70 m的5组试验数据拟合关系式,毛管铺设长度80 m的数据进行公式验证。
每次试验时间设定为15 min,秒表计时,压力表测试进出口水头,涡轮流量计(红旗仪表有限公司,0.5级)测试2个出口流量。在试验前,记录涡轮流量计的初始流量。试验中,用JT-HD61E摄像机拍摄左右两侧压力表摆动情况,并记录压力表摆动最大值和最小值。试验后,记录涡轮流量计最终流量。
1.3 测定与计算指标
射流脉冲三通及试验系统都是对称的,且左右两侧出口流量实测数据差异不明显,相对误差在1%以下,因此,水头振幅取左侧数据进行计算。根据试验测试结果得到出口水头的最大值和最小值,并通过计算得到进口流量、水头损失、脉冲频率、水头损失、灌水均匀系数和流量偏差率。进口流量为左右两侧涡轮流量计计算值之和;单侧涡轮流量计计算值为15 min后单侧流量计数值减去试验前流量计数值。射流脉冲三通水头振幅为出口水头脉冲最大最小值之差。水头损失通过进口水头减去出口水头平均值获得,出口水头平均值是出口水头最大最小值的平均值。
脉冲三通脉冲频率通过拍摄到的压力表摆动视频确定,慢放后计数一定时间内的压力表指针摆动次数,采用式(1)计算出射流脉冲三通的振荡频率:
=/(1)
式中为压力表指针的频率,即射流脉冲频率,Hz;为一定时间内压力表指针的摆动数,次;为读取视频的时间,s。
每分钟脉冲次数即:
=60(2)
式中为每分钟脉冲次数,次/min。
脉冲三通进口流量与水头损失关系采用灌水器流态指数公式表达,它反映灌水器内水流的流态和流量对压力变化的敏感程度[28]。射流脉冲三通进口流量与水头损失h关系可用灌水器流态指数表示:
=kh(3)
式中为流量系数;为流态指数。
滴灌灌水均匀性指标一般选择灌水均匀系数、流量偏差率,文中灌水均匀系数使用Christiensen公式计算得出的流量均匀系数[29-31]。流量偏差率为滴头最大流量和滴头最小流量之差与滴头平均流量的比值,%。
2 结果与分析
2.1 试验结果
在5~12 m工作压力下,6组单侧毛管长度不同试验得到的水头损失、进口流量、水头振幅、脉冲频率、灌水均匀系数(96.58%~98.33%)和流量偏差率(12.50%~19.88%)如表1所示。从表中可以看出,随着进口水头增大,水头损失和进口流量也逐渐增大,脉冲频率和水头振幅随进口水头的增大而增大。脉冲三通的脉冲特性是影响毛管灌水均匀度的主要诱因之一,5~12 m压力下脉冲频率均在200 Hz以上(203~278 Hz),水头振幅在2.25 m以上(2.27~4.73 m),脉冲频率远高于由电子装置控制供水的频率在100 Hz以下的低频发生器[21,32]。
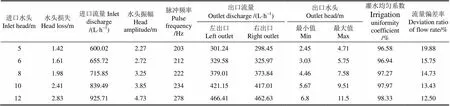
表1 毛管射流脉冲三通试验结果
2.2 水力特性与水头损失的关系
2.2.1 进口流量与水头损失的关系
根据水头损失和进口流量的5组数据,运用oringin 9.0绘图软件画出两者的关系曲线,并拟合关系式,2=0.98(<0.05),如图3a所示。采用式(3)拟合进口流量与水头损失的关系式,并将第6组进口流量数据代入图3a中关系式进行验证,计算结果如表2所示。由表2可知,试验值与计算值的差值均小于14 L/h,且相对误差均小于1.5%,表明拟合出的公式计算数据与试验数据较吻合,能较好地描述进口流量与水头损失的关系。
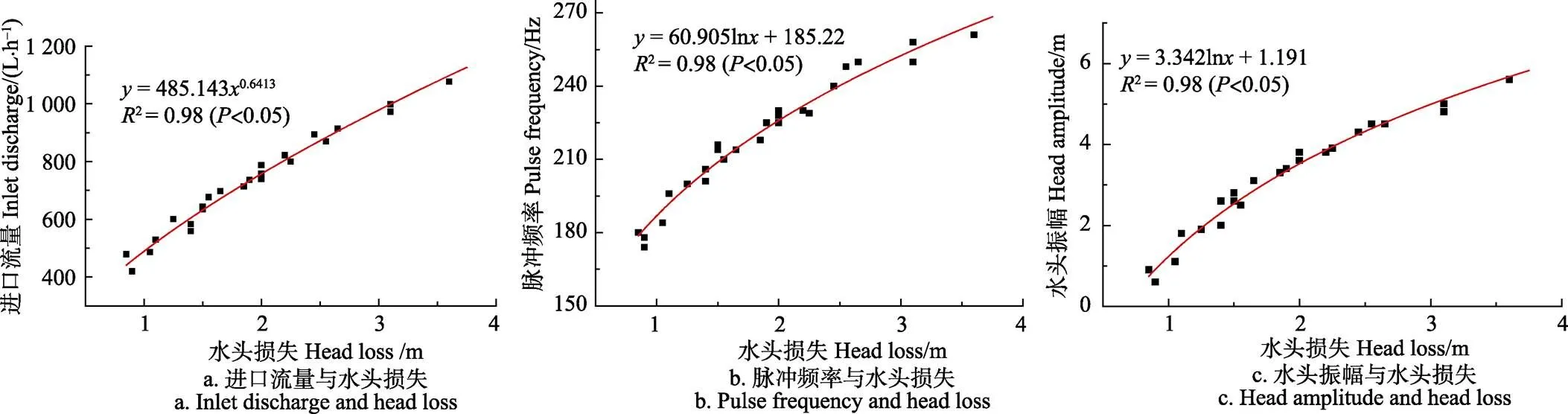
图3 水头损失与水力参数之间的关系
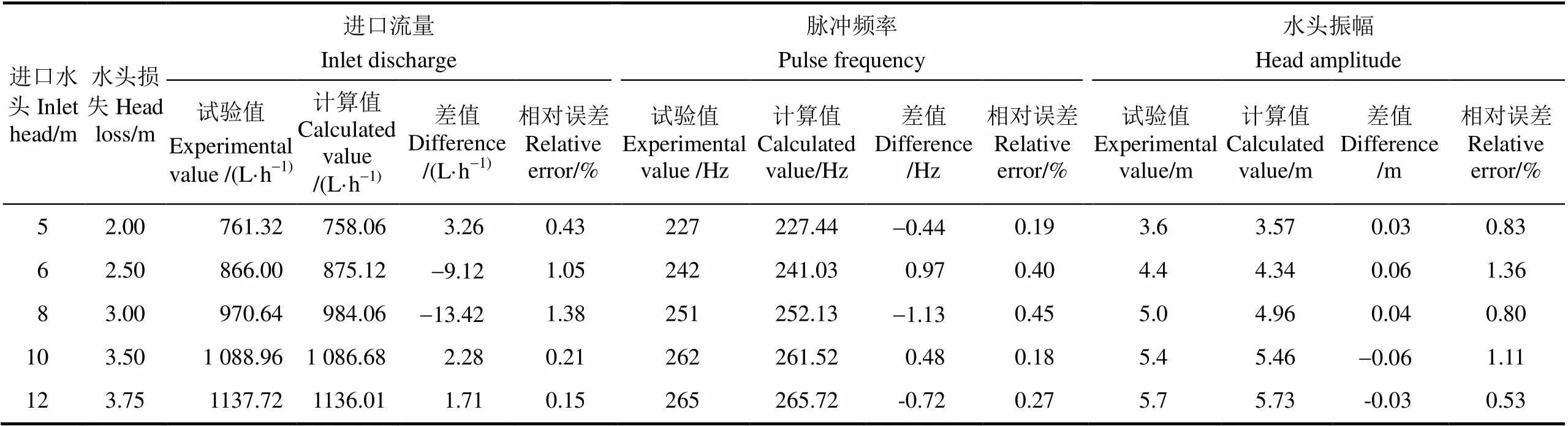
表2 拟合公式验证
注:毛管长80 m。
Note: Lateral pipe length is 80 m.
2.2.2 脉冲频率与水头损失的关系
根据脉冲频率及水头损失的5组数据,绘出两者的关系曲线,如图3b所示。根据图3b分别用乘幂、指数及对数曲线拟合发现对数曲线拟合度最高(2=0.98,< 0.05)。将第6组脉冲频率数据代入图3b中关系式进行验证,计算结果如表2所示。由表2可知,试验值与计算值的差值均小于1.5 Hz,且相对误差均小于0.5%,拟合出的公式计算数据与试验数据较吻合,能较好地描述脉冲频率及水头损失的关系。在5~12 m工作压力下,毛管中可观测到稳定的脉冲水流,水流在滴灌灌水器内形成强烈的紊动与冲击水流,有益于冲刷灌水器流道,增大抗堵塞能力和灌水均匀性。
2.2.3 水头振幅与水头损失的关系
根据水头损失和水头振幅的5组数据,绘出两者关系曲线,如图3c所示。根据图3c发现对数曲线拟合度最高(2=0.98,<0.05)。将第6组水头振幅数据代入图3c中关系式进行验证,计算结果如表2所示。由表2可知,试验数据与计算数据的差值均不大于0.06 m,且相对误差均小于1.5%,拟合出的公式计算数据与试验数据较吻合,能较好地描述水头损失和水头振幅的关系。水头振幅对扰乱毛管中水流流态有重要影响,当水头振幅较大时,水流紊动越强烈,脉冲在毛管中传播的距离就越远;同时,产生的水头振幅越大,射流三通水头损失越大,所需进口水头就越大。
2.3 脉冲特性与灌水均匀系数的关系
脉冲特性提高毛管的灌水均匀度[33],根据表2中脉冲频率、水头振幅和灌水均匀系数数据拟合关系式。水头振幅、脉冲频率与灌水均匀系数绘制两者的关系曲线,如图4所示。
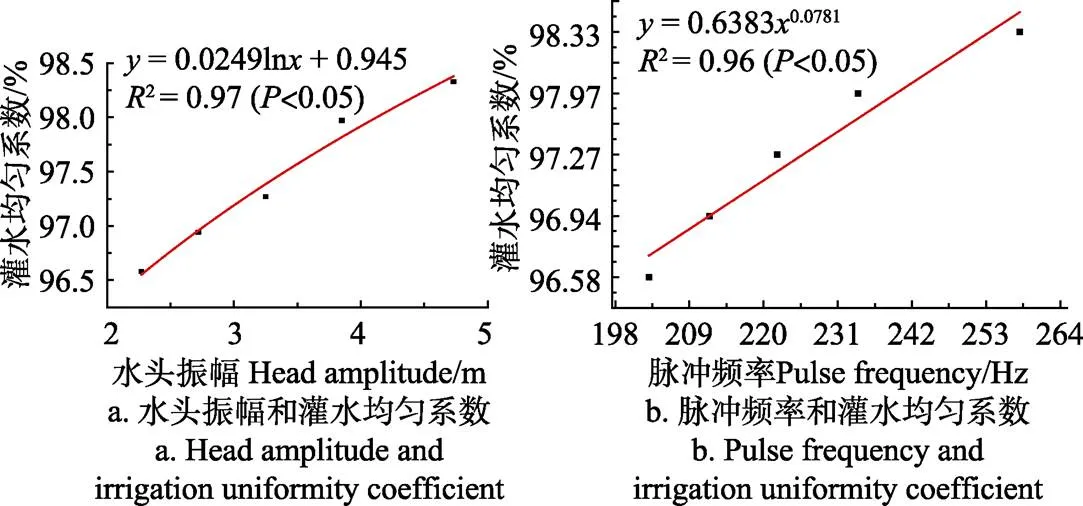
图4 水头振幅、脉冲频率和灌水均匀系数的关系
水头振幅、脉冲频率与灌水均匀系数的拟合度,对数、乘幂曲线最高(2>0.95,<0.05)。由图4可知,水头振幅增大时,灌水均匀系数随之增大,灌水均匀系数也随着脉冲频率增大而增大。其主要原因:在一定压力条件下,脉冲三通特殊结构能够诱发形成脉冲水流,脉冲水流具有脉冲能和稳定的频率;脉冲能可以使水流冲击力更大,水流冲击力一方面能起到冲刷灌水器流道的作用,一方面可以增大在毛管中的传播距离。
2.4 水力设计实例
对于灌水器的性能,许用水头范围应满足应用的要求[34-35]。毛管管径、长度及滴头参数确定后,根据滴头工作流量,得到毛管进口所需流量与压力,通过脉冲三通流量与水头损失关系式确定脉冲三通水头损失,进而得出脉冲三通的进口压力。试验用的滴灌带为内镶片式,滴头间距30 cm,滴头灌水器的压力与流量关系式符合管道流公式,为=0.83700.528,为给定压力下滴头的流量,L/h;0为滴头的入口压力水头,m。
以某田间作物滴灌带供水为例,已知作物需水量可以得到单个滴头的流量,假设滴头需要工作流量为2.2 L/h,田间滴灌带单侧铺设长度为60 m,计算出滴头的个数为400个,所以脉冲三通的进口流量是880 L/h。已知滴头流量,由=0.83700.528可以得到滴头的入口压力0为6.23 m。由脉冲三通进口流量880 L/h与水头损失拟合公式(图3),可以得出水头损失为2.53 m。脉冲三通进口压力等于入口压力6.23 m和水头损失2.53 m之和,即8.76 m。
通过获得的水头损失2.53 m,和水头损失与脉冲频率、水头振幅的关系式(图3),计算得到脉冲频率是242 Hz,水头振幅是4.29 m。再分别由拟合的脉冲频率、水头振幅与灌水均匀系数关系式(图4),可以得出灌水均匀系数分别为98.13%和98%。基于水头振幅和脉冲频率获得的灌水均匀系数绝对误差仅0.13%,差异很小。可见,已知作物需水量和灌溉使用的滴灌带性能及其参数时,可以由拟合得到的公式计算出脉冲三通的进口压力;在实际运用中,调节进口压力可以改变滴头流量的大小,进而满足作物的需水要求;并且可以由脉冲特性与灌水均匀系数的关系式预测出毛管的灌水均匀系数。
3 结 论
1)射流脉冲三通进口水头5~12 m时,可以观测到毛管内的脉冲水流持续且强烈,脉冲频率稳定在203~278 Hz之间,水头振幅在2.27~4.73 m之间,灌水均匀系数在96.58%~98.33%之间,流量偏差率在12.50%~19.88%之间。
2)分别建立了射流脉冲三通的进口流量、脉冲频率、水头振幅和水头损失之间的非线性方程,以及脉冲特性和灌水均匀系数的非线性方程。脉冲三通进口流量与水头损失的关系符合管道流幂函数关系,关系式的拟合度在0.95以上,计算精度满足使用要求。滴头工作流量和滴灌带确定后,由拟合的关系式可以得到脉冲三通的进口压力,并能预测毛管的灌水均匀系数。提出了射流脉冲条件下毛管的水力设计,可供微灌工程设计者试用。
还需要开展基于脉冲三通的脉冲滴灌系统田间试验,观测压力、流量及脉冲特性在管道的分布特征,提出脉冲滴灌系统的水力设计方法,并进一步评价灌水均匀性及抗堵塞能力。
[1] 金宏智,严海军,王永辉. 喷灌技术与设备在中国的适应性分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,4(1): 42-45. Jin Hongzhi, Yan Haijun, Wang Yonghui. Adaptability analysis of sprinkler irrigation technology and equipments in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 4(1): 42-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 李世英. 对我国节水灌溉技术发展的几点思考[J]. 排灌机械工程学报,2000,18(1): 6-8. Li Shiying. Reflections on the development of China's water- saving irrigation technology[J]. Drainage and Irrigation Machinery, 2000, 18(1): 6-8.
[3] 龚时宏,李久生,李光永. 喷微灌技术现状及未来发展重点[J]. 中国水利,2012 (2): 66-70. Gong Shihong, Li Jiusheng, Li Guangyong. Present situation and development of sprinkler irrigation and micro-irrigation techniques[J]. China Water Resources, 2012(2): 66-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 贺城,廖娜. 我国节水灌溉技术体系概述[J]. 农业工程,2014,4(2):39-44. He Cheng, Liao Na. Overview of water-saving irrigation technology system in China[J]. Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 4(2): 39-44. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 魏正英,苑伟静,周兴,等. 我国压力补偿灌水器的研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(1):94-101. Wei Zhengying, Yuan Weijing, Zhou Xing, et al. Research progress of pressure compensating emitters in micro- irrigation systems in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(1): 94-101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 刘璐,牛文全,Bob Zhou. 细小泥沙粒径对迷宫流道灌水器堵塞的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(1):87-93. Liu Lu,Niu Wenquan,Bob Zhou. Influence of sediment particle size on clogging performance of labyrinth path emitters[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(1): 87-93. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 王文娥,王福军,牛文全,等. 滴头流道结构对悬浮颗粒分布影响的数值分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2009,25(5):1-6. Wang Wen'e, Wang Fujun, Niu Wenquan, et al. Numerical analysis of influence of emitter channel structure onsuspended granule distribution[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2009, 25(5): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 牛文全,吴普特,喻黎明. 基于含沙量等值线的迷宫流道结构抗堵塞设计与模拟[J]. 农业工程学报,2010,26(5): 14-18. Niu Wenquan, Wu Pute, Yu Liming. Anti-clogging experimental investigation and optimized design of micro- channels of emitter based on isoline of sand content[J] . Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(5): 14-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 李刚,王晓愚,白丹. 地下滴灌中毛管水力计算的数学模型与试验[J]. 排灌机械工程学报,2011,29(1):87-92. Li Gang, Wang Xiaoyu, Bai Dan. Experiment and mathematical model on hydraulic calculation of laterals in subsurface drip irrigation[J]. Drainage and Irrigation Machinery, 2011, 29(1): 87-92. ( in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 王新坤,蔡焕杰. 微灌毛管水力解析及优化设计的遗传算法研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2005,36(8):55-58. Wang Xinkun, Cai Huanjie. Study on genetic algorithms of hydraulic analysis and optimum design for micro-irrigation laterals[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2005, 36(8): 55-58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 陈艳,白丹,任长江,等. 基于分形理论的地下滴灌灌水器水力特性研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2010,41(增刊):47-52. Chen Yan, Bai Dan, Ren Changjiang, et al. Research on the hydraulic properties of SDI emitter based on fractal theory[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2010, 41(Supp.): 47-52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] Lazarovitch N, Shani U, Thompson T L, et al. Soil hydraulic properties affecting discharge uniformity of gravity-fed subsurface drip irrigation systems[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering-ASCE, 2006, 132(6): 531-536.
[13] 王晓愚,白丹,李占斌,等. 地下滴灌田间管网室内试验测试系统[J]. 农业工程学报,2008,24(4):88-90. Wang Xiaoyu, Bai Dan, Li Zhanbin, et al. Laboratory test system of field pipe network under subsurface drip irrigation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2008, 24(4): 88-90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 仵峰,李王成,范永申,等. 地下滴灌滴头出口正压试验研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2003,22(2):48-52. Wu Feng, Li Wangcheng, Fan Yongshen, et al . Experimental study on positive pressure in area around emitter in subsurface drip irrigation[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2003, 22(2): 48-52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] Bakeerm G A A, El-Ebabi F G, El-Saidi M T, et al. Effect of pulse drip irrigation on yield and water use efficiency of potato crop under organic agriculture in sandy soils[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2009, 26(2): 736-765.
[16] Assouline S, Moller M, Cohen S, et al. Soil-plant system response to pulsed drip irrigation and salinity: Bell pepper case study[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2006, 70(5): 1556-1568.
[17] Elmaloqlou S, Diamantopouos E. Wetting front advance patterns and water losses by deep percolation under the root zone as influenced by pulsed drip irrigation [J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2007, 90(1-2): 160-163.
[18] 王庆安. 脉冲滴灌系统结构设计与工作原理[J]. 节水灌溉,2001(4):36-37. Wang Qingan. Structural design and working principle of pulse drip irrigation system[J], Water Saving Irrigation, 2001(4): 36-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) )
[19] 高胜国,黄修桥. 脉冲滴灌系统:201110074154. 1 [P].
[20] 王聪,芦刚,刘洁,等. 波动水压滴灌系统设计与实验分 析[J]. 中国农村水利水电,2012(6):69-72. Wang Cong, Lu Gang, Liu jie, et al. Design of dynamic pressure drip irrigation system and experimental analysis[J], China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2012(6): 69-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) )
[21] 刘洁,王聪,魏青松,等. 波动水压参数对灌水器水力性能影响试验[J]. 河海大学学报自然科学版,2014,42(4):361-366. Liu Jie, Wang Cong, Wei Qingshong, et al. Experimental study of effect of fluctuating water pressure factors on hydraulic properties of drip emitters[J]. Journal of Hohai University:Natural Sciences, 2014, 42(4): 361-366. (in Chinese with English abstract) )
[22] 王新坤. 一种射流三通:CN103203293A [P].
[23] 许鹏,王新坤,高世凯,等. 射流振荡三通与滴灌毛管脉冲初步试验研究[J]. 节水灌溉,2014(3):1-4. Xu Peng, Wang Xinkun, Gao Shikai, et al. Preliminary test of jet oscillation tee and puise flow in drip irrigation lateral pipe[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2014(3): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 杨玉超. 射流脉冲三通振荡特性影响因素研究[D]. 镇江:江苏大学,2016. Yang Yuchao. Study on Influence Factors of Oscillation Performance of Jet-pulse Tee[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 汪志明,薛亮. 射流元件附壁与切换流动规律研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展,2007,22(3):352-357. Wang Zhiming, Xue Liang. Study on the attached flow and alteration flow character in fluidic element of down hole pressure intensifier[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2007, 22(3): 352-357. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 熊青山,殷琨,田海. 自由切换射流元件模拟试验研究[J]. 液压与气动,2009(7):50-52. Xiong Qingsan, Yin Kun, Tian Hai. Analog test study of free switch efflux element[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2009(7): 50-52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 辛利. 音波振荡器振荡性研究及应用[D]. 大连:大连理工大学,2010. Xin Li. Study on the Oscillation of Sonic Oscillator and Application[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 常莹华,牛文全,王维娟. 滴灌灌水器迷宫流道的内部流体数值模拟与流动分析[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报自然科学版,2009,37(2):203-208. Chang Yinghua, Niu Wenquan, Wang Weijuan. Numerical simulation and flow analysis of labyrinth path of drip irrigation emitters[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University: Natural Science Edition, 2009, 37(2): 203-208. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 朱德兰,吴普特,王剑. 滴头制造偏差对灌水均匀度及毛 管造价的影响[J]. 排灌机械工程学报,2011,29(2):175-179. Zhu Delan, Wu Pute, Wang Jian. Effect of emitters manufacturing variation of micro-irrigation on uniformity and lateral cost [J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2011, 29(2): 175-179. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 牛文全,张若婵,罗春艳. 考虑滴头堵塞位置分布的灌水均匀度计算方法[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(6):147-152. Niu Wenquan, Zhang Ruochan, Luo Chunyan. Drip irrigation uniformity calculation considering distribution location of clogged emitters[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(6): 147-152. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 鞠学良,吴普特,朱德兰,等. 基于样本流量偏差率的微灌灌水均匀度评价方法[J]. 排灌机械工程学报,2016(2):173-178. Ju Xueliang, Wu Pute, Zhu Delan, et al. Estimation of micro- irrigation water application uniformity based on sample emitter flow variation[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2016(2): 173-178. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 曹伟,刘洁,朱月亭,等. 振动水压下滴灌灌水器水力性能研究[J]. 节水灌溉,2015(9):1-6. Cao Wei, Liu Jie, Zhu Yueting, et al. Study on hydraulic properties of drip emitter under vibration pressure[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2015(9): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 杨玉超, 王新坤, 朱燕翔, 等. 基于射流脉冲三通的滴灌带试验研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2015(9): 111-114. Yang Yuchao, Wang Xinkun, Zhu Yanxiang, et al. An experimental study of the jet pulse tee based on drip irrigation pipes[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2015(9): 111-114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 魏正英,马胜利,周兴,等. 压力补偿灌水器水力性能影响因素分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(15):19-25. Wei Zhengying, Ma Shengli, Zhou Xing, et al. Influence factors on hydraulic performance of pressure-compensating emitter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(15): 19-25. (inChinese with English abstract)
[35] 苑伟静,魏正英,楚华丽,等. 分流式灌水器结构优化设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(17):117-124. Yuan Weijing, Wei Zhengying, Chu Huali, et al. Optimal design and experiment for divided-flow emitter in drip irrigation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(17): 117-124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hydraulic performance experiment of lateral pipe jet-pulse tee
Wang Xinkun, Xiao Siqiang, Fan Erdong, Xu Shengrong
(212013,)
Previous studies show that pulse drip irrigation can work under low pressure, and has the characteristics of good anti-clogging performance and high irrigation uniformity. In this paper, the hydraulic performance experiment of the lateral pipe jet-pulse tee was studied. Furthermore, the design method of the lateral pipe jet-pulse tee was put forward, an experiment was carried out in the laboratory: 6 sets of different lengths of lateral pipe were installed at the 2 outlet ends of jet-pulse tee, the length of unilateral capillary laying was 30, 40, 50, 60, 70 and 80 m respectively, and the lateral pipe length linking with 2 outlet were same; in addition, the hydraulic characteristics of 6 groups of capillary tubes with different lengths were tested under 5 different inlet pressure conditions, which were 5, 6, 8, 10 and 12 m waterhead respectively in each group. Hydraulic characteristics were measured by a turbine flowmeter and a pressure gauge, including the inlet pressure, the inlet discharge, and the maximum and minimum of the outlet head. The head loss, the irrigation uniformity coefficient and deviation ratio of flow rate were calculated. And the irrigation uniformity coefficient was calculated using the Christiensen formula, the deviation rate of flow rate was the ratio of the difference between the maximum and the minimum flow of emitter and the average flow rate of the dripper. The results showed that continuous and strong pulsed water flow could be observed under 5-12 m inlet head in the lateral pipe, pulse frequency stabilized 203-278 Hz, head amplitude 2.27-4.73 m, irrigation uniformity coefficient 96.58%-98.33%, and deviation ratio of flow rate 12.50%-19.88%. The pulse frequency was much higher than the low frequency generator with a frequency of 100 Hz or less controlled by the electronic device. The nonlinear equation describing the pulsed hydraulic performance and head loss of jet-pulse tee was established, and the nonlinear equation of the pulse performance and the irrigation uniformity coefficient was established too. The fitting degrees of the equations were above 0.96. The calculated results were verified by experimental data, the relative error were less than 1.5%, indicating that the nonlinear equations could well reflect the variation of the hydraulic performance and the head loss and the irrigation uniformity coefficient. On the basis of this, the author put forward the steps of calculating the inlet pressure of jet-pulse tee. The uniform coefficients of irrigation, based on the head amplitude and pulse frequency, were 98.13% and 98%, respectively, the absolute error was only 0.13%. The inlet pressure of jet-pulse tee could be easily determined for crops with different water requirement, and the uniform coefficient of irrigation could be predicted. The results would promote the further development of drip irrigation system, and provided the calculation method and theoretical basis for the research of lateral pipe jet-pulse tee and drip irrigation pulse development platform. In the future research, it is also necessary to carry out field experiment of pulse drip irrigation system based on jet-pulse tee, observe the distribution of pressure, flow and pulse performance in pipeline, and put forward the hydraulic design method of pulse drip irrigation system and further evaluate irrigation uniformity and anti-clogging ability. In a word, this paper only studies the pulse capillary, the irrigation uniformity of pulse branch and pulse irrigation area will be studied deeply in the future, which not only extends the drip irrigation equipment, but also is an effective way to establish high-performance drip irrigation systems.
pressure; flow rate;irrigation; jet-pulse tee; hydraulic performance; drip irrigation
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.12.015
S275.6
A
1002-6819(2017)-12-0116-06
2016-10-31
2017-04-10
国家自然科学基金(51579116);江苏省农业科技自主创新资金(CX(14)2100)
王新坤,男,陕西临潼人,研究员,博士生导师,主要从事节水灌溉理论与新技术研究。镇江 江苏大学流体机械工程技术研究中心,212013。Email:xjwxk@126.com.
王新坤,肖思强,樊二东,徐胜荣. 滴灌毛管首部射流脉冲三通水力特性试验研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(12):116-121. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.12.015 http://www.tcsae.org
Wang Xinkun, Xiao Siqiang, Fan Erdong, Xu Shengrong. Hydraulic performance experiment of lateral pipe jet-pulse tee[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(12): 116-121. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.12.015 http://www.tcsae.org
