脑脊液PCR检测对中枢神经系统侵袭性曲霉菌感染的诊断价值
——系统评价和双变量Meta分析
2017-06-05刘真君贺光明赵丽丽
刘真君,贺光明,董 伟,赵丽丽
脑脊液PCR检测对中枢神经系统侵袭性曲霉菌感染的诊断价值
——系统评价和双变量Meta分析
刘真君,贺光明,董 伟,赵丽丽
目的 系统评价脑脊液多聚酶链反应(PCR)对中枢神经系统侵袭性曲霉菌感染的诊断价值。方法 计算机检索PubMed、The Cochrane Library、EMbase、CNKI、WanFang Data、CBM和VIP,查找评估PCR对中枢神经系统侵袭性曲霉菌感染诊断价值的相关研究,检索时限均为从建库至2015年1月10日。由两位评价者按照纳入与排除标准独立筛选文献、提取资料并评价纳入研究的方法学质量后,采用Stata 12.0软件统计并Meta分析,评估异质性及发表偏倚。结果 最终纳入8个研究,共130例病人,确诊/可信病人数为27例(20.8%)。针对3篇病例对照及1篇队列研究的Meta分析结果显示:敏感度(Sen)、特异度(Spe)、阳性似然比(+LR)、阴性似然比(-LR)、诊断比值比(DOR)、ROC曲线下面积(AUC)分别为0.984[95%CI(0.796,0.992 )]、0.930[95% CI(0.837,0.971)]、14.09[95% CI(5.87,33.82)]、0.016[95% CI(0.001,0.843)]、847 [95% CI(16,4536)]、0.99[95% CI(0.97,0.99)]。但有一定的异质性(I2=37%)和发表偏倚(P=0.095)存在。脑脊液PCR阳性率显著高于脑脊液GM检测(P=0.018)和血PCR检测(P=0.02)。结论 脑脊液PCR对中枢神经系统侵袭性曲霉菌感染有较高的诊断价值。但PCR检测方法学上存在异质性,发表偏倚可能高估PCR方法的诊断价值,上述结论仍需谨慎看待。
真菌感染;中枢神经系统;侵袭性曲霉菌;多聚酶链反应;系统评价
近年来,随着器官移植的开展、免疫抑制剂的使用,肿瘤(特别是血液系统肿瘤)发病率的上升,侵袭性曲霉菌(invasive aspergillosis,IA)导致的死亡有明显上升的趋势[1]。 侵袭性曲霉菌主要累及肺和鼻窦,中枢神经系统IA相对较少,但其预后极差,死亡率接近100%[2-3]。在使用伏立康唑后,预后有明显改善,但死亡率仍为29.2%~69.0%[4-5]。
早期诊断是改善中枢神经系统IA预后的关键,目前诊断真菌感染较公认的为EORTC/MSG标准[6],但其对早期、准确的诊断真菌感染尚有争议[7]。多聚酶链反应(polymerase chain reaction,PCR)采用特异性扩增方法能快速、准确检测出曲霉菌的DNA成分,系统评价表明了PCR方法在血和支气管肺泡灌洗液中对IA和肺IA有较好的诊断价值[8-9]。本研究探讨脑脊液PCR检测对中枢神经系统IA的诊断价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 纳入与排除标准 纳入探讨PCR对中枢神经系统IA感染诊断价值的研究,无语种限制。排除标准:①动物实验及基础研究;② 重复发表及重复检出的文献。
1.2 检索策略 计算机检索PubMed、The Cochrane Library、EMbase、CNKI、WanFang Data、CBM和VIP,检索时限均为从建库至2015年1月10日,并检索纳入研究的参考文献。检索词为主题词和自由词:聚合酶链反应(polymerase chain reaction)和中枢神经系统真菌感染(central nervous system fungal infections)或曲霉(aspergillosis/aspergillus)。
1.3 文献筛选、质量评价和资料提取 由两位研究者根据纳入与排除标准独立进行文献筛选,如遇分歧讨论解决。文献质量评价参照QUADAS-2工具[10]。采用自制的资料提取表提取资料,提取内容包括第一作者、研究时间、研究对象、研究设计、金标准、样本量、TP、FP、FN、TN值,PCR技术和方法。资料不全时通过电子邮件与作者联系。
1.4 统计学处理 采用Stata12.0软件进行统计分析,定量资料比较采用Kruskal-Wallis秩和检验,定量资料的比较采用χ2检验或Fisher确切概率法。Meta分析用Stata的midas模块,发表偏倚识别用pubbias选项。计算合并Sen、Spe、+LR、-LR和DOR,并绘制分层综合受试者操作特征曲线(HSROC,hierarchical summary receiver operating curves)。检验水准为α=0.05,双侧检验,P<0.05为有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 文献检索结果 初检出相关文献61篇,经阅读摘要及全文,共纳入8个研究[11-18]。详见表1、表2。4篇个案及3篇病例对照研究,1篇队列研究,共130例病人,确诊/可信病人数为27例(20.8%)。

表1 纳入研究特征
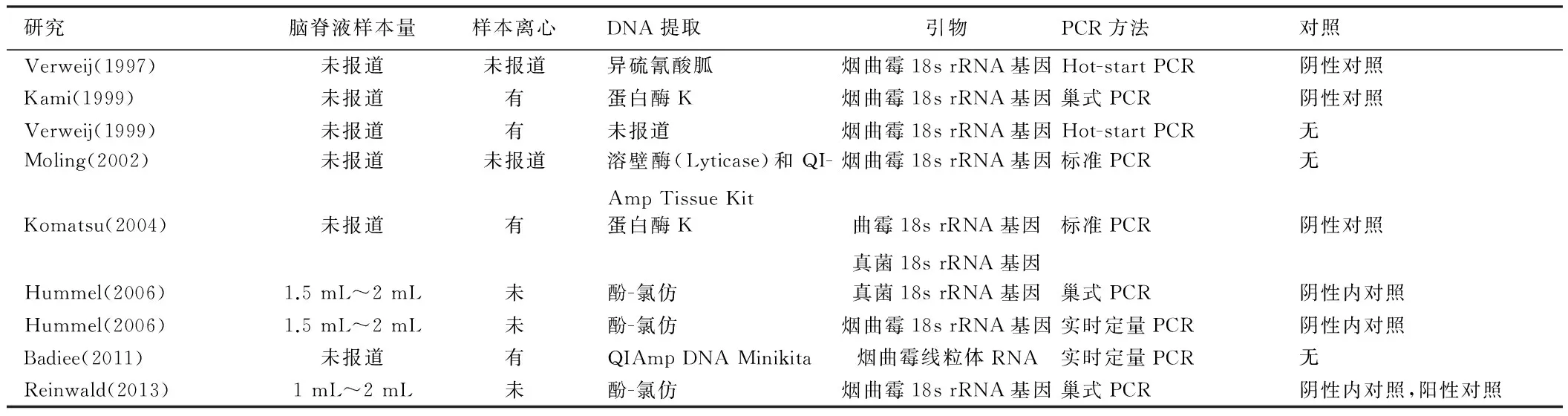
表2 PCR技术和方法
2.2 纳入研究基本特征及质量评价 4个研究的文献质量评价参照QUADAS-2工具,QUADAS-2工具从病人选择、实验指标(Index test,即待评价的诊断方法)、参考标准(reference standard,即金标准)和流程时间(flow and timing,即是否同步评价诊断方法和金标准,随访时间是否合理等)四个区域,偏倚风险(risk of bias)和适用性(applicability)两方面评价研究的质量(分为高危、低危和不确定)。详见表3。Kami 等[12]研究纳入已确诊病例,未采用盲法评价,有较高的偏倚风险,Badiee等[17]研究纳入脑外伤及脑肿瘤病人,适用性方面存在高风险,未报道实验指标和参考标准是否同步检测,其偏倚风险和适应性方面不确定。
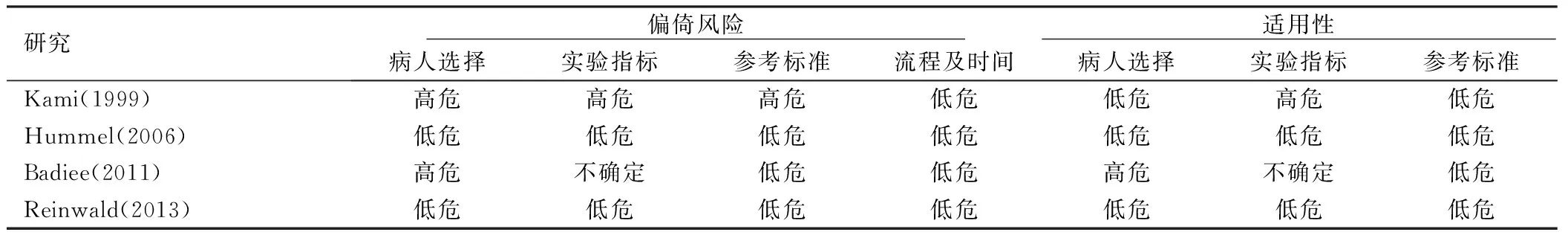
表3 纳入Meta分析研究的质量评价
2.3 Meta分析 将4个研究纳入Meta分析,脑脊液PCR用于中枢神经系统曲霉菌感染总的诊断价值:敏感度(Sen)、特异度(Spe)、阳性似然比(+LR)、阴性似然比(-LR)、诊断比值比(DOR)、ROC曲线下面积(AUC)分别为0.984[95%CI(0.796,0.992 )]、0.930[95% CI(0.837,0.971)]、14.09[95% CI(5.87,33.82)]、0.016[95% CI(0.001,0.843)]、847 [95% CI(16,4536)]、0.99[95% CI(0.97,0.99)]。分层综合受试者操作特征曲线(hierarchical summary receiver operating curves,HSROC)见图1。
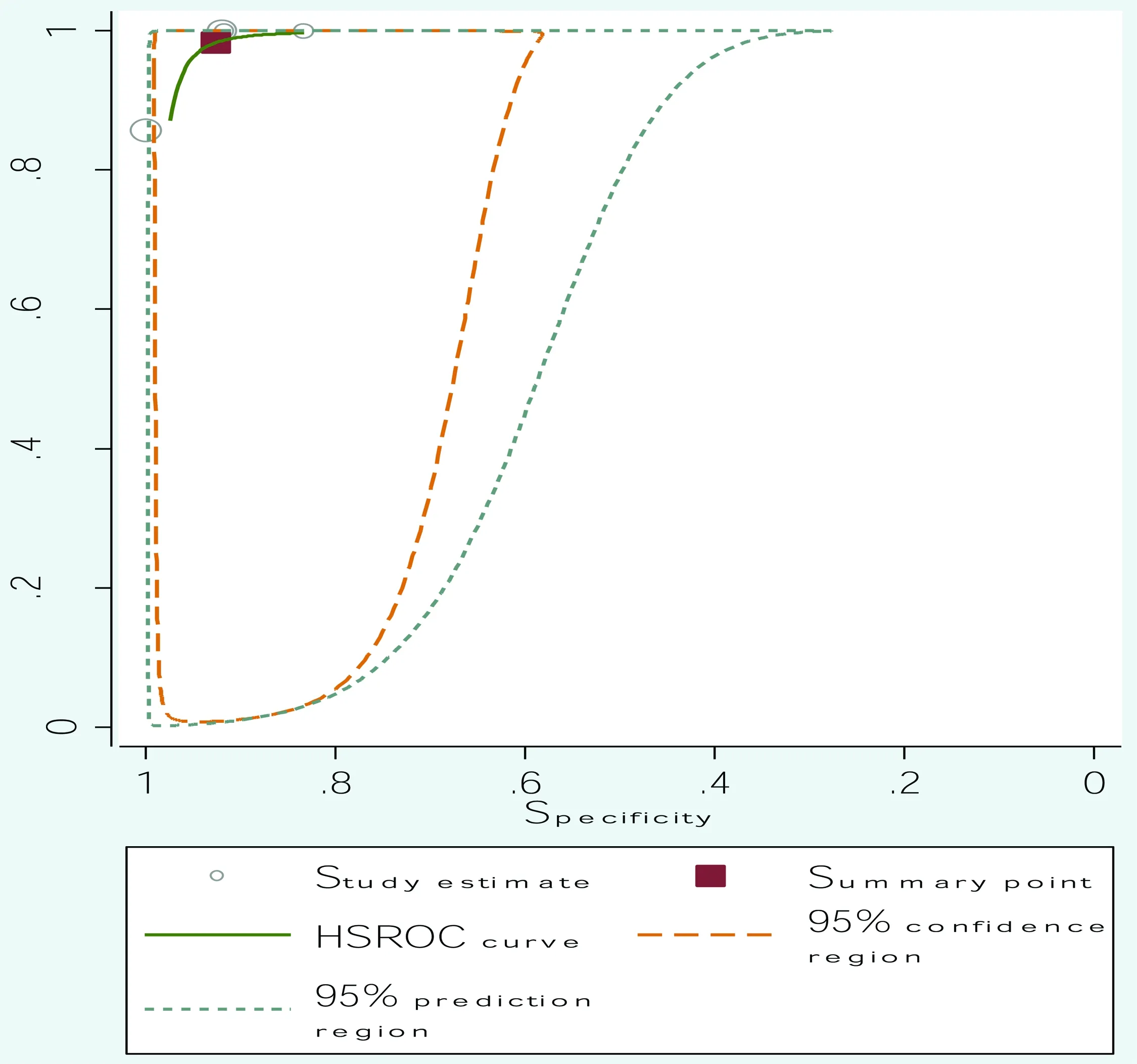
图1 分层综合受试者操作特征曲线图
2.4 与其他检测方法的比较 多个研究[11,13-14,16-18]比较脑脊液PCR与脑脊液半乳甘露聚糖(GM,galactomannan)检测,脑脊液PCR和血PCR检测在中枢神经系统IA感染的诊断价值。在确诊/可信中枢神经系统曲霉感染病人中,脑脊液PCR阳性率显著高于脑脊液GM检测(16/16和10/16,P=0.018),脑脊液PCR阳性率显著高于血PCR检测(9/10和3/10,P=0.02)。
2.5 异质性分析 异质性检验Q=0.835(P=0.329),I2=37%,提示有一定的异质性。各研究主要为血液疾病病人,年龄[12,16-17][38(四分位间距38,50) 对37.5(12,63) 对25.5(7,39)]和性别构成(男/女,3/2 对 2/4 对 7/3)无统计学意义(P>0.05)。各研究的中枢神经系统病变类型(孤立脑脓肿/多发脑脓肿/出血性梗死,1/2/2 对 3/3/0 对 1/4/0),原发或继发中枢神经系统IA(0/5 对 3/3 对 3/11)无统计学意义(P>0.05)[12,16,18]。
8个研究的PCR技术方法存在一定的异质性。脑脊液样本量(报道为1 mL~2 mL),DNA提取方法(离心或非离心,主要使用酶消化法和酚-氯仿提取),引物设计(主要为烟曲霉18s rRNA基因),DNA扩增方法(标准、巢式或实时定量PCR),是否有对照(阴性或阳性对照)等不同研究间有差异,但由于研究较少,难以做亚组及敏感性分析。Hummel 等[16]的研究比较了巢式PCR和实时定量PCR,发现巢式PCR有更高的敏感性。
2.6 发表偏倚的识别 发表偏倚检验的t值为-3.01(95%CI-49.90,8.85),P=0.095,提示可能有发表偏倚存在。
3 讨 论
EORTC/MSG诊断标准结合了宿主因素,临床表现和真菌学依据,诊断分为确诊(proven,无菌部位的显微镜分析或培养),临床诊断/可信(probable,非无菌部位有真菌学依据,包括痰液、尿液等显微镜分析或培养直接证据,葡聚糖DG /和半乳甘露聚糖抗原GM检测等间接证据),拟诊(possible,仅有宿主因素,临床表现或影像学表现)。但针对IA感染的病人,临床和影像学表现缺乏特异性,培养阳性率极低,针对拟诊的高危病人,临床上采用了经验性治疗方案,但增加了抗真菌药物不必要的使用,造成医疗资源的浪费和药物不良反应的增加。分子水平的诊断方法(曲霉抗原和DNA)能将拟诊提升到可信,避免上述问题的发生,但血DG 和GM实验的敏感性有限,有部分假阳性[19]。并且,有研究表明IA感染的病人中,血PCR阳性较GM阳性早68 d[20],提示PCR较其他方法更有早期诊断的价值。
传统的SROC(summary ROC)模型用于诊断试验的Meta分析有较多的方法学问题,如受到阈值效应的影响,没有考虑研究估计值的准确度,不能估计研究间的异质性,回归中解释变量测量错误,导致置信区间和P值的偏移[21]。本研究采用了双变量随机效应模型和HSROC模型,其估计了平均敏感度、特异度和受试点,估计了参数中不能解释的变量及其相关性。本研究表明,脑脊液PCR检测方法对中枢神经系统IA有较高的诊断价值,综合敏感度和特异度为0.984和0.930。阳性预测值>10和阴性预测值<0.1通常认为可以确立和排除诊断[22],PCR方法的综合+LR和-LR分别为 14.09和0.016,可用于肯定或否定中枢神经系统IA的诊断。
本研究表明对中枢神经系统IA的诊断,脑脊液的PCR优于血PCR检测和脑脊液GM检测。既往研究表明针对肺部IA,支气管肺泡灌洗液(bronchoalveolar lavage fliud,BAL)的GM检测诊断价值优于血清GM检测[23],BAL的PCR检测诊断表现与BAL的GM检测相似或略优[24-25]。对早期肺部IA,BAL的PCR检测阳性,而血的PCR检测为阴性[26]。提示局部IA感染,感染部位的抗原/DNA检测可能更有早期诊断的价值。
本研究的局限性:①纳入研究的总体质量和样本量不足,可能有发表偏倚的存在。但由于中枢神经系统IA低的发病率和临床识别困难,开展大样本、前瞻性研究可行性较困难,系统评价和Meta分析的目的就是全面收集相关研究,提高总的样本量和统计效能,减少抽样误差,进一步说明了本研究的必要性。②PCR的技术和方法上各研究间有较大的差异性。实际上,PCR方法的标准化问题是其未能进入EORTC/MSG诊断标准的主要原因。研究表明,针对全血PCR方法的敏感性与DNA提取方式(使用bead beating,增加的样本量和减少稀释液量)和内对照(排除假阴性)正相关,与DNA的扩增方式无关[27],针对血浆PCR方法标准化步骤减少(没有白细胞DNA的干扰),其敏感性与DNA提取方法、靶位点为真菌的内转录间隔区(ITS,internal transcribed spacer )、内对照正相关[28]。但目前没有针对脑脊液DNA方法标准化的相关研究。
PCR方法对中枢神经系统IA有较高的诊断价值,但对非血液疾病病人(ICU或实体器官移植)的诊断价值,以PCR诊断方法为基础的治疗能否改善病人的预后,PCR诊断方法的污染和标准化等方面还需要更多的研究。
[1] McNeil MM,Nash SL,Hajjeh RA,et al.Trends in mortality due to invasive mycotic diseases in the United States 1980-1997[J].Clin Infect Dis,2001,33(5):641-647.
[2] Lin SJ,Schranz J,Teutsch SM.Aspergillosis case-fatality rate:systematic review of the literature[J].Clin Infect Dis,2001,32(3):358-366.
[3] Denning DW.Therapeutic outcome in invasive aspergillosis[J].Clin Infect Dis,1996,23(3):608-615.
[4] Schwartz S,Ruhnke M,Ribaud P,et al.Improved outcome in central nervous system aspergillosis,using voriconazole treatment[J].Blood,2005,106(8):2641-2645.
[5] Herbrecht R,Denning DW,Patterson TF,et al.Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis[J].N Engl J Med,2002,347(6):408-415.
[6] De Pauw B,Walsh TJ,Donnelly JP,et al.Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group[J].Clin Infect Dis,2008,46(12):1813-1821.
[7] Rieger H, Lustig D,Barlow S,et al.Applicability of the EORTC/MSG criteria for IFD in clinical practice[J].Ann Hematol,2015,94(5):847-855.
[8] Sun W,Wang K,Gao W,et al.Evaluation of PCR on bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis:a bivariate meta analysis and systematic review[J].PLoS One,2011,6(12):e28467.
[9] Mengoli C,Cruciani M,Barnes RA,et al.Use of PCR for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis:systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Lancet Infect Dis,2009,9(2):89-96.
[10] Whiting PF,Rutjes AW,Westwood ME,et al.QUADAS-2:a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies[J].Ann Intern Med,2011,155(8):529-536.
[11] Verweij PE,Dompeling EC,Donnelly JP,et al.Serial monitoring of Aspergillus antigen in the early diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis.Preliminary investigations with two examples[J].Infection,1997,25(2):86-89.
[12] Kami M,Ogawa S,Kanda Y,et al.Early diagnosis of central nervous system aspergillosis using polymerase chain reaction,latex agglutination test,and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay[J].Br J Haematol,1999,106(2):536-537.
[13] Verweij PE,Brinkman K,Kremer HP,et al.Aspergillus meningitis:diagnosis by non-culture-based microbiological methods and management[J].J Clin Microbiol,1999,37(4):1186-1189.
[14] Moling O,Lass-Floerl C,Verweij PE,et al.Case Reports.Chronic and acute Aspergillus meningitis[J].Mycoses,2002,45(11-12):504-511.
[15] Komatsu H,Fujisawa T,Inui A,et al.Molecular diagnosis of cerebral aspergillosis by sequence analysis with panfungal polymerase chain reaction[J].J Pediatr Hematol Oncol,2004,26(1):40-44.
[16] Hummel M,Spiess B,Kentouche K,et al.Detection of Aspergillus DNA in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with cerebral aspergillosis by a nested PCR assay[J].J Clin Microbiol,2006,44(11):3989-3993.
[17] Badiee P,Alborzi A.Assessment of a real-time PCR method to detect human non-cryptococcal fungal meningitis[J].Arch Iran Med,2011,14(6):381-384.
[18] Reinwald M,Buchheidt D,Hummel M,et al.Diagnostic performance of an Aspergillus-specific nested PCR assay in cerebrospinal fluid samples of immunocompromised patients for detection of central nervous system aspergillosis[J].PLoS One,2013,8(2):e56706.
[19] Johnson G,Ferrini A,Dolan SK,et al.Biomarkers for invasive aspergillosis:the challenges continue[J].Biomark Med,2014,8(3):429-451.
[20] Cuenca-Estrella M,Meije Y,Diaz-Pedroche C,et al.Value of serial quantification of fungal DNA by a real-time PCR-based technique for early diagnosis of invasive Aspergillosis in patients with febrile neutropenia[J].J Clin Microbiol,2009,47(2):379-384.
[21] Leeflang MM,Deeks JJ,Gatsonis C,et al.Systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy[J].Ann Intern Med,2008,149(12):889-897.
[22] Jaeschke R,Guyatt GH,Sackett DL.Users’ guides to the medical literature Ⅲ.How to use an article about a diagnostic test B.What are the results and will they help me in caring for my patients? The Evidence-Based Medicine Working Group[J].JAMA,1994,271(9):703-707.
[23] Acosta J,Catalan M,del Palacio-Perez-Medel A,et al.A prospective comparison of galactomannan in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for the diagnosis of pulmonary invasive aspergillosis in medical patients under intensive care:comparison with the diagnostic performance of galactomannan and of (1--> 3)-beta-d-glucan chromogenic assay in serum samples[J].Clin Microbiol Infect,2011,17(7):1053-1060.
[24] Heng SC,Chen SC,Morrissey CO,et al.Clinical utility of Aspergillus galactomannan and PCR in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with haematological malignancies[J].Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis,2014,79(3):322-327.
[25] Avni T,Levy I,Sprecher H,et al.Diagnostic accuracy of PCR alone compared to galactomannan in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis:a systematic review[J].J Clin Microbiol,2012,50(11):3652-3658.
[26] Sav H,Atalay MA,Unal E,et al.The importance of bronchoalveolar lavage sample for galactomannan,1,3-ss-d-glucan and PCR tests].Mikrobiyol Bul,2012,46(4):695-701.
[27] White PL,Bretagne S,Klingspor L,et al.Aspergillus PCR:one step closer to standardization[J].J Clin Microbiol,2010,48(4):1231-1240.
[28] White PL,Mengoli C,Bretagne S,et al.Evaluation of Aspergillus PCR protocols for testing serum specimens[J].J Clin Microbiol,2011,49(11):3842-3848.
(本文编辑王雅洁)
Diagnostic Value of Cerebrospinal Fluid PCR Detection for Invasive Aspergillosis in the Central Nervous System:Systematic Review and Bivariate Meta-analysis
Liu Zhenjun,He Guangming,Dong Wei,Zhao Lili
Sichuan Cancer Hospital,Chengdu 610041,Sichuan,China
Objective Systematic review about diagnostic value of cerebrospinal fluid PCR detection for invasive aspergillosis in the central nervous system (CNS).Methods Computer retrieval of PubMed,The Cochrane Library,EMbase,CNKI,Wan Fang Data,CBM and VIP was conducted.Studies published from initiation of the databases until January 10,2015,assessing diagnostic performance of CSF PCR detection for invasive aspergillosis in the central nervous system were searched.Two reviewers independently searched literature on the grounds of inclusion and exclusion standards,extracted information and evaluated methodological quality of included studies.statistical calculation and meta-analysis were conducted via Stata 12.0 software and heterogeneity and publication bias were assessed.Results Totally eight studies were enrolled,with proven/probable 27 cases (20.8%) in 130 patients.Meta-analysis based on 3 case-control studies and 1 cohort study showed:sensitivity (Sen),specific (Spe),positive likelihood ratio (+ LR),negative likelihood ratio (-LR) and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR),the area under the ROC curve (AUC) were 0.984 [95% CI(0.796,0.992)],0.930 [95% CI(0.837,0.971)],14.09 [95% CI(5.87,33.82)],0.016 [95% CI(0.001,0.843)] and 847 [95% CI(16,453 6)],0.99 [95% CI(0.97,0.99)],respectively.But there were moderate heterogeneity (I2= 37%)and publication bias (P=0.095).PCR positive rate in CSF was significantly higher than that of GM test in CSF(P=0.018) and blood PCR detection (P=0.02).Conclusion PCR test in CSF for invasive aspergillosis of the central nervous system has high diagnostic value.However,due to methodological heterogeneity of PCR detection and possibly overestimated diagnostic performance of PCR by publication bias,aforementioned conclusion must be drawn conscientiously.
fungal infection;central nervous system;invasive aspergillosis;polymerase chain reaction;systematie review
四川省肿瘤医院(成都 610041),E-mail:lantianboyun@163.com
引用信息:刘真君,贺光明,董伟,等.脑脊液PCR检测对中枢神经系统侵袭性曲霉菌感染的诊断价值:系统评价和双变量Meta分析[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2017,15(9):1041-1045.
R473 R255
A
10.3969/j.issn.1672-1349.2017.09.007
1672-1349(2017)09-1041-05
2016-02-22)
