Associations of high altitude polycythemia with polymorphisms inKDM5B and LAMB3 in Chinese Tibetan populations※
2017-05-16ZHAOYiduoZHANGZhiyingLIULijunZHANGYaoMALifengLIYansongCAIPengKANGLongli
ZHAO Yi-duo,ZHANG Zhi-ying,LIU Li-jun,ZHANG Yao, MA Li-feng,LI Yan-song,CAI Peng,KANG Long-li#
(1.Key Laboratory for Molecular Genetic Mechanisms and Intervention Research on High Altitude Disease of Tibet Autonomous Region,School of Medicine,Xizang Minzu University,Xianyang 712082,Shaanxi,China; 2.Key Laboratory of High Altitude Environment and Gene Related to Disease of Tibet Ministry of Education, School of Medicine,Xianyang 712082,Shaanxi,China)
Associations of high altitude polycythemia with polymorphisms inKDM5BandLAMB3 in Chinese Tibetan populations※
ZHAO Yi-duo1,2*,ZHANG Zhi-ying1,2*,LIU Li-jun1,2*,ZHANG Yao1,2, MA Li-feng1,2,LI Yan-song1,2,CAI Peng,KANG Long-li1,2#
(1.Key Laboratory for Molecular Genetic Mechanisms and Intervention Research on High Altitude Disease of Tibet Autonomous Region,School of Medicine,Xizang Minzu University,Xianyang 712082,Shaanxi,China; 2.Key Laboratory of High Altitude Environment and Gene Related to Disease of Tibet Ministry of Education, School of Medicine,Xianyang 712082,Shaanxi,China)
Objective High altitude polycythemia(HAPC)is a serious public health problem among Chinese Tibetan populations,which is characterized by excessive erythrocytosis(females,hemoglobin≥190g/L;males,hemoglobin≥210g/L).Although chronic hypoxia is the main cause of HAPC,the molecular mechanism of HAPC is not yet clear.This study aims to explore the genetic basis of HAPC in the Chinese Tibetan populations.Methods A total of 70 Tibetan patients with HAPC and 30 healthy Tibetan control subjects were recruited for a case-control association study.Analysis of variance was used to evaluate the impact of polymorphism on HAPC based on genetic variation.Results Using the Chi-squared test and analyses of genetic models,rs1141109,rs7528426 and rs1141108 inKDM5B,rs2072938 and rs2072940 inLAMB3 showed a reduced risk of HAPC in Tibetan populations.Conclusions In summary,our study suggest that polymorphisms in theKDM5BandLAMB3 correlate with susceptibility to HAPC in Chinese Tibetan populations.
High altitude polycythemiaKDM5BLAMB3 Polymorphism
Introduction
The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is the world′s highest plateau,with an average elevation of more than 4000 meters.Most of the Tibetan people reside at altitude of 3000 m to 4500 m for a long time,they also possess heritable adaptations to the hypoxic environment[1].Tibetan have an unique genetic advantage to adapt to hypoxia environment,they have lower hemoglobin and hematocrit levels.In addition,the Tibetan have stronger hypoxia tolerance.These features help them adapt to high altitude and hypoxic conditions.However,a certain number of Tibetan who showed high level of hemoglobin may develop into High altitude polycythemia(HAPC).HAPC is common in long-time high altitude residents.Exorbitant hemoglobin increases blood viscosity and microcirculation disturbance,also leads to tissue hypoxia,stroke,myocardial infarction or even death by serious vascular thrombosis[2,3].However,the disease is still unmanageable and the related molecular mechanisms remain unclear.This is a serious public health problem in China and other Andean countries,as millions of highland inhabitants may be at risk.The prevalence of HAPC among Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau populations was 5% to 18%[4,5].The incidence of HAPC increased with increasing altitude,the disease affects most individuals living at high altitudes.Under hypoxic conditions,the body produces more red blood cells(RBCs)carry oxygen to organs and tissues[6,7].
The majority of populations may have a high level of RBCs after a long time exposure to high altitude hypoxic environment.However,with the number of RBCs continuing to increase,there may be lead to serious complications.Both high altitude natives and immigrants show susceptibility to HAPC,although the incidence of HAPC among immigrants was significant higher.Many studies have noted that there was a significant difference in genomics between the high altitude natives and immigrants,suggesting that genetic factors may contribute to the development of HAPC.Although the genetic basis of HAPC has long been proposed,only a few of these genetic factors have been reported,and most studies have focused on high-altitude populations and genes involved in hypoxia-inducible factor pathways.In Europeans,over the past few years,the prevalence and incidence of HAPC are higher than those in the Andean natives,the prevalence of HAPC in Andean natives was higher than Tibetan.In addition,Simonson et al.[8]reported that the hemoglobin concentration was closely related to the single nucleotide polymorphisms(SNP)of several genes in Tibetans.We found several new gene candidates and loci which have not been reported before.And these genes are significantly associated with the susceptibility to HAPC,especially in high altitude native Tibetans.
The humanKDM5BandLAMB3 genes were located on chromosome 1.Lysine-specific histone demethylase 5B(KDM5B),a member of the JmjC domain-containinghistone demethylases,is a histone demethylase that regulates self-renewal and differentiation in stem cells.Previous studies have shown thatKDM5Bis a well-defined transcriptional repressor,promotes double-strand break signaling and is required for efficient DNA repairs.KDM5Bis also a histone demethylase that regulates self-renewal and differentiation in stem cells.Li et al.reported[9,10]that Jarid1b was highly expressed in primitive hematopoietic compartments,and the genetic deletion of Jarid1b did not impact steady-state hematopoiesis.In contrast,acute deletion of Jarid1b from bone marrow increased peripheral blood T cells,and might lead to the loss of bone marrow reconstruction.This also may have an effect on the composition of the blood,especially red blood cells and hemoglobin.Epidermolysis bullosa(EB)is an inherited blistering genodermatosis,patients with EB due toLAMB3 mutations have widespread blisters and erosions of skin.Due to iron deficiency,chronic inflammation and malnutrition,many EB patients suffer from anemia.Kim et al.[11]suggested that chronic inflammation and iron deficiency lead to EB,the main reason was metabolic disorders of red blood cells and hemoglobin.In order to explore the pathological mechanisms ofKDM5BandLAMB3 polymorphisms in HAPC,we performed an association study between these genes and HAPC susceptibility.
Tibet is a high altitude region in Central Asia and the home to the indigenous Tibetan individuals.With an average elevation of 4,900 meters,it is the highest region on earth and is commonly referred to as the“Roof of the World”.Tibetan has a unique genetic background,dietary and lifestyle habits.These results thus offer a new strategy for the potential relationships betweenKDM5BandLAMB3 variations that are significantly associates with HAPC in Chinese Tibetan populations.
1 Materials and methods
Study population
After obtaining written informed consent,we recruited a total of 70 Tibetan patients with HAPC and 30 healthy Tibetan control subjects without chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,pulmonary infection,asthma,shunt conditions or congenital heart disease.The aim is to reduce the therapeutic factors and potential environmental impacting the variation of HAPC.All HAPC patients in this study were diagnosed by the Second People’s Hospital of Tibet Autonomous Region and Tibet military region general hospital.All Tibetans live in Tibet at an altitude of 3600 meters to 4400 meters.HAPC patients were defined as having Hb concentration≥210 g/L in males and≥190 g/L in females.The ethics Committee of Xizang Minzu University School of Medicine approved our use of blood samples and our protocol.
SNP selection and genotyping
Seventeen SNPs from three genes were chosen for analysis in this study.A total of 10 SNPs inKDM5Band seven SNPs inLAMB3 with minor allele frequencies greater than 5% in the Asian population HapMap data were selected for further genotyping.Genomic DNA was extracted from 5 mL of peripheral blood using the GoldMag-Mini Purification Kit(GoldMag Co.Ltd.Xian city,China),and DNA concentrations were measured using the NanoDrop2000(Thermo Scientific,Waltham,Massachusetts,USA).Sequenom Mass ARRAY Assay Design3.0 software was used to design multiplexed SNPMass EXTEND assay,and SNP genotyping was performed utilizing the Sequenom Mass ARRAY RS1000 recommended by the manufacturer.The SequenomTyper 4.0 Software was used to perform data management and analyses.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS version 18.0 statistical software(SPSS Inc.,Chicago,IL,United States)and Excel(Microsoft Corp.,Redmond,WA,United States).Differences in demographic characteristics between the patients and controls were evaluated by the Chi-square test or the Student’s t-test(The data considered were analyzed as continuous variables).Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium(HWE)was calculated using SHEs is online software for patients and controls,the odds ratios(ORs)and 95% confidence intervals(95% CIs)were calculated using unconditional logistic regression analysis with adjustment for age and sex.Three genetic models(dominant,recessive,and additive)were performed using PLINK software and SNPStats(a web based program available at http://bioinfo.iconcologia.net/snpstats/start.htm)to assess the association of SNPs with the risk of HAPC[12].All statistical tests were two-sides,and statistical significance was set atP≤0.05.
2 Results
Our study included 70 Tibetan patients with HAPC and 30 healthy Tibetan control subjects.The characteristics of cases and controls were listed in Table 1.
The basic information of candidate SNPs in Tibetan subjects in the case and control groups were summarized in Table 2.

Table 1 Basic characteristics of the control individuals and patients with high altitude polycythemia(%)
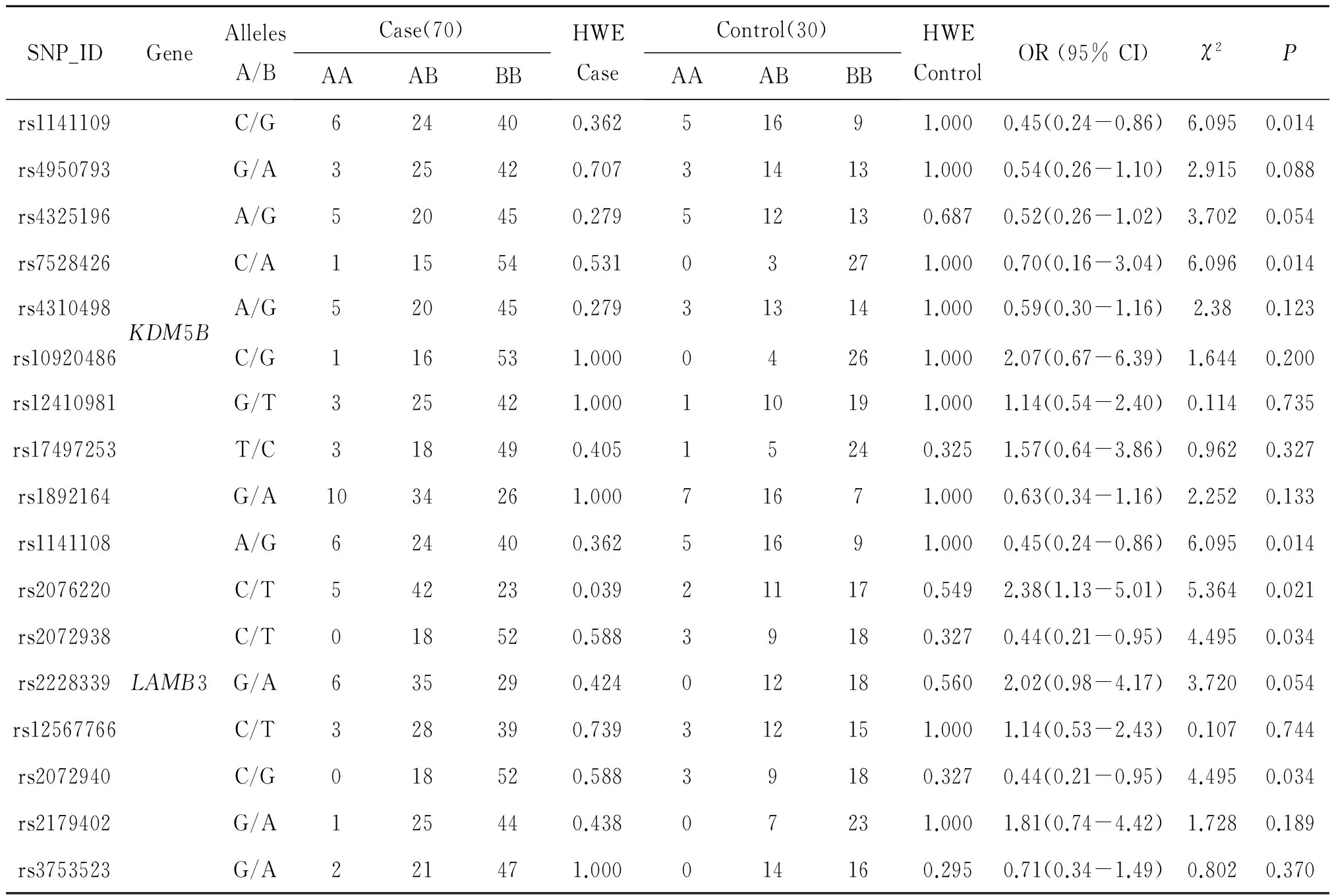
Table 2 Basic information of candidate SNPs in Tibetan subjects
SNP:Single-nucleotide polymorphism;OR:odds ratio;95% CI:95% confidence interval;HWE:Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium;Site with HWEP≤0.05 excluded;P<0.05 indicates statistical significance for allele model.
The location information of candidate SNPs in all subjects in the case and control groups were presented in Table 3.In Tibetan populations,we found the rs1141109(P=0.014),rs7528426(P=0.014)and rs1141108(P=0.034)inKDM5Bwere associated with decreased HAPC susceptibility,and the rs2072938(P=0.034)and rs2072940(P=0.034) inLAMB3 were associated with decreased HAPC risk.
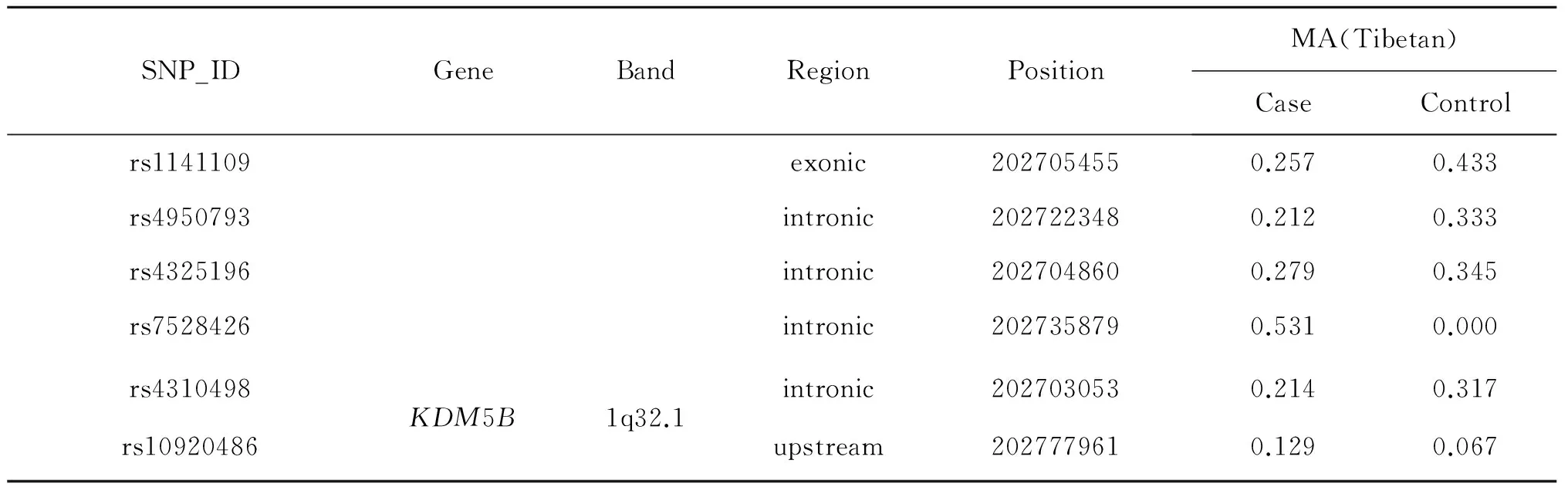
Table 3 Location information of candidate SNPs in this study
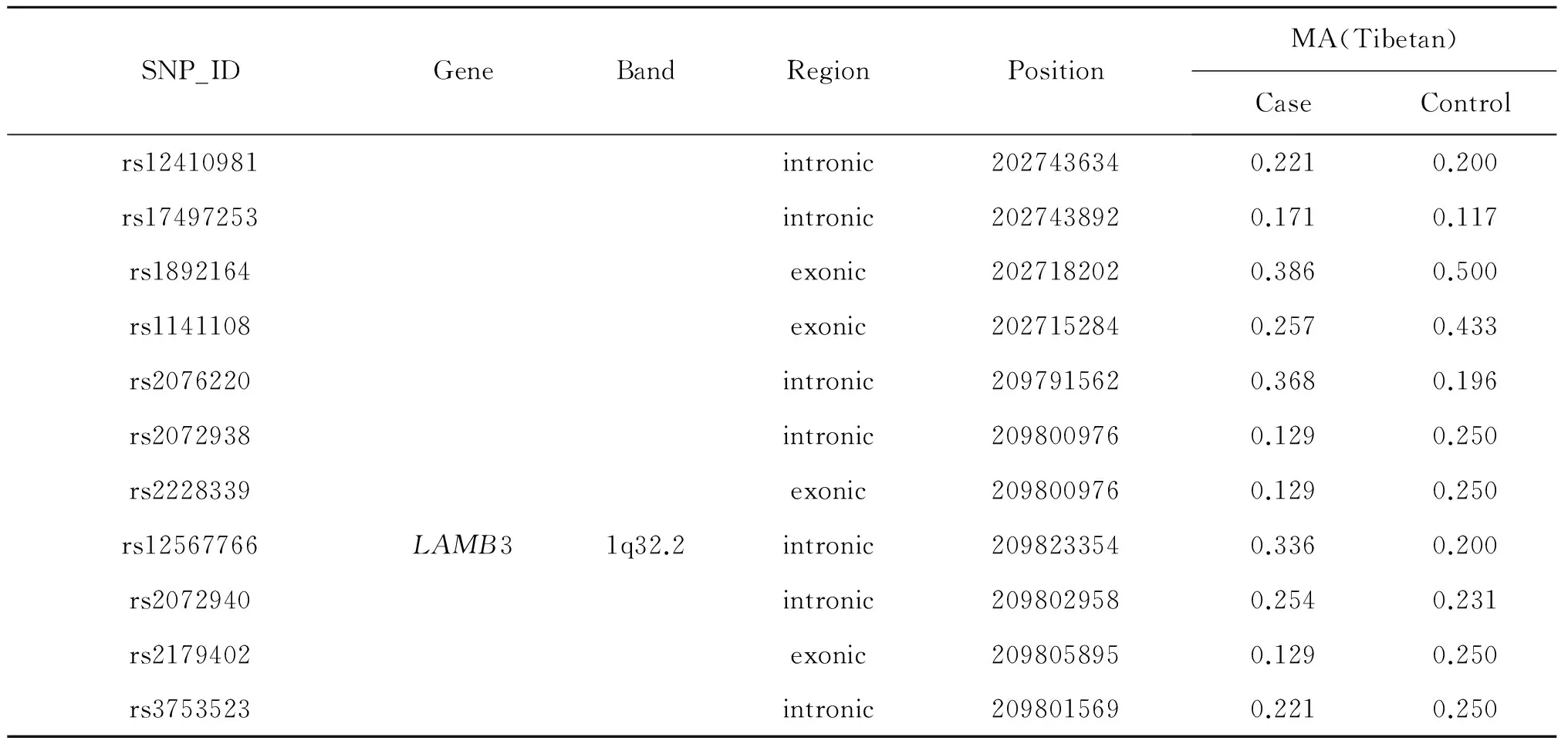
续表:
We further analyzed the association between SNPs and HAPC risk by unconditional logistic regression analysis using three models in Tibetan populations(Table 4).After stratifying by gender,we found the re1141109 inKDM5B(P=0.015)was associated with a decreased risk of HAPC in the dominant model.
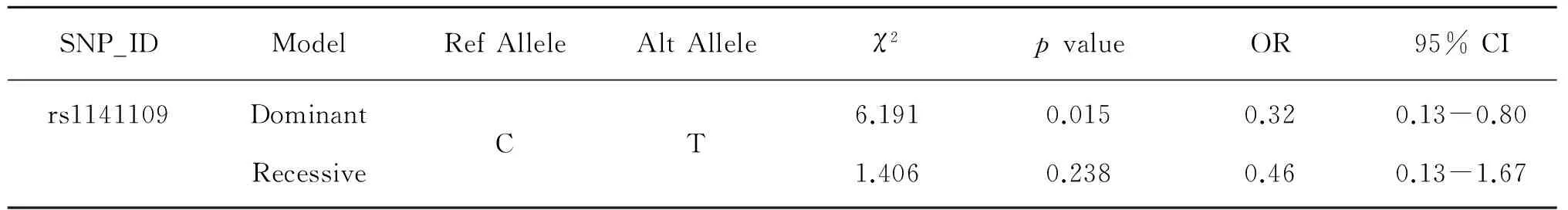
Table 4 Single loci associations with high altitude polycythemia risk in Tibetan subjects
P<0.05 indicates statistical significance for genetic model;OR:odds ratio;95% CI:95% confidence interval.
3 Discussion
This study is focused onKDM5BandLAMB3 polymorphisms and their association with HAPC susceptibility.We revealed several crucial findings.The SNPs examined(the rs1141109,rs7528426 and rs1141108 inKDM5B,the rs2072938 andrs2072940 inLAMB3)were strongly associated with HAPC.Taken together,these results suggest that polymorphisms in these genes may play important roles in HAPC in Chinese Tibetan populations.To our knowledge,this is the first report of an association between these genes polymorphism and HAPC susceptibility in Chinese Tibetan populations.It has been suggested that several genetic polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to HAPC,whereas each polymorphism may contribute to only a small relative risk of HAPC involves a complex interplay between exposure to multiple environmental stimuli and genetic background.As a unique geological condition in Central Asia,hypobaric hypoxia is a major geographical feature of the plateau region[13].In the plateau region,the long-term adaptation and natural selection of modern Tibetan changed their genetic structure[14].Chronic hypobaric hypoxia is the major cause of high altitude polycythemia[15].However,the related molecular mechanisms of HAPC remain unclear.
KDM5B,a member of the JmjC domain-containing histone demethylases,which is histone demethylase that regulates self-renewal and differentiation in stem cells.KDMB5 is highly expressed in primitive hematopoietic populations. In addition,adequate oxygenation is a necessary condition for the normal physiology of all cellular functions.In response to reduced oxygen tension,activation of the coordinated transcriptional response maintains intracellular homeostasis.This transcription process is required through hypoxia inducible factor 1 and 2(HIF-1 and HIF-2).HIF is necessary for several physiological processes,including normal development,pro-angiogenin production and wound healing.Xia et al.[16]reported that JmjC protein(KDM5B)were direct target gene of HIF-1 within their promoters and HIF-1 strongly combined in the hypoxic state up-regulated expression.This includesKDM5Band other family members,without evidence of direct HIF-1 binding.In HepG2 cells,17 of the 22 JmjC family members significantly increased mRNA abundance under hypoxic conditions.These results supported recent finding that HIF-1 up-regulatesKDM5B.In order to determine the potential relevance of these findings in vivo,Bratet al.[17]examined the expression of JmjC protein in human tumors,because most solid tumors were hypoxic compared to normal tissues. In glioma formation,hypoxia is one of the salient features,the expression of multiple JmjC proteins in the hypoxic tumor samples compared with the normal brain expression levels increased significantly.Using the expanded list of direct HIF-1 targets,we noted that the JmjC protein family members(mainlyKDM5B)are up-regulated by HIF.Moreover,the diversity of known HIF-1 target gene can be integrated into an important self-regulatory program that increases adaptation to hypoxia.This steady-state process is primarily an “oxygen delivery procedure” that increases oxygen delivery and vascular permeability through vasodilatation,and can induce angiogenesis and erythropoiesis for long periods of time.Thus,these results indicated a correlation between the expression ofKDM5Band erythropoiesis.
Laminin subunit beta 3(LAMB3),is a basement membrane protein.Epidermolysis bullosa(EB)is also a monogenic autosomal recessive disorder,LAMB3 mutations were significantly associated with EB.Most importantly,EB patients often accompanied withanemia,mainly due to iron deficiency,chronic inflammation and malnutrition.The incidence of EB in different populations is different;the main reason may be genetic background and consanguineous marriage,which is particularly related to recessive inheritance.Fuentes et al.[18]reported that mutations inLAMB3 gene plays an important role in the pathogenesis of EB in Chilean population.The most significant complication of EB is anemia,which is a major cause of excessive damage or loss of red blood cells.In aggregate,our findings strongly suggest thatLAMB3 has a direct impact on the normal metabolism of red blood,but the mechanism is not yet understood.Staff et al.[19]reported that in the high altitude hypoxia environment,LAMB3 have been shown to be involved in cellular movement.
It has been suggested that several genetic polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to HAPC,whereas each polymorphism may contribute to only a small relative risk of HAPC involves a complex interplay between exposure to multiple environmental stimuli and genetic background.Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is a unique geological condition in Central Asia,have different environmental characteristics and dietary habit,this is probably the main reason for differences between Tibetan and others populations in hereditary diseases.Although there are important discoveries revealed by the studies,there are also limitations.On the one hand,due to practical constraints,this paper cannot provide enough sample size for correlation studies.On the other hand,the functions of the genetic variants and their mechanisms have not been evaluated in this study.
The conclusion gives a brief summary of the findings.We analyzed SNPs in theKDM5BandLAMB3 genes and identified a relationship between genetic polymorphisms and HAPC in Chinese Tibetan populations.This study set out to determine paramount insights into the etiology of HAPC.However,additional genetic risk factors and functional investigations should be identified confirm our results.Finally,areas for further research are identified.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
[1]Jeong C,Di RA.Adaptations to local environments in modern human populations.Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 2014,29C:1-8.
[2]Leónvelarde F,Maggiorini M,Reeves JT,et al.Consensus Statement on Chronic and Subacute High Altitude Diseases.High Altitude Medicine & Biology,2005,6(2):147-157.
[3]Guan W,Ga Q,Li R,et al.Sleep disturbances in long-term immigrants with chronic mountain sickness:a comparison with healthy immigrants at high altitude.Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology,2014,206:4-10.
[4]Gallagher SA,Hackett PH.High-altitude illness.Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America,2004,22(2):329-355.
[5]Windsor JS,Rodway GW.Heights and haematology:the story of haemoglobin at altitude.Postgraduate Medical Journal,2007,83(977):148-151.
[6]Zhang R,Xiang Y,Ran Q,et al.Involvement of Calcium,Reactive Oxygen Species,and ATP in Hexavalent Chromium-Induced Damage in Red Blood Cells.Cellular Physiology & Biochemistry,2014,34(5):1780.
微生态制剂是以微生态理论为依据,应用有益生物并经由特殊工艺制成。作为制剂的组成之一,其具有较强的活菌性,在反刍动物生产中具有良好的应用价值。通过动物胃肠道内稳定平衡关系的建立,促使动物保持健康状态。但随着饲料添加剂中抗生素的应用,导致微生态平衡受到影响,进而出现诸多疾病。因此,益生素等微生态制剂的应用对于抗生素弊端的解决尤为重要。
[7]Lücker A,Weber B,Jenny P.A dynamic model of oxygen transport from capillaries to tissue with moving red blood cells.American Journal of Physiology Heart & Circulatory Physiology,2014,308(3):206.
[8]Simonson TS,Yang Y,Huff CD,et al.Genetic evidence for high-altitude adaptation in Tibet.Science 2010,329(5987):72.
[9]Li X,Liu L,Yang S,et al:Histone demethylaseKDM5Bis a key regulator of genome stability.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2014,111(19):7096-7101.
[10]Stewart MH,Albert M,Sroczynska P,et al.The histone demethylase Jarid1b is required for hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal in mice.Blood,2015,125(13):2075-2078.
[11]Kim M,Jain S,Harris AG,et al.Colchicine may assist in reducing granulation tissue in junctional epidermolysis bullosa. International Journal of Womens Dermatology,2016,2(2):56-59.
[12]Sole X,Guino E,Valls J,et al.SNPStats:a web tool for the analysis of association studies.Bioinformatics(Oxford,England),2006,22(15):1928-1929.
[14]Xu S,Li S,Yang Y,et al.A genome-wide search for signals of high-altitude adaptation in Tibetans.Molecular Biology & Evolution,2011,28(2):1003-1011.
[15]Painschab MS,Malpartida GE,Davila-Roman VG,et al.Association between serum concentrations of hypoxia inducible factor responsive proteins and excessive erythrocytosis in high altitude Peru.High Alt Med Biol,2015,16(1):26-33.
[16]Xia X,Lemieux ME,Li W,et al.Integrative Analysis of HIF Binding and Transactivation Reveals Its Role in Maintaining Histone Methylation Homeostasis.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2009,106(11):4260-4265.
[17]Brat DJ,Mapstone TB.Malignant glioma physiology:cellular response to hypoxia and its role in tumor progression.Annals of Internal Medicine,2003,138(8):659-668.
[18]Fuentes I,Campos M,Repetto G,et al.Molecular epidemiology of Junctional Epidermolysis bullosa:discovery of novel and frequentLAMB3 mutations in Chilean patients with diagnostic significance.British Journal of Dermatology,2016.
[19]Skowronski K,Andrews J,Rodenhiser DI,et al.Genome-Wide Analysis in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells Reveals Ischemia-Mediated Expression of Motility Genes via DNA Hypomethylation.Plos One 2014,9:e112576-e112576.
中国藏族人群高原红细胞增多症与KDM5B、LAMB3基因多态性之间的关联
赵一多1,2*,张致英1,2*,刘丽军1,2*,张 瑶1,2,马利锋1,2,李岩松1,2,蔡 鹏1,2,康龙丽1,2#
(1.西藏民族大学高原相关疾病分子遗传机制与干预研究省级重点实验室,陕西 咸阳 712082;2.高原环境与疾病相关基因研究高校重点实验室,陕西 咸阳 712082)
目的 中国藏族人群中高海拔红细胞增多症(HAPC)是一个严重的公共健康问题。其主要特点是红细胞过度增多(女性,血红蛋白≥190 g/L;男性,血红蛋白≥210 g/L)。虽然慢性缺氧是HAPC的主要原因,但是HAPC的分子机制目前还不清楚。本研究旨在探讨HAPC在中国藏族人群中的遗传基础。方法 共招募70名藏族HAPC患者和30名健康受试者进行病例对照研究。方差分析主要用于评估HAPC遗传变异的多态性影响。结果 使用卡方检验和遗传模型分析,KDM5B基因中的rs1141109位点,rs7528426位点和rs1141108位点,LAMB3基因中rs2072938位点和rs2072940位点在中国藏族人群中降低HAPC患病风险。结论 我们的研究表明KDM5B和LAMB3的基因多态性与中国藏族人群的HAPC易感性显著相关。
高原红细胞增多症KDM5BLAMB3基因多态性
R394
A
2017-01-23
10.13452/j.cnki.jqmc.2017.01.002
※:Research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.31460286;31660307;31260252;),the Natural Science Foundation of Xizang(Tibet)Autonomous Region(No.2015ZR-13-19;2016ZR),Innovation program of University Young Teacher,Tibet Autonomous Region(QC2016-29);the Social Science Foundation of the Chinese Ministry of Education(No.12YJA850011),the School Foundation of Xizang Minzu University(No.11myY20)and Xizang Minzu University graduate practice and innovation project in 2016(No.2016MDYJS001).
*:ZHAO Yi-duo,ZHANG Zhi-ying and LIU Li-jun are joint first authors.
#:Corresponding Authors,M.D.,Ph.D.& Professor,Tel:+86-029-33755247,E-mail:klongli@163.com
