Mechanism of spatial emplacement of Shanhou gold ore body in Laixi of Shandong and its prospecting significance
2016-10-31LIUFengxuWANGLiWANGDunrongXUJinggeandCUIZhiyong
LIU Fengxu, WANG Li*, WANG Dunrong, XU Jingge and CUI Zhiyong
1. College of Earth Sciences, Jilin University, Changchun130061, China;2. Geological Bureau of Nuclear Industry, Jilin Province, Changchun 130062, China;3. Shandong Gold Mining (Lacey) Co., LTD, Laixi 266600, Shandong, China
10.3969/j.issn.1673-9736.2016.03.03
Mechanism of spatial emplacement of Shanhou gold ore body in Laixi of Shandong and its prospecting significance
LIU Fengxu1, WANG Li1*, WANG Dunrong2, XU Jingge3and CUI Zhiyong3
1.CollegeofEarthSciences,JilinUniversity,Changchun130061,China;2.GeologicalBureauofNuclearIndustry,JilinProvince,Changchun130062,China;3.ShandongGoldMining(Lacey)Co.,LTD,Laixi266600,Shandong,China
Through analysis of geological characteristics of the gold deposit, the shape, occurrence, and spatial distribution of ore-controlling fault plane in the Shanhou mining area were investigated, and the regularities of enrichment and emplacement of ore body were summarized. The analysis shows that the Shanhou gold deposit was controlled by NE-NNE Zhaoping fault zone; the fault gouge developed in fault zone provides a barrier to ore-bearing hydrothermal solution, and the industrial ore body is all distributed within 40 m of footwall of main fault plane. The industrial ore body is mainly enriched in the NE positions of fault where the deep dips changed to flat dips, and shows the obvious regularity of NE lateral trending with angle around 75°. The stress analysis of fault in mineralization epoch showed that the ore-controlling structure presented the characteristics of right-handed rotation inverse-fault activity in mineralization epoch, and the host space tended to occur in NE regional tension positions where the dips become flat in the strike of fault, causing emplacement of ore body. It is thought by combining equal interval distribution of deposit with spatial variation of industrial ore body and ore-controlling fault structure that the Shanhou gold deposit recurred in regularity and the non-ore interval occurred in the ore body. Meanwhile, it is predicted that the favorable target area of prospecting lies in the areas of deep main fault plane with NE strike (>30°) and the deep dips changing to flat dips in the Shanhou mining area, and the prospecting should be emphasized. The favorable deep mineralization prospect exists in middle Beibo mining area, where is the key area for future prospecting.
spatial emplacement;Shanhou deposit;Laixi; Shandong
0 Introduction
The Shanhou gold ore in Laixi, Shandong is located in Zhaoping gold deposit belt where the mineralization belt in the eastern margin of North China Craton is superimposed on the mineralization belt in Pacific Rim, and was found by the Seventh Branch of the Gold Force under the Chinese Armed Police Force with proven gold resource over 20 tons. Since 1986, the Seventh Branch, the Second Troop of the Gold Force under the Chinese Armed Police Force, and the College of Earth Sciences of Jilin University have carried out the basic research on geology in the Shanhou area, and prospecting through induced polarization measurement, remote sensing, analysis of primary halo, and gravity survey. In recent years, many researchers have carried out the study on mineralization geological settings, geochemical characteristics and genesis of deposit (Liu H Tetal., 2015; Liu Z Yetal., 2008), but the research on the mechanism of spatial emplacement of ore body, and the direct theoretical basis for prospecting, is always in blank field. In the paper, the research on spatial emplacement of gold ore body was conducted through analysis of structural characteristics of ore-controlling fault, occurrence, fault activities in enrichment mineralization epoch of industrial ore body, to provide predict for prospecting.
1 Geological settings of mineralization
The strata exposed in the Shanhou mining area are mainly the Mesoarchean Tangjiazhuang Group and the Lower Proterozoic Jingshan Group, which have relationship of fault contact (Liuetal., 2008).The rocks of the Mesoarchean Tangjiazhuang Group (Ar2t) include biotite amphibole plagioclase granulite, bio- tite plagioclase gneiss, amphibolites intercalated with magnetic two-pyroxene granulite, amphibole two-pyroxene granulite, amphibole two-pyroxene granulite, and magnet hypersthene granulite, which are classified as the amphibole granulite-amphibolites metamorphic rocks, and generally in strike NE50°--65°, and dip NW with angles 40°--78°. The rocks of the Lower Proterozoic Jingshan Group (Pt1j) includes biotite schist, biotite leptynite and thin layer marble, with the metamorphic facies transited from low amphibolite facies to amphibole granulite facies, and generally strike NE50°--65°, and dip SE with angle of 40°--75°. The thickness of marble in the area is generally between 20--110 m, and the thickness of gneiss is between several meters and dozens of meters, which occur with interbedding. The rocks suffered from migmatization widely. Around the mining area, Quaternary residual deposit, slope deposit, alluvial deposit, and diluvium are exposed with small area in two sides of riverbed in Qingshan River.
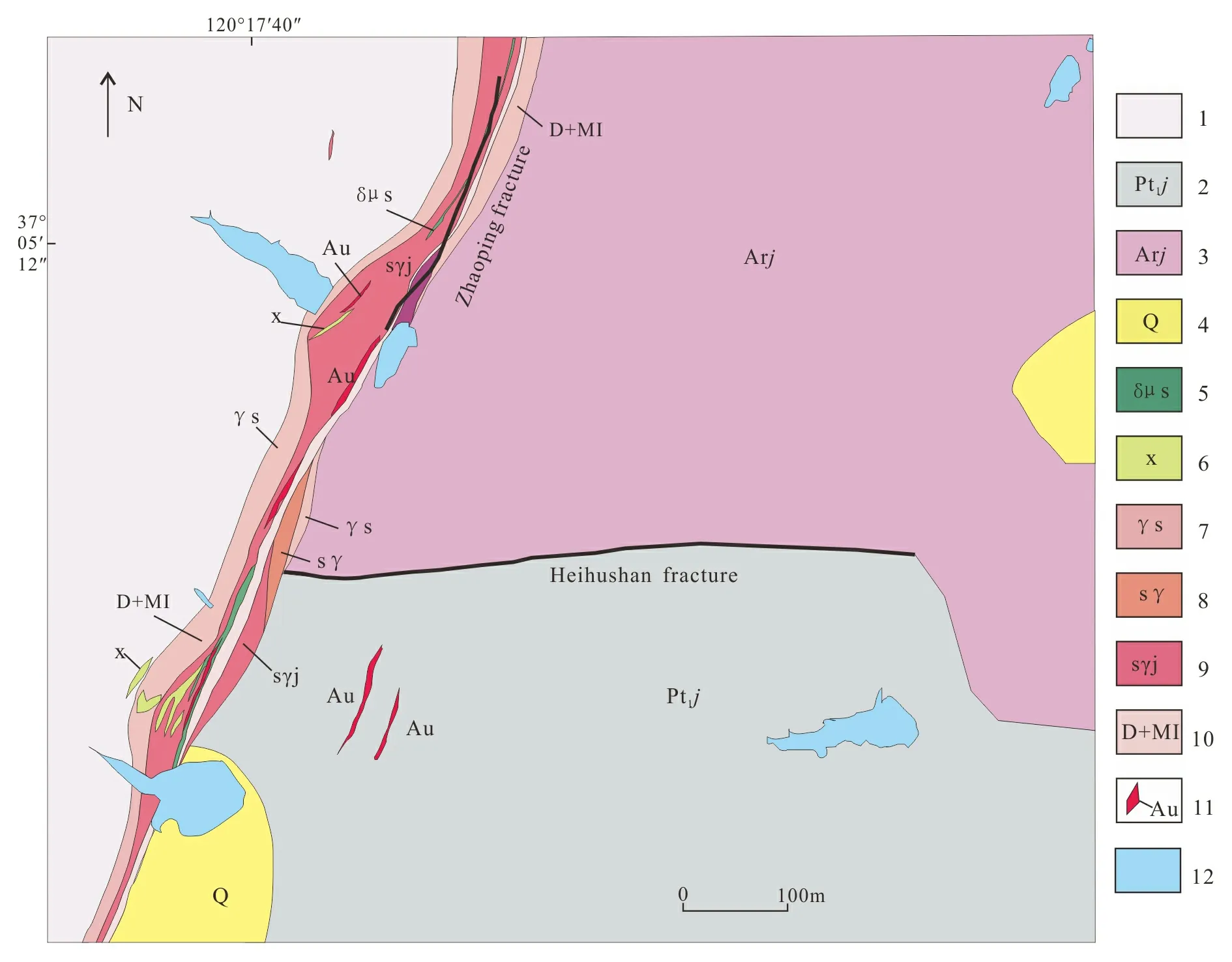
1. Mesozoic granite; 2. Paleoprterozoic Jingshan Group; 3. Neoarchean Jiaodong Group; 4. Quaternary; 5. diorite porphyrite; 6. lamprophyre; 7. cataclastic granite; 8. garanitic cataclstic rock; 9. sericite-quartz granitic cataclstic rock; 10. fault gouge and mylonite; 11.gold orebody; 12. reservoir.Fig.1 Detail geological map of Shanhou gold deposit mining area (after Wang, 2015)
The NE Zhaoping fault and EW Heifushan fault developed in the mining area. The Zhaoping main fault plane extends in the shape of slow wave, and generally strikes 30°, dips SE with angle of 26°--48°, averaging 40°, and grazes of oblique thrust, step, and extruded lenticle developed. Heihushan fault has strike of 90°, north dip with angle of 70°. The low sequence small-scale faults and EW drape developed in two sides of fault, and the tectonic lines are consistent with strike of Heihushan fault.
The magmatic rocks inside mining area are mainly granite and a small part of vein rock. The mesograin monzonitic granite is mainly distributed in the western and northwestern parts of mining area, and belongs to Cuizhao unit of Linglong super unit and occurs as batholith. The lamprophyre veins are dispersed in the mining area and parallel with Zhaoping fault zone with some EW-trending veins cutting the Zhaoping fault zone. Diorite-porphyrite veins are well developed in the mining area, in strike NNE or NW, and dip SE or NE with angle 65°--70°, long 100--1 100 m by wide 1--7 m.
2 Geological characteristics of deposit
2.1Characteristics of ore body
There are 16 industrial ore bodies delineated in the Shanhou gold deposit, including one main ore body No.Ⅰ--2 whose resource reserve accounts for 65.5% of the whole deposit, and one minor ore deposit No.Ⅰ--3. Ore bodies occur simply in vein-like, lenticular, and tabular shape (Table 1). With stable occurrence, ore bodies strike 23°--43°, dip SE with angle 26°--48°. The gold deposit has ore reserves ~1.64×106t, amount of metals 7 584 kg, and aver-age gold grade 4.62×10-6.
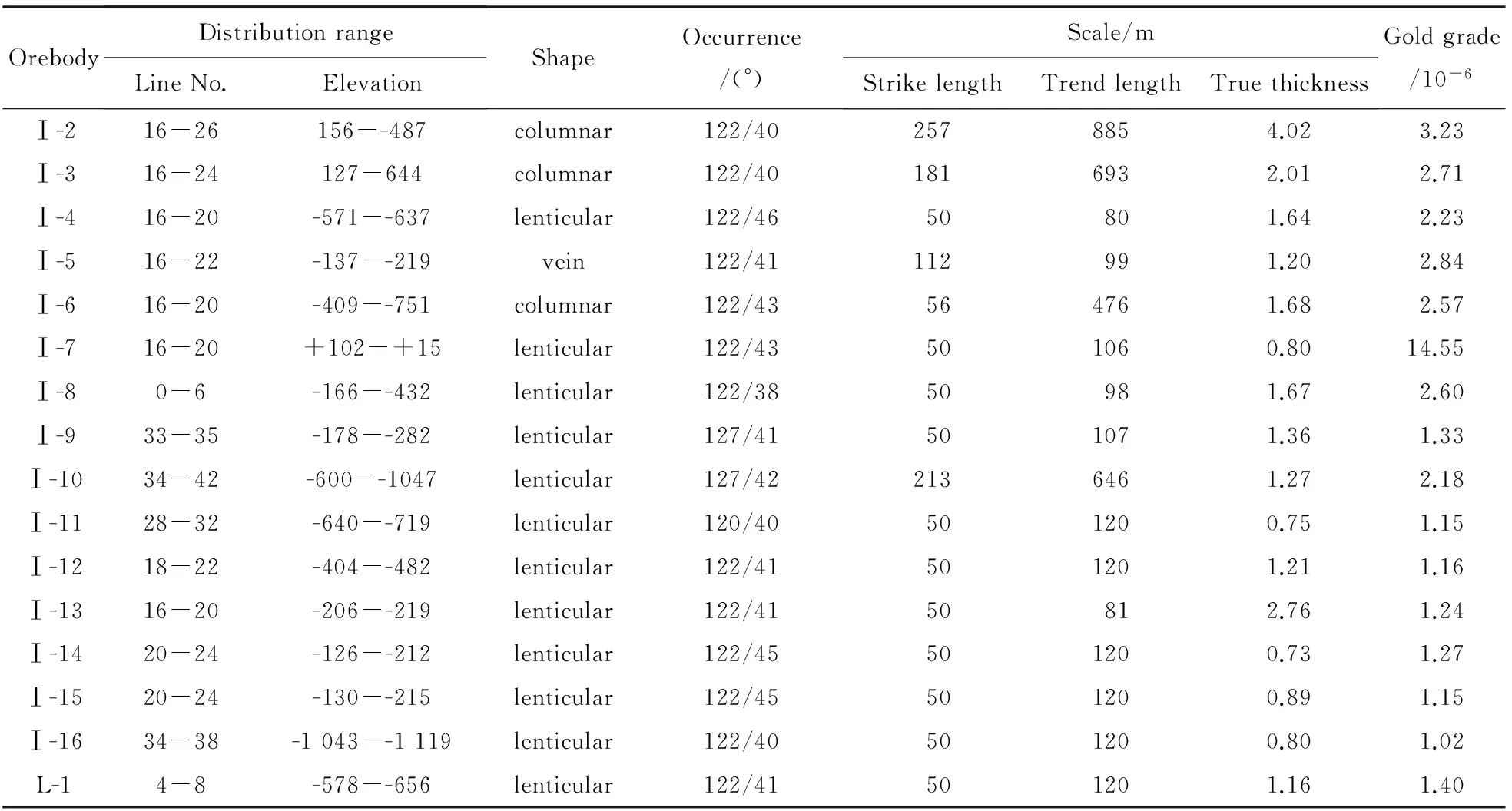
Table 1 Spatial features of orebodies in the studied area
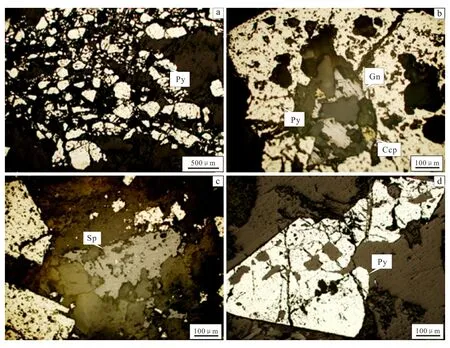
Fig.2 Microscopic characteristics of ore in Shanhou gold deposit
2.2Characteristics of ore
Ores in the Shanhou gold mining area are dominated by pyrite, chalcopyrite, sphalerite, galena, and native gold (Fig.2). The ore textures are dominated by crystalline grain(Fig.2a), metasomatic relict texture(Fig.2b), exsolution texture(Fig.2c), skeleton crystal (Fig.2d), etc. The ore structures are dominated by vein structure, mesh-vein structure, veinlet disseminated structure, and honeycomb structure.
2.3Characteristics of wall rock alteration
The wall rock alteration is developed in the Shanhou gold mining area, and distributed in the side of contact zone near granite. The sequence of alteration is divided into potassic alteration in early stage of mineralization, beresitization and silicification in the middle stage of mineralization, and choritization and carbonatization in the later stage of mineralization.
3 Analysis of mechanism of spatial emplacement of industrial ore bodies
The research on mechanism of spatial emplacement of industrial ore body includes the structural activities, evolution, and mineralization. Moreover, the correct mechanism of spatial emplacement of industrial ore bodies provides the theoretical basis for prediction of mineralization, and guidance to prospecting and exploration.
The spatial emplacement of ore bodies in the Shanhou gold deposit was controlled by fault structure.The fault structure plays important role during formation of gold deposit, and results in regularity of shape, scale, and occurrence of ore bodies. Through analysis of spatial distribution of orebodies and summary of mineralization enrichment belts and variation of fault plane, the mechanism of spatial emplacement of orebodies is determined.
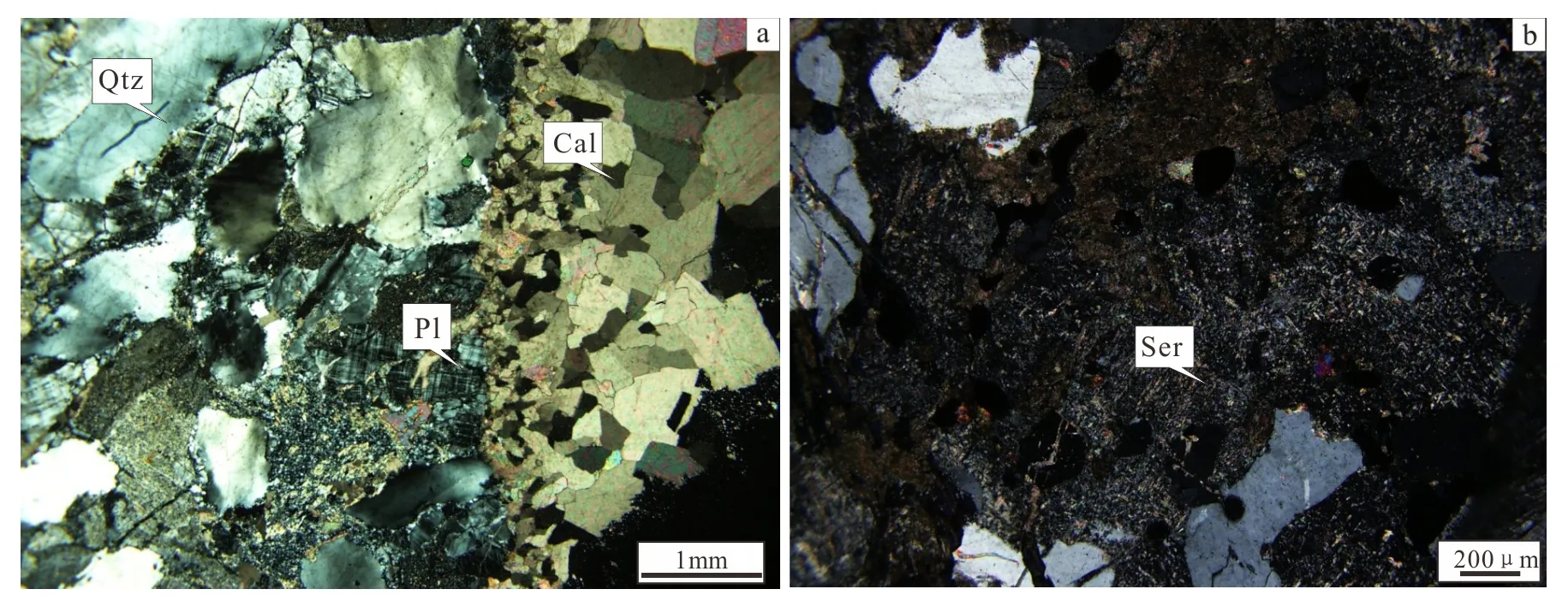
Fig.3 Microscopic characteristics of wall rock alteration in Shanhou gold deposit
3.1Fault gouge as a barrier for ore-bearing hydrothermal solution before mineralization
The ore deposit is controlled by the Zhaoping fault belt, and Shanhou gold deposit occured in the footwall of Zhaoping main fault plane.The fault gouge inside Zhaoping fault belt has successive and stable distribution, and shows characteristics of multi-period activities that some fault gouge is consolidated with tight texture, and some is loose with muddy texture(Fig.4). The fault gouge is mainly composed of clay minerals with tight texture and poor permeability, and the hydrothermal solution hardly flow through it. Therefore, the fault gouge acts as a barrier to ore-bearing hydrothermal solution. The crushed alteration belt in the footwall formed the place favorable to migration, circulation, and accumulation of ore-bearing hydrothermal solution, and the industrial ore bodies of Shanhou gold deposit are concentrated in the footwall of the Zhaoping main fault plane.

Fig.4 Photos of fault gouge in Zhaoping fault belt
3.2Relationship between ore bodies and strike of fault
Zhaoping fault generally strikes NE-NNE(between 19°--43°), and the main fault plane extends in the shape of slow wave and is subdivided to NNE- and NE- trending ones. During the research, the present middle section between 120 to -50 m of Shanhou gold deposit was logged systematically, and it was found that the industrial ore bodies are mainly distributed in 2#CM (transverse drift), 3#CM, and 4#CM, and the thickness of ore bodies in 1#CM, 5#CM, and 6#CM plummets, with weaker mineralization. During the logging, the occurrence of the Zhaoping main fault plane was measured systematically (Table 2), and it was shown by combining with analysis of geological map of the middle section that the ore bodies are mainly enriched in the NE-trending positions with strike >30° on the fault plane, with well developed and consecutive mineralization and ore bodies of big thickness and high grade (Fig.5).The mineralization is weak and discontinuous in the NNE-trending positions with strike <30°, where the industrial ore body is hardly developed, being a ore-free interval.
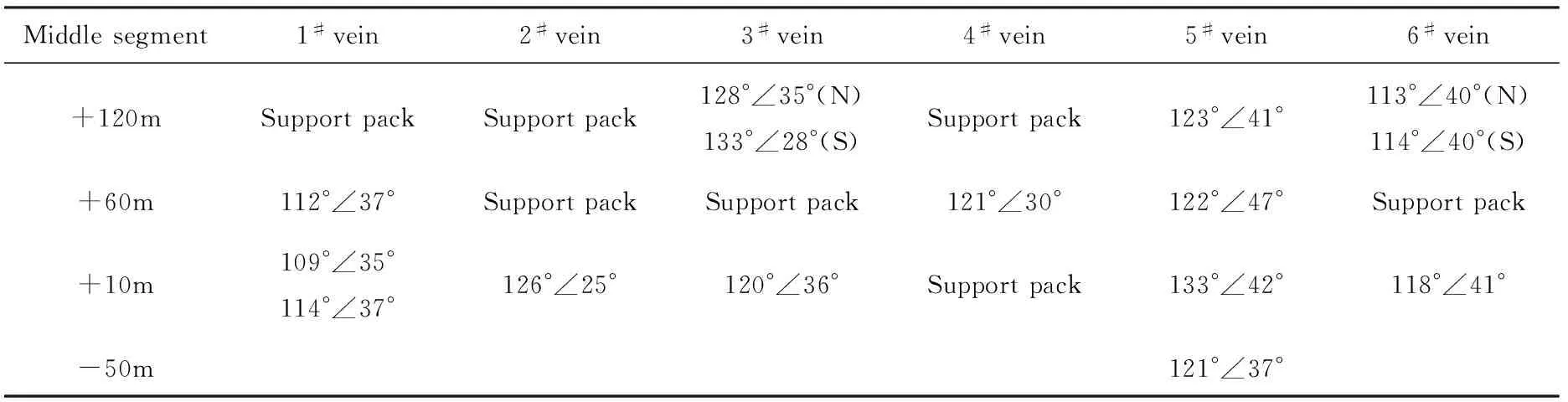
Table 2 Occurrences of main sections in all the middle segments
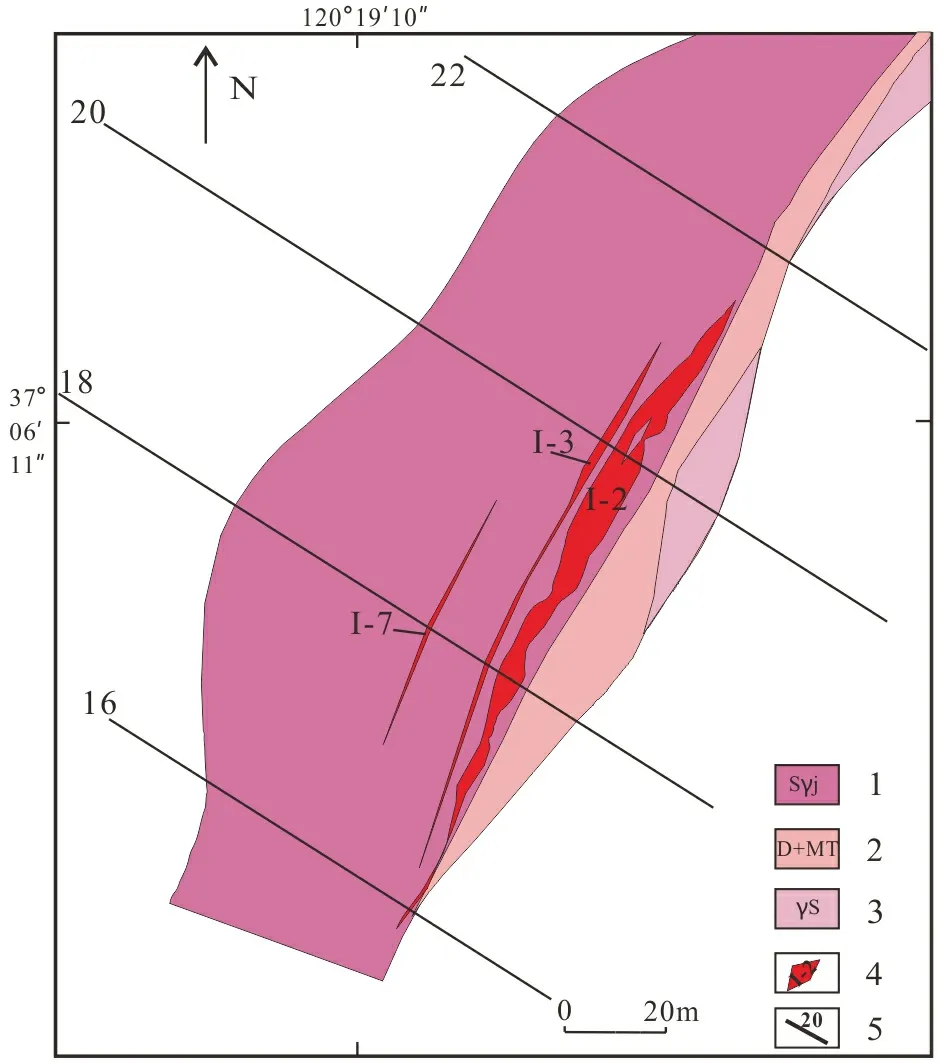
1.Phyllic granitic cataclasite; 2.gouge and mylonite; 3. cataclastic granite ; 4.orebody and number; 5.exploration line and number.Fig.5 Geological plane map for +60m middle segment of Shanhou gold deposit, Laixi, Shandong (after Wang, 2015)
3.3Relationship between ore bodies and dip angle of fault
The ore-controlling Zhaoping fault belt dip SE with angle 26°--48°. In the profile, the industrial ore bodies always occur in the positions with lower dip angle (<40°), forming large and thick industrial ore bodies (Fig.6).
3.4Dynamic characteristics of ore-controlling fault
The stress of ore-controlling structure in the mineralization epoch was analyzed based on occurrence of main fault plane and distribution of ore bodies of all transverse drifts in the middle section (Table 2), which are obtained based on the the plane map of the middle section, the profile of prospecting lines. Analysis shows that there is certain regularity of occurrence change of the fault plane and gold mineralization enrichment, i.e. ore bodies are enriched in NE-trending (>30°)locations along the strike, while the number of ore bodies obviously decreases in NNE-trending (<30°) locations along the strike. It is found in the profile that thick and big part of ore bodies occur in the steep to gentle locations and enrichment section of ore bodies is in the locations with gentle dip angle (≤40°).
3.5Lateral trending regularity of ore body
Ore bodies controlled by regional structure belt in the western part of eastern Shandong have lateral tren-ding regularity in certain directions. For ore bodies controlled by NE-trending main fault belt, ore bodies laterally trend SW when main fault plane dips NW, e.g. Xincheng-, Jiaojia-, and Sizhuang gold deposits; ore bodies laterally trend NE when main fault plane dips SE, e.g. Sanshandao-, Xinli-, and Cangshang gold deposits within the Sanshandao-Cangshang fault belt, and Dayigezhuang-, Xiadian-, Taishang-, and Shanhou gold deposits within the Zhaoping fault belt.
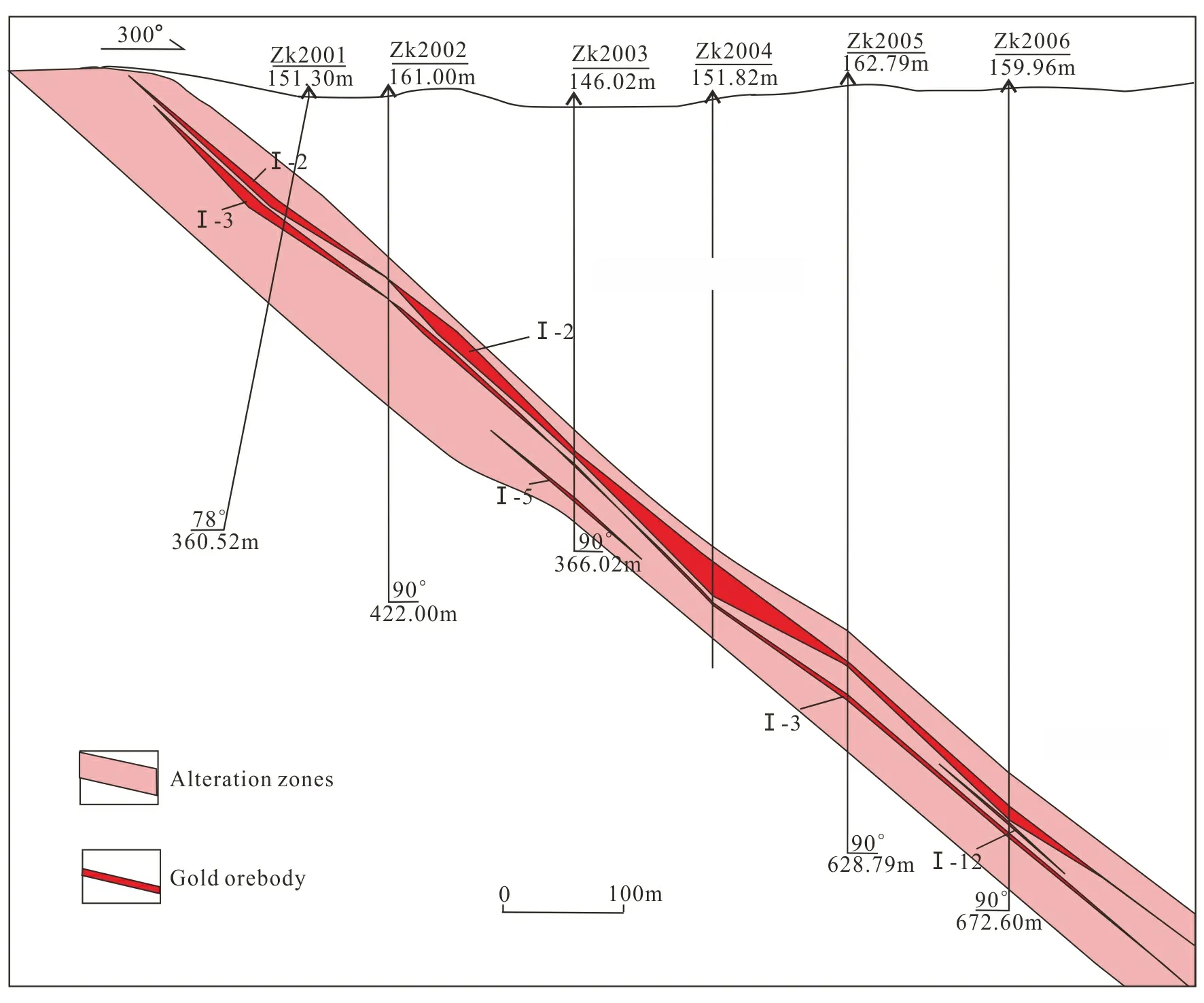
Fig.6 The 18th prospecting line profile map of Shanhou gold deposit (after Wang,2015)
Zhaoping main fault plane of Shanhou gold deposit dips SE. The vertical projection map of No.Ⅰ ore body of Shanhou gold deposit shows NE lateral trending with pitch 70°--80°, averaging 75°.
The lateral trending regularity of ore bodies in regional structure belt is related to left-lateral pressure-torsion of ore-controlling fault caused by regional NW-SE compression stress field or right-lateral tensional-shear caused by NW-SE trending stretch, and conjugate combination pattern of faults. NE trending ore-bearing fault belt belongs to the same stress field, which is in line with the regularity of regional uniform stress field.
3.6Mechanism of spatial emplacement of industrial ore body
Ore-controlling faults show characteristics of undulation no matter in terms of strike or dip, and industrial ore bodies occur in favorable structural locations with certain regularity, which controls segment enrichment of gold mineralization. Ore bodies like No.Ⅰ-2 and Ⅰ-3 of Shanhou gold deposit are characterized by segmentation enrichment and end-to-end alignment, i.e. ore shoots and lean ore sections are distributed alternately. Analysis shows that segmentation enrichment of ore bodies has a direct correlation with spacial undulation of the structural plane and the property of ore-controlling fault. In the mineralization epoch, ore-controlling fault has properties of a right-lateral reverse fault and thus ore holding space is likely to form in the local tension locations (with E-trending strike and more gentle dip) where ore bodies are placed.
Industrial ore bodies of Shanhou gold deposit are strictly controlled by Zhaoping fault structural belt and ore-controlling fault had right-lateral reverse fault activities during the mineralization epoch. Industrial ore bodies occur in the local tension locations with E-trending strike and more gentle dip angle, laterally trends NE with pitch 75°±. Ore-controlling faults show characteristics of undulation no matter in terms of strike or dip, and industrial ore bodies occur in favorable structural locations with certain regularity, which controls segment enrichment of gold mineralization.
4 Prospecting significance
Shanhou gold deposit is classified as orogenic gold deposit in terms of genesis type. The deposits have a deep and stable extension which can exceed 2 000 m from ore occurrence on the surface to the end. The measured reserve of Shanhou gold deposit is far smaller than Jiaojia gold deposit, Sanshandao gold deposit or Xiadian gold deposit, etc. Therefore, Shanhou gold deposit and its surrounding area have a big prospecting potential.
Mechanical properties of fault and control law of mineralization enrichment show that prospecting idea should not be just about veins and it is normal to have ore-free intervals in vein because ore bodies do not extend endlessly. Beyond ore-free intervals, more prospecting effort should be put into locations with E-trending strike (>30°) and more gentle dip angle along the main fault plane of Zhaoping fault.
Analysis of equal spacing distribution of deposits in the Zhaoping fault belt shows that southwestern end is relatively uplifted with most denudation, which is the current Mengshan-Wujiawa area. Beibo mining area in the middle part has moderate denudation.No.Ⅰ-2 ore body of Shanhou gold deposit in the northern part has a deep extension with no boundary being controlled, and has a NE lateral trending. Therefore, the northern part of Shanhou gold mining area has relative small denudation and its deep part is predicted to be a favorable target for prospecting. In addition, the deep part of Beibo mining area has a good prospect, and it is an important area for prospecting in the future.
5 Conclusions
(1) The ore bodies of the Shanhou gold deposit are strictly controlled by NE-NNE trending Zhaoping fault belt. Industrial ore bodies are mainly enriched in the NE-trending positions along the fault strike (>30° ) and in the locations with gentle dip angle (≤40°). Ore bodies have smaller thickness and weaker mineralization in locations where fault strikes towards NNE with steep dip angle.
(2) The fault gouge developed in the Zhaoping fault belt acts as a barrier to ore-bearing hydrothermal solution, which makes the industrial ore bodies of Shanhou gold deposit are concentrated in the footwall of Zhaoping main fault plane, covering 40 m. Industrial ore bodies laterally trend NE with pitch around 75°.
(3)The study shows that the ore-controlling fault in the mineralization epoch has properties of a right-lateral reverse fault and thus ore holding space is likely to form in the local tension locations with E-trending strike and more gentle dip, and ore bodies are placed.
(4) Preliminary findings show that the deep area with E-trending strike (>30°) and more gentle dip angle along the main fault plane of Zhaoping fault is a favorable target for prospecting. The deep part of Beibo mining area has a good prospect, and it is an important area for prospecting in the future.
Liu H T, Sun F Y, Zhang G D,etal. 2015. Characteristics of fluid inclusions of Shanhou gold deposit in Laixi, Shandong.GlobalGeology, 34(2): 372-378. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu Z J, Zhang W X, Song G H. 2008. Geological, geophysical and geochemical characteristics and ore-prospecting prognosis of the Shanhou gold deposit in Laixi City.MineralDeposit, 27(Suppl.): 182-189.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Ma S J, Lliu Z J. 2007. The geological and geochemical features and deep ore bodies prediction of Shanhou gold deposit in Laixi City.GoldScienceandTechnology, 15(1): 35-40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Sheng J H, Liu Z J, Diao S J,etal. 2010. The structural ore-controlling regularity and prospecting prediction of Shanhou gold deposit in Shandong Province.GoldScienceandTechnology, 18(3): 33-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Sun F Y, Shi Z L, Feng B Z. 1995. Gold ore geology lithogenesis related to the differentiation of mantle-derived C-H-O fluids in Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Changchun: Jilin People’s Press, 94. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang L, Sun F Y, Li B L,etal. 2007. Study on the localization of orebodies in Bushang orefield in Jinling gold deposit, Zhanyuan City, Shandong Province.Gold, 28(1): 13-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang D R. 2015. The study of the geological characteristics and enrichment regularities of mineralization of Shanhou deposit in Laixi City, Shandong Province: master’s degree thesis. Changchun: Jilin University. (in Chinese with English abstract)
8 April 2016, accepted 10 May 2016
Supported by Project of Shanhou Gold Deposit of Laixi of Shandong Province (SDLX2012-3-28).
(E-mail: wang_l@jlu.edu.cn)
Article ID: 1673-9736(2016)03-0144-09
杂志排行
Global Geology的其它文章
- Accumulation conditions of outside source heavy oil in Nepa-Botuoba Sub-basin, Russia and prediction of distribution
- Songjianghe biotite monzonitic granite zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemical significance
- Geochronology, geochemistry and Hf isotope of monzogranite in Niubiziliang of Qinghai
- Geochemical characteristics and petrogenesis of volcanic rocks from Baiyingaolao Formation in northeastern Hailar Basin
- Experimental study of seepage characteristics of single rock fracture based on stress states and stress history
- Experimental study on simulation test instrument and its penetration performance of soil infiltration clogging
