宽带变多通道窄带信号检测高速目标算法
2016-12-14史小斌顾红苏卫民
史小斌 顾红 苏卫民
(1.南京理工大学电子工程与光电技术学院,南京 210094;2.西安电子工程研究所,西安 710100)
宽带变多通道窄带信号检测高速目标算法
史小斌1,2顾红1苏卫民1
(1.南京理工大学电子工程与光电技术学院,南京 210094;2.西安电子工程研究所,西安 710100)
高速目标的宽带信号回波产生的目标距离走动会导致传统动目标检测相参积累信噪比损失较大. Keystone变换以及相关改进算法虽然能够校正目标距离走动,但该类算法需要预先估计目标较为精确的多普勒速度,难于应用到实际工程中. 文中采用一种宽带线性调频信号变多通道窄带信号处理方法,在没有目标速度先验知识的情况下,能够对高速目标回波信号能量进行有效积累,从而提高目标检测性能.给出了算法框图,经仿真验证该方法有效.
宽带线性调频雷达;高速运动目标;距离走动;动目标检测
DOI 10.13443/j.cjors.2015091501
引 言
随着现代军事的发展,低空飞行的巡航导弹、超高音速导弹、突防直升机已经成为地面战场侦察雷达面对的主要目标,该类型目标具有速度高、反射截面小的特点,因此对传统地面侦察雷达的信号检测能力提出了更高的要求. 增加相干处理时间[1-2]是提高雷达对微弱目标检测的一种手段.为解决该问题,Keystone变换方法[3]定义了一个虚拟的慢时间维采样时间,进而消除逐次目标回波频谱中使得波形平移的线性相位因子,然后利用相参积累来提高信噪比;但Keystone变换方法是假定目标匀速运动且速度不模糊,文献[4-9]提出在加速度影响可以忽略的情况下,在假定目标速度可能范围内对目标真实速度进行搜索,然后补偿目标多普勒的影响后进行相参积累检测,但搜索多普勒的误差会导致目标信噪比损失过大.文献[10]在具有加速度运动模型的基础上,对目标加速度、模糊多普勒频率和多普勒模糊度采用估计的方法进行补偿,积累效果好但算法较为复杂;文献[11-17]给出Radon-Fourier 变换检测高速目标的原理和性能比较,利用搜索目标多普勒的方法实现速度和距离的解耦,从而达到信号的相参检测,该方法同样较为复杂.
在宽带雷达探测高速目标时回波带宽扩展或压缩变化小于多普勒分辨单元的条件下,文中提出了宽带线性调频信号分割为多路窄带信号的处理算法,利用窄带处理降低了距离分辨力,使得运动目标在距离分辨单元间不产生走动,从而在不估计目标速度的情况下,对目标回波信号能量进行有效积累. 该算法使得宽带雷达可通过长时间积累的方法提高对高速运动小目标的检测能力,且计算量小,工程上易于实现.
1 回波信号模型
假设雷达发射线性调频信号[9]为
(1)


(2)
式中: A0为目标回波信号幅度; fd为目标多普勒频率; R(tm)=Ro-vtm为tm时刻雷达与目标间的距离,Ro是起始时刻目标与雷达之间的径向距离.

(3)
(4)

(5)
匹配滤波输出的频域信号SM(f,tm)为
(6)

(7)


2 宽带变多通道窄带信号算法

(8)


(9)


(10)
同理,将匹配参考信号通过滤波器组,可得到一组窄带信号. 经零中频处理后表示如下:
(11)

(12)
(13)

(14)


(15)
综上,宽带线性调频信号变多通道窄带信号处理算法流程如下:
1) 根据信号和目标参数,形成N路带通滤波器;
2) 宽带目标回波信号带通滤波形成N通道窄带回波信号;
3) 匹配参考信号和带通滤波器组卷积后也形成一组N通道窄带匹配参考信号;
4) 将2)、3)对应信号分别进行零中频处理,然后进行匹配滤波和MTD处理;
5) 对N路处理结果进行非相参积累.
具体算法原理框架如图1所示.
在完成超高速目标检测后,还可利用目标跟踪数据进行目标速度估计以补偿目标回波的相移,从而实现线性调频宽带信号的匹配处理和目标成像. 由于本文重点研究宽带线性调频信号分割为多通道窄带信号对超高速目标的检测算法,对目标检测后进一步的宽带成像处理可作为后续研究问题.

图1 算法实现原理框图
3 数据仿真验证与分析
为验证本文算法的有效性,建立如下仿真场景:某宽带地面雷达对超高速低空飞行目标进行实时监控.雷达工作参数如表1所示.
分析不同反射模型对算法的影响,仿真中设定了单个和多个强散射点高速目标,目标的输入信噪比为0.8 dB.目标参数如表2所示.

表1 雷达参数
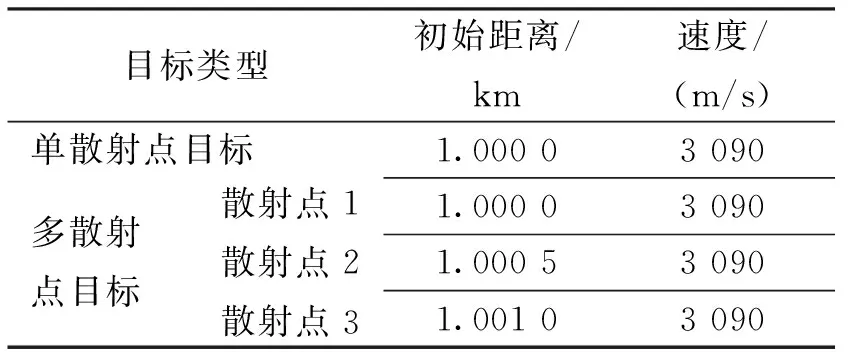
表2 目标参数
利用传统方法的单散射点目标信号处理结果如图2所示.可以看到,采用传统的相参积累处理方法不能对目标进行有效积累.
图3为本文算法的信号处理结果.选择数字带通滤波器数目为10,子窄带通道带宽为30MHz,对应距离分辨率为5 m,相干处理间隔(Coherent Process Interval,CPI)内目标的距离走动量为3.955 2 m,在每一子窄带内,目标距离走动可以忽略. 对比图2和图3可见,采用宽带变多通道窄带信号处理后,单目标回波信号能量得到了有效积累.

(a) 三维图

(b) 剖面图图2 宽带脉冲串经压缩-MTD处理结果

(a) 三维图

(b) 剖面图图3 单散射点宽带信号变多通道窄带信号处理结果

(a) 三维图

(b) 剖面图图4 多散射点宽带信号变多通道窄带信号处理结果
对于多散射点目标(3个散射点,各散射点距离相差并不超过1 m),由于各散射点间距离小于子窄带距离分辨力,因此目标逐次回波在进行脉冲压缩时以单散射点目标处理. 图4给出了多散射点宽带信号变多通道窄带信号处理结果. 图4(b)比图3(b)目标回波信号能量强,这是由于多个散射点目标能量部分累加的原因.
接下来,将本文算法与传统方法的检测性能进行比较.雷达参数如表1所示,分隔带通滤波器数目N为10,目标速度v为3 090 m/s,初始时刻目标与雷达的初始径向距离为1 km. 采用蒙特卡洛仿真的方法得到虚警概率和检测概率,绘制曲线如图5所示. 从图5中可看出,采用本文算法能够明显改善宽带雷达对高速运动目标的检测性能.

图5 两种处理方法的目标检测性能比较
4 结 论
本文提出了线性调频宽带信号变多通道窄带信号处理算法,通过将宽带信号变为多通道窄带信号,以降低雷达距离分辨力,从而使得在相参积累处理时高速目标距离走动不超出单个距离分辨单元,可提高雷达探测高速目标的能力.宽带雷达在利用本文算法实现超高速目标检测的基础上,还可利用目标跟踪信息实现距离维成像.
[1] MO L, WU S L, LI H. Radar detection of range migrated weak target through long-term integration[J]. Chinese journal of electronics, 2003, 12(4):539-544.
[2] 李道京, 尹建风, 吴一戎, 等.雷达成像与目标探测[J].现代雷达, 2006, 28(10): 5-8.
LI D J, YIN J F, WU Y R, et al. Rdar imaging and Target detection[J].Modern radar, 2006,28(10):5-8. (in Chinese)
[3] 保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M].北京:电子工业出版社,2005:35-39.
[4] 陈文驰, 刘飞. 一种低信噪比下的ISAR成像实现方法[J]. 电波科学学报, 2010, 25(3): 585-589.
CHEN W C, LIU F. An implementation method of ISAR imaging at the low SNR level[J]. Chinese journal of radio science, 2010, 25(3): 585-589.(in Chinese)
[5] 钱江, 孙光才, 李凉海, 等.一种多通道SAR地面快速目标高概率检测方法[J].电波科学学报, 2011, 26(2): 354-361.
QIAN J, SUN G C, LI L H, et al. Multi-channel SAR high speed target indication with improved detection probability[J]. Chinese journal of radio science, 2011, 26(2): 354-361. (in Chinese)
[6] 战立晓, 汤子跃, 朱振波. 高机动小RCS目标长时间相参积累检测新方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2013, 35(3): 511-516.
ZHAN L X, TANG Z Y, ZHU Z B. Novel method of Long term coherent integration detection for maneuvering small RCS targets[J]. Systems engineering and electronics, 2013, 35(3): 511-516.(in Chinese)
[7] 盛蔚, 毛士艺. 基于Keystone变换的地面运动目标检测研究[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2002, 11(24): 1-4.
SHENG W, MAO S Y. Ground moving target detection with an SAR system based on keystone transform[J]. Systems engineering and electronics, 2002, 11(24): 1-4. (in Chinese)
[8] 赵建宏, 杨建宇, 熊金涛, 等. 回波越距离单元走动的MTD研究[J]. 电波科学学报, 2007, 22(3): 481-485.
ZHAO J H, YANG J Y, XIONG J T, et al.Research on MTD with echoes migration through resolution cell[J]. Chinese journal of radio science, 2007, 22(3):481-485. (in Chinese)
[9] 蒋千, 孔令讲, 杨建宇. 一种径向匀加速目标包络徙动补偿新方法[J].雷达科学与技术, 2013, 11(1): 45-50.
JIANG Q, KONG L J, YANG J Y. A new method for envelope migration correction of target with radial acceleration[J]. Radar science and technology, 2013, 11(1): 45-50.(in Chinese)
[10] XING M D, SU J H, WANG G Y, et al. New parameter estimation and detection algorithm for high speed small target[J]. IEEE transactions on aerospace and electronic systems, 2009, 47(1): 214-224.
[11]吴兆平, 符渭波, 苏涛, 等. 基于快速Randon-Fourier变换的雷达高速目标检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 8(34): 1866-1871.
WU Z P, FU W B, SU T, et al. High speed radar target detection based on fast radon Fourier transform[J]. Journal of electronics & information technology, 2012, 8(34): 1866-1871. (in Chinese)
[12]JIA X, XIANG G X. Radar maneuvering target motion estimation based on generalized radon-Fourier transform[J]. IEEE transactions on signal processing, 2012, 12(60): 6190-6201.
[13]WEISS L G. Wavelets and wideband correlation processing[J]. IEEE signal processing magazine,1994, 11(1): 1053-5888.
[14]XU J, YU J, PENG Y N, et al. Radon-Fourier transform(RFT)for radar target detection(I): generalized Doppler filter bank processing[J]. IEEE transactions on aerospace and electronic systems, 2011, 47(2):1186-1202.
[15]XU J, YU J, PENG Y N, et al. Radon-Fourier transform(RFT) for radar target detection(II): Performance analysis and sidelobe suppression[J]. IEEE transactions on aerospace and electronic systems, 2011, 47(4): 2473-2489.
[16]XU J, YU J, PENG Y N, et al. Radon-Fourier transform(RFT)for radar target detection(Ⅲ): optimality and fast implementatios[J]. IEEE transactions on aerospace and electronic systems, 2012, 2(48): 991-1002.
[17]CHEN X L, GUAN J, LIU N B, et al. Maneuvering target detection via radon-fractional Fourier transform-based long-time coherent integration[J]. IEEE transactions on signal processing, 2014, 62(4): 939-953.
[18]YUAN S J, WU T, MAO M, et al. Application research of keystone transform in weak high-speed target detection in low-PRF narrowband Chirp radar[C]//9th International Conference on Signal processing. Beijing, October 26-29, 2008:2452-2456.

史小斌 (1977-),男,陕西人,西安电子研究所高级工程师,博士研究生,研究方向为地面雷达总体技术.

顾红 (1967-),男,江苏人,博士生导师,研究方向为新体制雷达、现代数字信号处理算法研究与实现.

苏卫民 (1959-),男,江苏人,博士生导师,研究方向为雷达成像理论、自适应阵列信号处理.
High speed targets detection algorithm based on multichannel narrow-band signal by wide-band signal decomposed
SHI Xiaobin1,2GU Hong1SU Weimin1
(1.NanjingUniversityofScienceandTechnologySchoolofElectronicandOpticalEngineering,Nanjing210094,China; 2.Xi’anElectronicEngineeringResearchInstitute,Xi’an710100,China)
The target range migration may decrease the performance of the conventional moving target detection(MTD) coherent integration, which means that the accumulation time is restrained by target motion. The Keystone transform can correct target range migration, but it need to accurately estimate the target velocity, which is difficult to satisfy. In this paper, an algorithm of the wide-band linear frequency modulation signal decomposed into narrow-band multichannel signal to detect high speed targets is present, which does not require prior knowledge of the speed of high-speed moving target and can improves the wideband radar performance of detection of high speed target. The simulation results demonstrate the availability of the proposed method.
wide-band LFM radar; high-speed moving target; rang migration; MTD
10.13443/j.cjors.2015091501
2015-09-15
国家自然科学基金(61471198); 中国航天科技集团公司航天科技创新基金(CASC04-02)
TN995+.2
A
1005-0388(2016)04-0647-07
史小斌, 顾红, 苏卫民. 宽带变多通道窄带信号检测高速目标算法[J]. 电波科学学报,2016,31(4):647-653.
SHI X B, GU H, SU W M. High speed targets detection algorithm based on multichannel narrow-band signal by wide-band signal decomposed[J]. Chinese journal of radio science,2016,31(4):647-653. (in Chinese). DOI: 10.13443/j.cjors.2015091501
联系人: 史小斌 E-mail: 57027236@qq.com
