The Relationship between Foreign Exchange Reserve and Money Supply in China
2017-04-30ChenJie
Chen+Jie

【Abstract】: In recent years, money supply has increased dramatically with the accumulation of foreign exchange reserve. This paper constructs three double logarithm regression models, using data of foreign exchange reserve and money supply (M0, M1, M2) from 2001 to 2015. The three models all show that the increasing foreign exchange reserve promotes the growth of money supply. Besides, the change of foreign exchange reserve has the greatest impact on M1.
【Key Words】: Foreign exchange reserve, Money supply
Introduction
Foreign exchange reserve is the convertible currency in external payment which is hold by monetary authority. Foreign exchange reserve can be used as insurance against financial crisis and default risk. China also use the accumulation of large scale foreign reserve as a tool of foreign exchange intervention to resist currency appreciation. However, the foreign exchange reserve in China has increased year by year since the reform of foreign exchange system in 1994.
The policies of encouraging export and limiting import, to some extent, cause the current account imbalances. The capital account surplus can be partly explained by the inflows of international hot money and foreign direct investment. According to the current foreign exchange administration system, the central bank has to purchase foreign exchange passively in the situation of continued surplus in international balance of payments to maintain the exchange rate stability. In the meantime, because of the compulsory foreign exchange settlement and quota management system, the large amount of foreign exchange which should be owned by companies and banks become the reserve of central bank. Therefore, China has experienced strong ‘double surplus in current and capital account, which has led to the situation that the supply of foreign exchange exceeds the demand and the rapid accumulation of foreign exchange reserve. As a result, the central bank has to purchase the excess foreign currency in market to maintain exchange rate stability. The RMB used to buy foreign currency leads to an increase in the money supply.
Monetary policy, is the core mechanism for central bank to regulate financial and macro-economic conditions. It is known that money supply acts as intermediate target in monetary policy transmission, therefore money supply has strong relationship with economic situation. In recent years, money supply has increased dramatically with the accumulation of foreign exchange reserve. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the effect of foreign exchange reserve on money supply.
There are many literature analyzing the influence of foreign reserve on economy and they are different in theories and methods. The correlation analysis of the data from 1985 to 1998 shows that explosion in foreign exchange reserve often takes a shock to money supply when foreign capital pours into China. Huang (2005) analyzes banking system and foreign exchange administration system respectively and the author finds that the abrupt increase of foreign exchange reserve has vibration effect on the economy. Based on the unit root test and Granger causality, Zhu(2005) finds that foreign exchange reserve has long-run equilibrium relationship with M2, leading to the rise in M2. Using Granger test and VAR model, Liu (2005) believes that foreign exchange reserve change leads to domestic inflation. The conclusion made by Chen (2007) shows that foreign exchange reserve structure generates difficulties in macroeconomic regulatory and the international hot money has the strongest correlation with pressure of policy. The author also think that changes in foreign exchange reserves have constraints on the monetary policy implementation. Foreign exchange accounts for a large proportion of base money, which impairs the independence of monetary policy.
Based on the literature above, we can find that few researches discuss the relationship between foreign exchange reserve and three money supply dimensions. The money supply has three dimensions. The first one is M0, which is the cash on hand. The second dimension is narrow money supply M1, which is M0 plus current deposit. The last one is broad money supply M2, which is M1 plus fixed term deposits, saving deposits and customer margin. This paper aims to explore the different influence of foreign exchange reserve on different money supply dimensions.
This paper firstly analyze the reason why the foreign exchange reserve increases rapidly and the transmission mechanism of foreign exchange reserve on money supply. Secondly this paper constructs double logarithm regression models, using data of foreign exchange reserve and money supply (M0, M1, M2) from 2001 to 2015.
Theory and Data
The monetary base can be divided into two parts. The first part is the cash hold by banks and cash in circulation and deposits of financial institutions in central bank. The second part is base money associate with foreign reserve. The central bank purchase foreign exchange with RMB currency, indicating that base money supply increases with foreign reserve. The money supply equation is M=m×B. In this equation, M is money supply, m is money multiplier, B is monetary base. According to modern money supply theory, the base money contributes to larger increase in money supply through the multiplier effect. The conflict that the total money supply exceeds the real demand will cause inflation phenomenon. Whats worse, in order to reduce the passive money supply, the monetary authority has to issue the central bank bills, which undermines the independence of monetary policy.
The empirical analysis in this paper is based on monthly data, sourced from website of central bank and Administration of Foreign Exchange. The analysis selects foreign exchange reserve (F) as dependent variable and three money supply (M0, M1, M2) as independent variables.
The table below demonstrates that the growth rate from 2001 to 2010 is extremely high due to the continuous surplus in international trade. However, the growth rate declines in recent five years. The global financial crisis reduces international demand and the economic recession slows down the growth in foreign exchange reserve. It is worth noting that reserve decreases in the year 2014 for the first time which is a remarkable economic signal.
As the table below shows, the changing tendency of M0, M1 and M2 is similar, however, the M0 change mildly compared with M1 and M2, indicating the fact that monetary multiplier amplify the fluctuations of M1 and M2.
Empirical Method and Results
The monetary policy is hard to take effect in current period because the policy has lag effect. Therefore, the following analysis put the lagged variables into the model. With the lagged dependent variables, this paper constructs three double logarithm regression models to estimate the relationship between foreign exchange reserve and money supply.
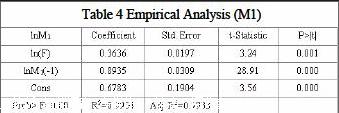
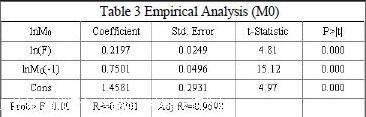
The results show that the coefficients of variables are statistically significant and the goodness of fit is high. Therefore, the model is:
ln (M0) =0.2197*ln (F) +0.7501*lnM0 (-1) +1.4581
ln (M1) =0.3636*ln(F)+0.8935*lnM1 (-1)+0.6783
ln (M2) = 0.0882*ln (F) + 0.8726*lnM2 (-1) + 0.8324
(1) According to regression results, the foreign exchange reserve has influence on M0. To be specific, if foreign exchange reserve is reduced by 1%, the M0 will be decreased by 0.21%. Take the year 2005 as example. The foreign reserve increased 30% in 2005, according to the estimation, it could leads in 6.3% increase in M0. In fact, the actual growth rate of M0 is 11.94%. Therefore, the increase caused by foreign exchange reserve accounts for 53% of the actual amount.
(2)The estimation shows that foreign exchange reserve has deeper effect on M1 than that of M0 and M2. The 1% increase in foreign reserve may cause 0.36% increase in M1. Take the year 2005 as example. The foreign reserve increased 30% in 2005, according to the estimation, it could leads in 10.8% increase in M1. In fact, the actual growth rate of M1 is 17.48%. Therefore, the increase caused by foreign exchange reserve accounts for 70% of the actual amount.
(3)The coefficient indicates that the foreign exchange reserve does not have significant influence on M2. Take the year 2005 as example. The foreign reserve increased 30% in 2005, according to the estimation, it could leads in 2.7% increase in M2. In fact, the actual growth rate of M2is 18.04%. Therefore, the increase caused by foreign exchange reserve accounts for 15% of the actual amount.
Conclusion
The society is under the pressure of inflation with the excess money supply so the independence of monetary policy is weakened gradually. This paper discuss the relationship between foreign exchange reserve and money supply through the double logarithm regression model.The three models all show that increasing foreign exchange reserve promotes the growth of money supply. In the meantime, the change of foreign exchange reserve has the greatest impact on M1.
References:
[1]Bai, Chong-en, Li, David D. & Tao, Z. A Multitask Theory of State Enterprise Reform [J], Journal of Comparative Economics, 2000(28): 716-738.
[2]Huang ZeMin. The Structural Risk of Increasing Foreign Reserve in China and Suggestions [J], Shanghai Finance, 2005(4): 4-7.
[3]Zhu MengNan & Huang XiaoDong. Co-integration Analysis and an Error Correction Model of Chinas Foreign Reserve and M2 [J]. Guangdong Social Science, 2005(3): 15-19.
