Research on comparative safety science
2016-10-19WUChaoSHIBoYICannan
WU Chao,SHI Bo,YI Can-nan
(School of Resources and Safety Engineering,Central South University,Changsha,410083,China)
Research on comparative safety science
WU Chao,SHI Bo,YI Can-nan
(SchoolofResourcesandSafetyEngineering,CentralSouthUniversity,Changsha,410083,China)
Safety science is a multi-and inter-disciplinary discipline with wide dimensions of time and scope,so it is very necessary and significant to do the interdisciplinary studies of comparative safety.Based on theories of comparison and safety science,the concept of comparative safety science(CSS)is defined,its connotation is analyzed,the framework of its subdisciplines is constructed from five categaries of theory,disaster types,safety management,engineering and vertical branches.Methodology and five basic features of CSS are analyzed.Four-dimensional structure system of its methodology is established,the general steps of CSS research is put forward.Research paradigm in comparative safety is built up.At last,some progress on the CSS were given.This researches show that CSS has become a new branch of safety science.
safety science;comparative study;discipline;methodology
0 Introduction
The origin of word “comparison” may not be known,however,we could imagine,consciousness and behavior of human to do comparison is almost with human evolution,and even the animals also have certain comparative consciousness and ability.Therefore,“comparison” is a kind of innate human capacity as it were,comparison is a common method for human beings to learn and change the world.
In 2007,the concept and idea of CSS was proposed by Wu Chao[1];moreover the connotation,system framework,practice and application prospects of CSS were published in another paper by WU Chao et al 2009[2].Because safety science is a multi-and inter-disciplinary discipline with wide dimensions of time and scope,comparison is undoubtedly more effective and general research method to explore issues of safety science from different perspective of time periods,levels and dimensions(Fig.1).Therefore this paper will focus on the comparative safety topics for further research.
1 Significance of CSS
CSS is of great significance in the field of safety science;its functions are mainly generalized as follows.
1.1Direct functions
To analyze safety events and data preliminarily.By comparative method,firstly events and data are sorted out in safety science research,then qualitative and quantitative analysis is done,lastly events and data are classified.After preliminary analysis,orderly events and useful data are abstracted from messiness to support the further research.
To discover new phenomena of safety science.In the process of identifying and sorting events,new collected materials could be compared with prior truth in safety science to discover new truth.Sometimes comparative method helps to reveal imperceptible motion and change.
To set up new concepts and disciplines in the field of safety science.In comparison with scientific achievements,experience and truth,historical origin of evolvement could be traced and sequence of development could be made clear.Furthermore,some empirical principles could be drawn out as the basis of theory and more precise theoretical discipline.
To judge the consistency between theory and practice.Not only can knowledge be derived from experience,it could be drawn more easily from the rational thinking by means of comparison.Comparison can be done to study safety law,safety culture,safety history and experiences in different fields,ranging from countries,regions,times,systems,industries and enterprises.From the results of comparison,something valuable can be found for reference.Multi-perspective research of CSS can provide a new methodology of safety science.By comparison of safety principles,theory,technology and engineering in different disciplines,industries,countries,regions and times,methodology of safety science could be established on the above basis.

Fig.1 Multidisciplinary integration of safety science
1.2Indirect functions
To boost development of modern safety science and form global safety concept.Preconditions of comparison are description and analysis.CSS supplies all-around information and knowledge about global development of safety science,and it contributes to a comprehensive grasp of safety science and has a great role in improving safety awareness to form global safety concept.
To provide an all-round horizon to study safety science.Research framework of CSS provides a wide horizon for researchers in the peak of the development trend,broadening horizon and emancipating mind.Variety,an identity of CSS,can stimulate sparkles of a variety of views and break cultural barriers of ethnocentrism.It can advance modernization of safety science.Comparison of safety science provides a wealth of information and development experiences of safety system in different countries,and it could enhance the national awareness of safety science and promote the development of modern safety science.
To promote national reform and development of safety science by comparison and reference.The advantages of safety study in other counties could be taken for reference by means of comparison,which is an important basis to develop CSS through its whole process of evolvement.Reference is to assimilate essence of others and select useful experience to improve domestic safety system.Comparative study in safety science makes it possible to learn the good of others and promote reform and development of domestic safety system.
To promote mutual communication greatly and joint progress.The study of CSS helps to promote mutual communication between countries about safety information and experience sharing,and it also contributes to build global safety system which is compatible with the characteristic of diversity.In addition,it can promote interaction and cooperation of safety research all over the world.Because development of safety science and technology differs greatly in different countries,comparative safety study can provide the latest advances of safety research and urge undeveloped countries to reform.It is also helpful to build a relationship of multilateral cooperation for mutural advance.
2 Discipline Features of CSS
2.1Definition of CSS
CSS is a discipline which discloses the true essence of safety,concealed laws and principles in developing process of safety science by comparative study of inter-disciplines and cross-time in order to protect human beings from external injury in life and work,and it can provide mutual reference and communication between countries and fields of safety to promote development and reform of safety science system in the world.CSS is a science,rather than a method or a methodology in this field.CSS emphasizes extensity of study fields and comparative orientation of inter-disciplines and cross-time.
2.2Disciplinary attribute of CSS
CSS is interdiscipline of comparison and safety.It is not only an extension of the comparative science in the field of safety science,but also a branch of safety science system.The scope of safety science is extensive in time,space and dimension,and it involves natural science and social science.Comprehensive attribute of CSS is also embodied in comparison and mutual reference of safety issues in different time and fields.The research field of CSS involves all aspects of safety which is a complex open system,and its extension relates to social culture,public management,administrative management,architecture,civil engineering,mining,traffic transportation,machinery,food,agriculture,forestry,biology,medicine,energy fields,aviation industry and other fields of human production,life and survival.
2.3Disciplinary identity of CSS
Comparative horizon of interdiscipline and cross-time.The special attribute of comparison determines that the educed research results of university and transferability are based on comparative horizon in wide sphere across national borders,across time periods,trough history.Comparative horizon across disciplines,across cultures,across national borders and across time periods is very important to draw out significant research achievements of safety which is a complex system with wide borders.Because there are great differences of safety science system in cultures,languages,countries and nations,it is necessary for researchers to have comparative horizon across cultures and countries to discover common potential rules from differences for reference and improvement;because the pursuit of safety is throughout the history of mankind,it is necessary to have comparative horizon across time periods to explore profound connotation and make the past serve the present;discipline system of safety science is very extensive and comprehensive and its formation and development are based on natural science and social science,many methods,techniques and theories are borrowed from other disciplines,its dependence on other dicsipines determines it is very necessary to have comparative horizon across disciplines.
Indigenization in international horizon,taking foreign things for reference,is the ultimate goal of CSS.Development history,characteristics and achievements of scientific safety system at home and abroad are described,compared and analyzed,based on which traceability,induction and conclusion are done to provide a lot of useful information;fundamentally description and analysis are done for comparison,and comparison is done to find the similarities and differences for reference in order to solve domestic problems of safety development and deficiency.So the ultimate purpose of CSS is to promote domestic development of safety science system by taking foreign things for reference in international horizon.
CSS is very informative,diversified and open-ended.CSS studies safety issues of all countries at various historical periods,which involves many disciplines,a large number of literatures,including collection,analysis and review of safety study in different countries,and its research methods include description,reasoning,inference and application.It is incomparable with large information and abundant materials.
Diversification of CSS is shown in diversification of disciplines,comparative objects,research method and theoretical factors.Safety is a complex and open-ended system,and its research contents and category of CSS is open-ended and extensive,involving comparison of national history in all branches of safety science,disciplines for safety disciplinization,safety issues and so on.It is because its research category and content are open-ended that CSS could get long-term development.
3 Disciplinary Foundation of CSS
CSS is an interdiscipline of safety science and comparison science,so its foundation of theory and discipline is also interdisciplinary.
The foundamental disciplines of CSS are safety science and comparison science,and it is the organic combination of the two.The scope of safety science is comprehensive and extensive,and it is closely relevant to other disciplines.It is typically an interdisciplinary subject,and its research contents include safety history,safety system,safety engineering,safety law,safety education,safety behavior,safety psychology,disaster,and so on.In addition,its content and theory updates constantly along with the improvement and systematization of the research.
Comparison science has a long history and its scope extended to many areas such as economics,sociology,political science,anthropology.It is not a single discipline but a cluster of disciplines,including comparative education,comparative law,comparative management,comparative economics,comparative literature and other branches.Comparison science provides efficient methods to study interdisciplines.Therefore,as the organic combination of comparison science and safety,CSS takes comparison science as one foundamental discipline.
Comparison process in CSS is not just a simple description of some safety problems,but includes analysis of its formation and development of cause and effect in order to discover techniques,general principles and even theory.Such comparative process will inevitably relate to many disciplines of social science,including philosophy,literature,history,sociology,political science,economics,management science,and so on.
4 Subdisciplinary Framework of CSS
Multi-perspective studies of CSS provide a new methodology of safety research,and it studies the methodology of safety science by comparison of principle,method,theory,technology and engineering across disciplines,industries,countries,regions and time periods.Safety science theory represents a set of general principles in safety science,instructive for safety study and relevant industries.One of the important roles of CSS is to extract safety theory and general principles.
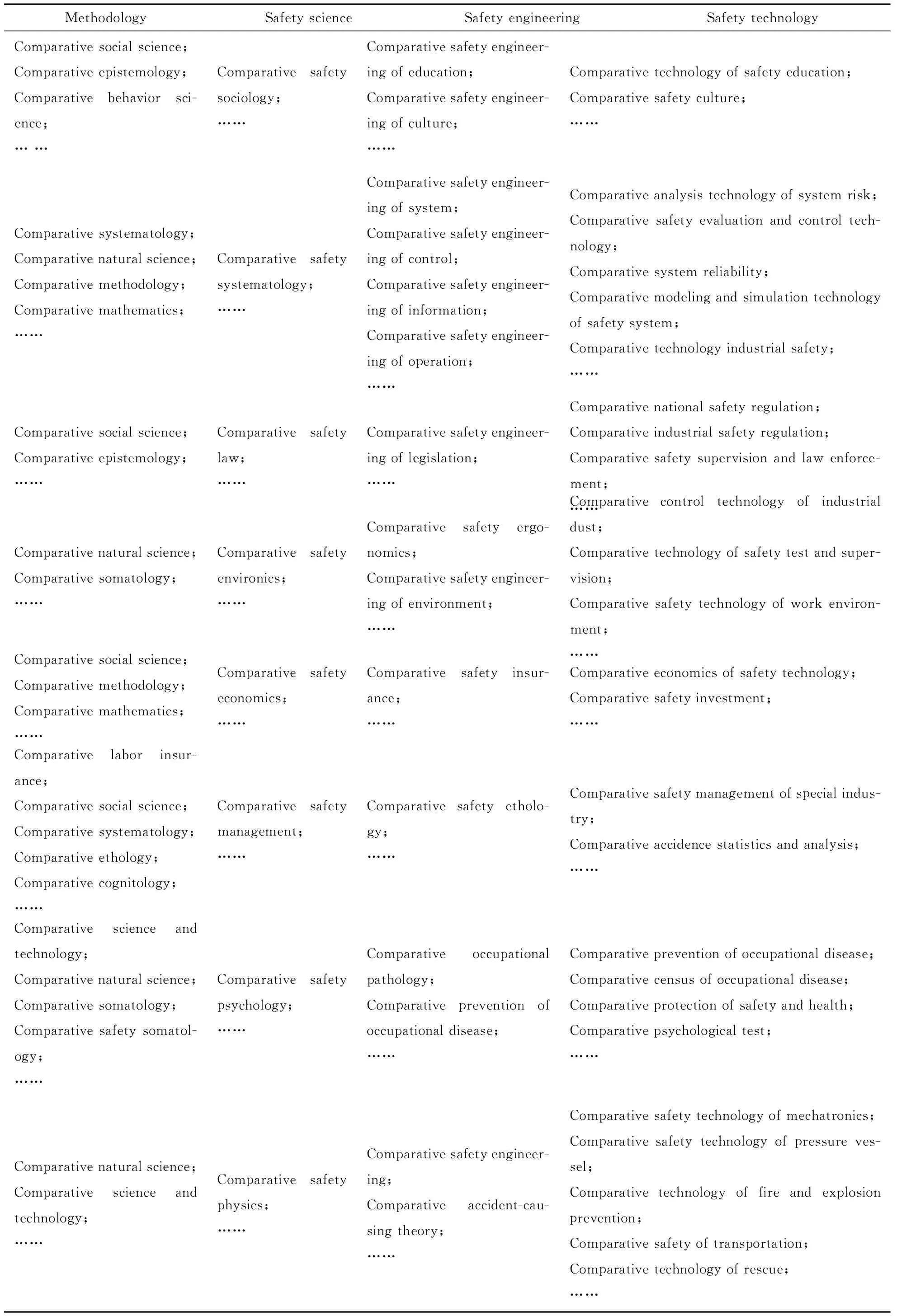
Because safety science is a comprehensive discipline with wide scope,it includes many subdisciplines and research priorities from different perspectives.There are many inferior branch systems of CSS across disciplines.Subdisciplinary framework of CSS are built up according to theory of safety science system,disaster category,safety management,safety engineering and vertical system of safety science as shown in Table 1.

Tab.1 Subdisciplinary Framwork of CSS from Four Perspectives
According to the vertical classification system of safety science and attribute classification of safety science,vertical classification of CSS is constructed as Table 2.
5 Methodology of CSS
5.1Research ideology
Dialectical materialism and historical materialism.Dialectical materialism is the correct reflection of
Tab.2 Subdisciplinary classification of CSS vertically
the objective law,and it guides us to do research of CSS from objective and dialectical perspective,seek truth from facts in order to confirm truth,objectivity and comprehensiveness of research materials;it guides us to do research of CSS with times in order to confirm efficiency and scientificity of research results.Scientific research should be used to practice the standard to test the theory,not judged by subjective imagination.In the research of comparison safety science,comparison,judgment and selection are just the first step,then results are used into practice to testify the truth.Only by adhering to the dialectical materialism and historical materialism,with guidance of scientific view of matter and practice,can the research of CSS be undergone smoothly and efficiently and develop into a real independent,energetic discipline.
People-centred value of safety.Safety concept is a general view of safety role,status,value,and it varies with time periods.People-centered value is the key concern of safety science we should adhere to in the study of CSS.Safety is the most basic need of human survival and development and the basic safeguard of life and health;if people lost their lives,we lose everything,so personal safety is the main concern of safety science.Safety is a kind of civilization,safety technology relies on science and technology,culture and education,economiy,social progress and the improvement of human quality.Safety and civilization are the fundamental interests of the development of human society[3].
5.2Research across disciplines and time periods
The research of CSS needs comparative perspective across disciplines,time periods and countries.Only from such wide perspective can we explore the inherent law and extract the essence.
Safety science includes some foundamental disciplines such as safety philosophy,historiography,safety safety science;it also includes some social disciplines such as safety sociology,safety economics,safety management,safety education,safety ethics and safety culture;in addition,it includes some great discipline systems such as safety material science,safety somatology and safety systematic.The construction and development of these disciplines are closely related to other disciplines such as literature,history,philosophy,astronomy,geography,biology,mathematics,physics and chemistry.Comparative interrelation study between safety and other disciplines can classify branches of safety science and make clear the relationship between safety and other disciplines.
Interdisciplinary research is one of the important thoughts and characteristics of comparative perspective,and it is very significant that comparison between safety and other disciplines is regarded as one branch of CSS.Research across time period focuses on comparison of formation,development,performance and achievement of safety social science and natural science throughout history across countries.
The establishment and development of safety science is inseperate from the achievements of other disciplines as shown in 3 aspects.
1)At different stages of ancient times in the east and the west,the independent discipline system is not established in a form of chaos.The interpenetration and interrelation of different fields appeared at that time,which supplied academic background for interdisciplinary research of CSS and becomed one of its parts.
2)In the process of establishment and development of safety science,safety science shows very obvious comprehensiveness.Its branches and system are all based on other disciplines,and its development is inseperate from other disciplines.Interdisciplinary study is important part of CSS for new discovery and breakthrough.
3)The development of modern safety science,popularization of safety culture and realization of safety are supported and promoted by other disciplines and their achievements.Combination and interaction between safety and other disciplines is another part of research contents in CSS.
Research focuses of CSS across disciplines and time periods are as follows.
CSS gives prominence to safety features and laws,focusing on the theme of safety.The discipline taken for comparison with safety is supposed to be an independent,systematic discipline and closely relevant to safety.Interdisciplinary study builds up an interrelated system which is the combination of two disciplines and shows the research results.Comparative research between safety science and relevant disciplines also belongs to CSS.
Safety law has broken through the shackles of the specialized technology,the science and technology of safety is removed from different disciplines of science and technology and integrated to form an independent discipline system of safety science and technology.It is an inevitable development trend of safety science to do interdisciplinary integration study among safety science,disaster science,environment science,management science,human science,sociology and ethics.Therefore,how to improve the communication and integration between safety science and other disciplines is important for safety researchers.CSS studies interrelation and intersection between safety science and other disciplines from past to present by interdisciplinary research across time periods,and even creates new discipline branches to improve safety system.
In terms of disciplinary attribute and methodology feature of CSS,comparison with methodology system of other disciplines taken for reference,four-dimensional methodology framework of CSS is established as Fig.2[4].
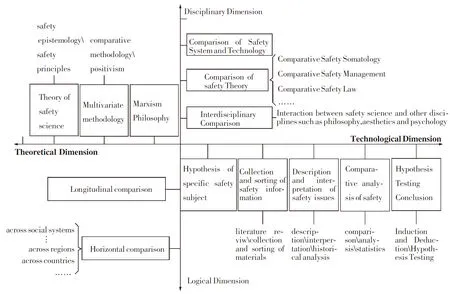
Fig.2 Four-dimensional methodology framework of CSS
Disciplinary dimension of comparative safety methodology:this dimension describes the category of research contents.Because safety system is open-ended and complex with multi-branch,its research content of CSS is extensive and open-ended.Comparison exists in all aspects of safety system.Comparative safety research may be concerned about interrelation between safty and other disciplines,comparison of theory branches in safety science and technique of safety science.
Technological dimension of comparative safety methodology:this dimension is about process,steps and methods of comparative safety study.CSS is interdisciplinary,so its research methods mainly share other disciplines’,including comparison,description,statistical analysis,induction,deduction,and historical method.Also,it may borrow more techniques and methods from other disciplines.
Logic dimension of comparative safety methodology:this dimension is about some logical issues such as selection of research subjects,structure and time periods in order to do comparative study of specific safety issue in a certain area about a certain culture at a period.
Theoretical dimension of comparative safety methodology:this dimension is a combination of several theories and methodologies.The dialectical materialist philosophy methodology is the foundation of comparative safety research;the methodology of positivism has a major impact on comparative study;Quantitative analysis is used to do efficient study of comparative safety;safety epistemology is theoretical foundation of safety science and comparative safety.
6 Research principles of CSS
According to its discipline attribure,combined with its research contents and feature,the research of CSS should adhere to the following basic principles.
6.1Principle of realism
Only based on reliable data can the acquired results be authentic.Principle of realism is shown in the whole process of research.Researchers engaged in comparative safety study should make detailed demonstration and in-depth analysis to draw out objective and useful information and then do objective comparison in order to conclude valid results.They should adhere to principle of realism in order to confirm the truth and objectivity of research.
6.2Principle of integrity
All events do not exist in isolation but in universal connexion with mutual influence,interaction and mutual restriction.The principle of integrity in the process of comparative safety study is that researchers should take everything relevant into consideration systematically including all factors in process of formation and development across countries and cultures,based on which they do comparison and analysis integrally and collaboratively.
The principle of integrity requires that researchers should consider the interaction between safety field and other social factors.Comparative study in safety science relates to the whole safety field,while safety is a subsystem of society and has interrelated and interdependent relationship with other subsystems.Comparative study in safety science must study the interrelation of safety systems across countries across fields,only in this way can the common nature of different safety systems and basic safety principles be disclosed and scientific conclusion be drawn out.
The research perspective of CSS should be comprehensive,involved in all aspects of safety itself.The feature of safety system is open,complex,broad and includes many aspects,composed of multiple subsystem with huge and interrelated branches.CSS is a combination of safety and comparison,and its complexity determines the diversity of its research contents.Principle of integrity requires that researchers not only consider interaction between safety and other social systems but analyze all subsystems of itself from all dimensions.
Comparative safety study can regard safety systems of all countries in the world as a whole,analyze and study safety phenomena from an angle of integrity.From this angle we can see whether it is collaborative among all factors in safety system and its developing process,whether the whole function is optimized,and we can grasp the overall trend and direction of safety development.
The principle of integrity also fully embodies the organic combination of diachrony and synchrony,taking into accounts both the longitudinal and transverse factors.The principle of integrity guides researchers of comparative safety to do comparison from a general angle of integrity in order to grasp overall trend and common principles.
6.3Principle of comparability
Similarities and differences exist ubiquitously among things in the world.CSS,a branch of comparative science,takes comparison as the basic research methods,so research materials in comparative safety must be comparable with inherent similarities and differences.
Manifestation of similarities and differences of safety development provides basis of safety comparability.We can breakthrough restrictions of languages and cultural traditions to study safety fearture and development trend from international and comparative perspective.
Strictly speaking,everything can be compared,but sometimes comparison is unconditional and absolute,and it could be influenced by time,place and condition.Therefore,comparability is of conditionality and relativity.Namely,comparison of two depends on time,place and condition.Essential similarity of two in nature is precondition of comparability;it would draw out wrong conclusion by external similarity but ignoring intrinsic similarity.Therefore,principle of comparability requires that safety comparison should be undergone in a certain social environment.Safety development in in different areas,countries and nations is regional and national as the product of of the specific social environment.When we do evaluation and analysis of different safety type,model and experience,we should consider specific background of the times and cultures in order to draw out scientific conclusions.
6.4Principle of development
Because all things in the world are in mutual connection and mutual restriction,and this kind of mutual interaction cause motion,change and development of things.The modern system theory reflects the principle of dialectics,it accurately reveals the developing world and reveals evolution mechanism in the world from simple to complex,from low to high,from disorder to order.The principle of development in comparative safety research requires that we should study various factors of safety from a view of development and analyze the reason of its formation and future trend in order to draw scientific conclusion.
CSS do not study safety phenomena in static state but use the correct conclusion to direct the development of safety science in the future,which requires the researchers study the dynamic process of safety development,including formation of safety issures and its present situation.Comparative safety study analyzes the similarities and differences of safety systems across countries and draws out the developing trend.Safety system,safety theory,safety technology and methods are on the march,so it is necessary to grasp the right developing direction to take comparative safety study.Though comparative safety study is mainly about the current situation of safety,attention must also be paid to longitudinal study of its history and developing trend according to the principle of development.
7 Research on method of classifications and procedures of CSS
7.1Classifications of comparative methods
Comparative study can be carried out from different angles of time,space,process,content,form,internal structure,external links etc.For example,the diachrony and the synchrony can be studies by longitudinal comparison(i.e.in comparison with the same object at different periods about its situation,characteristic and so on)and horizontal comparison(i.e.in comparison with the same period in different states with different features,etc.).Through the comparative analysis of the relevant things,it helps to understand the relationship and difference between things.According to different standards,comparative methods can be divided into the following 5 classes.
1)Specific comparison & comprehensive comparison according to the scope
Specific comparison is to compare one attribute of things,while comprehensive comparison is to compare all(or several)attributes of things.Comprehensive comparison is based on specific comparison;while only by comprehensive comparison can the essence of the objective be grasped.Because in the scientific research,it is necessary to combine the internal attributes with the external attributes in order to grasp the nature and rules of things.
2)Horizontal comparison & vertical comparison according to the time and space
Horizontal comparison is to compare present state of coexistent things;while longitudinal comparison is to compare the states of one thing at different periods in orde to learn its developing process and rules.
3)Comparison for similarities & comparison for differences in terms of comparative goals
Comparison for similarities is to seek the similarities and law in common among different things;while comparison for differences is to compare the different attributes between two things in order to find their particularity.By these two kinds of comparison,we can understand diversity and unity of things better.
4)Qualitative comparison & quantitative comparison according to comparison method
Everything is a unity of quality and quantity,so in the process of scientific research,we should grasp not only the quality of things but also their quantity.A qualitative comparison is to confirm the nature of things by comparison of things’properties;quantitative comparison is to quantitatively analyze things’properties to find the movement of things.Qualitative comparison and quantitative comparison are both of advantages,so we should combine the two to do comparative safety study.
5)Macro-comparison & micro-comparison according to the propertie
Macro-and micro-comparison are to do comparison between the whole and the local of system.Macro comparison is to compare the whole systems of different things in order to grasp its genral features;micro comparison is to compare all parts of things in order to grasp specific features.In practical application,the two are prerequisite for each other.Micro comparison is the indispensable basis of macro comparison;macro comparison is the inevitable trend micro comparison.
7.2General procedures of CSS
Generally speaking,research methods of CSS according to the work implementation can be divided into five steps:description,interpretation,parallel,comparison and summary.
Step 1:Description.Detailed description is the first step in comparative safety study in order to make careful,complete and objective description of research subjects as far as possible.Therefore collection of relevant documents is required in order to make clear comparative purpose and theme.Comparative objects and purposes are premise and foundation of comparative study.Researchers should confirm the content and the scope of comparison,that is to say,they should confirm research dimension and comparative standard.This step is the basis and foundation of comparative study.Selection of comparative dimension is premise of scientific comparison.This step inclues the following details:selection of the theme and content,confirmation of its scope and establishment of comparative standard.In order to collect more relevant materials from the literature,it is necessary to investigate the object emotionally and rationally.The researchers should collect enough relevant data to identify its objectivity.The relevant data and information should be representative to reflect the nature of things.This requires the scientific sampling,routine processing of data done by researchers with good qualities of theories.
Step 2:Interpretation.Theoretical interpretion of processed data is good foundation for further research with a realistic and historical significance.After detailed and objective description of a comparative safety issue,its present state is interpreted to analyze its significance and reason.That is to say,based on knowledge of other disciplines such as sociology,political science,economics,humanities,history,psychology,philosophy and other disciplines,the purpose of interprestation is to explain deep realistic and historical significance of present state of safety issues by combining its present state and general state in society.While interpreting materials,the researchers should do comprehensive analysis based on local reality scientifically,and ensure the objectivity of interpretation without any personal prejudice.
Step 3:Parallel.Parallel is to classify the comparative standards.Strictly speaking,comparative study begins from the stage of parallel.At this stage,objects interpreted will be sorted and classified to determine the comparative pattern and standards.Then data will be further analyzed and hypothesis of comparative analysis will be put forward.
Step 4:Comparison.In the comparison phase,hypothesis put forward in parallel phase will be validated.This stage will compare the collected data in terms of certain standard,analyze the reason of difference and give evaluation.Comparison is based on objective facts with objective and comprehensive analysis of all materials.
Comparison from all angles:Anything does not in isolation but be closed connected with others,so comparison from all angles is necessary.It is wrong to do arbitrary choice of data and materials without consideration of interrelationship between two things.
Comparison of essence:There are Similarities and differences of phenomena and essence.Comparative study should grasp the essence thought phenomena in order to know the things accurately.Comparison is to explore internal relation of many typical materials through a large amount of typical materials from the perspectives of history,society,economics,social customs,and so on.
Step 5:Conclusion.After a comparative study,the hypothesis and conclusion will be verified by theory and practice.
The above five steps are general procedure of comparative safety study and interrelated with each other.Selction of comparative objects is a prerequisite for comparative study;establishment of comparative standards is the basis of study;comparative analysis is its keystone;conclusion is its purpose.
8 Advances in Branch Disciplines of CSS
For the aim of establishing the comparative safety jurisprudence(CSJ)to promote the development of safety jurisprudence,combined with the comparative science,jurisprudence and safety jurisprudence,definition of CSJ was put forward and its connotation was analyzed based on its own space characteristics,also the horizontal branch systems and the vertical branch systems of CSJ were established[5].The comparison dimensions,time and space dimensions and knowledge dimension of the CSJ were proposed.Also the research layers,structure and space were determined.Based on the four aspects of safety law,the research contents of the CSJ were analyzed.The four-dimension methodology system was constructed,and then combining with the research characteristics of CSJ,its specific methods were analyzed based on the process of comparative study.At last,several comprehensive comparative paths,that is taking the norm comparative as started point,the function comparative as main contents and the culture comparative as supplement were constructed,meanwhile a multi-level research model called as the norm-function-culture model was built to guide and promote the research work of the CSJ.
For the aim of establishing the comparative safety management science(CSMS)to promote the development of safety management science,combined with comparative science,safety management and management science,definition of the comparative was put forward and its connotation was analyzed.The interaction among the relevant elements of the CSMS was described based on its comparative process[6].And the comparison dimensions,time and space dimensions and knowledge dimension of the CSMS were proposed.Also the research layers,structure and space were determined.Based on the four levels of organization’s safety management,the research contents of the CSMS were analyzed.The four-dimension methodology system which contains knowledge dimension,technical dimension,logic dimension and theoretical dimension is constructed,and then its specific methods are analyzed based on the process of comparative study.At last,the research paradigm to guide research work of the CSMS was established.
For the aim of establishing the comparative safety pedagogy(CSP)to promote the development of safety pedagogy,combined with the comparative science,safety pedagogy and practices on comparative safety education,definition of CSP was proposed and its connotation was analyzed from the view of discipline.Also the comparative study elements which are subject,object and dimension were analyzed.Based on the cross attribute of CSP,the multilevel framework,which takes the history as the base,the empirical analysis as the method and the multicultural analysis as the supplement,were put forward[7].Then the research process of CSP,which is the process of object-material-comparative-conclusion,was constructed based on the normal comparative process.At last,the comparative types and contents of CSP which includes theory,management,technology and practice of safety education,were built,also their application were listed.The research results could be used to guide the practical activities of CSP.
Aslo,the foundation of comparative safety ethics and its investigation was investigated[8].The research on elements,units and paths of comparative study for the CSS was conducted[9].Furthermore some practical comparative studies such as the work safety standardization system used in Chinese enterprizes versus the DuPont safety management system[10],and the “golden ten-year” development of safety science between China and USA[11]were done.By summarize all the research works on CSS,a new book titled Comparative Safety Science[12]was published by China Labor and Social Security Publishing House.
9 Conclusions
After the above researches,the discipline of CSS has been established.Firstly,the concept and connotation of CSS are defined and analyzed,and its importance for safety science is put forward to guide the following development of relevant research;Secondly,branch systems of CSS and its framework of disciplinary system are established,and its main method systems and principles are explored to complement the disciplinary system of CSS;Thirdly,methodology of CSS is constructed in the form of four-dimensional figure to show its diversity;Fourthly,eneral procedure of CSS is concluded to direct the relative research,including five steps of hypothesis,literature review,description and interpretation,comparative analysis and hypothesis-testing-conclusion.This study also provides a new methodology and direction to investigate safety science.At last,some advances achieved in the past several years on the CSS were summarized.
References
[1]WU Chao.Preliminary study of the science of safety science[J].China Safety Science Journal,2007,17(11):5-15.
[2]WU Chao,YI Can-nan,HU Hong.Study on comparative safety science and the construction of its framework[J].China Safety Science Journal,2009,19(6):17-28.
[3]WU Chao.Methodology of safety science[M].Beijing:China Labor and Social Security Publishing House,2011.
[4]CAO Ying-ying,WU Chao.Study methodology of comparative safety science[J].China Safety Science Journal,2013,23(5):3-9.
[5]YI Can-nan,WU Chao,HU Hong,LIAO Ke-bing.Establishment of comparative safety jurisprudence and its study[J].China Safety Science Journal,2013,23(11):3-9.
[6]YI Can-nan,WU Chao,LIAO Ke-bing,et al.Research on comparative safety management science[J].China Safety Science Journal,2013,23(10):3-8.
[7]YI Can-nan,WU Chao,LIAO Ke-bing,et al.Research on comparative safety pedagogy and its applications[J].China Safety Science Journal,2014,24(1):3-9.
[8]HUANG Lin-qi,WU Chao.Foundation of comparative safety ethics and its investigation[J].China Safety Science Journal,2014,24(3):3-8.
[9]YI Can-nan,WU Chao,HU Hong.Research on elemen-ts,units and paths of comparative study for comparative safety science[J].Journal of Safety Science and Technology,2015,11(4):140-146.
[10]YI Can-nan,HU Hong,WU Chao,et al.Comparative study on work safety standardization and DuPont safety management system[J].China Safety Science Journal,2014,24(4):110-116.
[11]ZHONG Qi-jin,WU Chao,LIU Hui.Comparative study on the “golden ten-year” development of safety science between China and USA[J].China Safety Science Journal,2010,20(4):3-13.
[12]WU Chao,YI Can-nan,CAO Ying-ying.Comparative sa-fety science[M].Beijing:China Labor and Social Security Publishing House,2014.
10.13800/j.cnki.xakjdxxb.2016.0518
1672-9315(2016)05-0719-13
2016-03-10责任编辑:杨忠民
国家自然科学基金(51534008)
吴超(1957-),男,广东揭阳人,教授,博士生导师,E-mail:wuchao@csu.edu.cn
比较安全学的研究*
吴超,施波,易灿南
(中南大学 资源与安全工程学院,湖南 长沙 410083)
安全科学是一门综合交叉学科,其具有广阔的时空维度,因此,极有必要对其开展比较安全学的跨学科研究。基于比较学与安全科学理论,提出比较安全学(CSS)的定义,并分析其内涵。基于此,从安全科学的理论类别、灾害类别、安全管理类别、工程类别与安全学的纵向分支5个方面构建比较安全学的学科分支体系,并分析比较安全学的方法论和5大特征。在此基础上,建立比较安全学方法论四维结构体系,确立比较安全学研究的一般步骤,并建立比较安全学研究的范式体系。最后,分析比较安全学的部分应用前景。结果表明,比较安全学是一门新的安全学科分支。
安全科学;比较研究;学科;方法论
X 9
A
