ABCG2过表达对乳腺癌细胞上皮间质化能力的影响
2016-11-01王小毅倪贵生
聂 伟,王小毅,邱 干,蒋 勇,倪贵生
(1.武警重庆总队医院甲乳血管外科 400061;2.重庆医科大学附属第一院普外科 400016)
ABCG2过表达对乳腺癌细胞上皮间质化能力的影响
聂伟1,王小毅2△,邱干1,蒋勇1,倪贵生1
(1.武警重庆总队医院甲乳血管外科 400061;2.重庆医科大学附属第一院普外科 400016)
目的探讨三磷酸腺苷结合转运蛋白G超家族成员2(ABCG2)过表达对乳腺癌细胞上皮间质转化(EMT)能力的影响。方法构建ABCG2稳定过表达乳腺癌细胞株,检测ABCG2稳定过表达前后MCF-7乳腺癌细胞中E-cadherin蛋白和N-cadherin蛋白的表达情况。结果E-cadherin蛋白表达在ABCG2过表达MCF-7乳腺癌细胞中明显低于常规MCF-7细胞(P<0.05),而N-cadherin蛋白表达在ABCG2过表达MCF-7乳腺癌细胞中明显高于常规MCF-7细胞(P<0.05)。结论ABCG2过表达可以通过调控EMT相关蛋白的表达进而增强乳腺癌细胞的EMT能力,可能与乳腺癌的转移密切相关。
乳腺肿瘤;肿瘤转移;上皮间质化;三磷酸腺苷结合转运蛋白G超家族成员2
远处转移是乳腺癌终末期的主要表现,并且是导致乳腺癌患者死亡的主要原因[1-2]。虽然预防远处转移在乳腺癌治疗中的意义重大,但是乳腺癌远处转移的机制尚不明确。近期许多研究发现,肿瘤细胞上皮间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)在乳腺癌的转移过程中起重要作用[3]。三磷酸腺苷结合转运蛋白G超家族成员2(adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette superfamily G member 2,ABCG2)是被广泛证实与乳腺癌转移密切相关的细胞因子[4],并有实验指出ABCG2与EMT关系密切[5],所以假设ABCG2可以通过诱发EMT而诱发乳腺癌转移。本实验检测ABCG2过表达乳腺癌细胞中EMT相关蛋白的表达情况,进而探讨ABCG2与EMT的相关性及其是否可以通过诱发EMT而诱发乳腺癌转移。
1 材料与方法
1.1主要试剂和细胞慢病毒载体及相关试剂由上海生工提供。人乳腺癌细胞株MCF-7购自中科院上海细胞所。MCF-7用含10%胎牛血清的RPMI1640培养(PAA公司)。PCR相关试剂购自Takara公司;引物合成与测序(上海生工);ABCG2抗体、E-cadherin抗体和N-cadherin抗体(Santa Cruz公司);GAPDH(中杉金桥)。
1.2方法
1.2.1慢病毒载体构建包装根据GenBank中ABCG2(NC_0000014.12)的序列,设计引物KL-ABCG2-F:5′-GAG GAT CCC CGG GTA CCG GTC CCA CCA TGT CTT CCA GTA ATG TCG AAG-3′,KL-ABCG2-R:5′-TCA CCA TGG TGG CGA CCG GAG AAT ATT TTT TAA GAA ATA ACA-3′。慢病毒载体构建及包装由上海生工完成。
1.2.2细胞转染正常对数生长细胞于6孔板中培育。将慢病毒混合液按感染指数10∶1加入细胞培养液中培养6~8 h后用磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)冲洗,再加入培养基继续培养48 h,以免疫荧光显微镜观察转染效果。
1.2.3蛋白免疫印迹法(Western blot)检测收集试验细胞提取总蛋白。蛋白裂解液凝胶电泳后行PVDF转膜,用5% BSA封闭1 h加一抗(1∶1 000)孵育过夜,次日用二抗孵育后行ECL显色曝光。
1.2.4逆转录PCR(RT-PCR)检测PCR引物E-cadherin(141 bp):5′-AAA CCT TGC CTT CTT TGT C-3′,5′-TTC CCA ACT CCT CTC CTG-3′。β-actin(300 bp):5′-ACT GGT CTC AAG TCA GTG TAC AGG-3′,5′-ACA GGA AGT CCC TTG CCA TC-3′。N-cadherin(454 bp):5′-CAG AAA ACT AAT TCC AAT CTG AAA-3′,5′-GCC ACC ATA TGA CTC CCT CTT AGT-3′。收取细胞放入离心管,加入Tripure Reagent裂解细胞。裂解液倒入离心管,分次加入氯仿、异丙醇、无水乙醇和75%DEPC乙醇,剧烈振荡混匀后高速离心。倒掉上清液,取适量RNA样品进行PCR扩增(按PCR操作说明书进行)。然后进行凝胶电泳;电泳结束摄取电泳图。计算不同条带的灰度值,与内参灰度值进行对比,获得灰度比值。
2 结 果
2.1ABCG2过表达乳腺癌细胞株的鉴定慢病毒转染48 h后行免疫荧光观察,ABCG2过表达的MCF-7细胞呈绿色荧光(图1A、B)。ABCG2过表达MCF-7乳腺癌细胞株中ABCG2蛋白含量(0.821±0.061)明显高于常规MCF-7乳腺癌细胞中ABCG2蛋白含量(0.021±0.006,P<0.05)。见图1C。
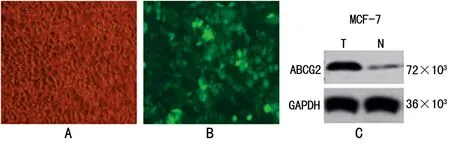
A、B:MCF-7细胞转染后的免疫荧光观察(A:可见光,B:荧光观察,×200);C:Western blot检测ABCG2蛋白表达。
图1ABCG2在MCF-7乳腺癌细胞中的表达
2.2ABCG2过表达和常规MCF-7乳腺癌细胞E-cadherin和N-cadherin mRNA表达情况构建ABCG2过表达的MCF-7乳腺癌细胞株后,以常规MCF-7乳腺癌细胞作为对照组。用RT-PCR检测不同组中E-cadherin和N-cadherin的mRNA表达情况。结果显示:ABCG2过表达的MCF-7乳腺癌细胞E-cadherin的mRNA表达(0.321±0.004)明显低于常规MCF-7乳腺癌细胞(0.814±0.009,P<0.05),见图2A;ABCG2过表达的MCF-7乳腺癌细胞N-cadherin的mRNA表达(1.007±0.089)明显高于常规MCF-7乳腺癌细胞(0.265±0.007,P<0.05),见图2B。
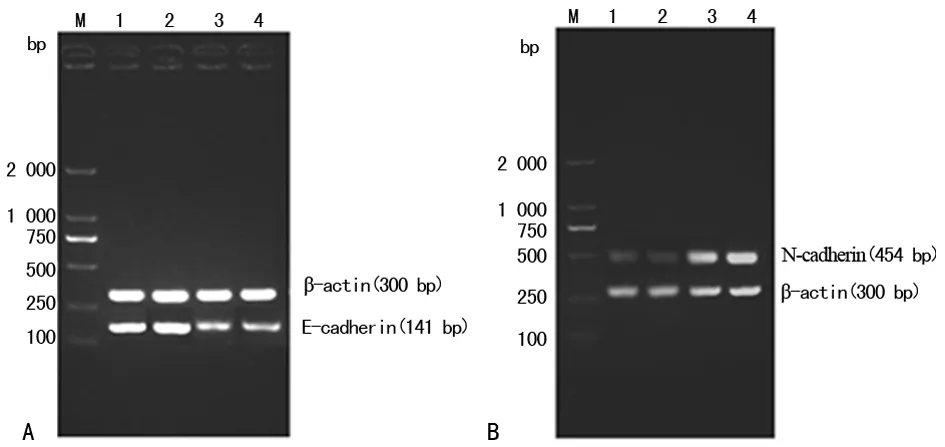
A:E-cadherin mRNA的检测;B:N-cadherin mRNA的检测;1和2为常规MCF-7乳腺癌细胞,3和4为转染后MCF-7乳腺癌细胞。
图2ABCG2过表达和常规MCF-7乳腺癌细胞中E-cadherin和N-cadherin mRNA表达情况
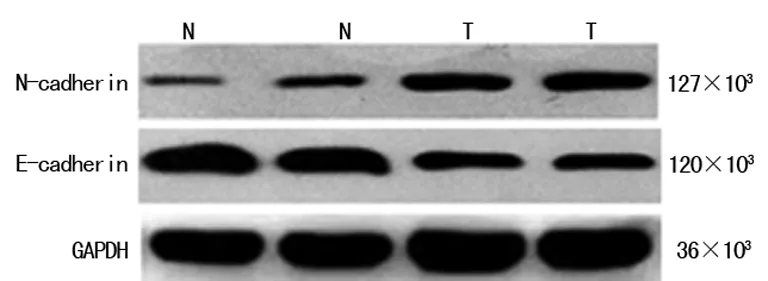
N:常规细胞,T:转染细胞。
图3ABCG2过表达前后E-cadherin和N-cadherin蛋白在MCF-7乳腺癌细胞中的表达情况
2.3ABCG2过表达和常规MCF-7乳腺癌细胞E-cadherin和N-cadherin蛋白表达情况构建ABCG2过表达的MCF-7乳腺癌细胞株后,以常规MCF-7乳腺癌细胞作为对照组。然后采用Western blot技术检测不同组中E-cadherin和N-cadherin的蛋白表达情况。结果显示:ABCG2过表达的MCF-7乳腺癌细胞N-cadherin的蛋白表达(0.356±0.007)明显高于常规MCF-7乳腺癌细胞(0.117±0.003,P<0.05),见图3;ABCG2过表达的MCF-7乳腺癌细胞E-cadherin的蛋白表达(0.311±0.007)明显低于常规MCF-7乳腺癌细胞(0.956±0.017,P<0.05),见图3。
3 讨 论
转移是恶性肿瘤主要的特征性临床表现之一,并且是导致肿瘤患者死亡的主要原因[6]。导致恶性肿瘤发生转移的机制尚不十分明确,但近期许多研究证实EMT在肿瘤转移过程中发挥着极其重要的作用[3]。ABCG2是于1998年发现的与乳腺癌耐药密切相关的跨膜转运蛋白[7]。近期许多研究证实ABCG2与乳腺癌肿瘤干细胞的关系密切,而肿瘤干细胞与EMT及肿瘤转移关系密切[8-9]。因此,推断ABCG2可能可以促进乳癌细胞发生EMT,进而促进肿瘤转移。EMT是多因子参与的复杂的分子生物学过程,其主要表现为上皮细胞发生间皮细胞样改变,参与EMT过程的因子主要包括上皮特异性因子和间质特异性因子[10-12]。E-cadherin是上皮细胞的一种主要功能蛋白,是最常见的上皮特异性因子之一,其作用主要是维持上皮细胞间的黏附能力;E-cadherin的缺失可以使细胞间的相互黏附能力下降,进而导致肿瘤细胞获得更强大的活动和侵袭能力,促进肿瘤的浸润和转移[13]。N-cadherin主要表达于间质细胞,是间质细胞的特征性蛋白之一;上皮细胞中出现N-cadherin的高表达证实上皮细胞已经获得了间质细胞的特性,获得了更强大的活动和侵袭能力,容易发生浸润和转移[14]。因此,本文选择E-cadherin和N-cadherin作为检测肿瘤细胞发生EMT的指标,拟探讨ABCG2蛋白是否可以通过促进EMT进而促进乳腺癌转移。
综上所述,通过慢病毒转染成功建立ABCG2过表达乳腺癌细胞,并且ABCG2过表达可以明显降低乳腺癌细胞中E-cadherin蛋白的表达(P<0.05),同时ABCG2过表达可以明显升高乳腺癌细胞中N-cadherin蛋白的表达(P<0.05)。证实ABCG2过表达可以促进乳腺癌细胞发生EMT,进而促进肿瘤转移,但具体机制尚不明确。许多研究证实ABCG2可以通过多种信号通路参与肿瘤转移,如Notch信号通路,Hedgehog信号通路,PI3K-AKT信号通路等[15-17],但其具体作用机制尚待进一步研究。
[1] Downs-Holmes C,Silverman P.Breast cancer:overview & updates[J].Nurse Pract,2011,36(12):20-26.
[2] Fan L,Strasser-Weippl K,Li JJ,et al.Breast cancer in China[J].Lancet Oncol,2014,15(7):e279-289.
[3] Burgess DJ.Breast cancer:Circulating and dynamic EMT[J].Nat Rev Cancer,2013,13(3):148.
[4] Xiang L,Su P,Xia SJ,et al.ABCG2 is associated with HER-2 Expression,lymph node metastasis and clinical stage in breast invasive ductal carcinoma[J].Diagnostic Pathology,2011,6(90):1-7.
[5]MatoE,GonzálezC,MoralA,etal.ABCG2/BCRP gene expression is related to epithelial-mesenchymal transition inducer genes in a papillary thyroid carcinoma cell line (TPC-1) [J].J Mol Endocrinol,2014,5252(3):289-300.
[6]Valastyan S,Weinberg RA.Tumor Metastasis:Molecular Insights and Evolving Paradigms[J].Cell,2011,147(2):275-292.
[7]Ni ZL,Bikadi Z,Rosenberg MF,et al.Structure and Function of the Human Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP/ABCG2)[J].Curr Drug Metab,2010,11(7):603-617.
[8] Ding XW,Wu JH,Jiang CP.ABCG2:a potential marker of stem cells and novel target in stem cell and cancer therapy[J].Life Sci,2010,86(17/18):631-637.
[9] Adrian B,Mackenzie IC.Cancer stem cells and EMT in carcinoma[J].Cancer Metastasis,2012,31(1-2):285-293.
[10] Voulgari A,Pintzas A.Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis:mechanisms,markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2009,1796(2):75-90.
[11] Kowalski PJ,Rubin MA,Kleer CG.E-cadherin expression in primary carcinomas of the breast and its distant metastases[J].Breast Cancer Res,2003(5):217-222.
[12]Nakajima S,Doi R,Toyoda E,et al.N-cadherin expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic carcinoma[J].Clin Cancer Res,2004,10(12 Pt 1):4125-4133.
[13] Med DR.Aydin F,Flügen G,et al.Epithelial-Mesenchymal-Transition (EMT):The role of E-cadherin transcription regulators SIP1,Twist and Snail in colorectal adenomas[J].Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2009,38(8):245-246.
[14]Rai H,Ahmed J.N-Cadherin:A Marker Of Epithelial To Mesenchymal Transition In Tumor Progression[J].Inter J Oncol,2014,10(1):55-61.
[15]Bhattacharya S,Das A,Mallya K,et al.Maintenance of retinal stem cells by Abcg2 is regulated by notch signaling[J].J Cell Sci,2007,120(15):2652-2662.
[16]Singh RR,Kunkalla K,Qu C,et al.ABCG2 is a direct transcriptional target of hedgehog signaling and involved in stroma-induced drug tolerance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J].Oncogene,2011,30(49):4874-4886.
[17] Goler-Baron V,Sladkevich I,Assaraf YG.Inhibition of the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway disrupts ABCG2-rich extracellular vesicles and overcomes multidrug resistance in breast cancer cells[J].Biochem Pharmacol,2012,83(10):1340-1348.
Influence of ABCG2 overexpression on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cell
Nei Wei1,Wang Xiaoyi2△,Qiu Gan1,Jiang Yong1,Ni Guisheng1
(1.DepartmentofThyroidMammaryandCardiovascularSurgery,ChongqingMunicipalCorpsHospital,Chongqing400061,China;2.DepartmentofGeneralSurgery,theFirstAffiliatedHospitalofChongqingMedicalUniversity,Chongqing400016,China)
ObjectiveTo observe the influence on EMT of breast cancer cell caused by ABCG2 overexpression and to approach the mechanism about how ABCG2 to affect metastasis of breast cancer.MethodsStable ABCG2 overexpression breast cancer cell line was constructed.Western-blot was used for detection of expression of E-cadherin and N-cadherin before and after transfection to approach the mechanism.ResultsExpression of E-cadherin in ABCG2 overexpression MCF-7 breast cancer cell was much lower than normal MCF-7 breast cancer cell (P<0.05).Expression of N-cadherin in ABCG2 overexpression MCF-7 breast cancer cell was much higher than normal MCF-7 breast cancer cell (P<0.05).ConclusionOverexpression of ABCG2 increases the expressions of EMT associated proteins of breast cancer cell so as to promote the EMT of breast cancer cell.ABCG2 might play an important role in promoting the metastasis of breast cancer.
breast neoplasms;neoplasm metastasis;EMT;ABCG2
聂伟(1968-),副主任医师,硕士,主要从事甲状腺乳腺和血管外科疾病的研究 。△
,E-mail:wxytsf@163.com。
论著·基础研究doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2016.26.007
R737.9
A
1671-8348(2016)26-3622-02
2016-02-12
2016-04-06)
