2011—2016年莱州市海水入侵发展趋势分析
2017-03-26赵景丽徐艳东
赵景丽, 邓 跃, 徐艳东, 喻 龙
2011—2016年莱州市海水入侵发展趋势分析
赵景丽1, 邓 跃2, 徐艳东1, 喻 龙3
(1. 山东省海洋资源与环境研究院, 山东省海洋生态修复重点实验室, 山东 烟台 264006; 2. 山东大学(威海) 海洋学院, 山东 威海 264209; 3. 烟台市海洋环境监测预报中心, 山东 烟台 264003)
基于莱州市2个海水入侵监测断面2011—2016年的监测数据, 分析了研究区域地下水氯度、海水入侵距离和速率的发展变化趋势, 探讨了海水入侵距离与降水量的关系。分析结果表明: 研究区域2013年地下水氯度最高, 2011—2016年呈现波动变化; 离岸距离与地下水氯度服从幂函数分布, 海庙断面海水入侵距离远大于朱旺断面且变化较大, 朱旺断面海水入侵趋势较为稳定; 研究区域2014年海水入侵速度最快, 之后呈减轻趋势, 海水入侵距离与降水量呈现明显的负相关关系, 2014年降水量的急剧减少, 是当年海水入侵严重的主要因素之一。本研究为莱州市防灾减灾管理提供参考依据。
海水入侵; 地下水氯度; 海水入侵距离; 降水量; 莱州市
海水入侵是指在自然或人为因素影响下, 滨海地带地下含水层的水动力条件发生改变, 破坏了淡水与海水之间的平衡状态, 导致海水或高矿化度的咸水沿含水层向内陆方向侵入的过程与现象[1]。海水入侵灾害污染地下淡水资源, 造成生态环境恶化, 人畜饮用劣质水导致疾病增加, 工农业生产使用被污染的地下水加速工业管道、设备的腐蚀和老化, 农业因地下水变咸导致土壤盐渍化而大量减产, 给海岸带区域的生产生活造成了严重影响[2-3]。因此, 开展海水入侵灾害的研究, 对提高海岸带地区防灾减灾能力和经济、社会可持续发展具有重要意义。
莱州市位于莱州湾东岸, 胶东半岛西北部。全市总面积1 928 km2, 海岸线长108 km, 常住人口88万, 是我国最早发现海水入侵的城市之一。自1976年发生海水入侵以来, 其海水入侵灾害经历了初始、发展、恶化、缓解等4个发展阶段[4-7]。自1996年首次引入大菱鲆养殖之后, 养殖规模迅速扩大, 因大量抽取地下咸水(60万~70万m3/d), 导致咸水区地下水位下降, 咸淡水界面向咸水一侧持续移动并最终保持稳定, 海水入侵面积由1995年的273 km2, 降至2003年的234 km2, 与高峰相比减少了14.2%[8], 截至2010年, 莱州市海水入侵面积232 km2, 基本保持稳定[9]。
本文基于莱州市2个海水入侵监测断面2011—2016年的监测数据, 掌握莱州市海岸带海水入侵现状, 分析评价莱州市海水入侵的时空分布特征及变化趋势, 初步探讨形成原因, 为后续的研究、海水入侵的治理和资源开发利用提供理论依据。
1 数据采样与分析方法
1.1 数据采样和监测项目
利用现有农业用水井, 在朱旺村和海庙一带区域分别布设2条监测断面, 监测断面垂直于海岸线方向布设, 两断面间距8.05 km。朱旺断面布设监测站位3个, 海庙断面布设监测站位4个, 站位布设原则上涵盖海水入侵区、过渡带和未入侵区。站位坐标见表1, 站位分布图见图1。
海水入侵采样选在每年4月枯水期进行, 受降水量少的影响, 此时的海水入侵程度是一年中较为严重的时期。为避开潮汐影响, 采样时间固定为上午10时至12时期间(非高低潮时刻)。监测项目主要包括水位观测、矿化度、氯度, 分析方法分别为测绳测量、重量法和硝酸银滴定法。

表1 监测站位坐标及离岸距离
1.2 数据分析和等级划分标准
离岸距离与地下水氯度关系使用Matlab中的CFtool曲线拟合工具箱, 海水入侵距离与降水量相关性分析使用SPSS24.0软件。
依据《海水入侵监测与评价技术规程(试行)》(以下简称《规程》), 海水入侵程度等级划分标准见表2。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 地下水氯度变化
地下水氯度变化分析结果(图2)表明: 空间上, 2个监测断面均存在不同程度的海水入侵现象, 氯度随离岸距离的增大而迅速减少。2011—2016年海庙断面氯度变化大于朱旺断面, 监测到的氯度最高值位于海庙断面的Ⅱ-1站位, 2013年该站位的氯度为10 821.64 mg/L, 超标(海水入侵指标氯度等于250 mg/L) 43倍。
时间上, 研究区域2013年地下水氯度最高, 2011—2016年地下水氯度呈现波动变化。

图1 莱州市海水入侵监测站位分布图

表2 海水入侵程度等级划分标准[10]
2.2 海水入侵距离变化
为得到研究区域离岸距离与氯度的关系, 分别使用幂、指数、逆、线性函数对2011—2016年的监测数据进行拟合, 结果表明: 研究区域离岸距离与氯度呈反比关系且服从幂函数分布。受文章篇幅限制, 文中以海庙断面2013年的数据为例, 展示几种函数模型的拟合情况(图3)。2011—2016年, 两个监测断面离岸距离与氯度的关系均以幂函数拟合效果最好, 而传统的线性插值拟合效果较差。离岸距离用()表示, 氯度用表示, 拟合公式见表3。
选取幂函数对监测数据进行拟合, 依据《规程》中海水入侵程度等级划分标准, 得到研究区域2011—2016年海水入侵距离汇总于表4, 统计量汇总于表5, 海水入侵距离随时间变化曲线见图4。

图2 研究区域地下水氯度变化趋势

图3 2013年4月海庙断面不同函数模型的拟合曲线
朱旺断面海水入侵距离最大值发生在2015年, 平均入侵距离为2 061 m, 海庙断面海水入侵距离最大值发生在2014年, 平均入侵距离为5 160 m, 海庙断面海水入侵程度较朱旺断面严重。2011—2016年, 海庙断面海水入侵距离变化较大且入侵和严重入侵间距较大, 朱旺断面则较为稳定。
图4中, 海庙断面2014年和2015年海水入侵距离和严重入侵距离呈现负相关, 这是由于2011—2016年, 离岸最远的监测站位的氯度只有在2014年和2015年均超过了250 mg/L, 相应年份的海水入侵距离变大, 且这两年各监测站位处的氯度比较接近, 拟合曲线较陡, 相应的入侵和严重入侵间距增大。

表3 不同函数模型拟合公式及统计量对比

表4 研究区域2011—2016年海水入侵距离

表5 海水入侵距离计算统计量汇总

图4 研究区域海水入侵距离变化趋势
2.3 海水入侵速率变化
研究区域2012—2016年海水入侵速率汇总于表6。依据《规程》, 海水入侵距离变化在50 m以内, 认为海水入侵趋势稳定。总体上, 朱旺断面海水入侵程度较轻, 且趋势比较稳定。研究区域2014年海水入侵速度最快, 之后呈减轻趋势。
2.4 海水入侵距离与降水量关系
海水入侵的机理本质上是海岸带咸淡水界面在地下水位的变化下水动力平衡被破坏。导致海水入侵现象的主要原因有气候变化、海面上升和人为超采地下水等自然与人为因素[11-15]。降水作为地下水的主要补给来源, 对地下水位的变化起着决定作用, 持续的干旱气候, 造成地下水位下降, 从而会引发海水入侵的发生和发展[16-17]。为了探讨海水入侵距离与降水量的关系, 本文搜集了研究区域2012—2015年各年3月的平均月降水量数据, 分别与两个断面的海水入侵距离作相关性分析, 结果如图5和表7所示。海水入侵距离与降水量呈现明显的负相关关系, 相关系数分别为朱旺断面–0.972(<0.05), 海庙断面–0.969 (<0.05)。分析结果表明: 研究区域2014年降水量急剧减少, 是当年海水入侵严重的主要因素之一。
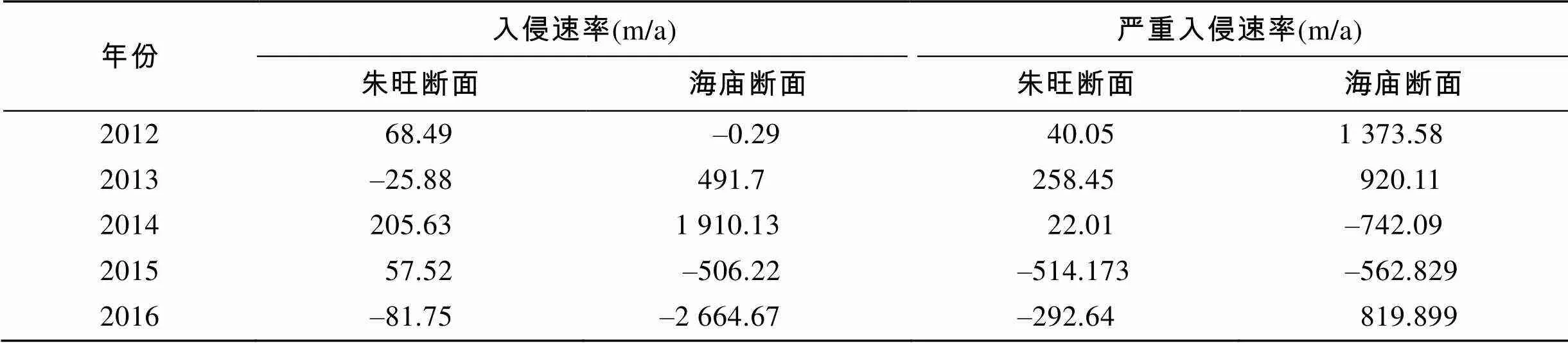
表6 研究区域2012—2016年海水入侵速率

图5 研究区域海水入侵距离与降水量变化趋势
3 结论
1) 2011—2016年, 研究区域均存在不同程度的海水入侵现象。整体上海庙断面地下水氯度要高于朱旺断面, 2013年地下水氯度最高, 2011—2016年间呈现波动变化。
2) 研究区域离岸距离与地下水氯度服从幂函数分布。朱旺断面和海庙断面海水入侵距离最大值分别发生在2015年和2014年, 海庙断面海水入侵距离远大于朱旺断面且变化较大, 朱旺断面海水入侵趋势较为稳定; 研究区域2014年海水入侵速度最快, 之后呈减轻趋势。
3) 研究区域海水入侵距离与降水量呈现明显的负相关关系, 2014年降水量的急剧减少, 是当年海水入侵严重的主要因素之一。
[1] 陈广泉. 莱州湾地区海水入侵的影响机制及预警评价研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2013. Chen Guangquan.Mechanisms underlying of seawater intrusion and evaluation of early warning systems in the Laizhou Bay area[D].Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2013.
[2] 张怡辉, 王玉广, 魏庆菲, 等. 地下水位变化在分析海水入侵中的应用[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2015, 34(5): 788-791. Zhang Yihui, Wang Yuguang, Wei Qingfei, et al. Application of the change groundwater level in analysing seawater intrusion[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2015, 34(5): 788-791.
[3] Barlow P M, Reichard E G. Saltwater intrusion in coastal regions of North America[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2010, 18: 247-260.
[4] 庄振业, 刘冬雁, 杨鸣, 等. 莱州湾沿岸平原海水入侵灾害的发展进程[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 1999, 29(1): 141-147. Zhuang Zhenye, Liu Dongyan, Yang Ming, et al. The role of anthropogenic activities in the evolution of saline water Intrusion processes[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 1999, 29(1): 141-147.
[5] 丰爱平, 谷东起, 夏东兴, 等.莱州湾南岸海水入侵发展动态和原因[J]. 海岸工程, 2006, 25: 7-13. Feng Aiping, Gu Dongqi, Xia Dongxing, et al. Developments and causes of seawater intrusion in the south coast area of the Laizhou Bay[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2006, 25: 7-13.
[6] 衣华鹏, 张鹏宴 , 毕继胜, 等. 莱州湾东岸海水入侵对生态环境的影响[J]. 海洋科学, 2010, 34(1): 29- 34. Yi Huapeng, Zhang Pengyan, Bi Jisheng, et al. The influence of seawater intrusion on ecological environment in the eastern coast of Laizhou Bay[J]. Marine Sciences, 2010, 34(1): 29-34.
[7] 刘典鹏, 季曙光, 周小丽. 莱州市海水入侵的防治措施及效果分析[J]. 山东水利, 2011, 1: 34-35. Liu Dianpeng, Ji Shuguang, Zhou Xiaoli. Prevention and effect analysis of seawater intrusion in Laizhou[J]. Shandong Water Resources, 2011, 1: 34-35.
[8] 程舜, 戴文涛, 罗伟华. 莱州市海水入侵治理实践与经验[J] . 山东水利, 2016, 3: 32-33. Cheng Shun, Dai Wentao, Luo Weihua. Governance practice and experience of seawater intrusion in Laizhou[J]. Shandong Water Resources, 2016, 3: 32-33.
[9] 苗青, 陈广泉, 刘文全, 等. 莱州湾地区海水入侵灾害演化过程及成因[J].海岸工程, 2013, 32(2): 69-78. Miao Qing, Chen Guangquan, Liu Wenquan, et al. Disaster evolution and genesis of seawater intrusion in the Laizhou Bay[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2013, 32(2): 69-78.
[10] 王玉广, 张永华, 胡莹莹, 等. 海水入侵监测与评价技术规程(试行)[R]. 大连: 国家海洋环境监测中心, 2014. Wang Y G, Zhang Y H, Hu Y Y, et al. Technical regulation of seawater intrusion monitoring and evaluation (try out)[R]. Dalian: National Marine Environmental Monitoring Center, 2014.
[11] Kopsiaftis G, Tigkas D, Christelis V, et al. Assessment of drought impacts on semi-arid coastal aquifers of the Mediterranean[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 2017, 137: 7-15.
[12] Ketabchi H, Mahmoodzadeh D, Ashtiani B A, et al. Sea-level rise impacts on seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: Review and integration[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 535: 235-255.
[13] Zeng X K, Wu J C, Wang D, et al. Assessing the pollution risk of a groundwater source field at western Laizhou Bay under seawater intrusion[J]. Environmental Research, 2016, 148: 586-594.
[14] 杜国云. 莱州湾东岸动力地貌对陆海相互作用的响应研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2016, 40(8): 70-75. Du G Y. Dynamic geomorphological response to land– sea interaction on the eastern coast, Laizhou Bay[J]. Marine Sciences, 2016, 40(8): 70-75.
[15] 黄洪城, 匡翠萍, 顾杰, 等.河口咸潮入侵研究进展[J]. 海洋科学, 2014, 38(9): 109-115. Huang Hongcheng, Kuang Cuiping, Gu Jie, et al.Research development in estuarine saltwater intrusion[J]. Marine Sciences, 2014, 38(9): 109-115.
[16] Giambastiani B M S, Colombani N, Mastocicco M, et al. Characterization of the lowland coastal aquifer of Comacchio (Ferrara, Italy): Hydrology, hydrochemistry and evolution of the system[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2013, 501(25): 35-44.
[17] 苗青. 降雨与潮汐作用对莱州湾地区海水入侵的影响机制研究[D]. 青岛: 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所, 2013. Miao Qing. Effects of precipitation and tide on seawater intrusion in the Laizhou Bay[D]. Qingdao: The First Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, 2013.
(本文编辑: 刘珊珊)
Development trend analysis of seawater intrusion in Laizhou from 2011 to 2016
ZHAO Jing-li1, DENG Yue2, XU Yan-dong1, YU Long3
(1. Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Restoration for Marine Ecology, Shandong Marine Resource and Environment Research Institute, Yantai 264006, China; 2. Department of Ocean Biology, Shandong University, Weihai, Weihai 264209, China; 3. Monitoring and Forecasting Center of Ocean Environment of Yantai, Yantai 264003, China)
Monitoring data of two seawater intrusion sections in Laizhou from 2011 to 2016 were used to analyze the development of groundwater chlorinity, seawater intrusion distance, and velocity and determine the relationship between seawater intrusion distance and precipitation. The results indicated that groundwater chlorinity reached the highest level in 2013 and fluctuated from 2011 to 2016, and the relationship between chlorinity and offshore distance followed the power function. The seawater intrusion distance of Haimiao section changed greatly and was much larger than that of Zhuwang section. The seawater intrusion trend was more stable in Zhuwang section. The seawater intrusion rate was the fastest in 2014 and then decreased. The seawater intrusion distance showed a negative correlation with precipitation. The sharp decline in precipitation might be one of the important reasons for the severe seawater intrusion in 2014. This result can be used as a reference for disaster prevention and reduction management in Laizhou.
seawater intrusion; groundwater chlorinity; seawater intrusion distance; precipitation; Laizhou
Dec. 28, 2016
赵景丽(1983-), 女, 河北唐山人, 助理研究员, 硕士, 主要从事海洋环境灾害研究, 电话: 0535-6958167-8704, E-mail: jingli_805@163.com
P641.7
A
1000-3096(2017)09-0136-07
10.11759/hykx20161228001
2016-12-28;
2017-04-25
海洋公益性行业科研专项(201205025); 国家海洋局海域管理技术重点实验室开放基金(201608); 水生动物营养与饲料“泰山学者”岗位基金(HYK201004)
[National Marine Public Welfare Research Project of China, No. 201205025; Key Laboratory of Sea-Area Management Technology, State Oceanic Administration, No.201608; Taishan Scholars Station of Aquatic Animal Nutrition and Feed, No. HYK201004]
