压缩感知中的概率约束优化模型及其D.C.近似
2017-06-27任咏红曹丽娜曲文静
任咏红, 曹丽娜, 姜 欢, 曲文静
(辽宁师范大学 数学学院,辽宁 大连 116029)
压缩感知中的概率约束优化模型及其D.C.近似
任咏红, 曹丽娜, 姜 欢, 曲文静
(辽宁师范大学 数学学院,辽宁 大连 116029)
带有噪声的压缩感知信号重建模型可表示为l1-范数问题.为了满足使用少量观测值重构出高精度的图像,在设置观测矩阵时需要满足受限等距性(RIP)和非相干性,然而判断一个矩阵的RIP是非常困难的.针对观测矩阵的不确定性,将该模型转化为具有概率约束的随机优化模型,即在约束条件以很大的概率被满足的情况下,求解最小l1-范数问题.构建了概率约束函数的一个D.C.近似函数,讨论了函数的性质,建立了相应的D.C.近似问题,证明了D.C.近似问题与概率约束优化问题的等价性.
压缩感知;概率约束;D.C.近似
近年来,信号处理领域出现了一种新颖的理论——压缩感知(Compressive Sensing)或叫压缩采样. 压缩感知的核心是利用特定矩阵把一个K-稀疏或可压缩的高维信号投影到低维空间上,然后利用信号的稀疏先验条件,通过一定的线性或非线性的重建模型重建出原始信号.而压缩感知信号重建模型可表示成l0-范数问题:
(1)
其中,Φ∈M×N为观测矩阵,x∈N,b∈M是观测值,N>M.
问题(1)是NP-hard问题,直接求解较困难,有效的求解方法是匹配追踪系列算法[1-3],此算法重建速度快,但精确度低且需要测量的数据多.
Donoho等[4-5]建立了问题(1)的等价问题l1-范数问题:
(2)
而在现实测量过程中,常存在各种各样噪声的干扰,破坏了信号的稀疏特性.因此,压缩感知需要恢复算法具有稳定性和对噪声的鲁棒特性.带有噪声ε≥0的压缩感知信号重建模型可以表示为
(3)
关于问题(3)的求解,常集中于凸优化算法[6-9].凸优化算法重建误差小,重建效果好,但是,速度慢,算法的复杂度高.
为了满足使用少量观测值重构出高精度的图像,在设置观测矩阵Φ时需要满足受限等距性(RIP)和非相干性,然而判断一个矩阵的RIP是非常困难的.本文针对观测矩阵的不确定性,将该模型转化为具有概率约束的随机优化模型,即在约束条件以很大的概率被满足的情况下,求解最小l1-范数问题.构建了概率约束函数的一个D.C.近似函数,讨论了近似函数的性质,建立了相应的D.C.近似问题,证明了D.C.近似问题与概率约束优化问题的等价性.
1 概率约束优化模型
考虑带有噪声的压缩感知信号重建模型:
其中,ε≥0代表噪声.
基于观测矩阵Φ的不确定性,将该模型转化为具有概率约束的随机优化模型如下:
(CCP)
其中,x∈X⊂N,‖·‖1为l1-范数,‖·‖2为l2-范数,Pr为概率,b∈M,ξ是支撑集Ξ上的随机向量,Φ:Ξ→M×N(M>N)为随机矩阵,ε≥0代表噪声,α∈(0,1)是置信水平.
问题(CCP)是具有概率约束的随机优化问题,求解该类问题具有代表性的方法主要有凸近似方法[10]、D.C.近似方法[11]等.
考虑问题(CCP), 若记
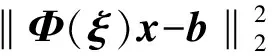
其中,
则问题(CCP)可变形为
(P)
2 D.C.近似问题
对∀t>0,定义函数

记
π(z,ε,t)=φ1(z,ε,t)-φ2(z,ε,t), ∀t>0.
由于φ1(z,ε,t)和φ2(z,ε,t)都是关于z的凸函数,则π(z,ε,t)是关于z的D.C.函数.
当t>0时,对所有的z∈有
π(z,ε,t)≥1(ε,+∞)(z).
则π(z,ε,t)是特征函数1(ε,+∞)(z)的一个凸保守的D.C.近似(如图1和图2所示).

图1 特征函数1(ε,+∞)(z)Fig.1 Characteristic function 1(ε,+∞)(z)
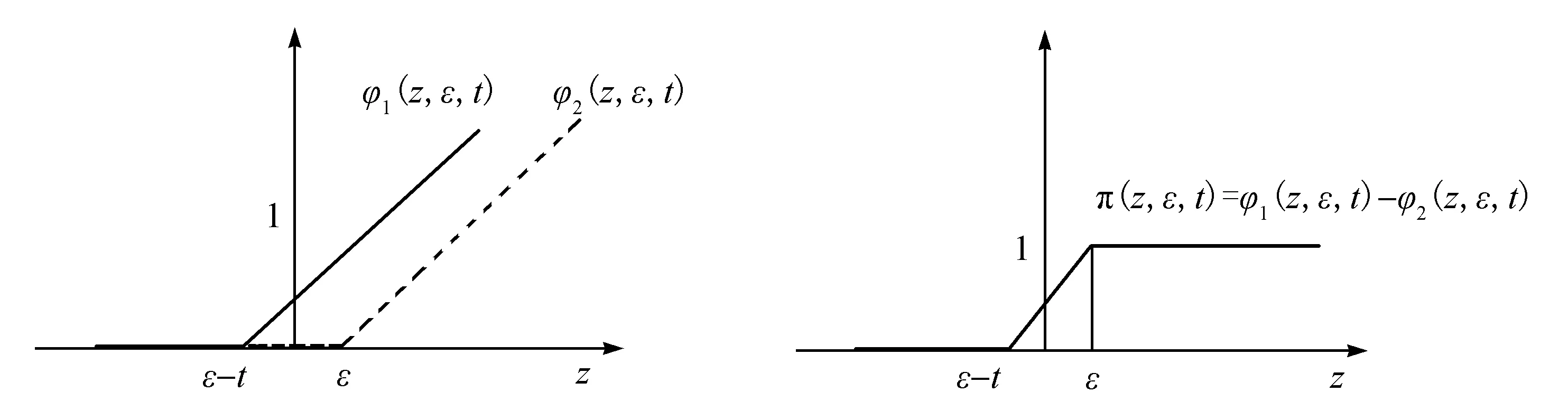
函数φ1(z,ε,t)和φ2(z,ε,t) D.C.近似函数π(z,ε,t)图2 特征函数1(ε,+∞)(z)的D.C.近似Fig.2 D.C. approximation function of characteristic function 1(ε,+∞)(z)
下述命题描述了函数π(z,ε,t)的性质.
命题2.1 对于∀t>0,函数π(z,ε,t)关于t是非减的.
证 对∀t>0,则有

则对于∀t1>t2>0,有

因此,当t>0时,π(z,ε,t)关于t是非减的.
证毕.
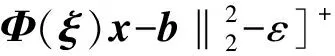
记
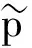
(4)
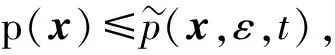


假设1X⊂N是凸紧致子集,ξ的支撑集Ξ是包含于k的闭集,Θ是使得X⊂Θ的一个有界开集.


证 由命题2.1可知,当t>0时,对∀z∈,π(z,ε,t)关于t是非减的,又由于
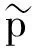

证毕.
引理2.2 若假设1和假设2成立,则g1(x,ε,t)在Θ×(-t,+t)上是可微的,并且有
xg1(x,ε,t)=E[‖2Φ(ξ)T(Φ(ξ)x-b)·1(ε-t,+∞)(‖Φ(ξ)x-b)],

证 记
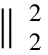
由于f(z)=[t+z-ε]+除了在点z=ε-t处都是可微的.则当z≠ε-t时,有
f′(z)=1(ε-t,+∞)(z).
xg1(x,ε,t)=E[‖2Φ(ξ)T(Φ(ξ)x-b)·1(ε-t,+∞)(‖Φ(ξ)x-b)],

由于g2(x,ε)=g1(x,ε,t),同理可得
xg2(x,ε)=E[‖2Φ(ξ)T(Φ(ξ)x-b)·1(ε,+∞)(‖Φ(ξ)x-b)].
证 由引理2.1,

由引理2.2得
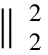

证毕.
[1] MALLAT S,ZHANG Z.Matching pursuits with time-frequency dictionaries[J].IEEE Transaction on Signal Processing,1993,41(12):3397-3415.
[2] TROPP J,GILBERT A.Signal recover from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit[J].IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,2008,53(12):4655-4666.
[3] NEEDELL D,VERSHYNIN R.Uniform uncertainty principle and signal recovery via regularized orthogonal matching pursuit[J].Foundations of Computational Mathematics,2009,9(3):317-334.
[4] CHEN S S,DONOHO D L,SAUNDERS M A.Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit[J].SIAM Review,2001,43(1):129-159.
[5] DONOHO D L,ELAD M,TEMLYAKOV V.Stable recovery of sparse overcomplete representations in the presence of noise[J].IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006,52(1):6-18.
[6] KIM S, KOH K, LUSTIG M,et al.An interior-point method for large-scalel1regularized least squares[J].IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing,2007,1(4):606-617.
[7] BOYD S,VANDENBERGHE L.Convex optimization[M].Cambridge, UK:Cambridge University Press, 2004:561-615.
[8] FIQUEIREDO M A T,NOWAK R D,WRIGHT S J.Gradient projection for sparse reconstruction:application to compressed sensing and other inverse problems[J].IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing,2007,1(4):586-598.
[9] DONOHO D L,TSAIG Y.Fast solution ofl1-norm minimization problems when the solution may be sparse[R].Palo Alto:Department of Statistics,Stanford University,USA,2008.
[10] NEMIROVSKI A,SHAPIRO A.Convex approximations of chance constrained programs[J].SIAM Journal on Optimization,2006,17(4):969-996.
[11] HONG L J,YANG Y,ZHANG L W.Sequential convex approximations to joint chance constrained programs:a monte carlo approach[J].Operation Research,2011,59(3):617-630.
Probability constrained optimization model and its D.C. approximation in compressed sensing
RENYonghong,CAOLina,JIANGHuan,QUWenjing
(School of Mathematics, Liaoning Normal University, Dalian 116029, China)
Compressed sensing signal reconstruction with noise can be expressed asl1-norm problem. In order to reconstruct a high-precision image with a small amount of observations, it is necessary to satisfy the restricted isometric (RIP) and non-coherence when setting the observation matrix. However, it is very difficult to judge the RIP of a matrix. In view of the uncertainty of the observation matrix, thel1-norm problem is transformed into a stochastic optimization model with probability constraint in this paper. That is, the minimuml1-norm problem is solved when the constraint is satisfied with a large probability. A D.C. approximation function of the probability constraint function is constructed. The properties of the function are discussed and the corresponding D.C. approximation problem is established. The equivalence between the D.C. approximation and the probability constrained optimization problem is proved.
compressed sensing;probability constraint;D.C. approximation
2017-01-20
辽宁省教育厅科学技术研究一般项目(L2015291);辽宁省自然科学基金指导计划项目(201602459);国家自然科学基金资助项目(11671184)
任咏红(1973-),女,辽宁朝阳人,辽宁师范大学副教授,博士.E-mail:ryhong@lnnu.edu.cn
1000-1735(2017)02-0154-05
10.11679/lsxblk2017020154
O221.5
A
