基于元胞自动机的海洋溢油模型
2017-03-26满苗苗魏国忠
满苗苗, 柳 林, 2, 程 鹏, 魏国忠, 张 省
基于元胞自动机的海洋溢油模型
满苗苗1, 柳 林1, 2, 程 鹏1, 魏国忠3, 张 省3
(1. 山东科技大学 测绘科学与工程学院, 山东 青岛 266590; 2. 海岛(礁)测绘技术国家测绘地理信息局重点实验室, 山东 青岛 266590; 3. 山东省国土测绘院, 山东 济南 250102)
本文采用三维元胞自动机模型, 对海洋溢油过程进行了模拟, 对风流、水流等水平方向的影响系数进行了改进。考虑了蒸发、垂直扩散、岸边附着、溶解、乳化等因子的影响, 并且引入乳化含水率将乳化因子进行实际量化, 构建了海洋溢油模型。并以“DeepSpill”的溢油实验为基础进行了模拟, 实验结果Kappa系数达到0.902, 与实际相比具有较好的一致性。本文对海洋溢油事故进行预测模拟, 为提出合理有效的应急预案提供科学依据。
元胞自动机; 海洋溢油; 模拟
2001年西班牙“威望”号油轮断裂、2010年墨西哥湾石油钻井平台溢油事故[1-2], 对海洋生物、生态环境造成了巨大损失。利用元胞自动机对海洋溢油扩散进行模拟, 能够更直观、真实地显示溢油的动态变化。近年来, 元胞自动机在海洋溢油方面得到越来越多的关注。Karafyllidis[3]综合了风、流、蒸发等因素, 采用元胞自动机研究了海洋溢油的运动和迁移[3]。王璐等[4]考虑了流场和风场等因素, 采用二维元胞自动机进行了水体污染带的模拟扩散研究。沈敬伟等[5]将元胞自动机与并行计算相结合, 综合考虑了多种因素, 模拟了水体污染物扩散。李维乾等[6]结合3S技术将智能体引入元胞自动机模型, 进行了水污染模拟仿真。尽管有众多学者早已利用元胞自动机研究海上溢油, 但考虑的影响因素不够全面、影响系数比较复杂。因此, 本文综合考虑了风流、水流、蒸发、溶解、乳化、岸边附着等影响因子, 对风流、水流等影响系数进行了改进, 构建了海洋溢油模型。
1 元胞自动机影响因子设定
本文不仅考虑了风、流因子的作用, 还考虑了重力、浮力作用。另外综合了岸边附着、溶解、乳化等因子的影响。
1.1 风流因子
风、流是影响污染物扩散的最重要因素, 用影响系数表示风、流状态下不同邻域元胞对中心元胞的影响, 该系数的计算由两部分组成:

假设风速的方向为从西向东, 则只有邻域元胞(–1,,)对中心元胞(,,)产生影响, 此时在时风产生的影响系数F中引入(,,)和(–1,,)处风速的平均值, 并以该平均值与最大风速的比值作为风的影响系数, 如公式(2)所示:

S为在时在某方向上水流产生的影响系数,S修正为该方向上的水流速度与流域内最大流速的比值。如公式(3)所示:

1.2 扩散因子


1.3 蒸发


其中,Z为蒸发率, 其方程表述为:

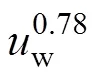
1.4 岸边附着


其中,为油浓度;为吸附常数,m为最大吸附量,为吸附指数。
1.5 溶解
溢油过程中有一部分会溶解于海水, 溶解于海水的溢油质量r的公式为:


1.6 溢油乳化

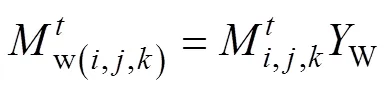
乳化含水率W(%)利用公式(10)计算:
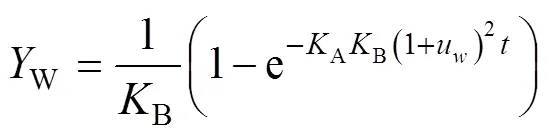

2 溢油模型的构建
元胞自动机(Cellular Automaton, CA)是定义在一个有限的、离散状态的元胞空间上并按照一定的局部转化规则, 在离散的时间维上演化的动力学系统[12]。它由4部分构成: 元胞、元胞空间、邻域和状态演化规则。用规则的几何图形将研究区域分为网格, 每一个网格就是一个元胞。所有的元胞按照一定规则排列组成的空间就是元胞空间。每个元胞都有自己的状态, 元胞的状态是它周围邻域中的其他元胞的状态共同作用决定的。邻域类型一般有冯.诺伊曼邻域[13](Von Neumann型)、摩尔(Moore)型、扩展摩尔型[14]三种, 如图1所示。状态演化规则是元胞自动机的核心, 是当前状态元胞进行下一时刻元胞状态转化的变换函数。



其中,是4个正方向的扩散系数;是4个斜角方向上的扩散系数, 且当=0.16、=0.084时可得到最佳模拟效果。
考虑风流对溢油的影响, 参照文献[6]可将公式(11)修正为:

因此, 通过对以上各因子进行分析, 综合考虑构建了海洋溢油模型, 其公式为:


图1 邻域类型图
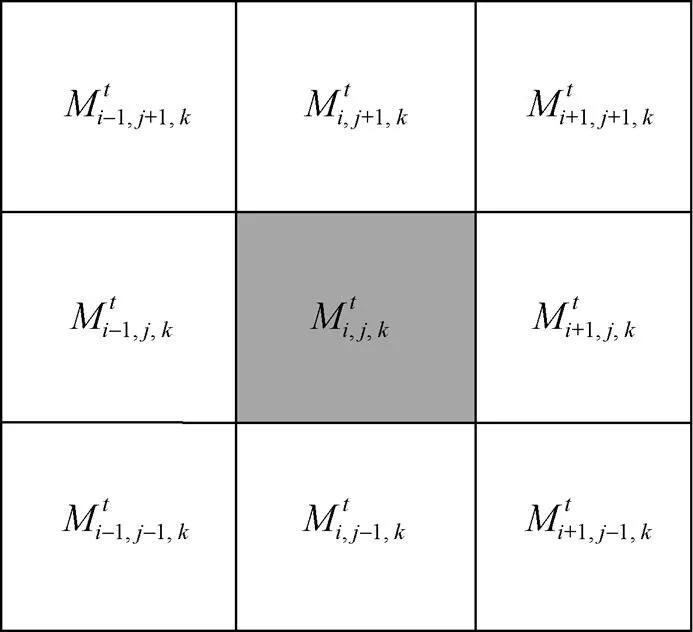
图2 质量传递图
3 元胞自动机扩散模拟
3.1 实验数据及参数选取

3.2 模拟结果
通过以上条件及演化规则得出模拟结果如图3, 并与初始图像、检验图像、对比图像进行对比, 其中对比图像为彭晓鹃等[15]的结果。从图4—图6可以看出溢油的方向相同, 吻合度较高。溢油范围向四周扩散, 整体朝东南方向扩散。与彭晓鹃等[15]实验中所得到的模拟结果进行了对比, 结果具有一定的改进(图7)。

图3 模拟结果
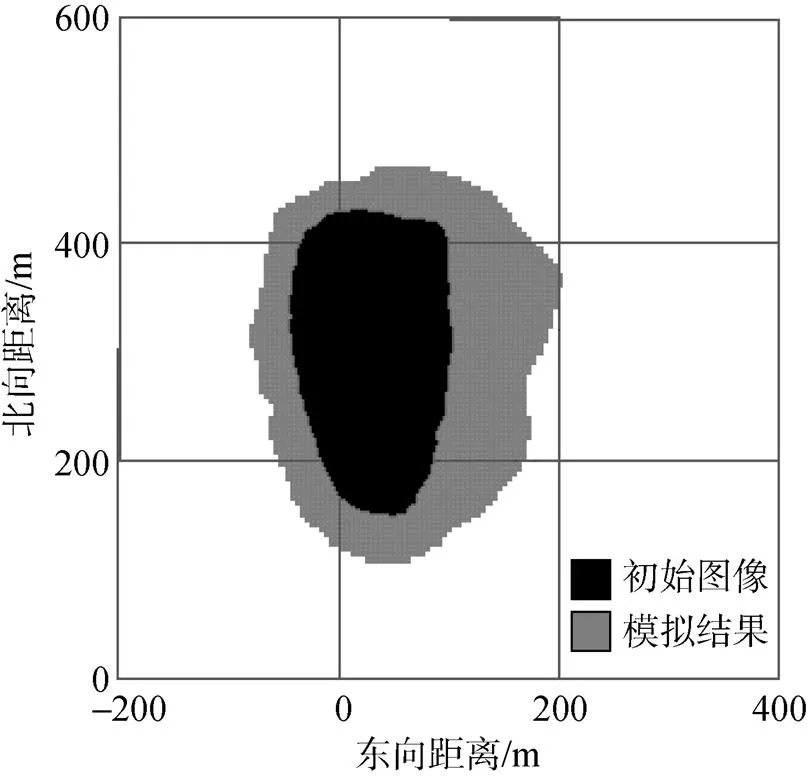
图4 初始图像与模拟结果
3.3 模拟结果检验
模型构建完成后需要进行检验, 本文通过混淆矩阵[17]计算了CA模型的模拟精度, 并通过Kappa系数a[18]定量地检验模型的模拟精度。

图5 模拟结果与及检验图像

图6 与检验、初始图像对比图

图7 与彭晓鹃实验结果对比图

表1 精度模拟及Kappa系数

Tab.1 Accuracy simulation and kappa coefficient
4 结语
该模型模拟溢油的扩散漂移, 不仅考虑了风、流等因素, 而且考虑了溢油消失过程, 综合了蒸发、乳化、溶解、岸边附着等溢油行为, 可以更加准确地模拟出溢油的时空变化过程。模拟了“Deepspill”海上溢油进行验证, 实验表明模拟结果的总精度、Kappa系数均较高, 因此认为该模型可以用来模拟海洋溢油的过程。
[1] Abascal A J, Castanedeo S, Mendez F J, et al. Calibration of a lagrangian transport model using drifting buoys deployed during the prestige oil spill[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2009, 25(1): 80-90.
[2] Mishra D R, Cho H J, Ghosh S, et al. Post-spill state of the marsh: Remote estimation of the ecological impact of the gulf of Mexico oil spill on Louisianan Salt Marshes[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2012, 118(6): 176-185.
[3] Karafyllidis I. A model for the prediction of oil slick movement and spreading using cellular automata[J]. Environment International, 1997, 23(6): 839-850.
[4] 王璐, 谢能刚, 李锐, 等. 基于元胞自动机的水体污染带扩散漂移仿真[J]. 水利学报, 2009, 4: 481-485. Wang Lu, Xie Nenggang, Li Rui, et al. Simulation of drift-diffusion of water pollution zone based on cellular automata[J]. Shuili Xuebao, 2009, 4: 481-485.
[5] 沈敬伟, 彭安琪, 周廷刚, 等. 基于并行元胞自动机的水体污染物扩散模拟[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2016, 1: 105-110. Shen Jingwei, Peng Anqi, Zhou Tingkang, et al.Water Pollutant Spreading Simulation Based on Parallel Cellular Automata[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2016, 1: 105-110.
[6] 李维乾, 解建仓, 李建勋, 等. 基于元胞自动机与智能体的水污染可视化模拟仿真[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 3: 213-220. Li Weiqian, Jiancang, LiJianxun, et al. Visualization simulation of water pollution based on Cellular Automata and intelligent agent[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University(Nat.Sci.Ed), 2013, 3: 213-220.
[7] 刘彦呈, 殷佩海, 林建国, 等. 基于GIS的海上溢油扩散和漂移的预测研究[J]. 大连海事大学学报, 2002, 3: 41-44. Liu Yancheng.Yiin Peihai, Lin Jianguo, et al. Prediction of oil spill spreading and transport over the sea[J]. Journal of DaLian Maritime University, 2002, 3: 41-44.
[8] 张存智, 窦振兴, 韩康, 等. 三维溢油动态预报模式[J]. 海洋环境科学, 1997, 1: 26-33. Zhang Cunzhi, Dou Zhengxing, Han Kang, et al. A Three Dimensional Model to Predict the Behavior of Oil Spills[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 1997, 1: 26-33.
[9] 李崇明, 赵文谦, 罗麟. 河流泥沙对石油的吸附、解吸规律及影响因素的研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 1997, 1: 25-28. Li Chongming, Zhao Wenqian, Luo Lin. Study on characteristics and effect factors of the absorption desorption of oil by sediment in rivers[J]. China Environmental Science, 1997, 1: 25-28.
[10] 庄学强, 陈坚, 孙倩. 海面溢油数值模拟及其可视化实现技术[J]. 中国航海, 2007, 1: 97-100. Zhuang Xueqiang, Chen Jian, Sun Qian. Numerical Simulation and Visualization Technology of Marine Spilled Oil[J]. Navigation of China, 2007, 1: 97-100.
[11] 过杰, 孟俊敏, 何宜军. 基于二维激光观测的溢油及其乳化过程散射模式研究进展[J]. 海洋科学, 2016, 2: 159-164. Guo Jie, Meng Junmin, He Yijun. Scattering model research based on two-dimensional laser observation of spilled oil and emulsification processes[J]. Marine Sciences, 2016, 2: 159-164.
[12] 周成虎, 欧阳, 马廷, 等. 地理系统模拟的CA模型理论探讨[J]. 地理科学进展, 2009, 6: 833-838. Zhou Chenghu, Ou Yang, Ma Ting, et al. Theoretical Perspectives of CA-based Geographical System Modeling[J]. Progress in Geography, 2009, 6: 833-838.
[13] 欧敏, 张永兴, 胡居义, 等. 基于Geo-CA和GIS的滑坡稳定性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2004, 4: 4-9. Ou Min, Zhang Yongxing, Hu Juyi, et al.The analysis of landslide stability based on Geo-CA and GIS [J].HONGGUO DIZHIZAIHAI YU FANGZHI XUEBAO, 2004, 4: 4-9.
[14] 罗平, 耿继进, 李满春, 等. 元胞自动机的地理过程模拟机制及扩展[J]. 地理科学, 2005, 6: 6724-6730. Luo Ping, Geng Jijin, Li Manchun, et al. M echan ism of Smi u lating Geographic Process and Extension of Cellular Automata[J].Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2005, 6: 6724-6730.
[15] 彭晓鹃, 张亦汉. 基于元胞自动机的海上溢油扩散模拟[J]. 海洋通报, 2015, 4: 415-422. Peng Xiaojuan, Zhang Yihan. Simulation of marine oil spill diffusion based on cellular automata[J].Marine Science Bulletin, 2015, 4: 415-422.
[16] 杨庆霄, 徐俊英, 李文森. 海上溢油溶解过程的研究[J].海洋学报(中文版), 1994, 3: 50-56. Yang Qingxiao, Xu Junying, Li Wenshen. Study of dissolution of marine oil spill[J]. Acta Qceanologica Sinica, 1994, 3: 50-56.
[17] 李宜展, 潘耀忠, 朱秀芳, 等. 土地覆盖类别面积混淆矩阵校正与回归遥感估算方法对比[J]. 农业工程学报, 2013, 11: 115-123. Li Yizhan, Pan Yaozhong, Zhu Xiufang, et al. Comparison analysis on land cover area estimators: confusion matrix calibration and regression[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2013, 11: 115-123.
[18] 全泉, 田光进, 沙默泉. 基于多智能体与元胞自动机的上海城市扩展动态模拟[J]. 生态学报, 2011, 10: 2875-2887. Quan Quan, Tian Guangjin, Sha Moquan.Dynamic simulation of Shanghai urban expansion based on multi-agent system and cellular automata model[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 10: 2875-2887.
(本文编辑: 李晓燕)
Marine oil spill model based on cellular automata
MAN Miao-miao1, LIU Lin1, 2, CHENG Peng1, WEI Guo-zhong3, ZHANG Sheng3
(1. Geomatics College, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China; 2. Key Laboratory of Surveying and Mapping Technology on Island and Reef, National Administration of Surveying, Mapping and Geoinformation, Qingdao 266590, China; 3. Shangdong Provincial Institate of Land Surveying and Mapping, Jinan 250102, China)
Based on the three-dimensional cellular automata model, this paper studies oil spill. The influence coefficients of the wind and flow in the horizontal direction are improved, in addition to considering the influence of evaporation and vertical diffusion in the vertical direction; the shore attachment, dissolution factor, and the emulsified water content parameters are ased in order to achieve a practical quantitative emulsifying factor. Based on the experiment “DeepSpill”, the simulation precision is considerably improved.
cellular automata; marine oil spill; simulation
Apr. 13, 2017
满苗苗(1992-), 女, 山东济宁人, 在读硕士研究生, 研究方向: 地理信息处理及应用, 电话: 13206427649, E-mail: 1509443062@qq.com; 柳林,通信作者, 副教授, 主要从事LBS、海洋GIS、智慧城市、3S集成等方面的研究, 电话: 0532-80681183, E-mail: liulin2009@126.com
X55
A
1000-3096(2017)09-0021-06
10.11759/hykx20170413003
2017-04-13;
2017-08-08
山东省自然科学基金(ZR2012FM015); 海岛(礁)测绘技术国家测绘地理信息局重点实验室资助项目(2013B08); 卫星测绘技术与应用国家测绘地理信息局重点实验室经费资助项目(KLAMTA-201407)
[Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, No.ZR2012FM015; the Key Laboratory of Surveying and Mapping Technology on Island and Reed, State Bureau of Surveying, Mapping and Geoinformation, No.2013B08; the Key Laboratory of Satellite Mapping Technology and Application, National Administration of Surveying, Mapping and Geoinformation , No. KLAMTA-201407]
