国外个人信息管理研究综述*
2016-09-23杨佳琪陈思言高志辉邓胜利武汉大学信息管理学院武汉430072
杨佳琪,陈思言,高志辉,邓胜利(武汉大学信息管理学院,武汉 430072)
国外个人信息管理研究综述*
杨佳琪,陈思言,高志辉,邓胜利
(武汉大学信息管理学院,武汉 430072)
个人信息管理(PIM)可反映个人的信息管理能力与信息素养。随着互联网的发展,个人信息量急剧增长,管理难度进一步加大,为提高工作效率,个人信息管理迫在眉睫。通过对2007—2016年的国外PIM文献调研,发现按照生活、工作、学术等不同情境,可从社交媒体、医疗健康、教育等视角对PIM进行研究。PIM的研究方法以问卷调查、访谈、文献调研以及案例分析为主;随着互联网技术与计算机技术的发展,PIM工具研究表现出阶段性特征。未来的PIM研究可重点关注以下内容:不同主体在PIM行为上的差异,PIM的实证研究,社交媒体上的PIM研究。
个人信息管理;社交媒体;研究综述
大量个人信息的产生,给用户工作和生活带来便利的同时,也带来信息过载和工作效率低下的问题。个人设备的多样化使用户进行跨平台信息管理的需求增大,因此,个人信息管理成为当前研究热点。
1988年,Lansdale首次提出“Personal Information Management”(PIM)一词,指出PIM是个人为完成相关工作内容而进行的一系列行为活动,包括获取、组织、保存、检索和使用信息项目(如纸质与电子文件、电子邮件等)[1]。随着互联网的发展,传统意义上的个人信息已经从个人图书、电话簿、信件等具体而少量的物品,进一步延伸到计算机与网络,尤其是社交媒体等服务类软件及网站。
1 数据来源与分析
本文用“personal information management”作为检索词,采用主题检索方式,在WOS所有数据库(含SCIE、SSCI、A&HCI、CPCI数据库)中进行检索,时间限定为2007—2016年。经主题筛选并对检索获取的英文文献的引文进行追溯来补充漏选文献,最终获得184篇文献。对纳入的文献进行领域分析,发现计算机科学发文量最多,占25%;其次是信息情报科学,占23%;健康医疗科学占13%。个人信息管理涉及领域很广,包括企业经济学、运筹学与管理科学、医学、社会学、心理学等。
2 PIM的内涵及主题分析
2.1 PIM的内涵
在学术研究中,PIM的定义并不统一。表1汇集了PIM的不同定义,综合考虑定义的完整性与系统性,并结合研究的需要,本文倾向于2009年PIM Workshop会议上对PIM的定义。
2.2 PIM的主题分析
2.2.1 PIM的研究视角
PIM的研究角度具有多样化特点。研究视角多样化的转变,能够让各行各业更加便捷地管理与利用信息。国外初期注重PIM的技术及优化,后期转移至社交媒体、在线教育、医疗健康等领域。而国内的PIM研究相比国外仍处于起步阶段,早期主要是对国外研究的总结和借鉴,随后不断深化,主要从移动终端的PIM工具角度出发,以提高个人信息管理的效率为主,除此之外还有从信息行为视角出发的PIM研究。
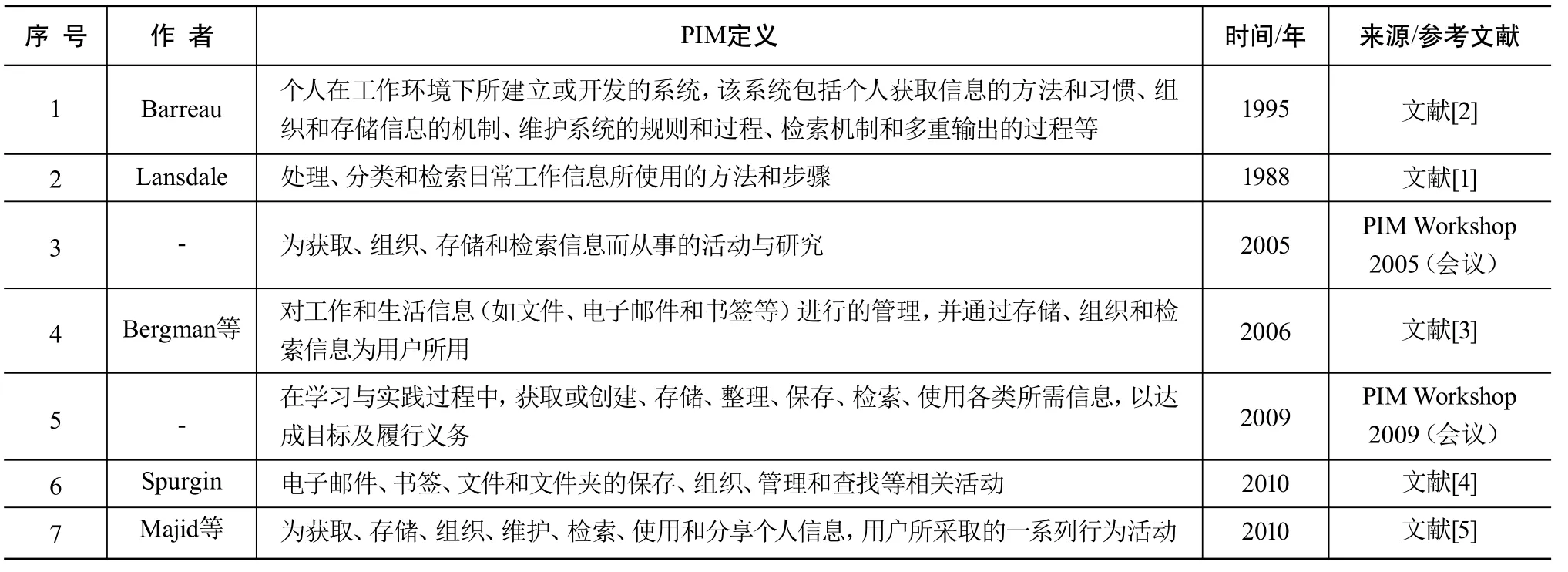
表1 PIM定义表
(1)社交媒体视角
随着社交媒体的兴起和快速发展,人们更加频繁地使用社交媒体浏览和发布信息,社交网站已成为人们获取信息的重要来源[6]。由于社交媒体上记录的信息具有情境性、真实性的特性,且具有时间轴功能,使信息回溯更加方便,这也是使用社交媒体进行个人信息管理的一个优点。
为了更有效地管理社交媒体上的个人信息,可以采用添加社会化标签的方法,Heckner等的研究显示,人们在使用youtube时,添加社会标签可以有效地帮助个人信息管理[7]。
随着社交媒体上个人信息的逐渐增多,隐私泄露以及信息安全问题也随之而来。个人信息在电脑PC端与移动设备间通过无线网络的传递非常脆弱,极易受到攻击[8],为了更好地保护个人信息,需要加强个人信息获取权限的认证,一些学者提出构建需要身份认证的系统,来保护个人信息不被泄漏[9-10]。
(2)在线教育视角
伴随着网络发展,MOOC等在线课程兴起,负责在线课程的员工如何管理相关电子资源(如电子邮件、电脑桌面、网上信息、学习管理系统等)的问题引起重视。不论是对教师的个人信息管理,还是对学生的PIM工具使用情况的调研结果,都显示个人信息管理会在一定程度上影响教学结果[11-12]。2014年Yeo等发现,使用个人博客的学生,其学术能力与自我效力得到明显提升。博客的个性化设计使他们更易收集和使用所需信息,从而创造了更有用的学习环境[13]。2014年,Jacques定义了大学生个人信息管理能力的三个维度:感知PIM工具优点和缺陷的能力、根据PIM工具的优缺点来选择适宜PIM活动的能力、对PIM活动的理解能力[14]。
(3)医疗健康视角
医疗健康领域主要关注点在老年人的PIM,如何让老人方便有效地进行在线个人健康信息管理是研究重点。为此,Turner等提出设计一个能够提供个人健康信息管理的入口网站[15]。Piras等认为,对病人的个人健康信息进行跟踪、分析、提取规律,病人可像医生那样了解自己的病情甚至对病情做出预测[16]。
(4)其他
个人信息管理还从行为偏好、个人隐私、互联网服务、搜索引擎的导航优化等方面进行研究[5,17-18]。与信息环境相关的研究视角有信息基础设施、个人信息环境、情景化程序等[19-21]。
2.2.2 PIM的情境研究
个人信息的管理,因为管理情境不同而有不同的管理方式,相较于国内重点关注学术情境下的研究,国外的研究更加全面,有针对一般用户的PIM研究,也有针对公司员工、学术工作者(学生、教师、图书馆员等)的研究,涉及个人工作、学术、生活三个方面。
(1)个人工作信息管理研究
公司员工的个人信息的管理大致分为以下四个过程:①发现、获取信息;②保存、组织和管理信息;③交流和分享信息;④再发现、使用和应用信息。这四个过程相互作用,必不可少。而公司的其他外部条件,如公司的相关规定、安排有信息管理知识的专业人才、制定有关于改善员工信息管理能力的政策等,都可以促进公司员工的PIM效率[6]。根据以上理论,可以构建出公司中个人信息管理的作用机制模型(见图1)。
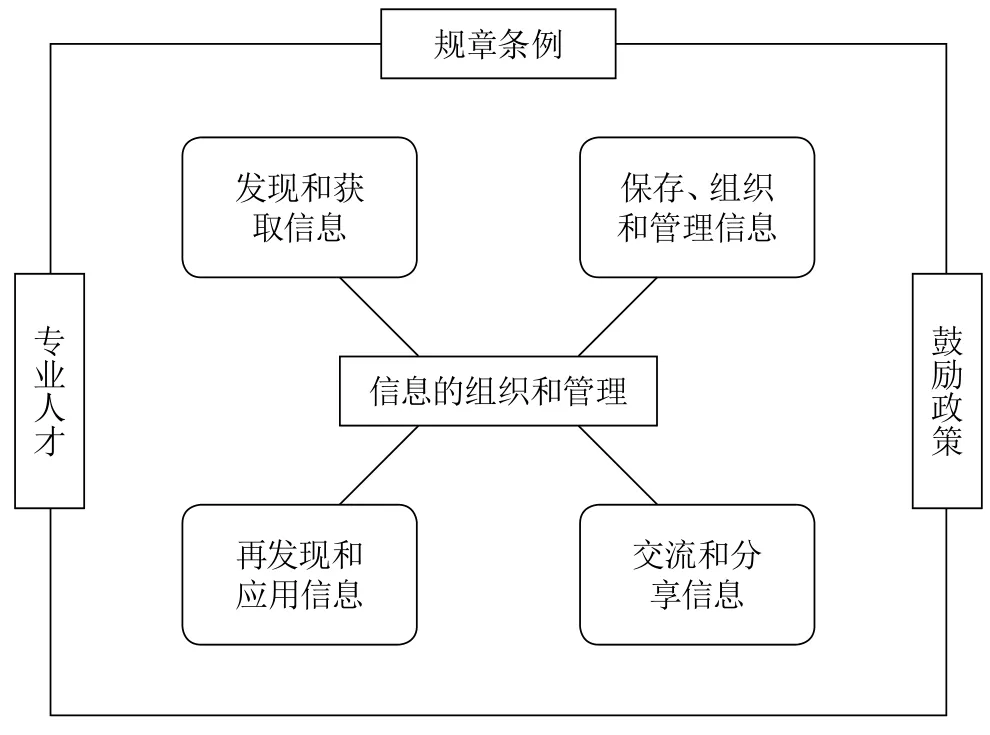
图1 公司中个人信息管理的作用机制
此外,公司中的个人信息管理与普通的个人信息管理相比,有其特殊性。比如,公司员工的邮件系统因为处理的信息种类更加多样,要求更多的操作,故需建立专门针对公司的邮件客户端,使员工能更高效地进行邮件的检索、分类和浏览[22]。而经常变换工作地点的员工则更应重视PIM,因为此时的PIM受到时间和空间的限制,要研究这种条件下信息的格式、维护、组织和存储,就需要设计符合这种工作性质的PIM工具[23]。
(2)个人学术信息管理研究
个人学术信息主要包括学术文章、网络课程、书籍等,研究对象分为教学工作者和学生两种。站在教学工作者的角度,国外文献主要研究负责在线课程的员工是怎样管理与课程相关的电子资源,包括电子邮件、电脑桌面、网上信息、学习管理系统这四个方面以及四个方面的交叉管理[11];此外,也有研究图书馆馆员应该如何帮助用户寻找学术信息以及个人学术信息的管理[24-25],图书馆员需要掌握PIM发展的最新动态、PIM的教学技巧等[26]。而在学生的角度,大学生在学习时,常需要搜集大量学术文章并进行科研创作,因此,学生学术信息管理的能力显得至关重要。Jacques从个人信息和知识管理的五个过程,即收集、组织、筛选、分享和创建进行研究[14];Huvila等研究了不同学科、不同性别、不同学位的学生在进行个人学术信息管理时的行为和习惯差异[27];Brückner等通过对泰国学生个人信息管理情况的研究,发现他们在撰写学术文章时,总是不能正确地引用,缺乏良好的管理引文的方式,因此推荐学校增加个人信息管理方面的相关课程[28]。
(3)个人生活信息管理研究
个人生活信息主要是指人们在生活当中产生的各种信息,例如邮件信息、文档信息、照片信息以及综合信息。在文档和照片方面,人们偏向于使用层级式的结构对文件进行整理以及搜索,而不是通过添加标签或使用文件搜索功能来进行文件管理[18]。Goncalves等人则持相反观点,认为人们在检索文件时是依靠文件的内容信息,因此可以建立文件的自传式介绍信息,用户可以据此进行检索[29]。而照片信息由于其图形的抽象性,比普通的信息管理更加困难,目前有学者研究了一种基于内容、概念和情境的在线个人照片管理系统,抽取照片简介中的特征词作为照片的标签,利用自动标签和元数据来标注、组织和检索照片[30]。还有学者考虑用户对于照片的情感因素,根据用户浏览照片的时间对情感分级,依此对照片进行分类[31]。此外,由于信息媒介的多样化,为方便处理多种类型的信息,制定各种不同信息类型的统一标准和统一处理方式显得至关重要,也引起了广泛研究[11, 32]。
3 PIM的研究方法与工具
3.1 PIM研究方法
(1)问卷调查法
问卷调查成本相对低廉、覆盖面较广,可以了解到用户进行个人信息管理时的心理、行为,包括经常使用的工具、数据管理类型、信息管理的频率等[33],其问卷设计结构大多以PIM管理过程为基础[12]。问卷法还可以帮助了解调查者对自身PIM能力的评价,借以衡量个人的信息素养水平[34-35]。
(2)访谈法
访谈法能够细致深入地了解被调查者的行为和心理,充分了解人们的PIM过程以及如何利用工具来组织个人信息[36]。对不同人群的PIM研究,都能通过访谈了解被调查者管理相关个人信息时的具体操作,包括在Windows浏览器上的操作、搜索辅助引擎上的操作等[37]。访谈法评估被调查者的PIM能力,如Jacques通过让用户描述某项具体PIM活动的优缺点,了解用户对这项PIM活动的实际掌握情况[14]。
(3)文献研究法
在理论研究方面,学者对美国研究图书馆协会的信息素养标准进行研究,探析PIM与信息素养之间的关系[38]。Fourie研究信息行为理论,发现在协同信息行为中,个人信息管理能力起着重要作用[39]。
在PIM工具的设计方面,Bai从CSSCI中检索出相关文献并研究,设计出了个人信息保护和利用的概念模型;Chatti基于个人知识管理,构建个人知识网络[40];Carrino通过建立一个momoria-mea的框架开发PIM工具[41];Riss通过研究用户的信息分享行为,为知识工作者设计了以主题为导向的个人信息整合方法[42];Kearns设计了个人信息管理模型来保护个人信息[11]。
(4)案例研究法
在进行案例研究时,研究者往往通过访谈、网络调查的方法,针对不同的对象来研究,如企业、政府等[43]。Huvila以研究生、艺术家为对象,研究其进行学术文章管理、档案管理和个人藏品管理的方法[44]。
(5)其他
除了以上方法外,国外研究者还利用了焦点小组、实地观察、德尔菲法、民族志法等其他多种方法进行研究,每种方法都各有优劣,在进行PIM研究时,常常是多种方法的相互配合使用[11,45,46]。
3.2 PIM工具的进展
根据2007—2016年的国外研究文献,发现PIM工具的发展具有明显的阶段性。2007—2011年,有关语义、本体技术应用于PIM的研究最多,具有代表性的是利用语义关系构建语义桌面,辅助用户搜索PC端的个人信息;2012—2016年的研究倾向于解决如信息过载、信息碎片等实际问题,帮助用户实现更高效率的信息管理,以及不同领域的PIM应用,如医疗领域等。
2007年,Elsweiler提出,支持人类记忆特征的PIM工具的构建可以提高用户再检索性能[37]。Maus设计了Nepomuk语义桌面,提出了用集成于Nepomuk的上下文感知任务管理系统支持知识密集型任务,其中上下文感知系统是基于用户观察、敏捷任务模型、自动任务预测以及主动提供相关信息项的个人知识空间[47]。Franz等则将X-COSIM语义桌面与普通桌面进行对比,发现语义桌面性能更高[48]。除此之外,Iverson根据web 2.0环境下的个人社会化信息管理的相关原则,设计了一个开源的web应用程序OPNTAG,该程序允许用户管理自己的个人信息与个人空间,支持各种虚拟社区的创建,采用基于标记的组织模型与内在元数据,支持更好的搜索与导航功能[49]。
2012年,研究的重点在如何设计系统帮助用户实现更高效率的信息管理。Zhou等设计的个人信息管理代理器原型PIMA,支持自然语言界面与应用程序的集成,能提高信息感知效率[50]。为了提高用户检索的准确度,Wang等提出一种多维搜索的方法,该方法通过给结构、元数据、关键字三个维度分别打分、综合排序,来有效地识别匹配多维查询最相关的文件[51]。
随着web 2.0的出现与发展,信息过载与碎片化问题愈加严重,为了解决问题,研究人员提出了基于语义或基于任务的个人信息管理范式。Trullemans等在两种范式的基础上,结合人类记忆方式,构建一个物体-概念-情境(Object-Concept-Context,OC2)概念模型,设想了一个跨媒介方法,使物理信息与用户的个人数字信息空间整合,实现了信息之间语义上的联系,从概念上获取信息[52]。Liu设计了一个网上系统,实现用户对通讯簿、邮件、个人资产、家庭消费、日程、附件等多种信息的管理,并利用应用程序服务WCF(Windows Communication Foundation)模型与微软银光技术,实现用户方便地远程登陆[53]。
另一随之出现的问题是信息泄露,为保护个人信息,金亨坤设计的模型将个人信息与普通信息区分,当企业等收集网上用户数据时,可以避开隐私信息[54]。Liu设计了一个去中心化的个人信息移动管理系统,通过算法与机制实现用户信息的删除,在一定程度上保护了个人信息[9]。
在医疗领域,使用信息管理工具以实现个人健康管理也是一大热点。2011年,Lee就对模型e-P.O.Box的发展进行了分析,并探讨了它在个人健康信息管理中的应用[55]。2013年,MOON等提出建立一个U-health系统,根据用户携带的传感器的数据,使用Zigbee模型收集数据并转化为NFC模型,并设计认证系统确保从NFC传递的数据安全性,使用数据库存储信息,用户则可以根据这些数据进行自我健康管理[56]。Wolff则设计了PHI-SQS系统模型,在对11款定量工具比较的基础上,采用合理的定量指标,引导用户使用SQS系统,并有效地进行自我健康管理的评价[57]。
4 国外PIM研究的特点
综合以上分析,可以看出国外PIM研究具有以下特点。
(1)研究主体细分化。国外对于PIM的研究越来越注重将主体进行分类后再进行研究,专注于具有区别性质的一小部分群体,如研究生、教师、图书馆员、工作环境不固定的员工等。此外,国外的研究还将信息进行分类,针对某一种信息类型进行PIM的研究,如研究个人照片管理、个人邮件管理、个人学术文章管理等。
(2)研究方法多样化。研究方法上多采用定性和定量研究相结合。对于PIM使用行为的研究,多采用问卷调查、访谈、案例研究等方法;对于PIM的框架、模型构建,多采用文献研究的方法。此外,还注重多种方法的相互结合,根据不同调查方法的特点应用于研究的不同阶段,使研究过程更加高效,研究结果更加可靠。
(3)研究内容理论与实践相结合。国外对PIM的理论研究,多集中在PIM框架和模型的构建、技术的改进上,对于PIM实证的研究,则集中在PIM的过程,如研究个体的PIM行为习惯、处理方法等。
5 总结与展望
本文从研究视角、研究情境、研究方法和工具及研究特点这几个方面对国外的PIM研究进行了梳理分析。虽然国外学者在PIM领域的研究已经有了很多成果,但是该领域的研究仍然不够完善,如目前的研究关注了不同领域人员的PIM,却忽略了主体的差异对PIM的影响;关注了PIM工具的设计,却大都只停留于理论阶段,没有实践验证;而在研究方法上,样本容量还较小,选取的样本缺乏代表性,此外,对于社交媒体上PIM的研究,还处于起步阶段。
根据当前国外的研究情况来看,未来可以从以下几个方面展开研究。
(1)关注不同的主体在PIM行为上的差异,研究差异背后的影响因素,如研究拥有不同的学术和工作背景的人在进行PIM活动时的行为习惯差异,探析这种PIM行为特点与主体背景间的深层联系。
(2)注重PIM的实证研究,如在PIM技术、模型、工具改善后,PIM将会有怎样的改进等。从实证角度证明改善后的技术确实可以提高PIM的效率,更具有说服性。
(3)社交媒体如今已成为沟通和获取资源不可或缺的工具,人们花费在社交媒体上的时间也越来越长,因此,研究社交媒体上的PIM是一个新的热点,对于社交媒体上的PIM研究,应充分结合社交媒体的特点,进行优缺点的比较,并分析如何基于社交媒体对PIM进行改进。
[1] LANSDALE M W.The Psychology of personal information management[J]. Applied Ergonomics,1988,19(1):55-66.
[2] BARREAU D K.Context as a factor in personal information management systems[J]. Journal of the American Society for Information Science,1995, 46(5):327-339.
[3] BERGMAN O,BEYTH-MAROM R,NACHMIAS R.The project fragmentation problem in personal information management[C]//CHI 2006 Proceeding·Personal Information Management Montreal,Quebec: 2006:271-274.
[4] SPURGIN K M.The-making approach and the study of personal information management[J].proceedings of the pim,2010:102-104.
[5] MAJID S,SAN M M,TUN S T N,et al.Using internet services for personal information management[C]//Technological Convergence and Social Networks in Information Management.Ankara: Springer Berlin Heidelberg,2010:110-119.
[6] CHAUDHRY A S,REHMAN S U,AL-SUGHAIR L. Personal information management practices in the kuwaiticorporate sector[J]. Malaysian Journal of Library & Information Science, 2015,20(3):27-42.
[7] HECKNER M,HEILEMANN M,WOLFF C. Personal information management vs.resource sharing: towards a model of information behavior in social tagging systems[C]//ICWSM,Proceedings of the 3th International Conference,California.2009:42-49.
[8] GEORGESCU M,POPESCUL D.Social media-a new challenge for the personal information and knowledge management[C]//Social Media in Academia: Research and Teaching, International Conference,June 6-9,2013,Proceedings of SMART,Bacău,România.2013:1-8.
[9] LIU Z H,YUAN Q,LIU L.Decentralized mobile SNS architecture and its personal information management mechanism[J].China Communications, 2016,13(2):189-199.
[10] MORIN J H. Towards socially-responsible management of personal information in social networks[C]//Recent Trends and Developments inSocial Software.Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 2010,6045:108-115.
[11] KEARNS L R,FREY B A,TOMER C. A study of personal information management strategies for online faculty[J].Journal of Asynchronous Learning Networks, 2014,18(1):17.
[12] DIEKEMA A R,OLSEN M W.Teacher personal information management (PIM) practices:finding, keeping, and refinding information[J]. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology,2014,65(11):2261-2277.
[13] YEO H I,LEE Y L.Exploring new potentials of blogs for learning: can children use blogs for personal information management (PIM)?[J]. British Journal of Educational Technology,2014,45(5):916-925.
[14] JACQUES J,FASTREZ P.Personal information management competences: a case study of future college students[C]//International Conference HCI,June 22-27,2014, Human Interface and the Management of Information. Switzerland:Springer International Publishing,2014:320-331.
[15] TURNER A,OSTERHAGE K,HARTZLER A,et al.Use of patient portals for personal health information management:the older adult perspective[J]. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics,2015:1234-1241.
[16] PIRAS E M,ZANUTTO A."One day it will be you who tells us doctors what to do!".exploring the "Personal" of PHR in paediatric diabetes management [J].Information Technology and People,2014,27(4):421-439.
[17] COLOMBO P,FERRARI E.Privacy aware access control for big data: a research roadmap[J].Big Data Research,2015,2(4):145-154.
[18] BERQMAN O,BEYTH-MAROM R,GRADOVITCH N,et al. Improved search engines and navigation preferencein personal information management[J].Acm Transactions on Information Systems,2008,26(4):3537-3551.
[19] GREBNER O.Using personal information management infrastructures to facilitate user-generated services for personal use[C]//International Workshops,November 23-27,2009,Service-Oriented Computing, Berlin: Springer-Verlag,2009:560-569.
[20] MOHAMMAD A F.Ubiquitousdata management in a personal information environment[M]// Innovations in Computing Sciences and Software Engineering,[S.1.]: Springer publishing,2010.
[21] DENGEL A,ADRIAN B.Helping people remember:coactive assistance for personal information management on a semantic desktop[C]// First International Joint Conference,October 6-8,2009,Knowledge Discovery,Knowledge Engineeringand Knowledge Management,Berlin: Springer-Verlag,2011,128:3-16.
[22] NUSSER S,CERRUTI J A,WILCOX E,et al.Enabling efficient orienteering behavior in webmail clients[C]//Proceedings of the 20th Annual ACM Symposium,October 7-10, 2007,User Interface Software and Technology,[S.1.]:2007.
[23] THOMSON L,JARRAHI M.Contextualising information practices and personal information management in mobile work[J].Information Research-An International Electronic Journal, 2014,19(ICSP44).
[24] CUSHING A L. "If it computes,patronshave brought it in": personal information management and personal echnology assistance in public libraries[J].Library and Information Science Research, 2016,38(1):81-88.
[25] KIM J, KIM D, KANG S, et al. Database using personal information management system[J].International Journal of Fuzzy Logic & Intelligent Systems, 2008,8(4):260-263.
[26] FOURIE I. Librarians alert: how can we exploit what is happening with personal information management(PIM),reference management and related Issues?[J].Library Hi Tech, 2011,29(3):550-556.
[27] HUVILA I,ERIKSEN J,HAUSNER E,et al.Continuum thinking and the contexts of personal information management[J].International journal of electronic information research, 2014,19(1):604.
[28] BRÜCKNER M,TETIWAT O. Evaluation of e-Learning readiness:a sudy of informational behavior of university students[J]. Research journal Polibits, 2010.
[29] GONCALVES D,GUERREIRO T,MARIN R,et al.Using autobiographic information to retrieve real and electronic documents[C]//Human Interface and the Management of Information,Berlin:Springer-Verlag,2007,4557:427-436.
[30] CAMBERA E, HUSSAIN A.Senticalbum:content-,concept-,and context-based online personal photo management system[J]. Cognative Computation, 2012,4(4):477-496.
[31] BAŽICAB,VlLADUŠIČD,MLADENĆI D. Shoebox:anatural way of organizing pictures according to user' s affinities[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2011,6763:519-524.
[32] WARREN P.Personal information management:the case for an evolutionary approach[J]. Interacting with Computers, 2014,26(3):208-237.
[33] HELVOORT A A J V. A Questionnaire for the institutional assessment of personal information management[J]. Communications in Computer & Information Science, 2012,317:138-149.
[34] ŚWIGOŃ M. Personal knowledge and information management behaviour in the light of the comparative studies among Polish and German students[J].Information Research, 2014,19(4).
[35] ŚWIGOŃ MM.Personal knowledge and information ianagementconception and exemplification[J]. Journal of Information Science,2013,39(6):832-845.
[36] BRUCE H,WENNING A,JONES E, et al.Seeking an ideal solution to the management of personal information collections[J]. InformationResearch, 2011,16(1):95-116.
[37] ELSWEILER D,RUTHVEN I, JONESC.Towards memory supporting personal information management tools[J]. Journal of the American Society for Information Science & Technology, 2007,58(7):924-946.
[38] STEWART K N, BASIC J.Information encountering and management in information literacy instruction of undergraduate,students[J]. International Journal of Information Management, 2014,34(2):74-79.
[39] FOURIE I. Collaboration and personal information management (PIM)[J]. Library Hi Tech, 2012,30(1):186-193.
[40] CHATTI M A. Knowledge management: a personal knowledge network perspective[J]. Journal of Knowledge Management, 2012,16(16):829-844. [41] CARRINO F,SOKHN M,CALVÉ A L,et al. Personal information management based on semantic technologies[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence & Humanized Computing, 2013,4(3):401-407.
[42] RISS U V.TAPIR:wiki-basedtask and personal information management supporting subjective process management[C]//4th International Conference,April 4-5, 2012,S-BPM ONE-Education and Industrial Developments,Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 2012.
[43] MÄKINEN S.Mobile work and its challenges to personal and collective information management[J]. Information Research, 2012,17(3):741-755.
[44] HUVILA I, ERIKSEN J, HÄUSNER E M, et al.Continuum thinking and the contexts of personal information management[J]. Information Research, 2014,19(1):21.
[45] LUCERO R J,SHEEHAN B,YEN P Y,et al. Developing self-management tools with vulnerable populations for use in personal health information management systems.[J]. Nursing informatics, 2012:248.
[46] MIZRACHI D, BATES M J. Undergraduates' personal academic information management and the consideration of time and taskurgency[J]. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology,2013,64(8):1590-1607.
[47] MAUS H, SCHWARZ S, HAAS J, et al. CONTASK: context-sensitive task assistance in the Semantic desktop[J]. Enterprise Information Systems, 2010,73:177-192.
[48] FRANZ T, ANSGAR S, STAAB S. Are semantic desktops better?: summative evaluation comparing a semantic against a conventional desktop[C]//The 5th international conference,2009,International Conference on Knowledge Capture, 2009:1-8.
[49] IVERSON L, RAZAXI M N, MIRZAEE V. Personal and social information management with OPNTAG[C]//ICEIS 2008 - Proceedings of the 10th International Conference, June 12-16, 2008,Enterprise Information Systems,2014:1-9.
[50] ZHOU L, MOHAMMED A S, ZHANG D. Mobile personal information management agent: supporting natural language interface and application integration[J]. Information Processing & Management, 2012,48(1):23-31.
[51] WANG W, PEERY C, MARINA A, et al. Efficient multidimensional fuzzy search for personal information management systems[J].IEEE Transactions on Knowledge & Data Engineering, 2012,24(9):1584-1597.
[52] TRULLEMANS S, SIGNER B.Towards a conceptual framework and metamodel forcontext-aware personal cross-media information management systems[C]//33rd International Conference,October27-29,Atlanta,GA,USA.Conceptual Modeling,Switzerland:Springer International Publishing,2014:313-320.
[53] LIU C, ZHU M L. Design and implementation of personal information management system in internet[C]//International Conference on Information, Business and Education Technology(ICIBET 2013),[S.1.]: Atlantis press,2013:624-627.
[54] HYOUNG-GYE K,HO-MIN,JUNG-SOOK K,et al. A model of authority management for the protection of personal information in OLAP[J].Journal of Information Technology Services, 2014,13(2):162-172.
[55] LEE J S,SUZUKI H,TAIRA N,et al.The development of a prototype e-P.O. box and its application to personal health information management system[C]//International conference on health informatics,January 26-29,2011,Rome, Italy,2011.
[56] MOON Y J, PARK J H, SONG W C, et al. NFC-based personal information management for u-health[C]// IEEE Icce-China Workshop, 2013.
[57] WOLFF C.Personal information management vs.resource sharing:towards a model of information behavior in social tagging systems[EB/OL].(2009-06-24)[2016-06-19].http://videolectures.net/icwsm09_wolff_pimrs/.
杨佳琪,女,1994年生,本科生,研究方向:网络用户信息行为。
陈思言,女,1996年生,本科生,研究方向:网络用户信息行为。
高志辉,女,1995年生,本科生,研究方向:网络用户信息行为。
邓胜利,男,1979年生,博士,教授,研究方向:网络用户信息行为,通讯作者,E-mail:victorydc@sina.com。
Research Review on Personal Information Management in Foreign Countries
YANG JiaQi, CHEN SiYan, GAO ZhiHui, DENG ShengLi
(School of Information Management, WuHan University, WuHan 430072, China)
Personal information management eflects both the competence of one' s information management and information literacy. With the development of the Internet, the personal information is mounting and thus the management of it is more difficult. To improve the efficiency of work, it is necessary for information management. Focusing on western countries' related literatures between 2007 and 2016, this essay has analyzed the research progress of PIM. The literature review has studied PIM from four aspects. Researchers has studied PIM from social media, medical health, education and some other perspectives. As for the research situation, it can be classified as academic, work and life situations. In the research of PIM' s tools, scholars have designed the systems and models to remedy defects of the present PIM. Today the literature over the PIM on social media is little. In the end, the focuses of future study are as follows: the differences on the PIM behaviors of different subjects;the time research of PIM; the research of PIM on social media.
Personal Information Management; Social Media;Research Review
G203
10.3772/j.issn.1673-2286.2016.6.010
* 本研究得到教育部人文社会科学重点研究基地重大项目“我国服务业信息化推进与保障机制研究”(编号:15JJD870001)和“武汉大学351人才计划项目”资助。
2016-05-30)
