五大连池水质现状及近30年前后变化*
2016-10-12王念民汤施展孙大江华振河
王念民,汤施展,李 喆,孙大江,纪 锋,华振河
(1:中国水产科学研究院黑龙江水产研究所,哈尔滨 150076) (2:中国水产科学研究院长江水产研究所,武汉 430223) (3:黑龙江省五大连池市日河渔业有限公司,黑河 164155)
五大连池水质现状及近30年前后变化*
王念民1,汤施展1,李喆1,孙大江1,纪锋2,华振河3
(1:中国水产科学研究院黑龙江水产研究所,哈尔滨 150076) (2:中国水产科学研究院长江水产研究所,武汉 430223) (3:黑龙江省五大连池市日河渔业有限公司,黑河 164155)
2012—2013年春、夏、秋季,对五大连池11个采样点的水质变化进行研究,分析湖水水质现状,比较30年前后湖泊的水质变化并评估五大连池富营养化程度. 结果表明,五大连池不同部分、季节、年份的水质参数指标波动剧烈,可能是受水产养殖及氮、磷浓度变化影响,2池和3池浮游生物量及叶绿素a浓度明显较低;同1980s相比,水质变化较大,一些指标显示水质已趋向好转,但5池却接近重度富营养化,说明近几年的还湿、迁居等保护措施初见效果,但整个湖泊水质恢复需要漫长过程.
水质;富营养化;五大连池
湖泊是主要的陆地生态景观之一,是水资源的重要组成部分,参与物质和能量收支,对区域物质及能量循环意义重大. 自然因素及人类活动对湖泊发育有重要影响,特别是后者,常常导致水质变化,使湖泊功能退化,加速其消亡[1]. 作为物质存储库,湖泊水质变化是复杂而且漫长的过程,掌握其变化规律是湖泊保护及开发的前提基础. 五大连池是具有代表性的高寒地区自然水体,兼具旅游、观赏、水产养殖、饮用水源等功能,由于人为活动的影响,五大连池水质受到一定程度的影响. 1980s初,曾对五大连池水环境进行系统调查[2],其后30年,除对其矿泉水及个别池子水质有少量研究[3-11],未再对该湖泊水质进行系统报道. 2012-2013年,我们再次对五大连池水质进行调查,研究其水质波动及其变化规律,并结合之前学者的研究成果,分析五大连池湖泊水质30年来演变趋势,为保护五大连池水环境,预防和控制湖泊富营养化,以及湖泊环境保护及资源开发利用协同推进提供基础数据.
1 研究区概况
五大连池(48°34′~48°38′N,126°00′~126°21′E)是我国第二大火山堰塞湖,位于黑龙江省黑河市西南部,地处大、小兴安岭与松嫩平原过渡带. 湖泊由5个呈串珠状小湖组成,面积18.47 km2,蓄水量1.57×108m3,水流流长5.25 km,由北至南由5池经4、3、2池,从1池流出,汇入石龙河后注入讷谟尔河.
五大连池是著名的火山地质公园,形成距今近300年,早期人为活动较少,自1950s国营农场建立以后,工农业生产、生活导致湿地萎缩,湖泊环境变化较大. 至2000年,整个流域面积106000 hm2,其中耕地54943 hm2,占总面积的51.8%;林地26787 hm2,占25.3%;牧草地11433 hm2,占10.8%;居民地及工矿用地1162 hm2,占1.1%;交通用地317 hm2,占0.3%;水域4864 hm2,占4.6%;未利用土地6494 hm2,占6.1%.
五大连池处于温带大陆性季风气候区,年平均气温-0.1℃,年平均降水量493.9 mm,主要集中在6-9月,占年降水量的80%,年蒸发量约为降水量3倍. 湖泊靠地下泉水及降水积聚补充.
2 研究方法
2.1采样点布设
根据湖泊自然概况、形态、利用程度,共设13个采样点. 其中,1池(P1)1个、2池(P2)3个、3池(P3)5个、4池(P4)1个、5池(P5)3个. 采样点集中在各池的进出水口和中心区域(图1). 水样采样时间分别为2012、2013年度春季(每年5月末至6月初)、夏季(每年8月中、上旬)和秋季(每年9月底至10月初).

图1 五大连池采样点设置Fig.1 Sampling sites in Lake Wudalianchi
2.2 样品采集及理化因子测定

2.3 数据处理及分析
采用单因素方差分析法(One-way ANOVA)对各采样点环境参数均值差异进行显著性检验. 选取 Chl.a、TP、TN、SD、CODMn五项指标,利用综合营养状态指数法(TLI)[13]确定各样点水体的营养状态及五大连池水体营养状态的总体评价.TLI以0~100的一系列连续数字对营养状态进行分级:TLI<30为贫营养;30
3 结果与分析
3.1 水质现状


表1 2012-2013年五大连池各池水质指标变化Tab.1 Variations of water quality of each pond in Lake Wudalianchi in 2012 and 2013
*由于洪涝灾害影响, 4池夏季水样无法采集,表中数据仅为春、秋季均值.
3.2 五大连池水质30年前后的变化
表2 1981-1982和2012-2013年五大连池 湖水水质指标比较*Tab.2 Contrast on water quality indexes of Lake Wudalianchi between 1981-1982 and 2012-2013
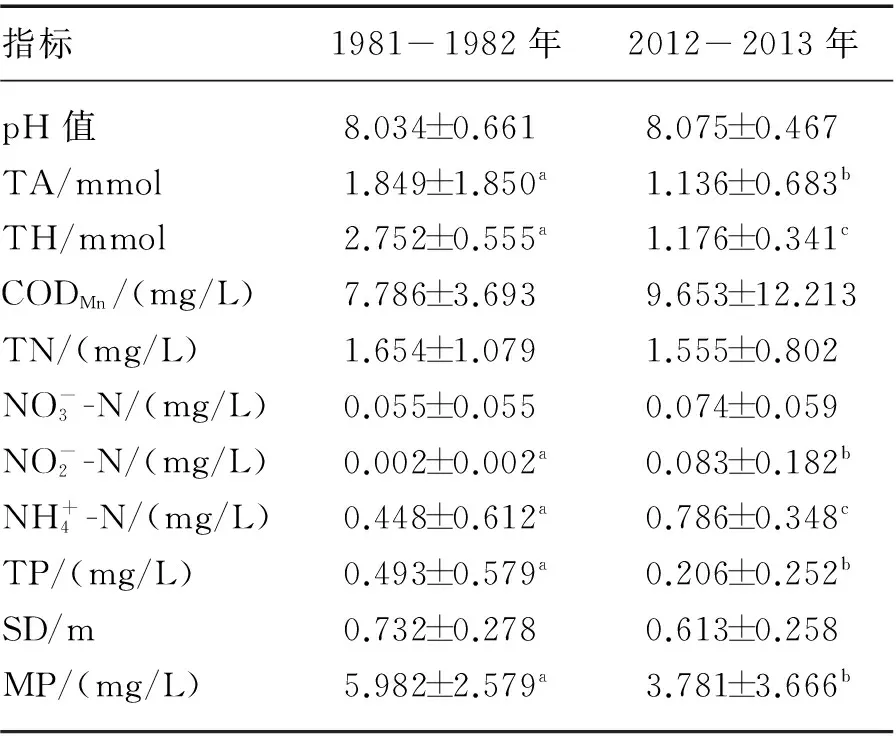
指标19811982年20122013年pH值8.034±0.6618.075±0.467TA/mmol1.849±1.850a1.136±0.683bTH/mmol2.752±0.555a1.176±0.341cCODMn/(mg/L)7.786±3.6939.653±12.213TN/(mg/L)1.654±1.0791.555±0.802NO-3-N/(mg/L)0.055±0.0550.074±0.059NO-2-N/(mg/L)0.002±0.002a0.083±0.182bNH+4-N/(mg/L)0.448±0.612a0.786±0.348cTP/(mg/L)0.493±0.579a0.206±0.252bSD/m0.732±0.2780.613±0.258MP/(mg/L)5.982±2.579a3.781±3.666b
*表中上标字母相邻有统计学意义(P<0.05),字母相间有统计学意义(P<0.01).
3.3 湖水水质评价
比较五大连池各季节综合营养指数:夏季湖水的综合营养指数最高,春季次之,而秋季最低;2012年夏季及2013年春、夏季,5池综合营养状态指数均超过70. 比较两年间各池综合营养指数,5池最高,3池次之,其后为4池、2池,1池最低(图2).
4 讨论
4.1 五大连池水质现状
五大连池平均深度5~6 m,属浅水型,各池温差较小. 湖水偏碱性,金属离子含量较高,为碳酸碱度型[8-11],硬度介于软水及中硬水之间;总碱度偏高,有盐碱化趋势[14]. 随着温度、天气以及降水作用,湖泊水质会发生剧烈变化,同其他北方湖泊相似[15],不同采样点季节变化趋势不同.
五大连池各池之间虽然存在水量交换,但由于独特串珠结构,各池有相对的独立性. 由于水流较缓,中下游没有污染源,湖泊污染程度大体是按照水流方向逆向升高,这与一般湖沼、河流不同[16-17]. 夏季5池TP浓度、TN浓度、CODMn及无机氮浓度有明显升高,可能是因为该池北侧、东侧有耕地,而夏季大量的降水将土壤中氮、磷及其他化学物质带入水中;而春、秋季则无显著差别,各池其他指标差别不大.

图2 五大连池各季节(A)和各池(B)综合营养状态指数变化Fig.2 Trophic status index evaluation results of each season (A) and each pond(B) of Lake Wudalianchi
浮游植物是湖泊主要的初级生产者,其生物量在一定程度上反映了湖泊水质的现状[18-19],Chl.a是浮游植物细胞中重要组分,是衡量浮游生物现存量及环境检测的重要指标[20-21],2、3池浮游植物生物量、Chl.a浓度明显低于5池,而SD高于5池. 导致上述情况可能存在两个原因:一方面是磷、氮浓度差异所致,因为二者与水体生产力密切相关[22],5池氮、磷量远高于2、3池;另一方面与2、3池存在大量的捕食者有关,自1950s引入鲢、鳙后,其年产量一直在100~150 t左右,而最近几年,年产量已达到250 t左右.
4.230年前后湖水水质变化

4.3 五大连池湖水水质评价
观察年度综合营养状态指数,除5池外,其他各池2013年指数低于2012年. 湖泊的营养化程度与季节密切相关,春、夏季富营养化程度加强,秋季降低,这与春、夏季温度升高,藻类加速生长,降水增多,陆地氮、磷等营养源大量补充等因素有关[26-27]. 6次调查中,5池综合营养指数半数超过70,已接近重度富营养化临界范围.
综上所述,近几年的居民搬迁、退耕还湿等保护措施初见效果,随着外源营养物质的减少,五大连池水质已有好转趋势. 但5池水质状况堪忧,因此,整个湖泊水质恢复需要长期过程.
[1]Li Xiaoping ed. Limnology. Beijing: Science Press, 2012: 9(in Chinese). [李小平. 湖泊学. 北京:科学出版社, 2012: 9.]
[2]Zhang Juemin. The fishery resources in Heilongjiang province. Mudanjiang: Heilongjiang Korean National Press, 1985: 161-182(in Chinese).[张觉民. 黑龙江省渔业资源. 牡丹江: 黑龙江朝鲜民族出版社, 1985: 161-182.]
[3]Yu Hongxue, Hao Linian. The physicochemical characteristics of natural mineral water and observation on annual changes in Wudalianchi Lake.TheResearchofLandandNaturalResources, 1982, (1): 61-64(in Chinese). [于洪学, 郝立年. 五大连池天然矿泉主要理化特点及其常年变化规律的观测. 国土与自然资源研究, 1982, (1): 61-64.]
[4]Wang Hongxing. Study on water environment in Wudalianchi Lake scenic area.HeilongjiangGeology, 1996, 7(4): 34-42(in Chinese). [王红星. 五大连池风景名胜区水环境研究. 黑龙江地质, 1996, 7(4): 34-42.]
[5]Kong Lingjun. Species distribution of phosphorus in water of Wudalianchi in winter.EnvironmentalScienceandManagement, 2011, 36(3): 123-126(in Chinese with English abstract). [孔令军. 五大连池冬季水体中磷的分布特征. 环境科学与管理, 2011, 36(3): 123-126.]
[6]Kong Lingjun. Research on distributing trend of nitrogen in water body of Wudalianchi.HeilongjiangEnvironmentalJournal, 2011, (1): 95-97(in Chinese with English abstract). [孔令军. 五大连池水体中氮素分布及规律的初步研究.黑龙江环境通报, 2011, (1): 95-97.]
[7]Dong Tielin, Zhang Shumin, Jin Kaizhong. The water sources and its use of Wudalianchi scenic spot.ChineseJournalofConvalescentMedicine, 1995, 4(3): 1-4(in Chinese with English abstract).[董铁林, 张树民, 金凯忠. 五大连池风景名胜区的水资源及利用.中国疗养医学,1995, 4(3): 1-4.]
[8]Yang Chen, Wei Xiaoxue, Pan Hongetal. Ecological environment evaluation of natural springs in Wudalianchi.EnvironmentalScienceandManagement, 2012, 37(10): 162-164(in Chinese with English abstract).[杨臣, 魏晓雪, 潘虹等. 五大连池地区天然矿泉生态环境评价. 环境科学与管理, 2012, 37(10): 162-164.]
[9]Bai Xue, Xu Qigong, Zhao Yue. Distribution of microorganisms correlated with N and P metabolism in the Wudalianchi water body.ResearchofEnvironmentalScience, 2012, 25(1): 51-57(in Chinese with English abstract). [白雪, 许其功, 赵越等. 五大连池水体氮和磷代谢相关的微生物类群分异特性. 环境科学研究, 2012, 25(1): 51-57.]
[10]Han Jianchao, Zhang Haiyan, Yang Yuesuoetal. Hydrogeochemistry evidence of groundwater circulation features in Yaowangshan, Wudalianchi.WaterSavingIrrigation, 2012, (8): 23-26, 30(in Chinese with English abstract).[韩建超, 张海燕, 杨悦锁等. 五大连池药泉山地下水循环特征的水化学证据. 节水灌溉, 2012, (8): 23-26, 30.]
[11]Wang Jinghua, Xie Zhenhua, Yang Chenetal. Health risk assessment of Mn and Fe in the natural carbonated cold mineral water of Wudalianchi.JournalofGreenScienceandTechnology, 2012, (8): 127-129(in Chinese with English abstract).[王菁华, 谢振华, 杨臣等. 五大连池重碳酸矿泉水中Mn 、Ni离子的健康风险评价. 绿色科技, 2012, (8): 127-129.]
[12]Pang Ke, Yao Jinxian, Wang Haoetal. Community structure characteristics of phytoplankton in Argun River drainage area in autumn.ActaEcologicaSinica, 2011, 31(12): 3391-3398(in Chinese with English abstract).[庞科, 姚锦仙, 王昊等. 额尔古纳河流域秋季浮游植物群落结构特征. 生态学报, 2011, 31(12): 3391-3398.]
[13]Wang Mingcui, Liu Xueqin, Zhang Jianhui. Evaluate method and classification standard on lake eutrophication.EnvironmentalMonitoringinChina, 2002, 18(5): 47-49(in Chinese with English abstract). [王明翠, 刘雪芹, 张建辉. 湖泊富营养化评价方法及分级标准. 中国环境监测, 2002, 18(5): 47-49.]
[14]Zhang Yu, Wang Hongbin, He Jiangetal. Investigation of water quality in the Dalinor Lake in inner Mongolia.FisheriesScience, 2008, 28(12): 671-673(in Chinese with English abstract). [张玉, 王洪滨, 何江等. 内蒙古达里诺尔湖水质现状调查. 水产科学, 2008, 28(12): 671-673.]
[15]Xie Guijuan, Zhang Jianping,Tang Xiangmingetal. Spatio-temporal heterogeneity of water quality(2010-2011) and succession patterns in Lake Bosten during the past 50 years.JLakeSci, 2011, 23(6): 837-846(in Chinese with English abstract). DOI: 10.18307/2011.0603.[谢贵娟, 张建平, 汤祥明等. 博斯腾湖水质现状(2010-2011 年)及近50 年来演变趋势. 湖泊科学, 2011, 23(6): 837-846.]
[16]Chen Jingsheng ed. Principle of river water quality and river water quality in China. Beijing: Science Press, 2006: 69(in Chinese).[陈静生. 河流水质原理及中国河流水质. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006: 69.]
[17]Ji Dongqing, Wen Ya, Wei Jianbingetal. Relationships between landscape spatial characteristics and surface water quality in the Liuxi River watershed.ActaEcologicaSinica, 2015, 35(2): 246-253(in Chinese with English abstract).[吉冬青, 文雅, 魏建兵等. 流溪河流域景观空间特征与河流水质的关联分析. 生态学报, 2015, 35(2): 246-253.]
[18]Whitton BA. Use of algae for monitoring rivers.JournalofAppliedPhycology, 1991, 3(3): 287-287.
[19]Beisner BE, Longhi ML. Spatial overlap in lake phytoplankton: Relations with environmental factors and consequences for diversity.LimnologyandOceanography, 2013, 58(4): 1419-1430.
[20]Yu Haiyan, Zhou Bin, Hu Zunyingetal. Study on correlation between chlorophyll a and algal density of biological monitoring.EnvironmentalMonitoringinChina, 2009, 25(6): 40-43(in Chinese with English abstract). [于海燕, 周斌, 胡尊英等. 生物监测中叶绿素a 浓度与藻类密度的关联性研究. 中国环境监测, 2009, 25(6): 40-43.]
[21]Du Shenglan, Huang Suiliang, Zang Changjuanetal. Correlation research between the indicators of phytoplankton standing stockⅠ: chlorophyll a and biomass.JournalofWaterResources&WaterEngineering, 2011, 22(1): 40-44(in Chinese with English abstract). 杜胜蓝, 黄岁樑, 臧常娟等. 浮游植物现存量表征指标间相关性研究: 叶绿素a与生物量. 水资源与水工程学报, 2011, 22(1): 40-44.
[22]Brönmark C, Hansson LA eds. The biology of lakes and ponds(Second Edition). Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2013: 26-32(in Chinese).[Brönmark C, Hansson LA. 湖泊与池塘生物学: 第二版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2013: 26-32.]
[23]Jin Xiangcan ed. Environment of lake in China (Vol. 1). Beijing: Ocean Press, 1996: 5(in Chinese).[金相灿. 中国湖泊环境(第1册). 北京: 海洋出版社, 1996: 5.]
[24]Gui Zhifan, Xue Bin,Yao Shuchunetal. Environmental changes of Wudalianchi lake inferred from lake sediments in the past century.QuaternarySciences, 2011, 31(3): 544-553(in Chinese with English abstract).[桂智凡, 薛滨, 姚书春等. 黑龙江省五大连池近百年环境变化研究.第四纪研究, 2011, 31(3): 544-553.]
[25]He Zhihui. Primary productivity of lake and reservoir and energy conversion efficiency in China.FisheriesScience, 1987,6(1): 24-30(in Chinese with English abstract).[何志辉. 中国湖泊水库的初级生产力及其能量转化效率. 水产科学, 1987, 6(1): 24-30.]
[26]Shen Xiaofei, Ma Wei, Luo Jiacuietal. Evaluation method of nutritional status and its applicability analysis in lakes and reservoirs.JournalofChinaInstituteofWaterResourcesandHydropowerResearch, 2013, 11(1): 74-80(in Chinese with English abstract).[沈晓飞, 马巍, 罗佳翠等. 湖库营养状态评价方法及适用性分析. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 2013, 11(1): 74-80.]
[27]Lu Bilin, Yan Pingchuan, Tian Xiaohaietal. Eutrophication and water characteristics of large and medium-sized reservoirs in Hubei Province.ResourcesandEnvironmentintheYangtzeBasin, 2012, 21(5): 634-640(in Chinese with English abstract). [卢碧林, 严平川, 田小海等. 湖北省主要大中型水库富营养状况及特征分析. 长江流域资源与环境, 2012, 21(5): 634-640.]
Status of water quality and succession changes in Lake Wudalianchi in the last 30 years
WANG Nianmin1, TANG Shizhan1, LI Zhe1, SUN Dajiang1, JI Feng2& HUA Zhenhe3
(1:HeilongjiangRiverFisheryResearchInstitute,ChineseAcademyofFisherySciences,Harbin150076,P.R.China) (2:YangtzeRiverFisheryResearchInstitute,ChineseAcademyofFisherySciences,Wuhan430223,P.R.China) (3:RiheFisheryCo.Ltd.ofWudalianchi,Heihe164155,P.R.China)
As the second largest volcanic avalanche lake in China, Lake Wudalianchi is a representatively natural water body in high latitude region of China, which is a famous and multifunctional natural landscape. For studying the current situation of water quality (WQ) of lake, changes of WQ during the past 30 years and evaluating the eutrophic grade of the lake, we collected and studied 15 WQ indices on 11 sampling sites of Lake Wudalianchi in the spring, summer, autumn during 2012 and 2013. The results showed that, the WQ parameters of Lake Wudalianchi as shallow lake in the temperate continental monsoon climate zone change intensively in different areas and different seasons and years. The plankton biomass and chlorophyll-a concentration from the Second and Third Ponds are lower than those of the Fifth Pond, probably as the results of reduction of phosphorus, nitrogen and incremental fishery production in the formers. Comparison with the lake WQ indices during 1980s, mass of phytoplankton, total phosphorus and total nitrogen concentrations decrease significantly now, noting that WQ may be tending to better status. However trophic level index of Fifth Pond is exceeding 70 with the 3 times of the 1980s, which is adjacent to severe eutrophication status. The environmental safeguards of Lake Wudalianchi such as relocation of residents, returning farmland to wetland are effective at beginning phase, but individual part of lake remains a bad WQ suggesting a long-term treatment required.
Water quality; eutrophication; Lake Wudalianchi
*黑龙江水产研究所中央级公益性科研院所基本科研业务费专项(HSY201201)、国家科技支撑计划项目(2012BAD25B10-05)和黑龙江省冷水性鱼类种质资源及增养殖重点开放实验室项目(201201)联合资助. 2015-06-30收稿;2015-12-25收修改稿. 王念民(1972~),男,硕士,助理研究员; E-mail: wnm0529@163.com.
