氡析出率快速测量的不确定度评定
2017-04-20李志强肖德涛赵桂芝吴喜军周青芝
李志强 肖德涛 赵桂芝 单 健 吴喜军 周青芝
氡析出率快速测量的不确定度评定
李志强1,2肖德涛2赵桂芝2单 健2吴喜军2周青芝2
1(衡阳师范学院 物理与电子工程学院 衡阳 421008)
2(南华大学 核科学技术学院 衡阳 421001)
氡析出率测量受外界环境因素影响较大,为科学合理地评定氡析出率快速测量结果的准确性。结合不确定度原理,建立氡析出率快速测量方法的理论分析模型,分析其不确定度来源,评定其不确定度。结果表明,快速测量方法在氡析出率0.39−2.62 Bq·m−2·s−1的标准装置上,105 min快速测量的结果其相对合成标准不确定度在12%以内。研究结果为氡析出率快速测量方法的置信程度评定提出了新的评价方法。
氡析出率,快速测量,不确定度
静电收集α能谱法是测量氡析出率的主流发展方向[9−13]。南华大学研制的NRE-I型便携式氡析出率自动测量仪采用高灵敏探测效率的静电收集方式,能够快速测量介质表面的氡析出率,其105 min的测量结果与南华大学氡析出率标准装置参考值的相对偏差在5%以内[14−15]。但对氡析出率标准装置快速测量以“相对偏差”分析测量结果已不适应国际交流的需要,需结合不确定度原理,通过分量量化实验结果,完善氡析出率快速测量结果的可信程度。为世界各国氡析出率测量及其所得到的结果可以进行相互比对,有必要对氡析出率测量结果进行不确定度评定[16]。随着测量不确定度理论的发展,将氡析出率测量的数据处理与不确定度评定相结合,提高测量结果的科学性、准确性是主要的研究方向[17]。为确保快速测量方法的准确性、可靠性和溯源性,本文结合氡析出率快速测量不确定度原理,利用南华大学研制的NRE-I便携式氡析出率自动测量仪对氡析出率快速测量方法引入的不确定度进行分析和评定,开展了氡析出率快速测量方法的可靠性研究。
1 不确定度分析计算模型
1.1 氡析出率快速测量模型
根据国际原子能机构(International Atomic Energy Agency, IAEA) 333号技术丛书《铀尾矿氡析出测量与计算》(1992)中给出了氡析出率测量最常用的积累法(又称局部静态法)[18−19],即在待测介质表面扣一集氡室,周边用不透气材料密封,通过两根硅胶管与NRE-I便携式氡析出率测量仪的测量腔进行连接,实验装置图如图1所示。

图1 氡析出率快速测量实验装置图Fig.1 Experimental setup of rapid determination for standard device of radon exhalation rate.
采用等时间间隔取样,以T为测量周期进行连续测量,根据集氡室内单位时间内氡浓度变化[19]:
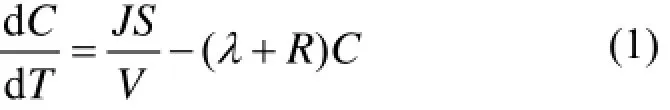
式中:J为氡析出率,Bq·m−2·s−1;S为集氡室底面积,m2;V为集氡室、硅胶连接管和氡析出率测量腔的总体积(简称收集总体积),m3;T为测量周期,s;C为集氡室中的氡浓度,Bq·m−3;λ为氡的衰变常量,2.1×10−6s−1;R为泄漏和反扩散率,s−1。
根据相邻两测量周期测量集氡室中氡浓度的关系:

通过多次测量提高测量精度,用最小二乘法线性拟合得到截距a、斜率b后求出氡析出率J[20]。
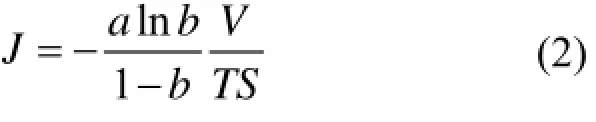
其中:

1.2 不确定度的来源及其传播律
氡析出率快速测量结果计算依据式(2),由式(2)可知,影响氡析出率测量结果的不确定度的来源有:a、b、V、T、S和n,其中a、b值的不确定度来源于测量的氡浓度Cn以及测量的次数n。
由于各分量a、b、T、V、S互不相关,氡析出率J的测量结果合成标准不确定度[21]:
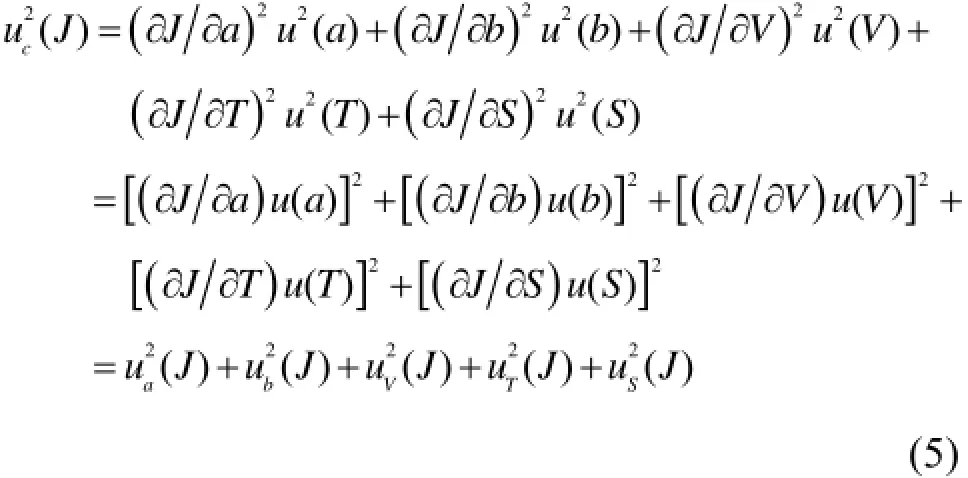
其中各分量的传播系数:


2 不确定度分量的量化分析
2.1 线性拟合参数a、b的不确定度
线性拟合参数a、b的不确定度包括A类不确定和B类不确定。其中A类是用对观测列的氡浓度Cn进行的统计分析,而B类是用不同于对观测列氡浓度Cn测的系统不确定度进行的统计分析。
2.1.1 线性拟合参数a、b的A类不确定度
式(3)、(4)中截距a和斜率b的A类标准不确定度分量为:


其中:其实验标准差:

2.1.2 线性拟合参数a、b的B类不确定度
测量数据Cn+1和Cn具有相同B 类不确定度uB(Cn)、uB(Cn+1),由于Cn+1及Cn的测量数据序列各测量值之间存在相关性,按照求和法进行合成,可得斜率b 的B 类总不确定度:
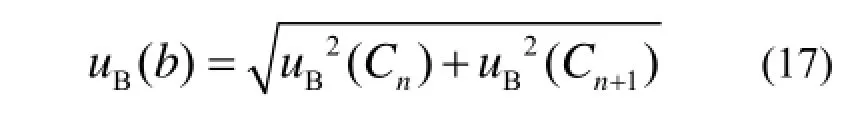
式中:uB(Cn)、uB(Cn+1)具有相同的不确定度,南华大学标准氡室相对不确定度uB(Cn+1)=2.9%,则斜率b 的B 类总不确定度uB(b)=2uB(Cn+1)= 0.041。
由于实验数据的分布符合均匀分布,且数据分布上下限比值趋于无穷大,截距a的uB(a) ≈0。
截距a和斜率b的合成标准不确定度为:

2.2 收集总体积V的标准不确定度
2.2.1 重复性测量引入的标准不确定度分量uA(V)采用A类方法评定,与重复性有关的合成标准不确定度均包含其中。对收集总体积进行5次重复性测定,所得结果如下:5712 mL、5735 mL、
5731mL、5720 mL、5727 mL,平均值5725mL。收集总体积的重复测量数据的实验标准差为:

则:
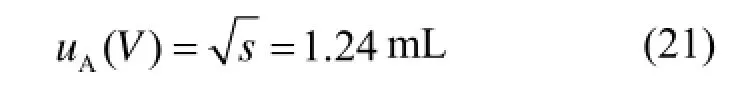
2.2.2 取样总体积引入的标准不确定度分量uB(V)
根据JJF1059.1-2012《测量不确定度评定与表示》的规定,用1000 mL的量筒进行测量收集总体积,其量筒的最大允许误差1 mL,以三角分布估算量筒校准引入的相对不确定度。量筒校准的标位偏差为u(V1)=16=0.408 mL。
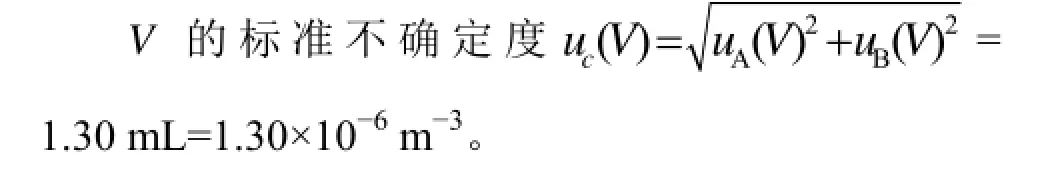
2.3 测量周期T的标准不确定
2.3.1 重复性测量引入的标准不确定度分量uA(T)
对于NRE-I氡析出率测量仪,快速测量氡析出率时其测量周期T=15 min,重复性测量周期选择T=900 s进行10 次测量,所得数据为900.41 s、901.33 s、900.87 s、901.80 s、901.32 s、901.76 s、901.35 s、901.52 s、901.43 s、901.32 s,其平均值为901.30 s。测量周期重复测量数据的实验标准差为:
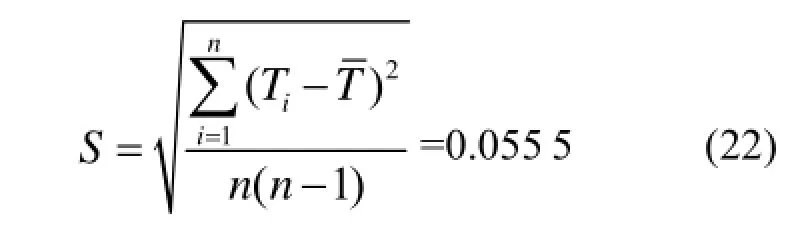
则:
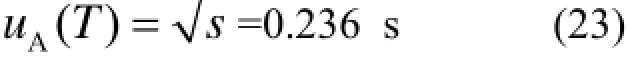
2.3.2 时间检定秒表引入的标准不确定度分量uB(T)
根据JJG601-2003时间检定仪的规程,秒表检定仪的准确度在1×10−7s,uB(T)=1×10−7/3= 6.671×10−8s,因此可忽略不计。
T的标准不确定uc(T)=uA(T)=0.236 s。
2.4 集氡室底面积S的标准不确定
2.4.1 重复性测定引入的标准不确定度分量uA(S)
集氡室的底部直径d的重复性测量进行5次测量,所得数据为291.5 mm、291.0 mm、292.0 mm、292.0 mm、291.5 mm,因此平均值为291.6 mm。其直径重复测量数据的实验标准差为:
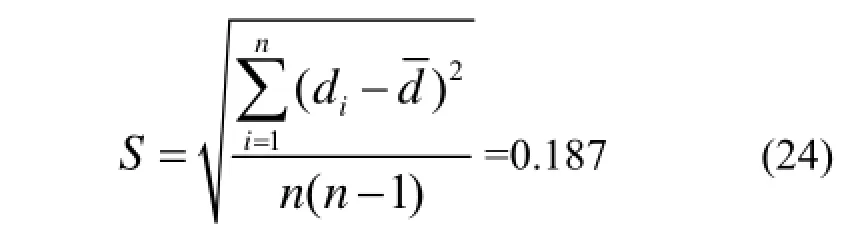
则:
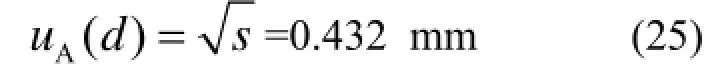
2.4.2 集氡室底面积S引入的标准不确定度分量
uB(S)
S的计算模型参考JJF1059.1-2012《测量不确定度评定与表示》的规定,采用S=π(d/2)2=0.25πd2计算模型,S的标准不确定度u(S)=0.25πu(d)。
直径d用米尺测量,其最大允许误差是1 mm,即uB(d)=1 mm。
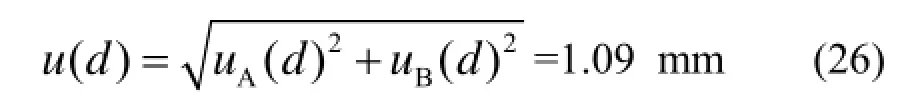
底部直径d的标准不确定度:集氡室底面积的标准不确定度uc(S)=
0.25 πu(d)= 0.855 mm2=8.55×10−7m2。
2.5 不确定度评定结果
南华大学氡实验室建立了一套氡析出率标准装置,提供了析出率稳定的测量对象,其氡析出率的参考值是用闪烁室法和活性炭盒γ谱法共同测定的,
1号标准装置的氡析出率参考值为
(1.48±0.05)Bq·m−2s−1,2号标准装置的氡析出率参考值为(2.60±0.08) Bq·m−2·s−1,3号标准装置的氡析出率参考值为(0.39±0.02) Bq·m−2·s−1。快速测量方法在1−3号标准装置上的测量结果如表1所示。

表1 1−3号标准装置不确定评定结果Table1 Evaluation of uncertainty in the 1−3# standard device.
表1结果表明,1号氡析出率标准装置的结果J=(1.52±0.12) Bq·m−2·s−1,其相对不确定度为8.00%;2号氡析出率标准装置的结果J=(2.67±0.21)Bq·m−2·s−1,其相对不确定度为7.79%;3号氡析出率标准装置的结果J=(0.38±0.04)Bq·m−2·s−1,其相对不确定度为11.03%。
表1的结果显示,在氡析出率0.39−2.62Bq·m−2·s−1的标准装置上采用快速测量方法对氡析出率标准装置进行快速测量,其结果的标准不确定度均比标准装置提供的不确定度要大,由于放射性测量存在统计涨落,在样本含量较小、测量时间短的情况下,快速测量方法的测量结果比标氡析出率标准装置定值结果的不确定度大,符合放射性测定的概率统计。但三个标准装置上快速测量的相对不确定度均在12%以内,且随着氡析出率的增大,其不确定度降低。
3 结语
本文从氡析出率测量原理出发,建立氡析出率标准装置快速测量的不确定度理论分析模型, 在不确定度概念的具体化和量化基础上,对氡析出率标准装置快速测量不确定度的来源进行分析及评定。较好地解决了传统评价氡析出率结果的单一性和不合理性。通过引入了最小二乘法线性拟合获得线性参数a、b的值,实现了氡析出率快速计算,对不确定度分析模型分量的不确定度进行分析,在南华大学建立的0.39−2.62 Bq·m−2·s−1氡析出率标准装置上,105min测量的结果其相对合成标准不确定度均不超过12%。为氡析出率快速测量方法的置信程度评定提出了新的评价方法。
1 Stajic J M, Nikezic D. Measurement of radon exhalation rates from some building materials used in Serbian construction[J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2015, 303(3): 1943−1947. DOI: 10.1007/ s10967-014-3726-5.
2 Jonassen N. The determination of radon exhalation rates[J]. Health Physics, 1983, 45(2): 369−376. DOI: 10.1097/00004032-198308000-00009.
3 Oberstedt S, Vanmarcke H. A radon exhalation monitor[J]. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 1996, 63(1): 69−72. DOI: 10.1097/00004032-199602000-00010.
4 Stajic J M, Nikezic D. Measurement of radon exhalation rates from some building materials used in Serbian construction[J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2015, 303(3): 1943−1947. DOI: 10.1007/ s10967-014-3726-5.
5 Ongori J N, Lindsay R, Newman R T, et al. Determining the radon exhalation rate from a gold mine tailings dump by measuring the gamma radiation[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2014, 140: 16−24. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2014.10.012.
6 Kansal S, Mehra R. Evaluation and analysis of226Ra,232Th and40K and radon exhalation rate in the soil samples for health risk assessment[J]. International Journal of Low Radiation, 2015, 10(1): 1−13. DOI: 10.1504/IJLR.2015.071747.
7 Immé G, Catalano R, Mangano G, et al. Radon exhalation measurements for environmental and geophysics study[J]. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 2014, 95: 349−351. DOI: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2013.02.033.
8 Duggal V, Mehra R, Rani A. Study of radium and radon exhalation rate in soil samples from areas of northern Rajasthan[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 2015, 86(3): 331−336. DOI: 10.1007/s12594-015-0319-z.
9 Sorimachi A, Takahashi H, Tokonami S. Influence of the presence of humidity, ambient aerosols and thoron on the detection responses of electret radon monitors[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2009, 44(1): 111−115. DOI: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2008.10.009.
10 Wang J X, Andersen T C, Simpson J J. An electrostatic radon detector designed for water radioactivity measurements[J]. Nuclear Instruments amp; Methods in Physics Research, 1999, 421(3): 601−609. DOI: 10.1016/ S0168-9002(98)01230-3.
11 Tan Y, Xiao D, Shan J, et al. A theoretical approach to the study of saturation phenomena of electrostatic collection efficiency of218Po[J]. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 2014, 100: 70−73. DOI: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2014. 03.033.
12 He X, Wang G. Surface radon exhalation rates of building material and soil affect on indoor air radon concentration[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2011, 18: 122−127. DOI: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.11.019.
13 Tan Y, Xiao D. A simple model for automatically measuring radon exhalation rate from medium surface[J]. Radiation Measurements, 2014, 64: 44−47. DOI: 10.1016/ j.radmeas.2014.04.006.
14 Hulland J. Use of partial least squares (PLS) in strategic management research: a review of four recent studies[J]. Strategic Management Journal, 1999, 20(2): 195−204.
15 单健, 肖德涛, 赵桂芝, 等. NRL-1型测氡仪的绝对湿度效应研究[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2014, 48(9): 1707−1711. DOI: 10.7538/yzk.2014.48.09.1707. SHAN Jian, XIAO Detao, ZHAO Guizhi, et al. Study on absolute humidity influence of NRL-1 measuring apparatus for radon[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2014, 48(9): 1707−1711. DOI: 10.7538/yzk. 2014.48.09.1707.
16 Smith M. Evaluation, uncertainty and motivation[J]. Ethical Theory and Moral Practice, 2002, 5(3): 305−320. DOI: 10.1023/A:1019675327207.
17 Snow A. Evaluating uncertain public projects with rival and non-rival benefits[J]. Journal of Natural Resources Policy Research, 2014, 6(6): 57−63. DOI: 10.1080/ 19390459.2013.865350.
18 苟全录, 张智慧. 静电收集式氡析出率仪的计算公式讨论[J]. 原子能科学技术, 1998, 32(5): 420−426. GOU Quanlu, ZHANG Zhihui. Discussion on the formula of electrostatic collection radon exhalation rate monitor[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 1998, 32(5): 420−426.
19 IAEA. Measurement and calculation of radon releases from uranium mill tailings[C]. Technical Report Series No.333, Vienna, 1992.
20 李志强, 肖德涛, 赵桂芝, 等. 便携式氡析出率自动测量仪研究[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2016, 50(2): 357−362. DOI: 10.7538/yzk.2016.50.02.0357. LI Zhiqiang, XIAO Detao, ZHAO Guizhi, et al. Research of portable automatic measuring monitor of radon exhalation rate[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2016, 50(2): 357−362. DOI: 10.7538/yzk. 2016.50.02.0357.
21 Zhang X Z, Ge A D, Ma J W, et al. Evaluation of measurement uncertainty from imperfect data[J]. Applied Mechanics amp; Materials, 2013, 457−458: 815−820. DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.457-458.815.
Uncertainty evaluation of rapid measurement of radon exhalation rate
LI Zhiqiang1,2XIAO Detao2ZHAO Guizhi2SHAN Jian2WU Xijun2ZHOU Qingzhi2
1(School of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Hengyang Normal University, Hengyang 421008, China) 2(School of Nuclear Science and Technology, University of South China, Hengyang 421001, China)
Background: Rapid measurement of radon exhalation rate is influenced strongly by external environmental factors. Purpose: This study aims to scientifically evaluate the accuracy of the measured result of radon exhalation rate according to the concept of uncertainty. Methods: A theoretical analytical model was estimated to study the measurement method of radon exhalation rate. The origin of the uncertainty was analyzed and employed to evaluate the accuracy of the result. Results: The result of the relative synthesis standard uncertainty diverges within 12% when the rapid measurement is applied on the standard device of the University of South China with a radon exhalation rate of 0.39−2.62 Bq·m−2·s−1in 105 min. Conclusion: This study provides a new method to evaluate the rapid determination of radon exhalation standard device.
Radon exhalation rate, Rapid measurement, Evaluation of uncertainty
氡析出是氡穿过两相介质界面的现象和过程,氡析出率是单位时间内穿过单位面积界面析出的氡量[1−3]。氡析出率测量是铀矿冶废石场、尾矿库防氡覆盖治理的关键,也是铀矿通风、环境污染及治理中寻找源项的关键,其中包括地下军事工程和民用建筑内的氡污染治理,目前在我国已引起普遍关注[4−8]。研究氡析出率快速测量是辐射防护领域中的一项重要的工作。
LI Zhiqiang, male, born in 1978, graduated from University of South Chinese with a doctoral degree in 2016, focusing on airborne
XIAO Detao, E-mail: 13307478601@189.cn
TL816.2
10.11889/j.0253-3219.2017.hjs.40.040201
No.11475082、No.11375083)、湖南省教育厅重点项目(No.16A028)、衡阳师范学院引进人才科研启动项目(No.16D02)、衡阳师范学院产学研用项目(No.16CXYY05)资助
李志强,男,1978年出生,2016年南华大学获博士学位,从事气载放射性测量及示踪技术研究
肖德涛,E-mail: 13307478601@189.cn
2016-11-26,
2017-01-17
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.11475082, No.11375083), Key Project of Hunan Provincial Department of Education (No.16A028), Introduction of Talent Research Projects of Normal University (No.16D02), Industry University Research Project of Normal University (No.16CXYY05)
radioactivity measurement and tracer technique
Received date: 2016-11-26, accepted date: 2017-01-17
