层状地基与弹性薄板相互作用的边界元解*
2017-05-15艾智勇蔡建邦
艾智勇,蔡建邦
(1.同济大学 地下建筑与工程系,上海 200092;2.同济大学 岩土及地下工程教育部重点实验室,上海 200092)
层状地基与弹性薄板相互作用的边界元解*
艾智勇1, 2†,蔡建邦1, 2
(1.同济大学 地下建筑与工程系,上海 200092;2.同济大学 岩土及地下工程教育部重点实验室,上海 200092)
将无限大薄板的基本解作为薄板边界积分方程的核函数,对薄板的内部和边界进行离散,并假定薄板内部和边界上的节点与地基反力的分布情况,得到薄板的边界元方程组;同时基于层状地基的解析层元解,通过Guass-Legendre积分得到地基柔度矩阵;结合地基与薄板接触面上的位移协调条件,得到层状地基与薄板共同作用问题总的边界元法方程组;求解该方程组,得到层状地基与薄板共同作用问题的解答.基于本文理论,编制了相应的FORTRAN程序,通过与已有文献结果对比验证本文理论及程序的正确性,数值分析结果表明:方形基础薄板情况下,离板中心越近,垂直于坐标轴y(x)方向、距离相等的2条线段的竖向位移差越小,且该位移差随着板-土刚度比减小而减小;随着板长宽比的增大,板中心点与长边中点位移差变化不明显,而短边中心与边界角点的位移差也有相类似的规律.
边界元;层状地基;薄板;解析层元
筏板基础具有刚度大、整体性好、能较好地抵抗不均匀沉降的优点,因此在高层建筑中得到了广泛的应用.目前,地基与板相互作用分析的方法主要有:有限差分法[1]、有限单元法[2-4]、边界单元法[5]、边界单元-有限单元耦合法[6]、广义微分求积法[7]、半解析数值方法[8-10],以及有限网格法[11]等.相比于有限元、有限层等方法,边界单元法能将求解过程的维数降低一维,并具有计算时间短、精度高等优点.因此,很多学者运用边界元法来研究筏板与地基的相互作用问题.佘颖禾和朱万宁[12]将地基效应归并到地基板的弯曲微分方程内,得到了含有第三类复变量的Bessel函数的基本解,再根据该问题的边界积分方程,建立了Winkler和双参数地基上薄板的无奇异边界单元法.王建国和黄茂光[13]提出了双参数地基上薄板问题的边界单元解法.邓安福等[14]采用边界单元法研究了双参数地基上的厚板问题.Rashed等[15]通过边界元法研究了Winkler地基上的厚板问题.闫富有等[16]基于Reissner 板的边界积分方程,建立了有限压缩层地基上厚筏基础与地基相互作用分析的边界元法.
由以上研究可知,目前板-土相互作用的边界单元法研究所采用的地基模型大多是Winkler和双参数地基模型.Winkler地基模型将地基对板的作用看做是一系列相互独立的弹簧,忽略了弹簧之间的剪切作用,因此只适用于很软弱的地基土.双参数地基模型虽然在独立弹簧之间引入力学的相互作用以消除其不连续性,但其参数较难获取,因而限制了它的工程应用.天然地基由于沉积而常常呈层状分布,因此采用层状地基模型更加符合工程实际.而层状地基上板的边界元研究还很少见诸报道.为此本文对层状地基与弹性薄板的共同作用问题进行边界元分析,以便精确、高效地求解基础板问题.
1 弹性薄板的边界积分方程
考虑横向分布荷载p时,弹性薄板的控制方程为:
D22s=p.
(1)
式中:s为板中面的横向位移;2为Laplace算子;)],为薄板的抗弯刚度,其中,hp,Ep和νp分别为板的厚度、弹性模量和泊松比.
由式(1)可得无限大平面薄板(如图1所示)的基本解为[17]:

(2)
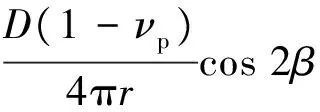
(3)
2(1+νp)(lnr+1)},
(4)
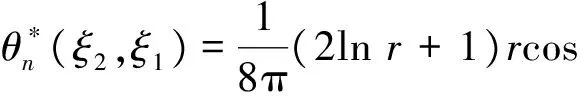

图1 薄板边界元法示意图Fig.1 The diagram of the BEM for a thin plate
采用由式(2)—(5)得到的基本解作为边界积分方程的核函数,于是可以得到具有光滑边界的薄板挠度边界积分方程:
(6)
式中:当源点在板内部时,即ξ1∈Ω时,c(ξ1)=1,当源点在板边界时,即ξ1∈Γ时,c(ξ1)=0.5;Mn,Vn和θ分别表示薄板边界的弯矩、横向力、转角;Γ和Ω分别表示薄板的边界域和内域;α为nξ与x的夹角,θ为幅角,β=α-θ,其中,tξ和nξ分别为ξ2点处的切线方向和外法线方向.
2 层状地基与薄板的共同作用
假设板四边自由,有:
Vn(ξ2)=0,
(7)
Mn(ξ2)=0.
(8)
结合地基反力分布假设和式(7)与式(8),当源点为内点及边界点时,式(6)可分别表示为式(9)和式(10),即:
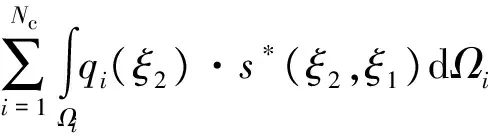
(9)
(10)
式中:Γi(i=1,2,…,Ne)对应于各段边界的单元;Ωi对应于反力qi(i=1,2,…,Nc)的作用面积;sc和se分别表示薄板内点、边界点的竖向位移.

图2 层状地基与薄板相互作用图Fig.2 The draft of the interaction betweenlayered soils and a thin plate
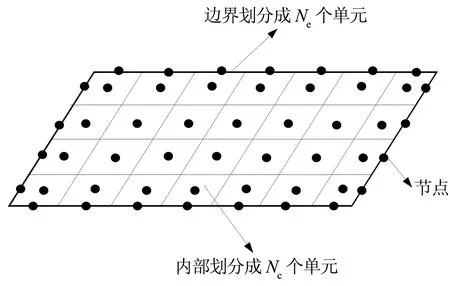
图3 弹性薄板单元及节点图Fig.3 The elements and nodes of an elastic thin plate
当板上作用均布荷载p时,薄板的边界积分方程可表示为:
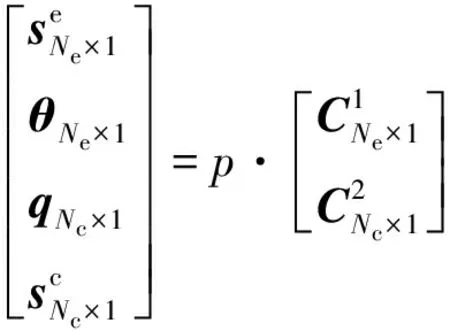
(11)
其中,
(12)
(13)
(14)
(15)
(16)
(17)
(18)
(19)
(20)
(21)
(22)
(23)
(24)
式中:se,θ,sc,q分别为薄板边界节点位移、边界节点转角、内节点位移、地基反力矩阵;Ic为元素是D的Nc阶对角矩阵.
根据层状各向同性弹性地基的解析层元解[18],通过两维Guass-Legendre积分可得单位均布荷载作用在反力qj区域时,板节点i处的沉降为:
δij=∬δ(i,ψ,R)dΓj.
(25)
式中:δ(i,ψ,R)为地基的基本解,它表示层状地基表面任意点ψ作用单位点荷载在点i引起的沉降,R为点ψ到点i的距离.
地基反力引起的板内点及边界点的竖向位移可表示为:
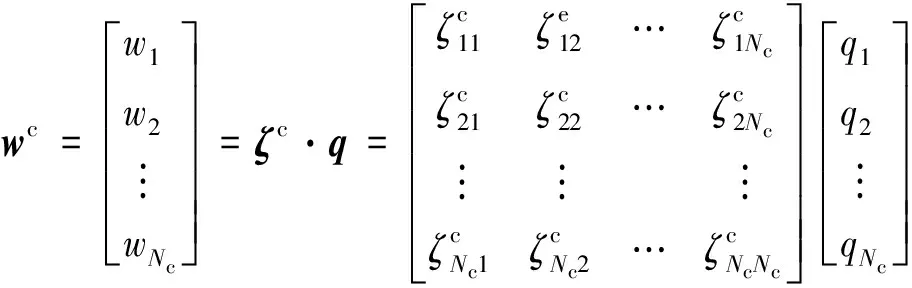
(26)
(27)
假设加载前后板与地基不脱离,则有:
we=se,
(28)
wc=sc.
(29)
将式(26)-(29)代入式(11),可得:
(30)
求解式(30),得到地基与弹性薄板相互作用的板边界节点转角和地基反力,再通过式(26)和(27)可求得薄板内部点和边界点的竖向位移.
3 数值计算与分析
3.1 理论与程序验证
为了验证本文理论及程序的正确性,将本文的计算结果与Wang&Cheung[4]的结果进行对比(如图4所示),其中,bp=4.0 m,νs=0.4,hp=0.2 m,Es=0.343×103MPa,νp=0.167,Ep=0.343×105MPa,均布荷载p=0.98 MPa(见图5).本文采用厚度为1 000m的单层土来模拟弹性半空间地基.由图5可知,本文的结果与Wang&Cheung[4]的结果吻合较好,这表明本文理论与程序的正确性.
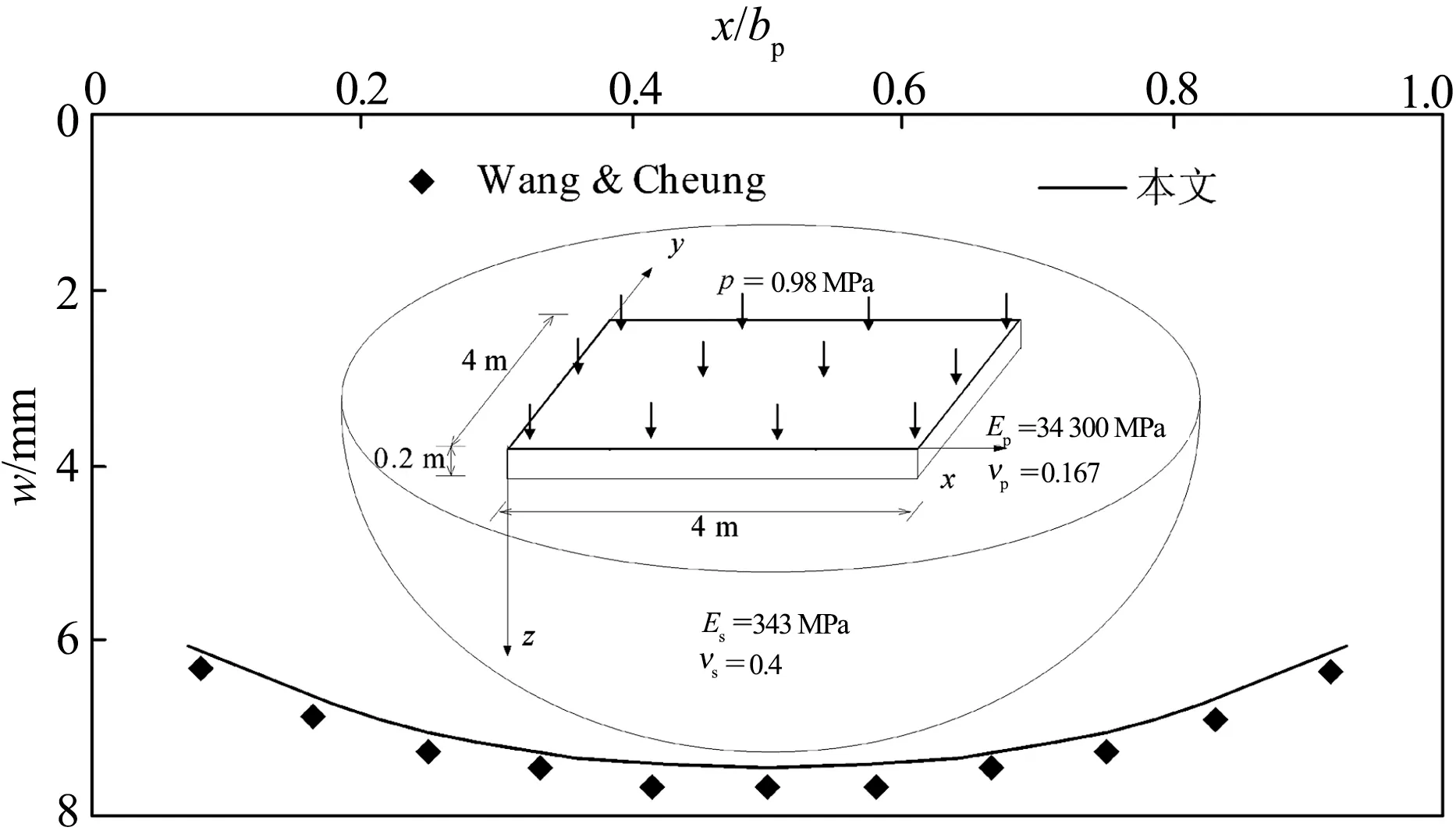
图4 方形基础薄板边界的挠度对比图Fig.4 The comparison of vertical displacementsof the boundary of a square foundation thin plate
3.2 板-土刚度比的影响
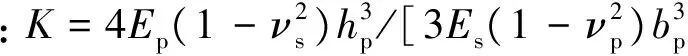

图5 弹性半空间上的方形薄板Fig.5 A square thin plate on an elastic half-space
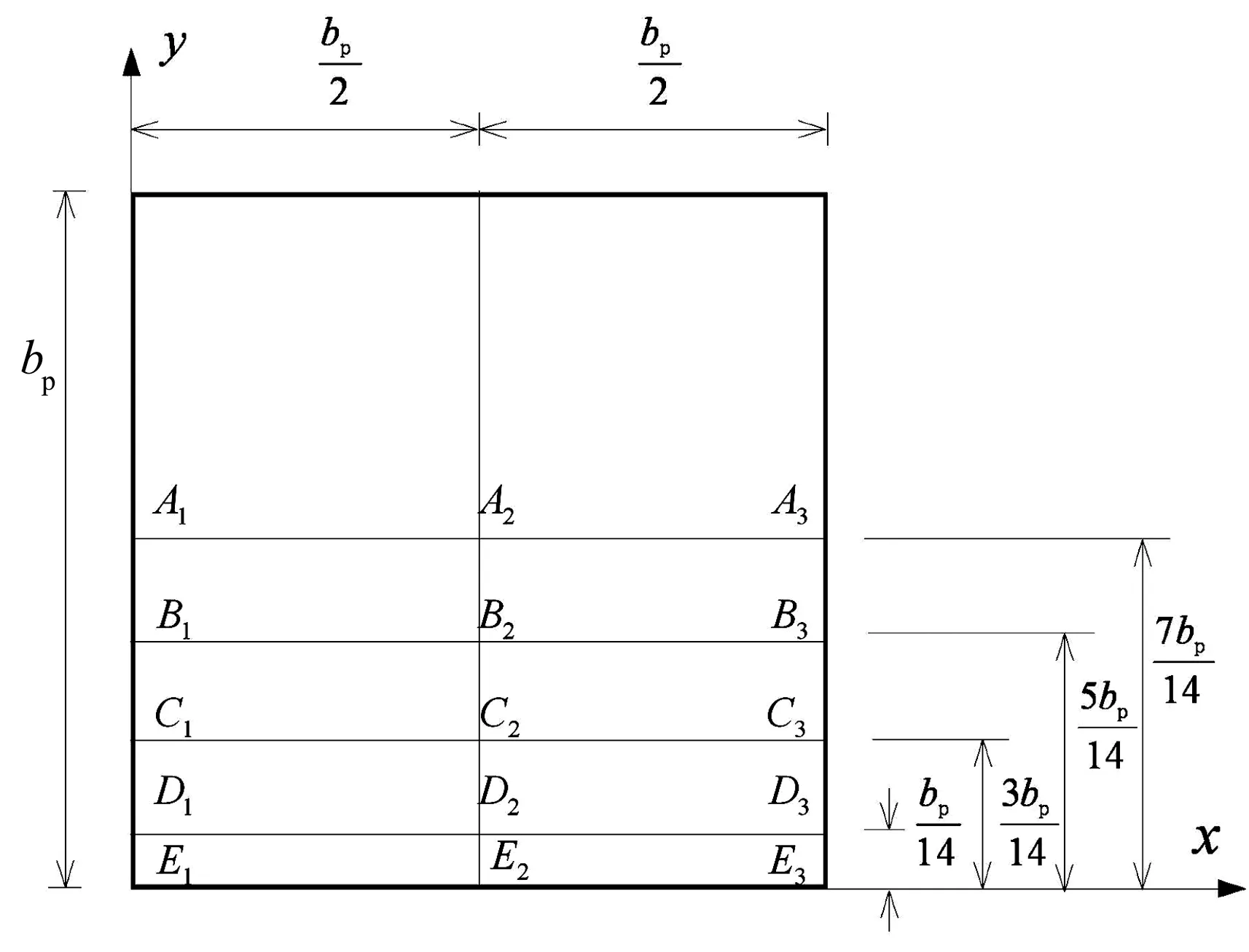
图6 方形薄板平面图Fig.6 The plane graph of a square thin plate
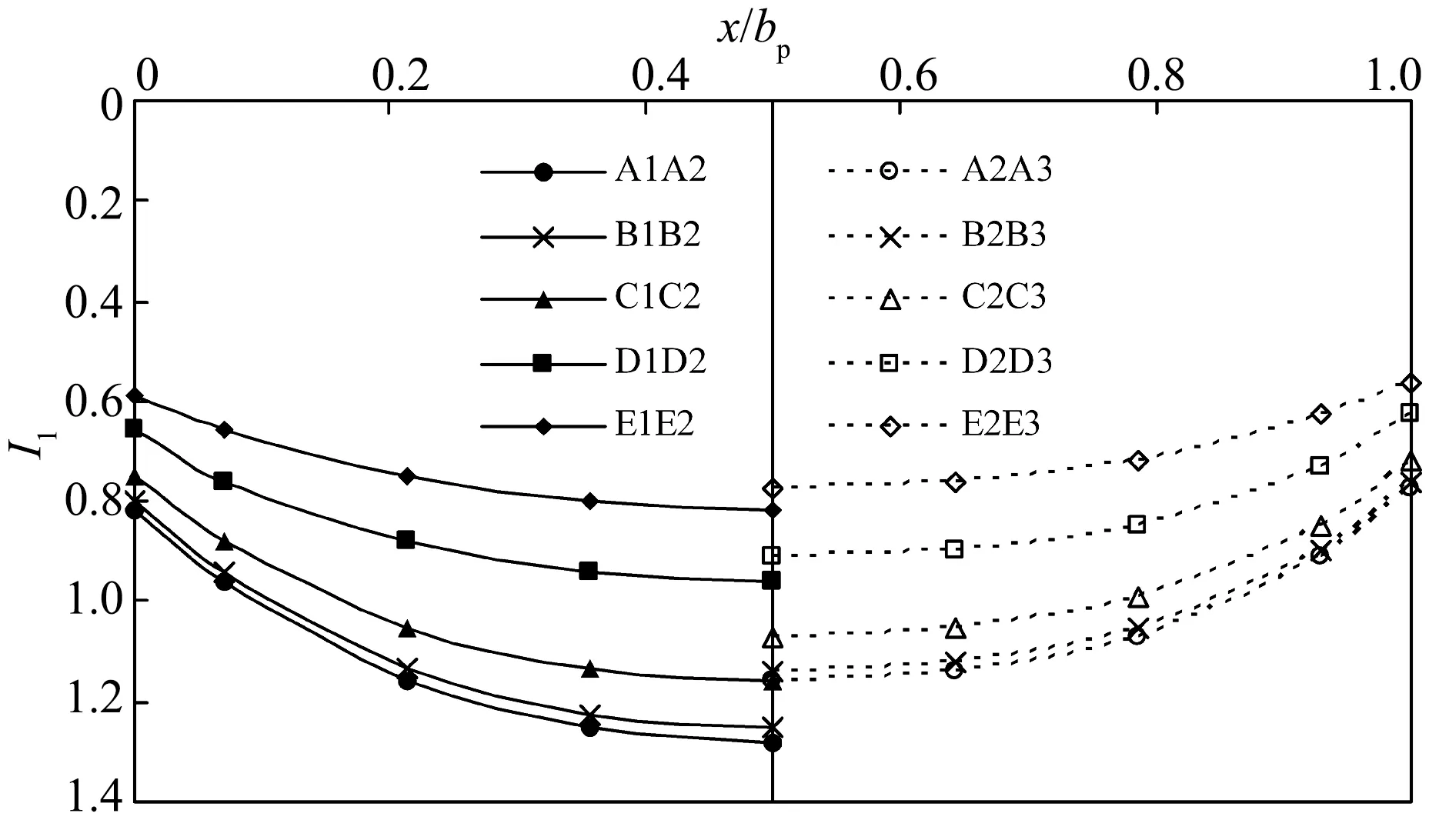
图7 当K=0.05(实线)和0.01(虚线)时 各线段的竖向位移曲线Fig.7 The settlement curves of the lines on the plate when K=0.05(solid line) and 0.01(imaginary line)
3.3 矩形板长宽比η的影响
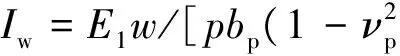
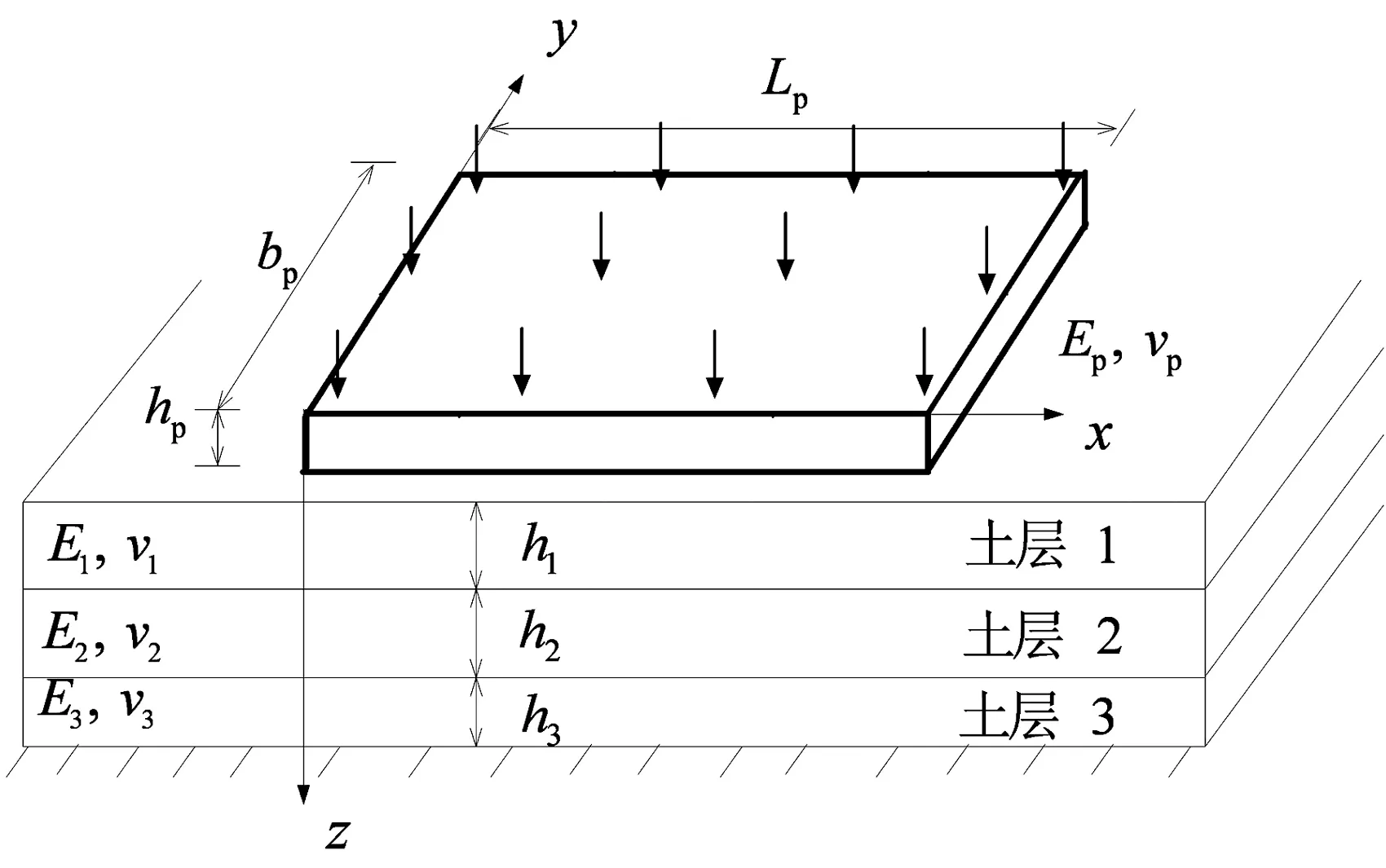
图8 三层地基上矩形薄板Fig.8 A rectangular plate on three-layered soils

η图9 板边界角点、短边中点、长边中点 和板中心点的挠度随η的变化曲线Fig.9 The settlement-η curves of the boundaryangular dot, the midpoits of the long sideand the wide side, and the center of the plate
4 结 论
本文基于更加符合工程实际的层状地基模型,采用边界单元法来求解地基与弹性薄板的共同作用问题,并通过与已有文献结果对比,验证了本文理论与计算程序的正确性.数值分析结果表明:
1)方形基础薄板情况下,离板中心越近,垂直于y(x)方向、距离相等的2条线段的竖向位移差越小,且其随板-土刚度比减小而减小.
2)随着长宽比的增大,短边中点与长边中点的挠度差也增大;但板中心点与长边中点位移差变化不明显,且短边中心与边界角点位移差也有相类似的规律.
相比于有限元、有限层等方法,边界单元法能将求解过程的维数降低一维,并具有计算时间短、精度高等优点.另外,基于层状地基的动力解析层元解[19]及达朗贝尔原理[9],还可进一步将本文工作拓展,用以分析层状地基上弹性薄板的动力响应.
[1] VALLABHAN C V G, STRAUGHAN W T, DAS Y C. Refined model for analysis of plates on elastic foundations[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics Division, ASCE, 1991, 117(12): 2830-2843.
[2] CHEUNG Y K, NAG D K. Plates and beams on elastic foundations-linear and non-linear behaviour[J]. Geotechnique, 1968, 18(2): 250-260.
[3] 王元汉, 邱先敏, 张佑启. 弹性地基板的等参有限元法计算[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1998, 20(4): 10-14.
WANG Yuanhan, QIU Xianmin, CHEUNG Y K. Plate on an elastic foundation calculated by isoparametric element methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1998, 20(4): 10-14. (In Chinese)
[4] WANG Y H, CHEUNG Y K. Plate on cross-anisotropic foundation analyzed by the finite element method[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2001, 28(1): 37-54.
[5] DE PAIVA J B, BUTTERFIELD R. Boundary element analysis of plate-soil interaction[J]. Computers & Structures, 1997, 64(1): 319-328.
[6] 许金余, 吴彰春, 冷培义. 弹性地基板的无界边界元-有限元耦合计算法[J]. 工程力学, 1994, 11(3): 137-143.
XU Jinyu, WU Zhangchun, LENG Peiyi. A calculation method of coupling infinite BE and FE for plate based on elastic half space[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 1994, 11(3): 137-143. (In Chinese)
|[7] NOBAKHTI S, AGHGAM M. Static analysis of rectangular thick plates resting on two-parameter elastic boundary strips[J]. European Journal of Mechanics—A/Solids, 2011, 30(3):442-448.
[8] 李刚, 罗世平, 尚守平. Vlazov地基上Reissner板相互作用的加权残值分析法[J]. 湖南大学学报:自然科学版, 2006, 33(1): 20-24.
LI Gang, LUO Shiping, SHANG Shouping. Weighted residual method for the analyzing of the interaction of Reissner’s plate on Vlazov’s elastic foundation[J]. Journal of Hunan University: Natural Sciences, 2006, 33(1): 20-24.(In Chinese)
[9] 李刚, 丁翔, 尚守平. 有限条法分析双参数地基板的动静响应[J]. 湖南大学学报:自然科学版, 2008,35(4): 7-10.
LI Gang, DING Xiang, SHANG Shouping. Finite stripe method for the static and dynamic analysis of plates on two-parameter elastic foundation[J]. Journal of Hunan University: Natural Sciences, 2008, 35(4): 7-10.(In Chinese)
[10]LIANG X, WANG Z, WANG L,etal. Semi-analytical solution for three-dimensional transient response of functionally graded annular plate on a two parameter viscoelastic foundation[J]. Journal of Sound & Vibration, 2014, 333(12): 2649-2663.
[11]KARASIN H, GULKAN P, AKTAS G. A finite grid solution for circular plates on elastic foundations[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2015,19(4):1157-1163.
[12]佘颖禾, 朱万宁. 弹性地基板的无奇异边界元解法[J]. 计算结构力学及其应用, 1991, 8(3): 267-274.
SHE Yinghe, ZHU Wanning. A boundary element solution for the bending problem of the thin plates on elastic foundation[J]. Computational Structure Mehanics and Applications, 1991, 8(3): 267-274. (In Chinese)
[13]王建国, 黄茂光. 两参数弹性地基板的边界元分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 1992, 25(3): 51-59.
WANG Jianguo, HUANG Maoguang. Boundary element analysis of thin plates on the two-parameter elstic foundation[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 1992, 25(3): 51-59. (In Chinese)
[14]邓安福, 周永明, 李正良, 等. 双参数弹性地基厚板分析的边界元法[J]. 重庆建筑大学学报, 1997, 19(2): 6-16.
DENG Anfu, ZHOU Yongming, LI Zhengliang,etal. Boundary element method for analysis of thick plates on two-parameter elastic foundations[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jianzhu University, 1997, 19(2): 6-16. (In Chinese)
[15]RASHED Y F, ALIABADI M H, BREBBIA C A. The boundary element method for thick plates on a Winkler foundation[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1998, 41(8): 1435-1462.
[16]闫富有, 吴义章, 郭院成. 有限压缩层地基上筏基沉降的边界元分析[J]. 岩土力学,2011, 32(S2): 604-609.
YAN Fuyou, WU Yizhang, GUO Yuancheng. Boundary element analysis of settlements of raft on finite compressible strata[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(S2): 604-609. (In Chinese)
[17]杜庆华. 边界积分方程方法——边界元法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1989:135-137.
DU Qinghua. Boundary integral equation method—boundary element method[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1989: 135-137.(In Chinese)
[18]艾智勇, 董洲, 成怡冲. 多层地基轴对称弹性空间问题的解析层元解[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2012, 44(4): 150-153.
AI Zhiyong, DONG Zhou, CHENG Yichong. Analytical layer element solution of axisymmetrically elastic problem for multilayerd soils[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2012,44(4): 150-153. (In Chinese)
[19]AI Z Y, LI Z X, CANG N R. Analytical layer-element solution to axisymmetric dynamic response of transversely isotropic multilayered half-space[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2014, 60(5): 22-30.
Foundations and an Elastic Thin Plate
AI Zhiyong1, 2†, CAI Jianbang1, 2
(1. Department of Geotechnical Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China; 2. Key Laboratoryof Geotechnical and Underground Engineering of Ministry of Education, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China)
The kernel functions of the boundary integral equations for thin plate were determined by the fundamental solutions for an infinite thin plate. By the discretization of the plate interior and boundary as well as the assumption of the distribution states of plate nodes and foundation reaction forces, the BEM equations of the plate can be established. Meanwhile, based on the analytical layer element solutions for layered foundations, the flexibility matrix of the foundation was obtained by a two-dimensioned Guass-Legendre quadrature. Taking into account the compatible conditions of the displacements at the soils-plate interface, the global BEM equations for the interaction problem between the layered foundation and the thin plate were then established. The solutions for the problem were further obtained by solving the global BEM equations. The accuracy of the present method was verified by comparing existing solutions with the numerical results obtained from the corresponding FORTRAN program in this study. It is observed from numerical examples that when a square thin plate is placed on a foundation, the settlement difference between the two lines perpendicular to y or x coordinate decreases as they approach the center of the plate, and the difference decreases with the decrease of the plate-soil stiffness ratio. Furthermore, the settlement discrepancy between the plate center and the midpoint of the long side is unapparent with the increasing length-width ratio, and the similar variation trend can be found between the midpoint of the wide side and angular point.
boundary element; layered soils; thin plates; analytical layer element
2015-11-26
国家自然科学基金资助项目(50578121), National Natural Science Foundation of China(50578121)
艾智勇(1966-),男,江西余江人,同济大学教授,博士 †通讯联系人,E-mail:zhiyongai@tongji.edu.cn
1674-2974(2017)03-0120-06
10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbzkb.2017.03.015
TU443
AA BEM for Interaction between Layered
