华北克拉通岩石圈地幔熔体与橄榄岩反应及相关高温高压实验
2017-06-10陈康唐红峰
陈康+唐红峰

摘要:基于大量地幔包体的岩石学和地球化学研究,推断在大陆岩石圈地幔内部发育着熔体与橄榄岩反应,以华北克拉通岩石圈地幔最具典型。依据地幔捕虏体的矿物交代特征和相关元素地球化学指标,华北克拉通岩石圈地幔发育着硅酸盐熔体与橄榄岩反应(如吉林辉南、安徽女山、山东山旺、河北汉诺坝、内蒙古集宁、河北符山等地区)和碳酸岩熔体与橄榄岩反应(如河南鹤壁、山东铁铜沟、河南信阳等地区)。已有的熔体与橄榄岩反应高温高压实验研究的初始熔体也可以归为硅酸盐熔体和碳酸岩熔体两大类。这些实验研究为探讨异剥橄榄岩、纯橄岩、高镁安山岩、高镁埃达克质岩等特殊岩石成因及岩石圈地幔组成的变化提供了直接证据。今后通过进一步的熔体与橄榄岩反应高温高压实验研究,建立反应产物特征与初始熔体性质、组成的对应关系,是揭示华北克拉通岩石圈地幔从古老难熔型向“年轻”饱满型演化的重要途径。
关键词:实验岩石学;熔体与橄榄岩反应;高温高压实验;岩石圈地幔;硅酸盐熔体;碳酸岩熔体;华北克拉通
中图分类号:P589.1文献标志码:A
Abstract: It has been concluded that there are meltperidotite reactions occurring within continental lithospheric mantles from the petrological and geochemical studies on a large number of mantle xenoliths. This case is especially typical in the lithospheric mantle of North China Craton. Based on the mineralogical metasomatic characteristics in mantle xenoliths and the related element geochemical signatures, it is identified that the melt reacted with peridotite within the lithospheric mantle of North China Craton is silicate melt such as in Huinan of Jilin, Nushan of Anhui, Shanwang of Shandong, Hannuoba of Hebei, Jining of Inner Mongolia and Fushan of Hebei, and carbonatite melt such as in Hebi of Henan, Tietonggou of Shandong and Xinyang of Henan. The starting melts used in previous reaction experiments under hightemperature and highpressure conditions can be also classified into silicate and carbonatite melts. The experimental studies have provided direct evidence for the origin of some special rocks, such as wehrlite, dunite, highMg andesite, highMg adakite, and for the compositional change in lithospheric mantle. Further experimental study on meltperidotite reaction under hightemperature and highpressure conditions, in which the characteristic of run product is correlated with the property and composition of the starting melt, is an important way to reveal lithospheric mantle evolution of North China Craton from ancient refractory to “young” fertile.
Key words: experimental petrology; meltperidotite reaction; experiment under hightemperature and highpressure conditions; lithospheric mantle; silicate melt; carbonatite melt; North China Craton
0引言
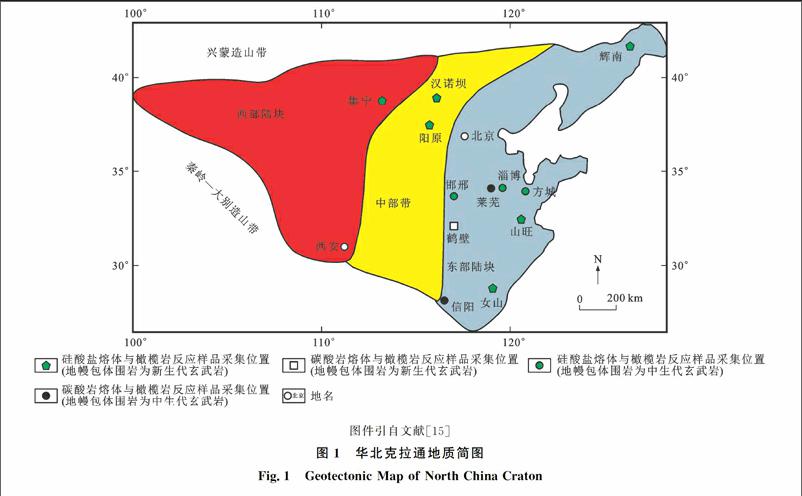
图件引自文献[15]
岩石圈地幔是地球内部连接地壳和软流圈的重要圈层,是岩石圈的主体。大陆岩石圈地幔以莫霍面为界,下伏于大陆地壳,上覆于软流圈。特殊的位置决定了大陆岩石圈地幔对大陆地壳和整个大陆岩石圈的性质和组成有重要影响。古老的克拉通型岩石圈地幔主要由富Mg的方輝橄榄岩组成,其主要矿物是橄榄石和斜方辉石[17]。根据前人对大陆岩石圈地幔的研究,南非Debeers、Jagersfontein及Bultfontein等地金伯利岩区中常出现主要含有金云母、角闪石和富含不相容元素的FeTi氧化物等交代矿物[814]。这些交代矿物的出现意味着富含K、Ba、Ti、Zr、Nb和稀土元素(REE)等不相容元素的熔体与地幔橄榄岩发生了反应,改变了岩石圈地幔的组成。前人通过对中国华北克拉通古生代金伯利岩、中生代玄武岩或闪长岩、新生代玄武岩所携带的地幔岩包体系统的岩石学、矿物学和地球化学研究(图1),推断在华北克拉通岩石圈地幔演化过程中较为广泛地发育着橄榄岩与不同性质熔体的反应。
这些通过对实际样品研究得到的反演推论有一定合理性,但是对于准确揭示岩石圈地幔橄榄岩与熔体反应机制和温度压力条件、参与反应的初始熔体的组成,上述推论存在不确定性。高温高压实验研究则可以通过一定的方案设计,建立参与反应的初始熔体组成、温度压力条件以及与反应产物特征之间的对应关系,为检验依据实际样品研究得到的反演推论,正确认识熔体橄榄岩反应机制和条件,深入揭示大陆岩石圈地幔演化过程提供直接证据,因此,其越来越受到地质科学家的重视,也获得了一些重要进展。
基于此,本文通过总结对比华北克拉通岩石圈地幔内部发育的熔体与橄榄岩反应地质实例及相关高温高压实验,阐释高温高压实验研究可以建立反应后的矿物组合特征、反应带新生矿物元素组成和分配行为与初始熔体性质和组成的对应关系,为阐明华北克拉通岩石圈地幔从古老难熔型向“年轻”饱满型演化的机制提供直接证据。
1熔体与橄榄岩反应
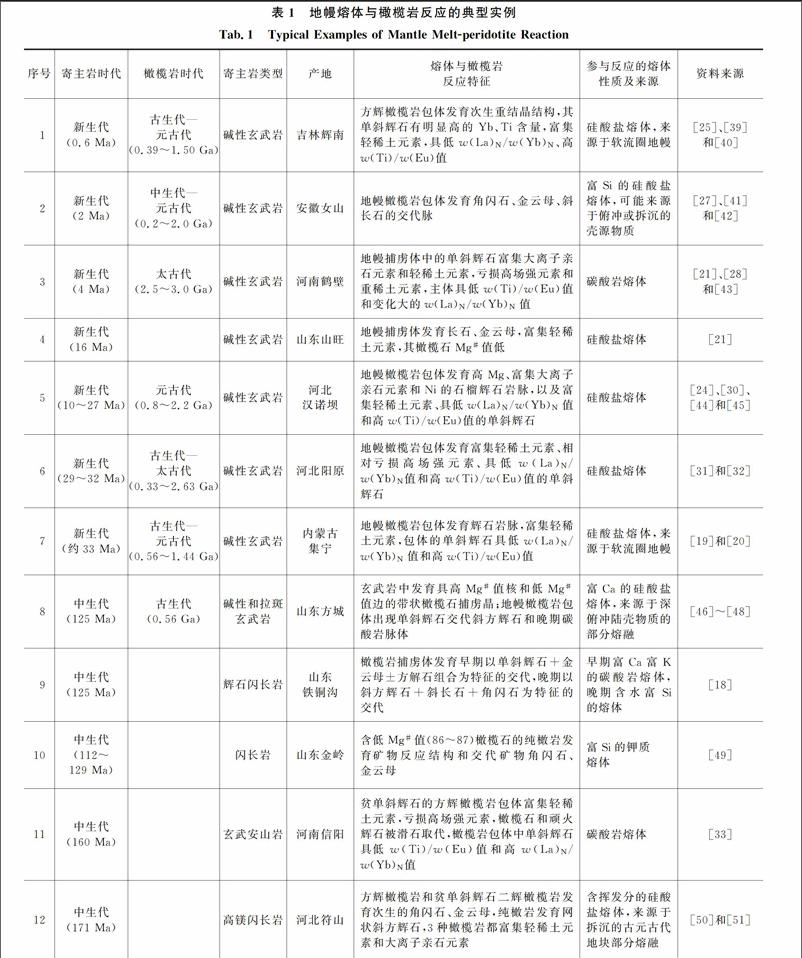
熔体与橄榄岩反应在大陆岩石圈地幔中普遍存在,在华北克拉通岩石圈地幔内部尤其发育。按照寄主岩的时代和类型、熔体与橄榄岩反应特征、熔体性质和来源等,总结华北克拉通地幔熔体与橄榄岩反应的典型实例(表1)。
前人依据地幔捕虏体的矿物交代特征及相关元素地球化学指标[1617],推断在华北克拉通发育着导致地幔由难熔型向饱满型演化的熔体与橄榄岩反应。在吉林辉南、安徽女山、山东山旺、河北漢诺坝、内蒙古集宁、河北符山等地区,地幔包体发育交代成因硅酸盐矿物(辉石、角闪石、金云母、斜长石等)和/或次生重结晶结构、交代脉体等显性交代特征,包体全岩富集大离子亲石元素(LILE)、轻稀土元素(LREE),包体中单斜辉石具低w(La)N/w(Yb)N值、高w(Ti)/w(Eu)值等隐性交代特征,由此推断上述地区岩石圈地幔发生了硅酸盐熔体与橄榄岩反应(表1、图2);而在河南鹤壁、山东铁铜沟、河南信阳等地区,地幔包体发育交代成因单斜辉石、方解石等富钙矿物,包体全岩富集轻稀土元素、亏损高场强元素(HFSE),包体中单斜辉石具低w(Ti)/w(Eu)值、高w(La)N/w(Yb)N值等隐性交代特征,据此推断上述地区岩石圈地幔主要发生了碳酸岩熔体与橄榄岩反应(表1、图2)。实际上,前人获得的部分岩石圈地幔橄榄岩定年结果(表1)显示,形成于太古代的华北克拉通岩石圈地幔局部不同程度地发生了年轻化,这一现象也意味着岩石圈地幔受到了后期熔体和/或流体的改造。
硅酸盐熔体、碳酸岩熔体交代作用分区引自文献[16];吉林辉南数据引自文献[25]、[26];安徽女山数据引自文献[27];河南鹤壁数据引自文献[23]、[28];山东山旺数据引自文献[22]、[29];河北汉诺坝数据引自文献[24]、[30];河北阳原数据引自文献[31]、[32];内蒙古集宁数据引自文献[19]、[20];河南信阳数据引自文献[33];w(·)为元素含量(质量分数,下同);w(·)N为元素含量球粒陨石标准化后的值
在华北克拉通古老岩石圈地幔向新生地幔转变过程中,参与反应的熔体既有单一性质,也有复合性质。在铁铜沟地区,熔体与橄榄岩反应早期以碳酸岩熔体交代为主,晚期又发生了富硅熔体与橄榄岩反应[18],在不同时期经历了不同性质熔体与橄榄岩反应过程。研究表明,熔体橄榄岩相互作用不仅发生在已经遭到破坏和减薄的华北克拉通东部地区,也同样发生在华北克拉通西部地区[1920]。从岩石圈地幔性质角度来看,华北克拉通东部橄榄岩包体所表现出的新、老地幔共存,分布不均匀的特征可能是软流圈物质对古老岩石圈地幔的不均一侵蚀导致了东部岩石圈的剧烈减薄[2124],而华北克拉通西部岩石圈地幔是原始地幔经过不同程度部分熔融之后的产物,既有饱满地幔,又存在过渡类型地幔。因此,不管在华北克拉通东部还是西部都存在不同性质熔体与橄榄岩反应,总体显示出时空分布上的无规律性。
2相关高温高压实验
2.1不同性质熔体与橄榄岩反应
由于地球内部熔体组成的复杂性,加上根据实际样品难以准确确定参与反应的初始熔体组成(因为实际样品保留下来的只是发生了反应后的信息),所以前人在开展熔体与岩石(矿物)反应的高温高压实验研究时,依照各自拟解决的科学问题选择了不同初始物以模拟初始熔体(表2)。综合已有研究,可以将前人的熔体与橄榄岩反应实验的初始熔体划归为两大类:硅酸盐熔体和碳酸岩熔体[34]。硅酸盐熔体还可以具体区分为SiO2含量较低的贫硅熔体(包括拉斑玄武质贫硅熔体[3538]和碱性玄武质贫硅
表1地幔熔体与橄榄岩反应的典型实例
Tab.1Typical Examples of Mantle Meltperidotite Reaction
序号寄主岩时代橄榄岩时代寄主岩类型产地熔体与橄榄岩反应特征参与反应的熔体性质及来源资料来源
1新生代(0.6 Ma)古生代—元古代(0.39~1.50 Ga)碱性玄武岩吉林辉南方辉橄榄岩包体发育次生重结晶结构,其单斜辉石有明显高的Yb、Ti含量,富集轻稀土元素,具低w(La)N/w(Yb)N、高w(Ti)/w(Eu)值硅酸盐熔体,来源于软流圈地幔[25]、[39]和[40]
2新生代(2 Ma)中生代—元古代(0.2~2.0 Ga)碱性玄武岩安徽女山地幔橄榄岩包体发育角闪石、金云母、斜长石的交代脉富Si的硅酸盐熔体,可能来源于俯冲或拆沉的壳源物质[27]、[41]和[42]
3新生代(4 Ma)太古代(2.5~3.0 Ga)碱性玄武岩河南鹤壁地幔捕虏体中的单斜辉石富集大离子亲石元素和轻稀土元素,亏损高场强元素和重稀土元素,主体具低w(Ti)/w(Eu)值和变化大的w(La)N/w(Yb)N值碳酸岩熔体[21]、[28]和[43]
4新生代(16 Ma)碱性玄武岩山东山旺地幔捕虏体发育长石、金云母,富集轻稀土元素,其橄榄石Mg#值低硅酸盐熔体[21]
5新生代(10~27 Ma)元古代(0.8~2.2 Ga)碱性玄武岩河北汉诺坝地幔橄榄岩包体发育高Mg、富集大离子亲石元素和Ni的石榴辉石岩脉,以及富集轻稀土元素、具低w(La)N/w(Yb)N值和高w(Ti)/w(Eu)值的单斜辉石硅酸盐熔体[24]、[30]、[44]和[45]
6新生代(29~32 Ma)古生代—太古代(0.33~2.63 Ga)碱性玄武岩河北阳原地幔橄榄岩包体發育富集轻稀土元素、相对亏损高场强元素、具低w(La)N/w(Yb)N值和高w(Ti)/w(Eu)值的单斜辉石硅酸盐熔体[31]和[32]
7新生代(约33 Ma)古生代—元古代(0.56~1.44 Ga)碱性玄武岩内蒙古集宁地幔橄榄岩包体发育辉石岩脉,富集轻稀土元素,包体的单斜辉石具低w(La)N/w(Yb)N值和高w(Ti)/w(Eu)值硅酸盐熔体,来源于软流圈地幔[19]和[20]
8中生代(125 Ma)古生代(0.56 Ga)碱性和拉斑玄武岩山东方城玄武岩中发育具高Mg#值核和低Mg#值边的带状橄榄石捕虏晶;地幔橄榄岩包体出现单斜辉石交代斜方辉石和晚期碳酸岩脉体富Ca的硅酸盐熔体,来源于深俯冲陆壳物质的部分熔融[46]~[48]
9中生代(125 Ma)辉石闪长岩山东铁铜沟橄榄岩捕虏体发育早期以单斜辉石+金云母±方解石组合为特征的交代,晚期以斜方辉石+斜长石+角闪石为特征的交代早期富Ca富K的碳酸岩熔体,晚期含水富Si的熔体[18]
10中生代(112~129 Ma)闪长岩山东金岭含低Mg#值(86~87)橄榄石的纯橄岩发育矿物反应结构和交代矿物角闪石、金云母富Si的钾质熔体[49]
11中生代(160 Ma)玄武安山岩河南信阳贫单斜辉石的方辉橄榄岩包体富集轻稀土元素,亏损高场强元素,橄榄石和顽火辉石被滑石取代,橄榄岩包体中单斜辉石具低w(Ti)/w(Eu)值和高w(La)N/w(Yb)N值碳酸岩熔体[33]
12中生代(171 Ma)高镁闪长岩河北符山方辉橄榄岩和贫单斜辉石二辉橄榄岩发育次生的角闪石、金云母,纯橄岩发育网状斜方辉石,3种橄榄岩都富集轻稀土元素和大离子亲石元素含挥发分的硅酸盐熔体,来源于拆沉的古元古代地块部分熔融[50]和[51]
熔体[5254])和SiO2含量较高的富硅熔体[5559]。这些实验研究为探讨岩石圈地幔组成的变化、某些特殊地幔岩(如异剥橄榄岩、纯橄岩)和喷出岩(如高镁安山岩和埃达克质岩、原始洋中脊玄武岩、洋岛玄武岩)的成因提供了重要的直接证据[6061]。例如,富硅的英云闪长质熔体与二辉橄榄岩反应后,在橄榄岩的橄榄石边缘形成了斜方辉石+石榴石的反应带[图3(a)][62],其矿物组成特征与Liu等报道的汉诺
坝地幔包体中发育的石榴辉石岩脉体[图3(b)][30]近于一致。因此,富硅熔体与地幔橄榄岩反应的高温高压实验为揭示华北克拉通岩石圈地幔中石榴辉石岩脉的形成机制提供了直接证据。相比硅酸盐熔体,碳酸岩熔体具有低密度、低黏度和高反应活性,极易发生渗滤流动,能够与地幔橄榄岩保持化学平衡,被认为是最有效的地幔交代介质[6667]。例如,以白云岩为初始物的碳酸岩熔体,在高温高压下与地幔橄榄岩的反应主要是与橄榄岩中的斜方辉石发生反应[34]。其反应式为
CaMg(CO3)2+2Mg2Si2O6=CaMgSi2O6+
2Mg2SiO4+2CO2
CaMg(CO3)2+Mg2Si2O6=CaMgSi2O6+2MgCO3
上述反应的产物是橄榄石和富钙的单斜辉石,因此,碳酸岩熔体与地幔二辉橄榄岩或方辉橄榄岩反应的实验结果可以解释岩石圈地幔内异剥橄榄岩的成因[34]。
硅酸盐熔体与橄榄岩反应后橄榄石Fo牌号通常略有降低,新生单斜辉石富集强不相容元素;而碳酸岩熔体与橄榄岩反应后橄榄石Fo牌号略有升高,新生单斜辉石富集大离子亲石元素和轻稀土元素,亏损高场强元素[7,54,68]。
2.2高温高压实验研究的岩石学意义
2.2.1低镁纯橄岩成因
一般情况下,硅酸盐熔体相对于地幔橄榄岩富Si、Ca、Fe,而贫Mg、Ni。硅酸盐熔体与地幔橄榄岩反应的结果会使橄榄岩向富Si、Ca、Fe,贫Mg的方向演化,从而形成低Mg的地幔岩。在1 500 ℃、35 GPa温压条件下,利用角闪榴辉石岩与尖晶石二辉橄榄岩进行高温高压实验,橄榄石Mg#值从反应前的89~90降低到反应后小于
85[64]。在1 300 ℃、10 GPa温压条件下,碱性玄武岩(SiO2含量为471%)熔体与二辉橄榄岩反应的产物是自熔体二辉橄榄岩接触面往橄榄岩内部依次形成纯橄岩、方辉橄榄岩、二辉橄榄岩的岩性序列[53],而且3种橄榄岩中橄榄石的Mg#值自纯橄岩、方辉橄榄岩到二辉橄榄岩内部呈现单调递增,其中纯橄岩带中橄榄石的Mg#值普遍较小(低于88)[53]。上述熔体与橄榄岩反应的实验结果证实,岩石圈地幔内部的硅酸盐熔体与橄榄岩反应不仅促使橄榄石向低Mg#值的转变,而且橄榄岩中辉石与熔体反应生成橄榄石,从而可以导致低镁纯橄岩的形成。
2.2.2高镁安山岩和埃达克质岩的形成
与正常的岛弧安山岩和埃达克质岩相比,高镁安山岩和埃达克质岩以富Mg(Mg#值高于50)、Cr、Ni为特征,以及含有相对较少的Al2O3(含量低于16%)和CaO(含量低于10%)[6970]。实验岩石学证明,玄武岩部分熔融产生的熔体Mg#值小于45,因此,一些新生代与俯冲带有关的、具有低SiO2含量(低于65%)和高Mg#值(47~70)的高镁安山岩和埃达克质岩可能是岩浆被地幔橄榄岩混染的结果[7172]。图4中实验数据与天然高镁安山岩有明显的系统误差,其原因很可能是实验采用的初始熔体组成与地质实际情况有差异;但是主量元素组成[7375]显示,华北克拉通内部多处典型高镁安山岩MgO、SiO2含量呈现负相关关系(图4),高温高压条件下硅酸盐熔体与橄榄岩反应后熔体从低MgO、高SiO2向高MgO、低SiO2方向演化,MgO、SiO2含量呈现出与华北克拉通内部高镁安山岩类似的负相关关系。因此,安山质硅酸盐熔体与地幔橄榄岩反应可能是形成华北克拉通内部安山岩和高镁埃达克质岩的一种重要机制。
高镁安山岩数据引自文献[73]~[75];实验反应后熔体数据引自文献[55]、[58];实线箭头是高镁安山岩的变化趋势;虚线箭头代表实验反应后熔体的变化趋势
2.2.3对大陆岩石圈地幔演化的制约
大陆岩石圈地幔在空间上介于陆壳与软流圈之间,其演化自然与后两个层圈有密切联系。陆壳物质通过俯冲作用或者拆沉作用进入岩石圈地幔,然后发生熔融而形成SiO2含量较高的硅酸盐熔体;该熔体在岩石圈地幔内部运移过程中可以与地幔橄榄岩中相对贫硅的矿物发生反应,如“橄榄石+富硅熔体→斜方辉石+贫硅熔体”[35]。另一方面,来自软流圈地幔的物质(如相对贫硅的拉斑玄武质熔体、碱性玄武质熔体)在上涌进入岩石圈地幔后可以与地幔橄榄岩中相对富硅的矿物发生反应,如“斜方辉石+贫硅熔体→橄榄石+富硅熔体”[35]。此外,目前对岩石圈地幔中碳酸岩熔体的来源和组成尚不明确,但无论是来自俯冲板片的壳源碳酸盐岩,还是来自软流圈地幔的碳酸岩岩浆,由于其富钙特征,都可以与岩石圈地幔中相对贫钙的矿物发生反应,如“斜方辉石+碳酸岩熔体→单斜辉石+橄榄石+CO2”[34]。因此,熔体与橄榄岩反应在大陆岩石圈内较为发育(图1)。由于熔体相对于地幔橄榄岩明显富集Al、Ca、Na等主量元素和许多微量元素,所以持续的熔体与橄榄岩反应无疑将会导致岩石圈地幔由难熔型向饱满型演化[7677]。
3结语
高温高压实验在模拟地球内部的物理和化学过程具有不可替代的优势,属于当今地球科学研究的前沿领域。模拟大陆岩石圈地幔的熔体与橄榄岩反应的高温高压实验,可以为认识华北克拉通以及世界其他地区古老克拉通岩石圈地幔的演化机制与过程提供重要的直接依据。
然而,已有熔体与橄榄岩反应的高温高压实验使用的橄榄岩初始物几乎都被研磨成很细的粉末而容易发生熔融,因此,反应产物中难以观察到像地幔岩捕虏体那样清楚的矿物交代现象和反应带矿物组合特征,对于熔体与橄榄岩反应新生矿物的微量元素组成更是不容易获得。基于此,今后开展较粗粒的地幔矿物或保持结构不变的橄榄岩与熔体反应的高温高压实验,研究反应带的矿物组合特征、残余熔体和新生矿物元素组成及其与初始熔体性质和组成的对应关系,是揭示如华北克拉通岩石圈地幔那样从古老难熔型向“年轻”饱满型演化的重要途径。
相对于硅酸盐熔体,前人对于碳酸岩熔体与橄榄岩或其组成矿物反应的实验研究很不足。而实际情况是岩石圈地幔橄榄岩与碳酸岩熔体的反应确实存在,因此,相关实验研究需要大力加强。此外,熔体与橄榄岩反应的机制和动力学关系到橄榄岩转变的起因和程度,是探讨岩石圈地幔演化的关键因素,而实验研究可以通过对时间、温度、压力等参数的控制,结合反应结果(如反应边宽度等)获得反应机制和速率的重要信息,这也是今后高温高壓实验研究需要加强的方向。
参考文献:
References:
[1]KELEMEN P B,HART S R,BERNSTEIN S.Silica Enrichment in the Continental Upper Mantle via Melt/Rock Reaction[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1998,164(1/2):387406.
[2]XU W L,HERGT J M,GAO S,et al.Interaction of Adakitic Meltperidotite:Implications for the HighMg# Signature of Mesozoic Adakitic Rocks in the Eastern North China Craton[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2008,265(1/2):123137.
[3]YING J F,ZHANG H F,KITA N,et al.Nature and Evolution of Late Cretaceous Lithospheric Mantle Beneath the Eastern North China Craton:Constraints from Petrology and Geochemistry of Peridotitic Xenoliths from Junan,Shandong Province,China[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2006,244(3/4):622638.
[4]FAN W M,ZHANG H F,BAKER J,et al.On and off the North China Craton:Where Is the Archaean Keel?[J].Journal of Petrology,2000,41(7):933950.
[5]GRIFFIN W L,OREILLY S Y,AFONSO J C,et al.The Composition and Evolution of Lithospheric Mantle:A Reevaluation and Its Tectonic Implications[J].Journal of Petrology,2009,50(7):11851204.
[6]POLLACK H N.Cratonization and Thermal Evolution of the Mantle[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1986,80(1/2):175182.
[7]WULFFPEDERSEN E,NEUMANN E R,VANNUCCI R,et al.Silicic Melts Produced by Reaction Between Peridotite and Infiltrating Basaltic Melts:Ion Probe Data on Glasses and Minerals in Veined Xenoliths from La Palma,Canary Islands[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1999,137(1):5982.
[8]PASTERIS J D,BOYD F R,NIXON P H.The Ilmenite Association at the Frank Smith Mine,R.S.A.[C]∥BOYD F R,MEYER H O A.The Mantle Sample:Inclusion in Kimberlites and Other Volcanics.Washington DC:American Geophysical Union,1979:265278.
[9]LE ROEX A P,BELL D R,DAVIS P.Petrogenesis of Group I Kimberlites from Kimberley,South Africa:Evidence from Bulkrock Geochemistry[J].Journal of Petrology,2003,44(12):22612286.
[10]HAGGERTY S E.Oxide Mineralogy of the Upper Mantle[J].Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry,1991,25:355416.
[11]HAGGERTY S E.Superkimberlites:A Geodynamic Diamond Window to the Earths Core[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1994,122(1/2):5769.
[12]DAWSON J B.The MARID (Micaamphibolerutileilmenitediopside) Suite of Xenoliths in Kimberlite[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1977,41(2):309323.
[13]WATERS F G.A Suggested Origin of MARID Xenoliths in Kimberlites by High Pressure Crystallization of an Ultrapotassic Rock such as Lamproite[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1987,95(4):523533.
[14]GIBSON S A,MALARKEY J,DAY J A.Melt Depletion and Enrichment Beneath the Western Kaapvaal Craton:Evidence from Finsch Peridotite Xenoliths[J].Journal of Petrology,2008,49(10):18171852.
[15]ZHAO G C,WILDE S A,CAWOOD P A,et al.Archean Blocks and Their Boundaries in the North China Craton:Lithological,Geochemical,Structural and PT Path Constraints and Tectonic Erolution[J].Precambrian Research,2001,107(1/2):4573.
[16]COLTORTI M,BONADIMAN C,HINTON R W,et al.Carbonatite Metasomatism of the Oceanic Upper Mantle:Evidence from Clinopyroxenes and Glasses in Ultramafic Xenoliths of Grande Comore,Indian Ocean[J].Journal of Petrology,1999,40(1):133165.
[17]HAURI E H,SHIMIZU N,DIEU J J,et al.Evidence for Hotspotrelated Carbonatite Metasomatism in the Oceanic Upper Mantle[J].Nature,1993,365:221227.
[18]陳立辉,周新华.鲁西中生代闪长岩中的深源超镁铁质岩捕虏体及其富硅交代特征[J].中国科学:D辑,地球科学,2003,33(8):734744.
CHEN Lihui,ZHOU Xinhua.Ultramafic Xenoliths in Mesozoic Diorite in West Shandong Province[J].Science in China:Series D,Earth Sciences,2003,33(8):734744.
[19]周媛婷,郑建平,余淳梅,等.内蒙古集宁新生代玄武岩中橄榄岩包体矿物化学特征及其地幔演化意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志,2010,29(3):243257.
ZHOU Yuanting,ZHENG Jianping,YU Chunmei,et al.Peridotite Xenoliths in Jining Cenozoic Basalts:Mineralchemistry and Significance for Lithospheric Mantle Evolution Beneath the North China Craton[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,2010,29(3):243257.
[20]ZHANG H F,SUN Y L,TANG Y J,et al.Meltperidotite Interaction in the PreCambrian Mantle Beneath the Western North China Craton:Petrology,Geochemistry and Sr,Nd and Re Isotopes[J].Lithos,2012,149:100114.
[21]鄭建平,路凤香,GRIFFIN W L,等.华北东部橄榄岩与岩石圈减薄中的地幔伸展和侵蚀置换作用[J].地学前缘,2006,13(2):7685.
ZHENG Jianping,LU Fengxiang,GRIFFIN W L,et al.Lithospheric Thinning Accompanying Mantle Lateral Spreading,Erosion and Replacement Beneath the Eastern Part of North China:Evidence from Peridotites[J].Earth Science Frontiers,2006,13(2):7685.
[22]ZHENG J P,OREILLY S Y,GRIFFIN W L,et al.Nature and Evolution of Cenozoic Lithospheric Mantle Beneath Shandong Peninsula,North China Block[J].International Geology Review,1998,40(6):471499.
[23]ZHENG J P,OREILLY S Y,GRIFFIN W L,et al.Relict Refractory Mantle Beneath the Eastern North China Block:Significance for Lithosphere Evolution[J].Lithos,2001,57(1):4366.
[24]余淳梅,郑建平,GRIFFIN W L.汉诺坝橄榄岩捕虏体的单斜辉石LAMICPMS分析及其岩石圈地幔演化意义[J].地球科学,2006,31(1):93100.
YU Chunmei,ZHENG Jianping,GRIFFIN W L.LAMICPMS Analysis on Clinopyroxenes of Peridotite Xenoliths from Hannuoba and Its Significance on Lithospheric Mantle Evolution[J].Earth Science,2006,31(1):93100.
[25]XU Y G,MENZIES M A,THIRLWALL M F,et al.“Reactive” Harzburgites from Huinan,NE China:Products of the Lithosphereasthenosphere Interaction During Lithospheric Thinning? [J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2003,67(3):487505.
[26]张志海,郑建平,马鸿文.吉林汪清—辉南地幔透辉石微量元素及其记录的地幔熔融与交代作用[J].地质科技情报,2006,25(6):916.
ZHANG Zhihai,ZHENG Jianping,MA Hongwen.Trace Elemental Compositions of Peridotitic Diopsides and the Record of Partial Melting and Metasomatism in Lithosphere Beneath Wangqing and Huinan Areas,Jilin Province[J].Geological Science and Technology Information,2006,25(6):916.
[27]刘志超,吴福元,储著银,等.安徽女山地幔橄榄岩捕虏体的同位素组成:中国东部新生代岩石圈地幔时代制约[J].岩石学报,2010,26(4):12171240.
LIU Zhichao,WU Fuyuan,CHU Zhuyin,et al.Isotopic Compositions of the Peridotitic Xenoliths from the Nushan Area,Anhui Province:Constraints on the Age of Subcontinental Lithospheric Mantle Beneath the East China[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica,2010,26(4):12171240.
[28]SUN J,LIU C Z,WU F Y,et al.Metasomatic Origin of Clinopyroxene in Archean Mantle Xenoliths from Hebi,North China Craton:Traceelement and Srisotope Constraints[J].Chemical Geology,2012,328:123136.
[29]ZHENG J P,GRIFFIN W L,OREILLY S Y,et al.Mineral Chemistry of Peridotites from Paleozoic,Mesozoic and Cenozoic Lithosphere:Constraints on Mantle Evolution Beneath Eastern China[J].Journal of Petrology,2006,47(11):22332256.
[30]LIU Y S,GAO S,AEOLUSLEE C T,et al.Meltperidotite Interactions:Links Between Garnet Pyroxenite and HighMg# Signature of Continental Crust[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2005,234(1/2):3957.
[31]陈曦,郑建平.河北阳原新生代玄武岩中橄榄岩捕虏体矿物化学:华北岩石圈地幔演化[J].地球科学,2009,34(1):203219.
CHEN Xi,ZHENG Jianping.Mineral Chemistry of Peridotite Xenoliths in Yangyuan Cenozoic Basalts:Significance for Lithospheric Mantle Evolution Beneath the North China Craton[J].Earth Science,2009,34(1):203219.
[32]XU Y G,BLUSZTAJN J,MA J L,et al.Late Archean to Early Proterozoic Lithospheric Mantle Beneath the Western North China Craton:SrNdOs Isotopes of Peridotite Xenoliths from Yangyuan and Fansi[J].Lithos,2008,102(1/2):2542.
[33]ZHENG J P,SUN M,ZHOU M F,et al.Trace Elemental and PGE Geochemical Constraints of Mesozoic and Cenozoic Peridotitic Xenoliths on Lithospheric Evolution of the North China Craton[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2005,69(13):34013418.
[34]DALTON J A,WOOD B J.The Compositions of Primary Carbonate Melts and Their Evolution Through Wallrock Reaction in the Mantle[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1993,119(4):511525.
[35]KELEMEN P B,JOYCE D B,WEBSTER J D,et al.Reaction Between Ultramafic Rock and Fractionating Basaltic Magma:II.Experimental Investigation of Reaction Between Olivine Tholeiite and Harzburgite at 1 150 ℃1 050 ℃ and 5 kbar[J].Journal of Petrology,1990,31(1):99134.
[36]LAMBART S,LAPORTE D,SCHIANO P.An Experimental Study of Focused Magma Transport and Basaltperidotite Interactions Beneath Midocean Ridges:Implications for the Generation of Primitive MORB Compositions[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,2009,157(4):429451.
[37]VAN DEN BLEEKEN G,MUNTENER O,ULMER P.Melt Variability in Percolated Peridotite:An Experimental Study Applied to Reactive Migration of Tholeiitic Basalt in the Upper Mantle[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,2011,161(6):921945.
[38]VAN DEN BLEEKEN G,MUNTENER O,ULMER P.Reaction Processes Between Tholeiitic Melt and Residual Peridotite in the Uppermost Mantle:An Experimental Study at 0.8 GPa[J].Journal of Petrology,2010,51(1/2):153183.
[39]魯江姑,郑建平.辉南新生代玄武岩中橄榄岩捕虏体矿物化学与华北岩石圈地幔演化[J].地质学报,2011,85(3):330342.
LU Jianggu,ZHENG Jianping.Mineralogical Chemistry of Peridotite Xenoliths from the Huinan Cenozoic Basalts:Implication for Evolution of the Lithospheric Mantle Beneath the North China Craton[J].Acta Geologica Sinica,2011,85(3):330342.
[40]WU F Y,WALKER R J,REN X W,et al.Osmium Isotopic Constraints on the Age of Lithospheric Mantle Beneath Northeastern China[J].Chemical Geology,2003,196(1/2/3/4):107129.
[41]支霞臣,REISBERG L,徐夕生.安徽女山幔源橄榄岩捕虏体ReOs同位素地球化学[J].中国科学技术大学学报,2007,37(8):945952.
ZHI Xiachen,REISBERG L,XU Xisheng.ReOs Geochemistry of Mantle Peridotite Xenoliths from Nushan[J].Journal of University of Science and Technology of China,2007,37(8):945952.
[42]支霞臣,秦協.中国东部地幔橄榄岩捕虏体的ReOs同位素地球化学:岩石圈地幔的形成年龄和减薄作用的制约[J].岩石学报,2004,20(5):989998.
ZHI Xiachen,QIN Xie.ReOs Isotope Geochemistry of Mantlederived Peridotite Xenoliths from Eastern China:Constraints on the Age and Thinning of Lithosphere Mantle[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica,2004,20(5):989998.
[43]余淳梅.华北克拉通中东部典型地区橄榄岩捕虏体年龄及地幔不均一性[D].武汉:中国地质大学,2009.
YU Chunmei.Ages of Peridotitic Xenoliths from the Central and Eastern Areas of North China Craton and Mantle Heterogeneity[D].Wuhan:China University of Geosciences,2009.
[44]夏琼霞,支霞臣,孟庆,等.汉诺坝幔源橄榄岩包体的微量元素和ReOs同位素地球化学:SCLM的性质和形成时代[J].岩石学报,2004,20(5):12151224.
XIA Qiongxia,ZHI Xiachen,MENG Qing,et al.The Trace Element and ReOs Isotopic Geochemistry of Mantlederived Peridotite Xenoliths from Hannuoba:Nature and Age of SCLM Beneath the Area[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica,2004,20(5):12151224.
[45]ZHANG H F,GOLDSTEIN S L,ZHOU X H,et al.Comprehensive Refertilization of Lithospheric Mantle Beneath the North China Craton:Further OsSrNd Isotopic Constraints[J].Journal of the Geological Society,2009,166(2):249259.
[46]ZHANG H F.Transformation of Lithospheric Mantle Through Peridotitemelt Reaction:A Case of SinoKorean Craton[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2005,237(3/4):768780.
[47]许文良,周群君,杨德彬,等.大陆深俯冲作用对邻区岩石圈地幔改造的时间、方式与过程:鲁西橄榄岩类与辉石岩类捕虏体证据[J].科学通报,2013,58(23):23002305.
XU Wenliang,ZHOU Qunjun,YANG Debin,et al.Timing,Style and Process of Modifying Adjacent Lithospheric Mantle by Melts Derived from Deeply Subducted Continental Crust:Evidence from Peridotite and Pyroxenite Xenoliths in Western Shandong[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2013,58(23):23002305.
[48]杨红梅,凌文黎,张军波,等.华北克拉通岩石圈减薄机制:来自山东白垩纪基性—中基性岩浆岩ReOs同位素地球化学特征的制约[J].地球科学,2013,38(3):529540.
YANG Hongmei,LING Wenli,ZHANG Junbo,et al.The Lithospheric Thinning Mechanism of North China Craton:ReOs Isotopic Geochemistry Constraint from the Cretaceous Basic to Intermediate Basic Igneous Rocks in Shandong Province[J].Earth Science,2013,38(3):529540.
[49]许文良,王冬艳,高山,等.鲁西中生代金岭闪长岩中纯橄岩和辉石岩包体的发现及其意义[J].科学通报,2003,48(8):863868.
XU Wenliang,WANG Dongyan,GAO Shan,et al.Discovery of Dunite and Pyroxenite Xenoliths in Mesozoic Diorite at Jinling,Western Shandong and Its Significance[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2003,48(8):863868.
[50]黄福生,薛绥洲.邯邢侵入体中幔源超镁铁质包体的发现及其矿物地球化学特征[J].岩石学报,1990,11(4):4046.
HUANG Fusheng,XUE Suizhou.The Discovery of the Mantlederived Ultramafic Xenoliths in HandanXingtai Intrusive Complex and Their Mineralogicalgeochemical Characteristics[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica,1990,11(4):4046.
[51]XU W L,YANG D B,GAO S,et al.Geochemistry of Peridotite Xenoliths in Early Cretaceous HighMg# Diorites from the Central Orogenic Block of the North China Craton:The Nature of Mesozoic Lithospheric Mantle and Constraints on Lithospheric Thinning[J].Chemical Geology,2010,270(1/2/3/4):257273.
[52]MORGAN Z,LIANG Y.An Experimental and Numerical Study of the Kinetics of Harzburgite Reactive Dissolution with Applications to Dunite Dike Formation[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2003,214(1/2):5974.
[53]MORGAN Z,LIANG Y.An Experimental Study of the Kinetics of Lherzolite Reactive Dissolution with Applications to Melt Channel Formation[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,2005,150(4):369385.
[54]CLIFF S J S,DONALD B D.Experimental Peridotitemelt Reaction at One Atmosphere:A Textural and Chemical Study[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,2008,155(2):199214.
[55]RAPP R P,SHIMIZU N,NORMAN M D,et al.Reaction Between Slabderived Melts and Peridotite in the Mantle Wedge:Experimental Constraints at 38 GPa[J].Chemical Geology,1999,160(4):335356.
[56]王超,金振民,高山,等.華北克拉通岩石圈破坏的榴辉岩熔体橄榄岩反应机制:实验约束[J].中国科学:地球科学,2010,40(5):541555.
WANG Chao,JIN Zhenmin,GAO Shan,et al.Eclogitemelt/Peridotite Reaction:Experimental Constrains on the Destruction Mechanism of the North China Craton[J].Science China:Earth Sciences,2010,40(5):541555.
[57]MALLIK A,DASGUPTA R.Reaction Between MORBeclogite Derived Melts and Fertile Peridotite and Generation of Ocean Island Basalts[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2012,329/330:97108.
[58]王明梁,唐红峰.英云闪长质熔体与地幔橄榄石反应的实验研究:对克拉通内部高镁安山岩成因的约束[J].中国科学:地球科学,2014,44(3):405413.
WANG Mingliang,TANG Hongfeng.Reaction Experiments Between Tonalitic Melt and Mantle Olivine and Their Implications for Genesis of HighMg Andesites Within Cratons[J].Science China:Earth Sciences,2014,44(3):405413.
[59]JOHNSTON A D,WYLLIE P J.The System TonaliteperidotiteH2O at 30 kbar,with Applications to Hybridization in Subduction Zone Magmatism[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1989,102(3):257264.
[60]杨晓志.浅谈高温高压实验地球科学:方法和应用[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报,2015,34(3):509525.
YANG Xiaozhi.A Brief Introduction of High Temperature and High Pressure Experimental Geosciences:Methods and Advances[J].Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry,2015,34(3):509525.
[61]杨晓志,李岩.高温高压实验和硅酸盐地幔中的水[J].中国科学:地球科学,2016,46(3):287300.
YANG Xiaozhi,LI Yan.HighP/T Experimental Studies and Water in the Silicate Mantle[J].Science China:Earth Sciences,2016,46(3):287300.
[62]王明梁.硅酸盐熔体与地幔岩石(矿物)反应的实验研究[D].贵阳:中国科学院地球化学研究所,2014.
WANG Mingliang.Experimental Study on Reactions Between Silicate Melts and Mantle Rocks and Minerals[D].Guiyang:Institute of Geochemistry,Chinese Academy of Sciences,2014.
[63]WANG C G,LIANG Y,XU W L,et al.Effect of Melt Composition on Basalt and Peridotite Interaction:Laboratory Dissolution Experiments with Applications to Mineral Compositional Variations in Mantle Xenoliths from the North China Craton[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,2013,166(5):14691488.
[64]于洋,许文良,刘晓旸,等.高温高压条件下角闪石榴辉石岩橄榄岩反应:初步实验结果及其地质意义[J].自然科学进展,2009,19(6):644651.
YU Yang,XU Wenliang,LIU Xiaoyang,et al.Hornblende Eclogite Reaction with Peridotite Under High Temperature and High Pressure:Preliminary Experimental Results and Geological Significance[J].Progress in Natural Science,2009,19(6):644651.
[65]ZHANG J F,WANG C,WANG Y F.Experimental Constraints on the Destruction Mechanism of the North China Craton[J].Lithos,2012,149:9199.
[66]GRASSI D,SCHMIDT M W.The Melting of Carbonated Pelites from 70 to 700 km Depth[J].Journal of Petrology,2011,52(4):765789.
[67]GRASSI D,SCHMIDT M W,GUNTHER D.Element Partitioning During Carbonated Pelite Melting at 8,13 and 22 GPa and the Sediment Signature in the EM Mantle Components[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2012,327/328:8496.
[68]YAXLEY G M.Experimental Study of the Phase and Melting Relations of Homogeneous Basalt+Peridotite Mixtures and Implications for the Petrogenesis of Flood Basalts[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,2000,139(3):326338.
[69]KUSHIRO I.Partial Melting of Mantle Wedge and Evolution of Island Arc Crust[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,1990,95(B10):1592915939.
[70]ARCULUS R J.Aspects of Magma Genesis in Arcs[J].Lithos,1994,33(1/2/3):189208.
[71]KAY R W.Aleutian Magnesian Andesites:Melts from Subducted Pacific Ocean Crust[J].Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,1978,4(1/2):117132.
[72]YOGODZINSKI G M,VOLYNETS O N,KOLOSKOV A V,et al.Magnesian Andesites and the Subduction Component in a Strongly Calcalkaline Series at Piip Volcano,Far Western Aleutians[J].Journal of Petrology,1994,35(1):163204.
[73]GAO S,RUDNICK R L,YUAN H L,et al.Recycling Lower Continental Crust in the North China Craton[J].Nature,2004,432:892897.
[74]黃华,高山,胡兆初,等.辽西彰武地区中生代高镁安山岩地球化学及其对新生下地壳拆沉作用的指示[J].中国科学:D辑,地球科学,2007,37(10):12871300.
HUANG Hua,GAO Shan,HU Zhaochu,et al.Geochemistry of Mesozoic HighMg Andesite and Its Instructions of the New Crust from Western Liaoning[J].Science in China:Series D,Earth Sciences,2007,37(10):12871300.
[75]巫祥阳,徐义刚,马金龙,等.鲁西中生代高镁闪长岩的地球化学特征及其成因探讨[J].大地构造与成矿,2003,27(3):228236.
WU Xiangyang,XU Yigang,MA Jinlong,et al.Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of the Mesozoic HighMg Diorites from Western Shandong[J].Geotectonica et Metallogenia,2003,27(3):228236.
[76]周金城,王孝磊.实验及理论岩石学[M].北京:地质出版社,2005.
ZHOU Jincheng,WANG Xiaolei.Experimental and Theoretical Petrology[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House,2005.
[77]TANG Y J,ZHANG H F,YING J F,et al.Widespread Refertilization of Cratonic and Circumcratonic Lithospheric Mantle[J].Earthscience Reviews,2013,118:4568.
