北斗卫星导航系统
2016-09-20编者按
·编者按·
北斗卫星导航系统
·编者按·
2015年9月30日,第20颗北斗导航卫星发射升空。这是我国自主建设的北斗卫星导航系统自 2012年完成亚太区域服务开通之后,成功发射的第4颗新一代导航卫星。
中国北斗卫星导航系统(BeiDou Navigation Satellite System,BDS)是中国自行研制的全球卫星导航系统。是继美国全球定位系统(GPS)、俄罗斯格洛纳斯卫星导航系统(GLONASS)之后第三个投入运行的卫星导航系统。北斗卫星导航系统由空间段、地面段和用户段三部分组成,可在全球范围内全天候、全天时为各类用户提供高精度、高可靠定位、导航、授时服务,并具短报文通信能力,已经初步具备区域导航、定位和授时能力,定位精度10 m,测速精度0.2 m/s,授时精度10 ns。
北斗于2000年以2颗卫星小幅起步,建成了具有位置报告和短电文通信等显著特色的北斗试验系统,使我国成为世界上第3个拥有自我卫星导航系统的国家。随后,于2012年12月,利用14颗卫星完成了北斗区域系统建设,实现了对亚太地区的连续覆盖。按照“从无到有、从区域到全球”的三步走发展规划,北斗系统预计于2020年完成全球组网。
北斗区域系统开通3年以来,运行状态稳定良好,行业应用稳步推进,北斗终端社会持有量已超过 1000万套,未来还将呈现爆炸式增长。北斗全球系统目前处于顶层设计与试验验证阶段,工程建设有序推进之中,多方面技术体制可能有所调整,服务性能也必将在区域系统基础上大幅提升,期待北斗在 2020年左右成为世界一流的全球卫星导航系统,为国家和全世界做出更大的贡献。
本专题得到杨元喜研究员(陕西省西安测绘研究所)、李小红教授(武汉大学测绘学院)、李子申副研究员(中国科学院光电研究院/中国科学院卫星导航总体部)、武子谦博士(中国科学院上海天文台)的大力支持。
·热点数据排行·
截至2016年8月1日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WOS)的数据报告显示,以“北斗卫星导航系统(BeiDou Navigation Satellite System,BDS)”为词条可以检索到的期刊文献分别为544条与187条,本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下。
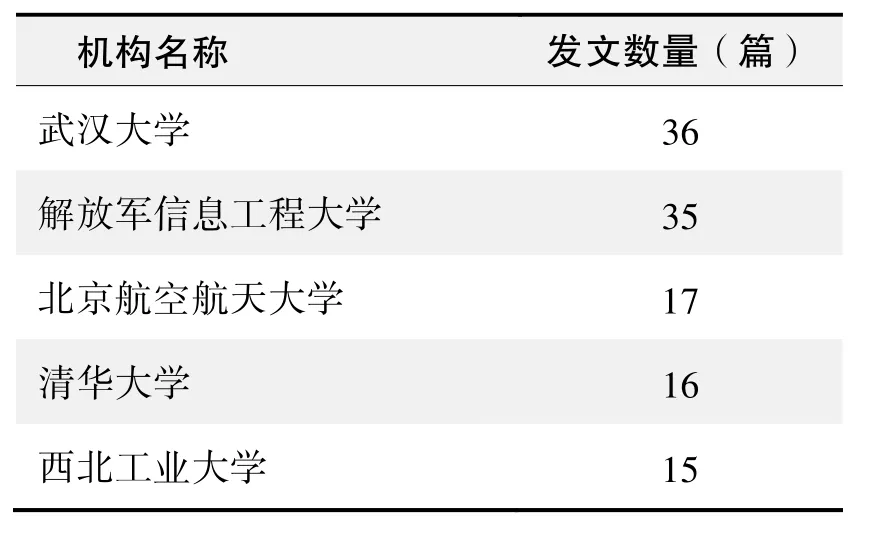
研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)
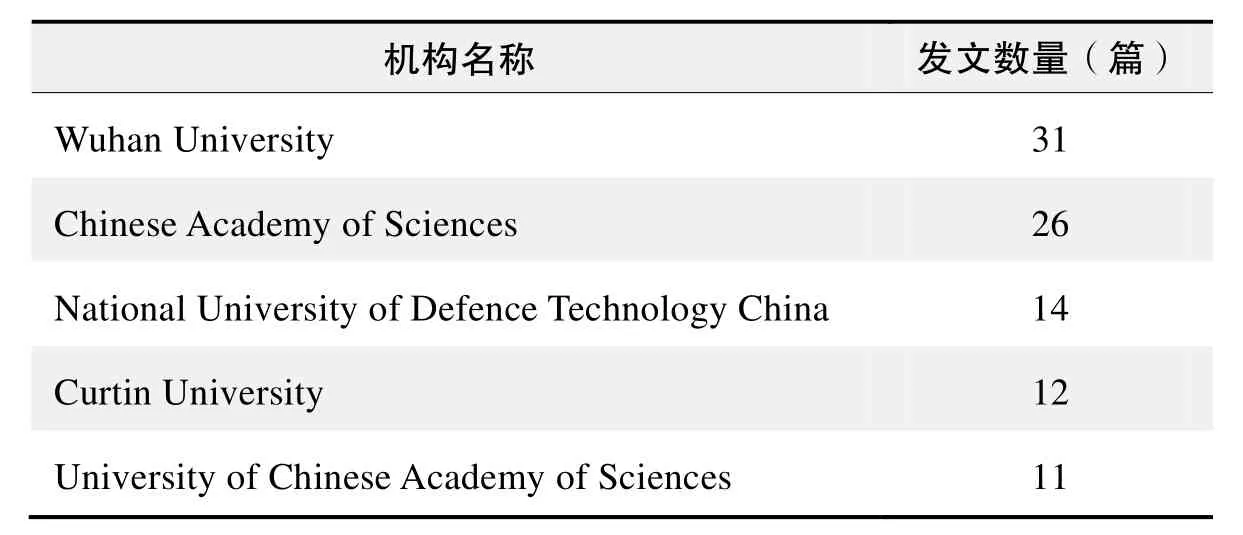
研究机构发文数量排名(WOS)

作者发文数量排名(CNKI)
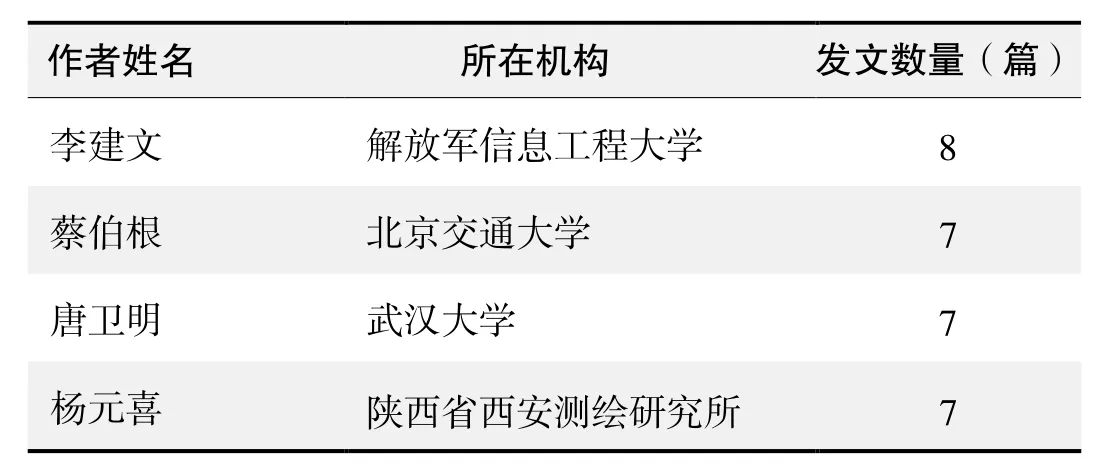
?

作者发文数量排名(WOS)

(数据来源:中国知网、Web of Science,检索时间:2016-08-01)
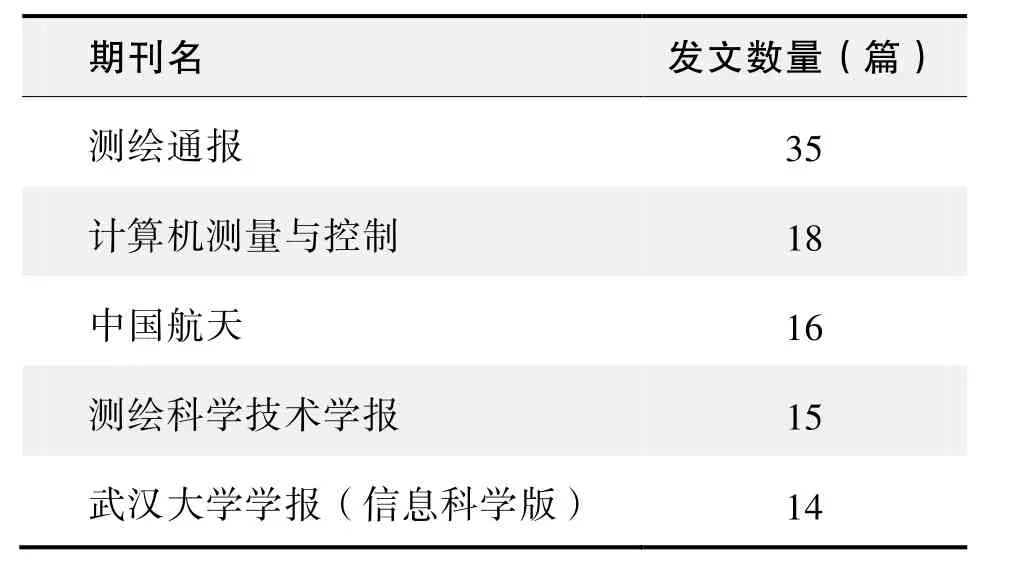
期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)
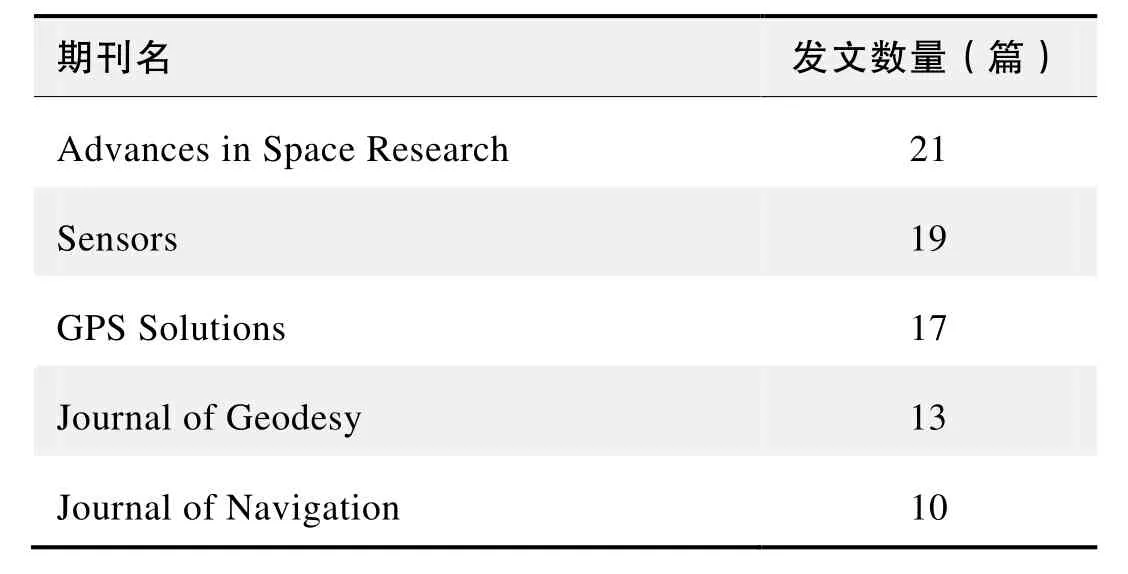
期刊发文数量排名(WOS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以“北斗卫星导航系统(BeiDou Navigation Satellite System,BDS)”为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。
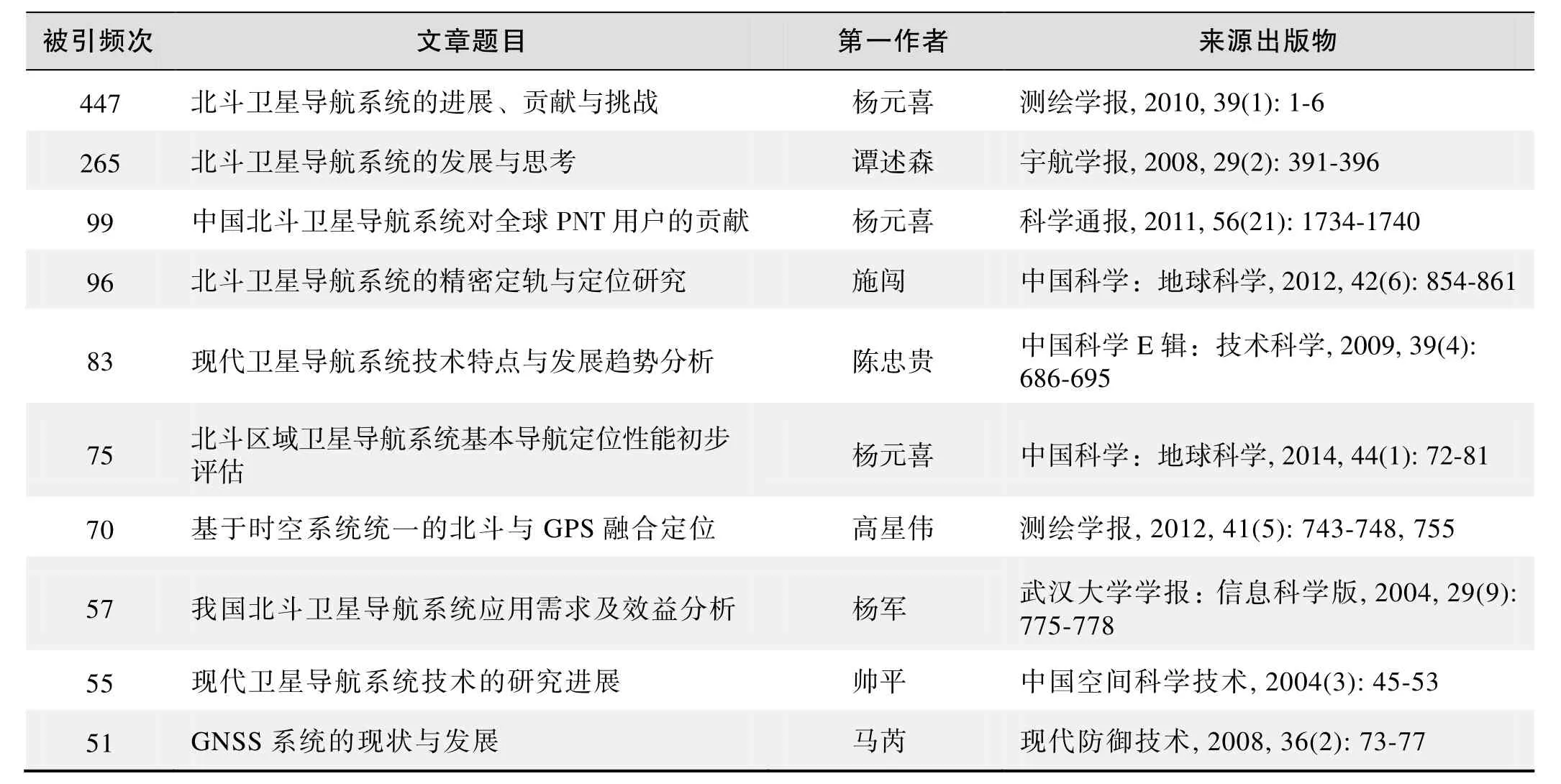
国内数据库高被引论文排行
根据Web of Science统计数据,以“北斗卫星导航系统(BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, BDS)”为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。
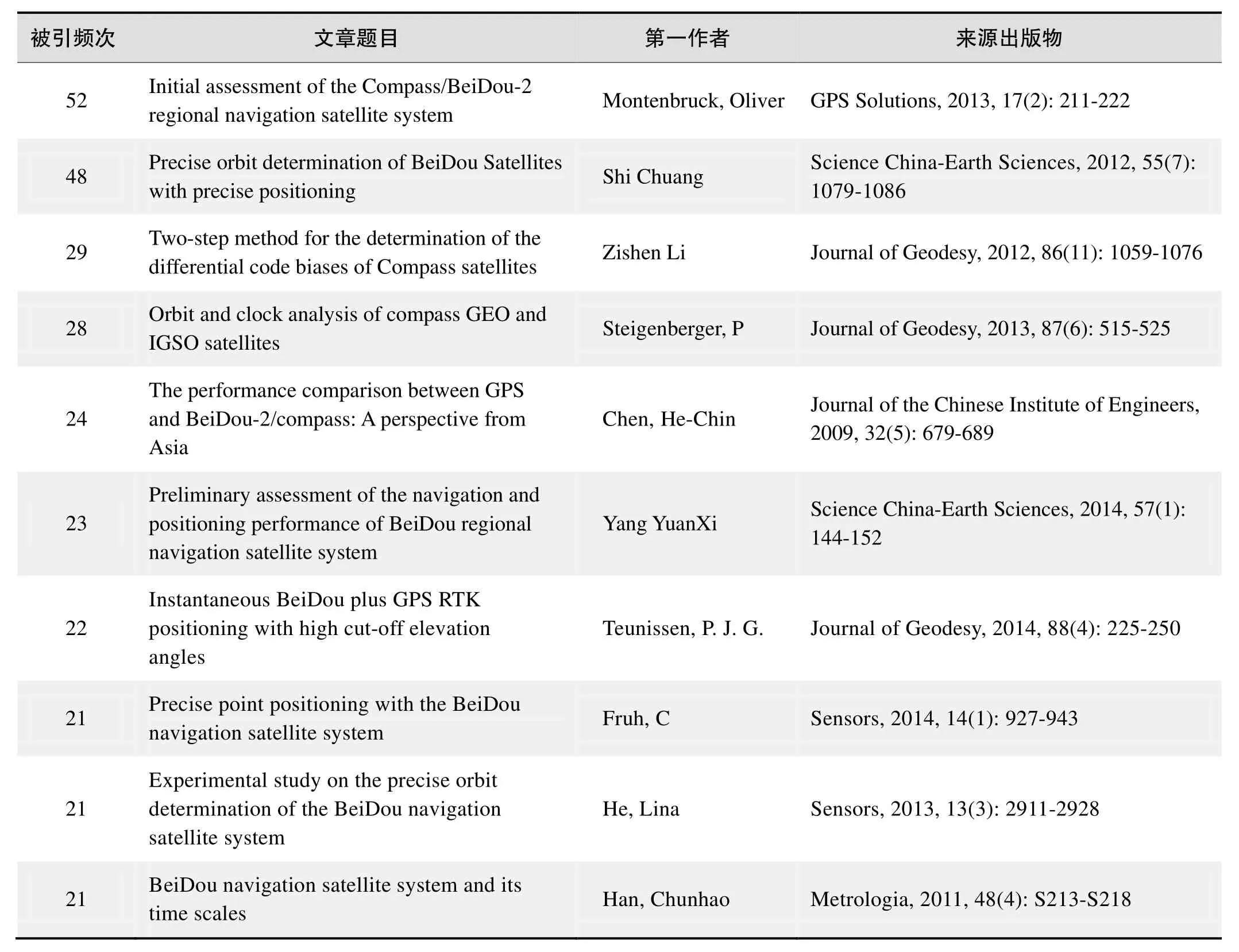
国外数据库高被引论文排行
·经典文献推荐·
基于Web of Science检索结果,利用Histcite软件选取LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次数)TOP50文献作为节点进行分析,得到本领域推荐的经典文献如下。
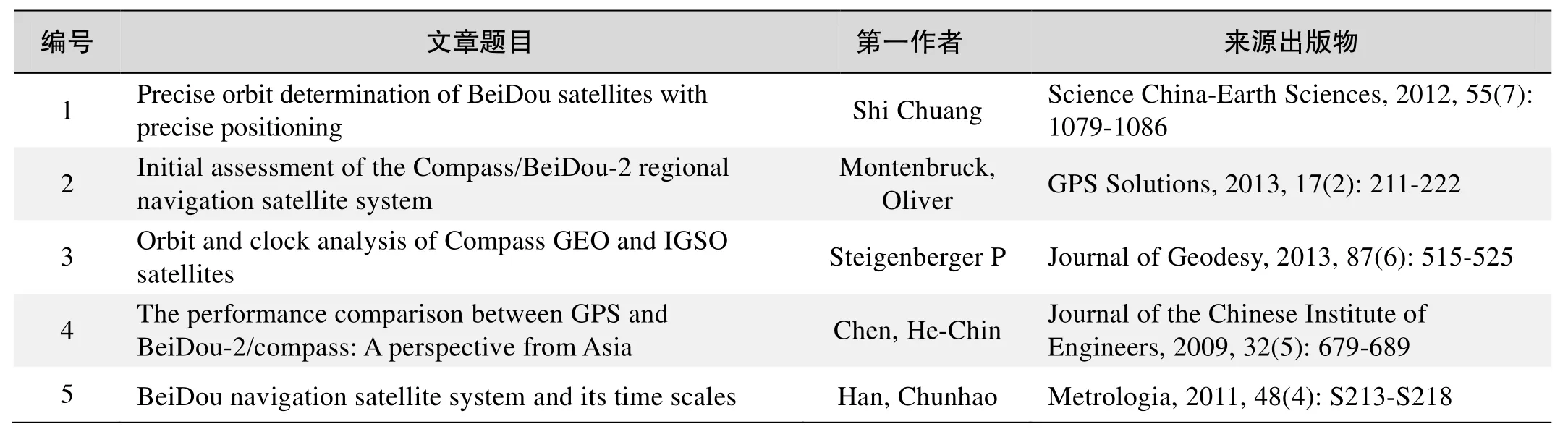
本领域经典文献
来源出版物:Science China-Earth Sciences, 2012, 55(7): 1079-1086
Initial assessment of the Compass/BeiDou-2 regional navigation satellite system Montenbruck, Oliver; Hauschild, Andre;
Steigenberger, Peter; et al.
Abstract: An initial characterization and performance assessment of the Compass/BeiDou-2 regional navigation system is presented. Code and carrier phase measurements on up to three frequencies have been collected in March 2012 with a small regional network of monitoring stations. The signal and measurement quality are analyzed and compared with the Japanese Quasi Zenith Satellite System. A high level of stability is demonstrated for the inter-frequency carrier phase biases, which will facilitate the application of triple-frequency)undifferenced)ambiguity)resolution techniques in future precise point positioning applications. The performance of the onboard Rubidium frequency standards is evaluated in comparison to ground-based hydrogen masers and shown to be well competitive with other GNSS satellite clocks. Precise orbit and clock solutions obtained in post-processing are used to study the presently achievable point positioning accuracy in Compass/BeiDou-2-only navigation. Finally, the benefit of triple-frequency measurements and extra-wide-lane ambiguity resolution is illustrated for relative positioning on a short baseline.
Keywords: Compass; BeiDou-2; QZSS; clock stability; RAFS; ambiguity resolution; extra-wide-lane combination; PPP; triple-frequency combination
来源出版物:GPS Solutions, 2013, 17(2): 211-222
Orbit and clock analysis of Compass GEO and IGSO satellites
Steigenberger P; Hugentobler U; Hauschild A; et al.
Abstract: China is currently focussing on the establish-ment of its own global navigation satellite system called Compass or BeiDou. At present, the Compass constellation provides four usable satellites in geostationary Earth orbit (GEO) and five satellites in inclined geosynchronous orbit (IGSO). Based on a network of six Compass-capable receivers, orbit and clock parameters of these satellites were determined. The orbit consistency is on the 1-2 dm level for the IGSO satellites and on the several decimeter level for the GEO satellites. These values could be confirmed by an independent validation with satellite laser ranging. All Compass clocks show a similar performance but have a slightly lower stability compared to Galileo and the latest generation of GPS satellites. A Compass-only precise point positioning based on the products derived from the six-receiver network provides an accuracy of several centimeters compared to the GPS-only results.
Keywords: GNSS; BeiDou-2; satellite orbits; allan deviation
来源出版物:Journal of Geodesy, 2013, 87(6): 515-525
The performance comparison between GPS and BeiDou-2/Compass: A perspective from Asia
Chen, He-Chin; Huang, Yu-Sheng; Chiang, Kai-Wei; et al.
Abstract: The next decade promises drastic improvements to global navigation satellite systems. The USA is modernizing GPS, Russia is refreshing GLONASS, Europe is moving ahead with its own Galileo system, and the People’s Republic of China is expanding its BeiDou-1 system from a regional navigation system to a full constellation global navigation satellite system known as BeiDou-2/Compass, which consists of thirty five satellites including geostationary satellites, MEO satellites and geosynchronous satellites in the coming year. Extra satellites will make possible improved performance for all applications, and especially where satellite signals can be obscured, such as in urban canyons, under tree canopies or in open-pit mines. The benefits of the expected extra satellites and their signals can be evaluated in terms of availability, accuracy, continuity, and reliability issues. The advent of a hybrid GNSS constellation has drawn a lot of attention to study compatibility and interoperability. A number of performance analyses have been conducted on a global scale with respect to availability, reliability, accuracy and integrity in different simulated scenarios (such as open sky and urban canyons) for each system individually as well as for combined systems with all the possible combinations. Since the BeiDou-2/Compass has gained more attention from GNSS communities, the main objective of this paper is to study the performance of BeiDou-2/Compass comparied to GPS in the greater Asia region; and also to explore whether the combination of BeiDou-2/Compass with GPS would yield performance improvements in this region. The performance analysis can be analyzed by either the signal or the geometrical conditions. However, the scope of this study is limited to investigating the impact of current and future GNSS based on geometrical conditions. Therefore, the satellite visibility and DOP (Dilution of Precision) values of each system or possible combinations between them are used as the major indices for performance evaluation with the emphasis on the addition of Compass. In addition, those indices are further analyzed in terms of their spatial and temporal distributions with the emphasis on the greater Asia region. Moreover, the spatial performance analyses are conducted on both global and regional scales to provide more insightful comparisons to illustrate the importance of future Compass for users in the greater Asia region.
Keywords: global navigation satellite systems; compass; dilution of precision; GPS
来源出版物:Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, 2009, 32(5): 679-689
BeiDou navigation satellite system and its time scales
Han, Chunhao; Yang, Yuanxi; Cai, Zhiwu
Abstract: The development and current status of BeiDou Navigation Satellite System are briefly introduced. The definition and realization of the system time scales are described in detail. The BeiDou system time (BDT) is an internal and continuous time scale without leap seconds. It is maintained by the time and frequency system of the master station. The frequency accuracy of BDT is superior to 2×10-14and its stability is better than 6×10-15/30 days. The satellite synchronization is realized by a two-way time transfer between the uplink stations and the satellite. The measurement uncertainty of satellite clock offsets is less than 2 ns. The BeiDou System has three modes of time services: radio determination satellite service (RDSS) one-way, RDSS two-way and radio navigation satellite service (RNSS) one-way. The uncertainty of the one-way time service is designed to be less than 50 ns, and that of the two-way time service is less than 10 ns. Finally, some coordinate tactics of UTC from the viewpoint of global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) are discussed. It would be helpful to stop the leap second, from our viewpoint, but to keep the UTC name, the continuity and the coordinate function unchanged.
来源出版物:Metrologia, 2011, 48(4): S213-S218
·推荐综述·
北斗区域卫星导航系统基本导航定位性能初步评估
杨元喜,李金龙,王爱兵,等
随着 2012年 10月 25日最后 1颗地球静止轨道(Geostationary Orbit, GEO)卫星发射升空,北斗区域卫星导航系统宣告建成。北斗区域卫星导航系统由 14颗卫星组成,包括5颗GEO卫星,5颗倾斜地球同步轨道(Inclined Geosynchronous Orbit, IGSO)卫星和4颗中圆地球轨道(Medium Earth Orbit, MEO)卫星。北斗区域卫星导航系统发播三个导航信号,频率分别为1561.098 MHz(B1), 1207.14 MHz(B2)和1268.52 MHz(B3),其中B1I和B2I为民用信号,码速率均为2.046 cps。2012年12月27日,北斗区域卫星导航系统宣布投入正式运行。
中国卫星导航系统按照“先试验、后区域、再全球”的三步走战略稳步推进系统建设。自从 2003年北斗卫星导航试验系统建成以来,中国立即着手北斗区域卫星导航系统的建设。于 2007年和 2009年分别发射 1颗MEO和GEO卫星,之后加快了建设速度,2010年发射了5颗北斗导航卫星(3颗GEO和2颗IGSO),2011年发射了3颗IGSO卫星,2012年发射了6颗卫星(2 颗GEO和4颗MEO)。其中前几颗发射的卫星,顾及了与北斗卫星导航试验系统的衔接与平稳过渡。
北斗区域卫星导航系统建设过程中,其卫星钟性能、测距码性能、定位精度和可靠性等性能指标也得到了逐步验证。尤其是从近期的导航定位实践中可知,北斗卫星导航系统的定位、导航和授时(PNT)服务性能已基本达到或超过设计性能指标。此外,关于北斗卫星导航系统与其他GNSS的兼容与互操作以及北斗卫星导航系统对全球导航定位授时用户的贡献均有学者作了分析和描述。
本文侧重描述北斗区域卫星导航系统正式运行后系统的服务区域和基本导航定位性能,包括服务区域内的卫星可见性和PDOP值、伪距和载波相位测量精度、单点定位、伪距差分定位和载波相位差分定位性能等。通过多种定位模式的试验与分析,从用户角度探讨北斗区域卫星导航系统的导航定位性能和潜在的应用推广价值,从而为亚太地区用户使用北斗卫星导航系统提供基本参考。实验中,用于收集北斗和GPS伪距和载波相位观测数据的接收机均为和芯星通科技(北京)有限公司生产的UR240-CORS-IIBDS/GPS双系统四频(B1/B2+L1/L2)测量型接收机。数据处理中,北斗B1/B2 和GPS L1/L2观测值之间采用等权策略,而每颗卫星观测量采用高度角加权策略。
1北斗服务区域
利用2013年1月22日至29日共7天的北斗卫星导航系统实际广播星历,以5 min的时间间隔计算了高度截止角为 5°时全球及亚太北斗服务区域内北斗区域卫星导航系统的可见卫星数和定位精度衰减因子(PDOP),并以可见卫星数大于等于5和PDOP值小于6作为指标分别统计了北斗全球区域和服务区域内的可用性。计算全球区域时,经纬度间隔为5°×2.5°,计算北斗区域卫星导航系统服务区域时,即 55°S~55°N和55°E~180°E范围内区域(China Satellite Navigation Office, 2011),经纬度间隔取1°×l°。
在70°S~70°N和40°E~180°E区域内,北斗可见卫星数基本在5颗以上,PDOP值也基本小于12,可实现基本的导航定位需求;在60°S~60°N和65°E~150°E区域内,北斗可见卫星数增加到7颗以上,PDOP值也一般小于5;而在50°S~50°N和85°E~135°E区域内,北斗可见卫星数可达8颗以上,PDOP值也进一步减小到2~3。
在中国境内,北斗卫星导航系统的可见卫星数均在7颗以上,PDOP值均小于5,而以PDOP值小于6统计的可用性均97.5%以上。
2北斗伪距和载波相位测量精度
2.1零基线单差残差
零基线单差(Single Difference, SD)观测值消除了卫星轨道误差、卫星钟误差、电离层延迟误差、对流层延迟误差和多路径效应误差的影响,扣除接收机钟差后(取各卫星单差残差的均值作为接收机钟差)仅含观测值噪声,可用来评估接收机的伪距和载波测量精度。使用两台接收机通过公分器连接同一天线形成零基线,在北京地区进行了约21 h的北斗和GPS静态数据采集,即从2012年8月21日02:55至2012年8月22日00:15 (GPS时间),采样间隔为1 s。
从以上计算结果可知:
1)卫星高度角越小,相应的伪距和载波相位残差一般越大;北斗GEO卫星的高度角基本保持不变,其伪距和载波相位残差也基本不变;北斗 GEO卫星伪距和载波相位观测值的精度随高度角降低逐渐变差,北京地区北斗CoS号GEO卫星的高度角最低,仅为16°,故其伪距和载波相位观测值的精度最差。
2)北斗卫星B2频点的伪距和载波测量精度均高于B1频点:B2I伪距测量精度约为5 cm,而B1I伪距测量精度约为11 cm;B2频点载波相位精度约为0.3 mm,而B1频率载波相位精度约0.5 mm。
3)GPS L1频点上C/A码伪距和载波相位观测值精度均高于L2P,L1C/A码伪距的精度约为10 cm,L2P码伪距的精度约为15 cm,L1载波相位的精度为0.5 mm, L2载波相位精度为1 mm。
4)上述零基线结果表明,北斗B1/B2与GPSL1/L2上伪距和载波的测量精度基本在同一水平。
2.2超短基线单差残差
超短基线单差观测值一般仅含观测值噪声和多路径效应的影响,可用来评估接收机野外观测值质量。利用两台接收机在北京某地区进行了北斗和GPS 4.2 m超短基线的静态数据采集,数据长度约8 d,即从2012年12月19日0时至2012年12月27日1时(GPS时间),采样间隔为10 s,共69662个历元,高度截止角为10°。同样通过固定已知基线(参考基线为北斗/GPS长时间数据的静态基线固定解)的方法,计算了北斗B1B2和GPS L1/L2伪距和载波相位单差观测值的残差序列,进而得到非差伪距和载波相位观测值精度。
从以上计算结果可知:
1)非差伪距观测值残差的RMS约20~50 cm,非差载波相位观测值残差的RMS约1~3 mm,与零基线观测值残差统计结果相比大许多,这主要是由于多路径误差所致。
2)北斗GEO卫星的伪距和载波相位残差存在较为明显的天周期多路径效应影响,这与北斗 GEO卫星运行周期为1 d是相符的。
3)北斗 MEO卫星伪距和载波相位残差一般较GEO和IGSO卫星大,主要是因为MEO卫星观测时段中,低高度角观测值比例较大,导致其观测值精度统计结果较差。IGSO卫星观测时段中,低高度角观测值比例较低,因而其观测值统计结果最好。
4)对北斗所有卫星进行统计,北斗B1I和B2I伪距野外测量精度约33 cm,B1和B2载波野外测量精度约2 mm。
5)对于GPS所有卫星进行统计,GPS L1C/A伪距野外测量精度约 43 cm,L2P伪距野外测量精度约 39 cm,L1载波相位野外测量精度为2.5 mm,L2载波相位野外测量精度约为3.7 mm。
6)上述短基线结果表明,北斗B1/B2与GPS L1/L2上伪距和载波的野外测量精度也基本在同一水平。
3北斗导航定位性能
3.1单点定位
从北斗区域卫星导航系统宣布正式运行(2012年12月27日)起,利用北斗导航型接收机在北京地区进行了连续的北斗单点定位监测,并对每天的定位误差进行统计。监测过程中,高度截止角设为5°,采样间隔为1 s,电离层延迟误差采用北斗广播星历中播发的8参数Klobuchar模型进行改正(中国卫星导航系统管理办公室,2012),对流层延迟误差采用 Hopfield模型进行改正。至2013年3月20日,获得了共71 d(其中有13 d未监测)的北斗B1I单频伪距单点定位结果,从相应的水平精度、高程精度和三维位置精度统计结果及相应的DOP值。可以看出,仅用北斗单频伪距进行实时导航,水平位置精度一般小于6 m(95%),高程精度一般小于10 m(95%),三维位置精度一般小于12 m(95%)。将71 d统计结果取平均可知:监测期间HDOP,VDOP和PDOP平均值分别为2.21,2.32和2.93;北斗B1I伪距单点定位水平、垂直和三维定位精度平均值分别为4.8,7.8和8.8 m。
3.2伪距差分定位
为了评估北斗伪距差分定位精度,使用两台接收机从北斗区域卫星导航系统开通之日起在北京某地区采集了7 d的北斗/GPS静态数据(1月3号由于电源故障其中一台接收机数据采集中断了3 h),即从2012年12 月28日至2013年1月4日,基线长度为8.2 km,采样间隔l0 s,共58287个历元。分别采用北斗B1,GPS L1以及北斗/GPS B1和L1频点伪距观测值进行伪距差分定位,以北斗/GPS长时间的静态基线固定解作为参考值。
由伪距差分定位误差序列可知:1)北斗高程分量和北分量误差均具有较大波动,而且高程分量具有较明显的天周期性的系统误差。这是由于北斗区域星座以GEO和IGSO卫星为主,其中5颗GEO卫星相对地面待定点基本不动,而且均在定位点(北京)南面,这些GEO卫星的观测值对高程分量和北分量的几何约束较弱,进而相应分量的几何精度衰减作用较小,于是高程误差明显大于水平误差,北分量误差大于东分量误差。2)北斗 B1I伪距差分定位在东、北和高程分量的RMS分别为0.71,1.14和1.90 m,三维位置RMS为2.28 m;而GPS L1 C/A伪距差分定位东、北和高程分量的RMS分别为0.31, 0.39和0.81 m,三维位置RMS 为0.95 m。显然,现有北斗区域卫星导航系统的单频伪距差分定位精度与GPS相比仍存在差距。短基线条件下,卫星轨道误差、卫星钟差、电离层延迟误差、对流层延迟误差等基本被消除,残留误差主要为伪距噪声和多路径效应影响。而从北斗伪距差分定位存在明显的天周期性误差现象不难推断,北斗伪距差分定位较GPS差,主要是由于北斗GEO卫星伪距多路径误差较大所致。
3.3载波相位差分定位
3.3.1单历元模糊度解算性能
采用与 3.2节相同的实验数据,进行了北斗、GPS以及北斗/GPS组合三种星座条件下的单历元双频模糊度解算实验。实验中使用 LAMBDA算法(Teunissen, 1993, 1995)进行模糊度固定,利用比值法(ratio test)进行模糊度验证(ratio>2.0)。并统计了不同高度截止角条件下单历元模糊度解算的固定率和固定错误率。固定率为通过验证历元数占总历元数的比率,固定错误率为通过验证的历元中模糊度固定错误历元所占的比率。
以上计算结果表明:
1)当高度截止角较低时(<25°),北斗区域卫星导航系统单历元双频模糊度解算的固定率大于90%,稍低于GPS,而固定错误率与GPS相当。这说明北斗单历元双频模糊度解算性能已与GPS处在同一水平,由此可知北斗系统已具备双频RTK定位能力。
2)当高度截止角增大时,北斗和GPS的模糊度固定率均迅速降低,且北斗模糊度固定率降低速度远大于GPS。这是由于在北京地区北斗GEO卫星的高度角一般在15°~40°左右,当高度截止角增大时,北斗GEO卫星不再可见,可视卫星数量迅速减少,从而导致模型的几何强度显著减弱。
3)当北斗和 GPS组合定位时,截止高度角至 30°时,模糊度固定率依然接近 100%,且固定错误率几乎为零;高度截止角达40°时,模糊度固定率接近94%,且固定错误率仅为1.47%;由此可见,北斗与GPS组合定位对模糊度固定率和可靠性具有显著贡献。
3.3.2载波相位差分定位精度
利用2.2节4.2 m超短基线和3.2节8.2 km短基线的两次实验数据评估载波相位差分动态定位的精度,分别计算了模糊度固定后北斗、GPS以及北斗/GPS组合三种星座条件下的载波相位差分动态定位结果。
分析载波相位差分动态定位结果可知:
1)超短基线情况下,北斗和GPS定位的高程分量均存在周期性的系统误差,这主要是由于北斗和GPS星座构型变化均存在天周期性,而且北斗星座包括 GEO卫星(相对地面点基本不动),其天周期性的多径效应更为明显,故北斗定位北分量和高程分量的周期性系统误差较GPS更为明显。
2)短基线情况下北斗和GPS载波相位差分定位的周期性误差没有超短基线明显,可能是由于短基线情况下两台接收机所处的多径环境差异相对较大,且还存在着部分双差大气延迟残余误差,而多种误差的叠加效应淹没了定位结果中的周期性误差。
3)不论是超短基线还是短基线,北斗区域卫星导航系统载波相位差分定位精度都与GPS处在同一水平。在 4.2 m的超短基线上,北斗与 GPS定位水平分量的RMS均优于0.3 cm,高程分量的RMS均在0.5 cm左右;在8.2 km的短基线上,北斗与GPS定位水平分量的RMS均在1 cm左右,高程分量的RMS分别优于2.5 和2 cm。
4)与伪距差分定位结果相类似,由于北斗区域卫星导航系统的特殊星座配置,其 N分量误差也明显大于E分量,而GPS的N分量与E分量定位精度基本相当。
5)北斗与GPS组合定位的精度改进效果明显。在4.2 m的超短基线上的组合定位各分量的 RMS优于0.3 cm,三维点位RMS仅为0.33 cm;在8.2 km的短基线上,组合定位水平分量RMS均优于0.6 cm,高程分量在1 cm左右,而三维点位RMS也仅为1.35 cm。在不同基线长度上,北斗与GPS组合定位对GPS定位的改善不同,在4.2 m的超短基线上,北斗/GPS组合定位对GPS定位精度的改善约为35%,而在8.2 km的短基线上,改善约为20%。这可能是由于更长基线情况下,大气残留误差导致北斗和 GPS观测值之间的相关性更强所致。
4总结
北斗区域卫星导航系统于2012年12月27日宣布正式运行后,正在为亚太地区用户提供独立的导航定位服务,也显著增强了亚太地区单GPS导航定位服务的精确性、可用性和可靠性。本文基于北京地区北斗实测数据,初步分析了北斗区域卫星导航系统的基本导航定位性能,试图为北斗系统用户提供相关参考信息。通过试验、计算及分析可知:
1)北斗区域卫星导航系统在亚太地区具有良好的几何覆盖,在60°S~60°N和65°E~150°E之间的区域内,北斗可见卫星数在7颗以上,PDOP值一般小于5,可满足不同用户的导航定位需求。
2)北斗伪距和载波测量精度已与 GPS处在同一水平,伪距测量精度约为 33 cm,载波测量精度约为2 mm。
3)北斗B1单频伪距单点定位水平精度优于6 m,高程精度优于l0 m,三维点位精度优于12 m,已满足设计要求。
4)短基线条件下,北斗 B1I伪距差分定位的平面精度优于1.5 m,高程精度优于2 m,三维精度优于2.5 m,与GPS相比仍存在差距。
5)北斗区域卫星导航系统已具备双频 RTK定位能力,其单历元双频模糊度解算成功率几乎与 GPS相当,且北斗与GPS组合定位时,模糊度解算的固定率和可靠性均显著提高。
6)北斗区域卫星导航系统载波相位差分定位精度与GPS相位差分定位处在同一水平,超短基线情况下,三维定位精度优于1 cm,而在短基线情况下优于3 cm。北斗与 GPS组合定位对单系统定位精度的改善也较明显,在短基线情况下,北斗/GPS组合载波相位差分动态定位精度相对于单一的 GPS系统定位的改善可达 20%以上。
需要指出的是,本文的计算与分析仅使用了北京地区一种接收机采集的数据,还无法对北斗区域卫星导航系统整体性能做出全面的评估,更科学客观的评估还需要进行大量的覆盖不同地区、不同季节以及不同类型接收机的试验。此外,从本文实验分析可知,由于北斗区域卫星导航系统星座由GEO,IGSO和MEO三类卫星构成,三类卫星的可见性和观测误差特性各异,如GEO 和IGSO卫星可见时段长,而GEO卫星观测值存在明显的周期性多径误差等。如何更好地开发北斗特殊星座配置的优势,消除其不利因素影响,进而提高北斗系统导航定位的精确性、可用性和可靠性需要重点研究。
【作者单位:地理空间信息国家重点实验室;中国卫星导航应用管理中心;信息工程大学地理空间信息学院;北京卫星导航中心;西安测绘信息技术总站】
(摘自《中国科学:地球科学》2014年1期)
中国北斗卫星导航系统对全球PNT用户的贡献
杨元喜,李金龙,徐君毅,等
全球导航卫星系统 GNSS(Global Navigation Satellite System)正呈现百花齐放的局面。美国 GPS (Global Positioning System)、俄罗斯的 GLO-NASS (Global Navigation Satellite System,与GNSS取至相同的英文单词)、欧盟伽利略系统(Galileo)、中国北斗系统(Beidou/Compass)、日本准天顶卫星系统(IRNSS)以及印度的区域导航卫星系统(IRNSS)等,使卫星导航星空群星璀璨,卫星导航用户的可用信号资源极大丰富。2020年后,天空将有30颗GPS卫星(3个频率信号),24颗GLONASS卫星(3个频率信号),30颗Galileo卫星(4个频率信号),35颗Compass/北斗卫星(3个频率信号),3颗QZSS卫星(4个频率信号)和7颗IRNSS卫星(2个频率信号)。全球用户可以无限制地使用多星座提供的多频观测信息进行定位、导航、定时(PNT)应用,可减弱对单一星座的依赖,降低电磁干扰、地形/建筑物遮挡、电离层闪烁、拒绝服务等因素导致的性能下降或服务中断风险。
在GNSS多星座多频数据融合下,经过数据探测、筛选、组合,将显著增加卫星和测距信号的数量,大幅提升各个导航性能指标。其主要优点如下:1)可见卫星数目增多,可减小精度衰减因子(DOP),提高导航精度(accuracy);2)各卫星系统具有不同的时间系统差和坐标系统差及轨道系统差,通过多卫星系统信号融合,可补偿单一导航系统的系统误差影响,进而精化各星座的卫星轨道、卫星钟差以及监测站坐标,提高导航卫星系统及用户PNT的可靠性(reliability);3)多频率信号的综合利用可有效解决非故意干扰问题,减弱某单一卫星系统出现重大故障或拒绝服务等带来的隐忧,提高导航的可用性(availability);4)观测冗余信息增多,便于故障诊断、报警和隔离,提高卫星导航用户的完好性(integrity);5)多卫星观测几何结构的改善,有利于诊断因电离层闪烁、多径、遮挡而导致的观测异常,提高用户系统的异常误差影响控制能力,提高用户PNT的抗差性(robustness);6)卫星数目增多可极大限度地减弱卫星导航盲区,缓解单一星座下卫星故障、地形/建筑物/树木遮蔽等因素引起的导航信号缺失问题,提高卫星导航系统的连续性(continuity);7)综合利用多星座的多频信号,能大幅缓解单一星座卫星信号随时间变化的有色噪声的影响,提高动态用户 PNT的收敛性(convergence);8)多频率信号的使用更能消除或精确估计电离层延迟的影响;9)综合利用多星座多频信号,可望实现载波相位模糊度的快速固定,并在中长距离情况下也能可靠地确定模糊度,提高对流层延迟参数估计的时间分辨率,进而全方位提升高精度实时与近实时测量的性能;10)各星座卫星的高度、轨道面倾角不同,可改善地球自转、极移等参数的估计精度。
为了分析Compass对用户PNT的贡献,需要描述多卫星导航系统环境下,相应的随机误差、系统误差的影响。其中,精度衰减因子(DOP)是随机误差补偿和系统误差补偿能力以及可用性、完好性的重要指标。DOP值反映的是测距信号统计量和位置参数统计量之间的误差传播关系。点位误差正是测距误差与水平精度衰减因子(HDOP)及垂直精度衰减因子(VDOP)的乘积。
本文采用仿真计算分析Compass的贡献。类似的研究分析工作已有大量成果。本文侧重讨论Compass对用户卫星可见性的改善,用户PNT的DOP理论值改善,并通过仿真计算分析Compass对全球用户的卫星可见数和精度衰减因子(DOP)的改善。
1增加卫星星座对用户导航定位 DOP值的贡献
精度衰减因子(DOP)被广泛用于分析导航精度和观测几何结构强度。关于精度衰减因子(DOP)的定义,有许多文献可供参考。假定伪距观测量是Pi,则观测模型可写为
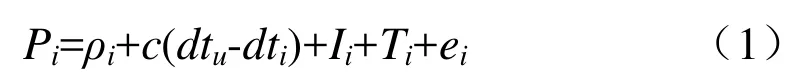
其中,ρi是信号接收时刻接收机天线相位中心到信号发射时刻卫星天线相位中心间的几何距离,dtu和 dti分别为接收机钟差和卫星钟差;Ii和Ti不分别为电离层延迟和对流层延迟;ei为观测噪声和未模型化误差,c是真空中的光速。
进一步,假定伪距观测量中的卫星钟差和大气层延迟已经得以改正,在观测模型中只考虑接收机钟差。如此,观测模型可表示成

其中,L是观测向量,该观测向量是改正后的伪距观测量与由坐标近似值计算的伪距之差。X是包含3维位置和接收机钟差(单位:m)在内的未知参数向量,A 是n×4设计矩阵,若考虑观测向量L的权矩阵P,则未知参数向量的最小二乘解为
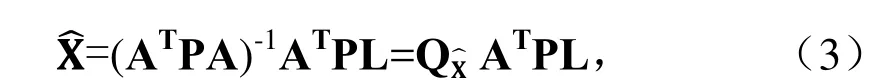
其中,QX=(ATPA)-1,几何精度衰减因子(GDOP)定义为
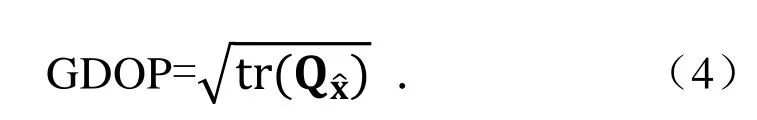
水平精度衰减因子(HDOP)为
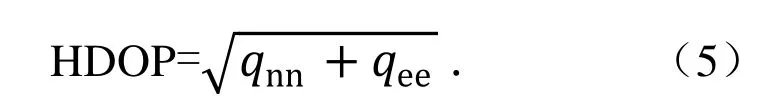
垂直精度衰减因子(VDOP)为

时间精度衰减因子(TDOP)为


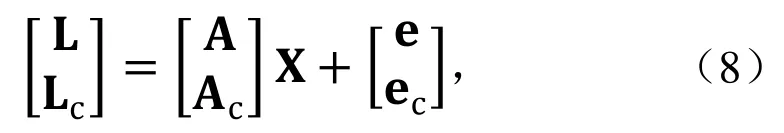
其中,Lc和Pc分别为Compass的观测向量及其权矩阵,Ac为Compass设计矩阵。从而加人Compass信号后未知参数向量 X的新协因素矩阵:
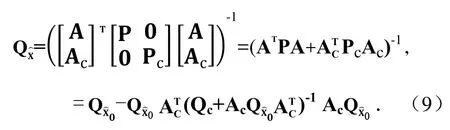
其中,QX 0=(ATPA)-1,Qc=Pc-1是Compass观测向量权矩阵的逆矩阵。则PNT参数的协因素矩阵的改善值为
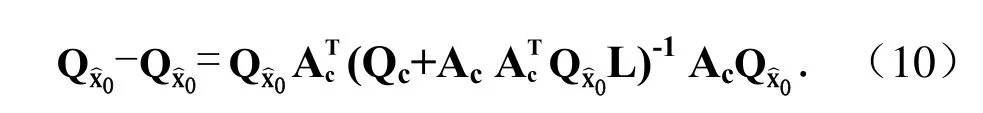
精度衰减因子DOP的改善值为
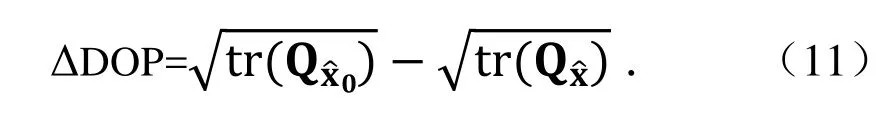
精度衰减因子DOP值得改善百分比为
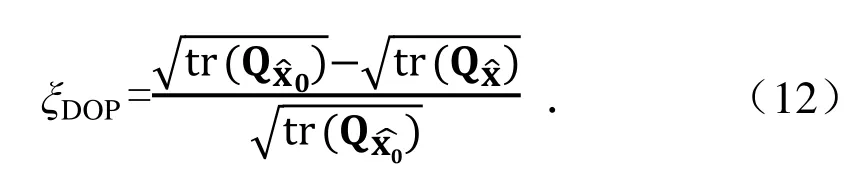
多模导航条件下,需要考虑各系统之间的不兼容性,主要有各系统坐标系统差和时间系统差,GPS坐标系统WGS-84、Galileo坐标参考框架GTRF以及Compass坐标系统CGCS2000与国际地球参考框架(ITRF)之间仅相差几个厘米,对于导航应用来说,它们之间的差别均可忽略。GLONASS坐标系统PZ-90与ITRF略有差异,但许多组织已经求出了其与WGS-84的转换参数,对于米级精度的导航应用来说,只要顾及这些转换参数即可,无需在函数模型中增加待定的转换参数,于是不影响DOP值计算。
对时间系统差,一般采取以下两种处理方式。1)在导航电文中将各系统之间的时间系统差发播给用户;2)在参数估计时附加一个未知的时间系统差参数进行估计。在仿真时,我们将分两种情况来计算DOP值,并分析Compass的贡献。
2仿真计算与分析
本次仿真时间段为2010年3月28日0时—2010年3月29日0时,共24 h,采样率为300 s。GPS和GLONASS星座使用当天广播星历计算卫星位置,Compass和Galileo星座采用列开普勒轨道根数计算卫星位置。仿真时间内,有30颗GPS卫星,21颗GLONASS卫星,27 颗Galileo卫星和35颗Compass卫星。
Compass星座 5颗 GEO卫星的轨道位置分别为58.75°,80°,110.5°,140°和160°E。3颗IGSO的倾角为55°,交叉点经度为118°E。计算分为8个方案:
方案一:GPS(G);
方案二:GPS+Compass (G+C);
方案三:GPS+GLONASS (G+R);
方案四:GPS+GLONASS+Compass (G+R+C);
方案五:GPS+Galileo (G+E);
方案六:GPS+Galileo+Compass (G+E+C);
方案七:GPS+GLONASS+Galileo (G+R+E);
方案八:GPS+GLONASS+Galileo+Compass (G+R+E+C)。
括号内为各系统缩写,“G”代表GPS,“R”代表俄罗斯的GLONASS,“E”代表欧洲的Galileo,“C”代表中国的Compass,以下部分将使用这些缩写来表示各方案。
以经度间隔5°,纬度间隔2.5°,高程取为25 m,计算了经度范围-180°~180°、纬度范围-90°~90°内高度截止角为10°和20°,30°和40°时不同系统的卫星可见数以及在高度截止角为 10°时的卫星可见性(95%>),DOP值(95%<)、DOP值的改善百分比。
由计算结果可以看出:
1)当卫星截止高度角为10°时,单卫星星座 GPS基础上加人Compass后,全球平均可见卫星数从7.3增加为17.1,增加约134%;比较方案3和4、方案5和6可见,在GPS+GLONASS和GPS+Galileo的基础上,加入Compass后,可见卫星数分别增加约79%和68%;即使在GPS+GLONASS+Galileo基础上,加人Compass后,可见卫星数也从20.7增加到31.1,增加约50%。可见卫星数的增加,将极大改善卫星的几何分布,改善PNT服务的连续性。
2)Compass对不同系统GDOP值的改善百分比随着各系统兼容性的增强而增大。若所有导航星座信号完全兼容(即各系统间无系统误差),则在GPS星座的基础上,增加Compass后对全球地区GDOP值改善约为50%;在 GPS与 GLONASS共同使用的基础上,加人Compass后GDOP值改善约32.7%;在GPS与Galileo共同使用的基础上,加人Compass后对GDOP值改善约29.5%;即使在GPS,GLONASS和Galileo同时使用的基础上,加人Compass后,GDOP值依然能改善约22.6%。各系统兼容性的加强将获得GDOP值的改善,进而改善PNT的精确性。
3)不管是否考虑各系统时间差,在GPS星座的基础上,增加Compass后对PDOP值改善为49%左右;在GPS与 GLONASS共同使用的基础上,加人 Compass后对PDOP值改善为32%左右;在GPS与Galileo共同使用的基础上,加人Compass后对PDOP值改善为28%左右;即使在GPS,GLONASS和Galileo同时使用的基础上,加人Compass后,PDOP值依然能改善22%左右。PDOP值的改善将提高用户导航定位的精确性,进而提高系统服务的可用性。
4)对于一些受遮挡较为严重的地区,如高楼林立的城市街道,单一系统的卫星数较少,且几何分布也较差。当卫星高度角达到40°时,单一系统在大多数时段卫星数达不到4颗,将给用户应用带来不便,而4个系统同时使用时,可见卫星数将平均达到10.1颗,因此,多个导航系统的共同使用,将显著提高导航定位服务的可用性。
最后必须指出,当卫星星座兼容性较差时,GNSS数据融合时需要增加过多兼容性补偿参数,此时,增加卫星星座也不会明显改善GDOP值;此外,当各类导航卫星观测之间具有不同的随机模型,不同的观测权,则分析各类卫星的贡献时不能简单通过等权 DOP值计算,实践中可采用方差分量估计实时标定各类卫星观测的权,并计算具有不等权的 DOP值,这类问题将另文讨论。
【作者单位:中国卫星导航定位与应用管理中心;信息工程大学测绘学院;北京环球信息应用开发中心】
(摘自《科学通报》2011年21期)
·高被引论文摘要·
被引频次:447
北斗卫星导航系统的进展、贡献与挑战
杨元喜
卫星导航发展已进入百花齐放、群星争艳的时代。主要评述我国北斗卫星导航系统的发展、应用、贡献及面临的挑战。介绍北斗卫星导航系统的建设原则和建设步骤;介绍我国北斗卫星导航系统在兼容与互操作框架下在频率、坐标系统、时间系统方面的兼容与互操作实现概况;描述北斗导航系统在冗余度概念下的主要贡献;简要说明北斗导航验证系统的重要应用和面临的主要挑战。
北斗卫星导航系统;进展;挑战
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2010, 39(1): 1-6
被引频次:265
北斗卫星导航系统的发展与思考
谭述森
摘要:从世界卫星导航发展史出发,评述了中国北斗卫星导航系统从中获得的有益启示,阐明了中国北斗卫星导航系统小幅起步的研制建设思路。在分析国际卫星导航系统发展趋势的基础上,论述了北斗全球系统的必要性、可行性和战略价值,提出了北斗GNSS的发展思路。
关键词:卫星导航;GNSS;北斗卫星导航系统
来源出版物:宇航学报, 2008, 29(2): 391-396
被引频次:99
中国北斗卫星导航系统对全球PNT用户的贡献
杨元喜,李金龙,徐君毅,等
摘要:北斗卫星导航系统作为全球四大卫星导航系统之一,不仅增加中国及周边地区定位、导航和授时(PNT=Positioning, Navigation and Timing)用户的卫星可见性和可用性,而且也将提高全球用户的PNT精度。在全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)兼容与互操作条件下,分析全球导航定位定时用户的卫星可见性和精度衰减因子改善情况;利用仿真数据分析北斗卫星导航系统对全球用户的贡献,侧重分析北斗卫星导航系统与GPS,GLONASS和Galileo多卫星导航系统组合模式下用户获得的收益。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;定位;导航;授时;精度衰减因子;卫星可见性
来源出版物:科学通报, 2011, 56(21): 1734-1740
被引频次:96
北斗卫星导航系统的精密定轨与定位研究
施闯,赵齐乐,李敏,等
摘要:我国北斗卫星导航系统已建成由8颗导航卫星组成的区域导航星座,初步形成了亚太地区的导航定位服务能力。本文采用“北斗卫星观测实验网”实测数据和我国自主研制的精密数据处理软件 PANDA,实现了北斗导航卫星系统的高精度定轨,静态精密单点定位、相对定位,以及动态伪距差分、相位差分定位。研究成果显示:北斗卫星精密定轨径向精度优于10 cm,静态精密单点定位精度达到厘米级、基线相对定位达到毫米级;动态伪距差分定位精度达到2~4 m、RTK定位精度达到5~10 cm,接近目前GPS所能实现的精密定位水平。本研究验证了北斗卫星导航系统在地面参考站网的支持下,具备广域米级至分米级的精密定位,以及区域厘米级精密定位服务能力。可为北斗系统在我国精密导航定位领域的推广应用和科学研究提供技术积累和重要参考。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;PANDA;精密定轨;北斗差分
来源出版物:中国科学:地球科学, 2012, 42(6): 854-861
被引频次:83
现代卫星导航系统技术特点与发展趋势分析
陈忠贵,帅平,曲广吉
摘要:简要介绍了美国 GPS系统、俄罗斯 GLONASS系统、欧洲Galileo系统、中国北斗卫星导航系统、以及日本和印度的区域卫星导航系统的发展状况。重点研究了GPS系统星座维持、有效载荷、自主导航、信号调制和地面站改造等最新技术特征,以及GPSⅢ系统技术及研究进展,分析论证了卫星导航系统技术的发展趋势,为我国卫星导航系统建设规划提供参考。
关键词:卫星导航系统;星座维持;自主导航;星间链路;导航信号调制
来源出版物:中国科学 E辑:技术科学, 2009, 39(4): 686-69
被引频次:75
北斗区域卫星导航系统基本导航定位性能初步评估
杨元喜,李金龙,王爱兵
摘要:北斗区域卫星导航系统(也称北斗2代1期)于2012 年12月27日正式开始运行,系统由14颗卫星组成,包括5颗地球静止轨道卫星、5颗倾斜地球同步轨道卫星和4颗中圆地球轨道卫星。本文初步评估了北斗区域卫星导航系统建成运行后的基本导航定位性能,包括卫星可见性、位置精度衰减因子、伪距和载波相位观测量精度、单点定位和差分定位精度以及模糊度解算性能等。通过实验分析可知:北斗伪距和载波相位测量精度已与GPS处在同一水平,伪距测量精度约为33 cm,载波测量精度约为2 mm;北斗伪距单点定位水平精度优于6 m,高程精度优于10 m,已满足设计要求;北斗区域卫星导航系统已具备独立的双频RTK定位能力,其单历元双频模糊度解算成功率几乎与GPS相当;北斗载波相位差分定位精度与GPS相位差分定位处在同一水平,超短基线情况下,定位精度优于1 cm,而在短基线情况下优于3 cm;北斗与GPS组合定位时,模糊度解算的固定率和可靠性均显著提高;在短基线情况下,北斗/GPS组合载波相位差分动态定位精度相对于单一的 GPS定位的改善可达20%以上;北斗单频伪距差分定位精度优于2.5 m,与GPS相比仍存在较大差距,其主要原因可能为北斗 GEO卫星伪距多路径误差较大。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;服务区域;位置精度衰减因子;伪距和载波相位测量精度;单点定位;伪距差分定位;模糊度解算;载波相位差分定位
来源出版物:中国科学:地球科学, 2014, 44(1): 72-81
被引频次:70
基于时空系统统一的北斗与GPS融合定位
高星伟,过静珺,程鹏飞,等
摘要:我国的北斗卫星导航定位系统目前已经发射9颗北斗卫星,北斗区域卫星导航系统的基本系统已建设完成,正开展星地联调和测试评估工作,已经具备我国范围内的初步三维定位导航能力。本文研究北斗和GPS的时间系统/坐标系统的统一、卫星广播星历与卫星位置计算,以及二者的高精度定位算法,并实现了北斗和GPS载波相位的数据融合和高精度联合定位,最后通过2011-09-29的实测数据和处理结果证明了本文方法的正确性,同时为北斗二号系统的调试提供了相关试验与结果。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;全球定位系统;融合定位
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2012, 41(5): 743-748, 755
被引频次:57
我国北斗卫星导航系统应用需求及效益分析
杨军,曹冲
摘要:在介绍我国卫星导航系统应用概况的基础上,比较分析了北斗卫星导航系统民用的优势和劣势,对我国北斗卫星导航系统民用市场的用户数和产值进行了预测,并对其作了经济效益和社会效益分析。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;市场预测;效益分析
来源出版物:武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2004, 29(9): 775-778
被引频次:55
现代卫星导航系统技术的研究进展
帅平,曲广吉,向开恒
摘要:首先,文章详细地分析了美国GPS系统的技术特征及其现代化进程;然后,论述俄罗斯的GLONASS系统现状与不足,及其与GPS系统的差异,并介绍了欧洲的Galileo系统的建设进展及相关技术;最后,阐述北斗卫星导航系统尚不能满足中国各行业广大用户的需求,初步提出发展中国第二代卫星导航系统的总体构想及其关键技术。
关键词:卫星导航;关键技术;发展趋势;述评
来源出版物:中国空间科学技术, 2004(3): 45-53
被引频次:51
GNSS系统的现状与发展
马芮,孔星炜
摘要:介绍了当前 GNSS系统(GPS, GLONASS, GALILEO)的现状和发展方向,并分析了国内北斗卫星导航系统(BD-I/BD-Ⅱ)的组成应用和发展方向。对这4种卫星导航系统的异同进行了综合对比说明,并对GNSS系统的发展前景进行了分析和预测。
关键词:全球卫星导航系统;全球卫星定位系统;全球导航卫星系统;伽利略卫星导航系统;北斗导航卫星系统
来源出版物:现代防御技术, 2008, 36(2): 73-77
被引频次:52
Initial assessment of the Compass/BeiDou-2 regional navigation satellite system
Montenbruck, Oliver; Hauschild, Andre; Steigenberger, Peter; et al.
Abstract: An initial characterization and performance assessment of the Compass/BeiDou-2 regional navigation system is presented. Code and carrier phase measurements on up to three frequencies have been collected in March 2012 with a small regional network of monitoring stations. The signal and measurement quality are analyzed and compared with the Japanese Quasi Zenith Satellite System. A high level of stability is demonstrated for the inter-frequency carrier phase biases, which will facilitate the)application)of triple-frequency)undifferenced ambiguity resolution techniques in future precise point positioning applications. The performance of the onboard Rubidium frequency standards is evaluated in comparison to ground-based hydrogen masers and shown to be well competitive with other GNSS satellite clocks. Precise orbit and clock solutions obtained in post-processing are used to study the presently achievable point positioning accuracy in Compass/BeiDou-2-only navigation. Finally, the benefit of triple-frequency measurements and extrawide-lane ambiguity resolution is illustrated for relative positioning on a short baseline.
来源出版物:GPS Solutions, 2013, 17(2): 211-222
被引频次:48
Precise orbit determination of BeiDou Satellites with precise positioning
Shi Chuang; Zhao QiLe; Li Min; et al.
Abstract: Chinese BeiDou satellite navigation system constellation currently consists of eight BeiDou satellites and can provide preliminary service of navigation and positioning in the Asia-Pacific Region. Based on the self-developed software Position And Navigation Data Analysis (PANDA) and Beidou Experimental Tracking Stations (BETS), which are built by Wuhan University, the study of BeiDou precise orbit determination, static precise point positioning (PPP), and high precision relative positioning, and differential positioning are carried out comprehensively. Results show that the radial precision of the BeiDou satellite orbit determination is better than 10 centimeters. The RMS of static PPP can reach several centimeters to even millimeters for baseline relative positioning. The precision of kinematic pseudo-range differential positioning and RTK mode positioning are 2-4 m and 5-10 cm respectively, which are close to the level of GPS precise positioning. Research in this paper verifies that, with support of ground reference station network, Beidou satellite navigation system can provide precise positioning from several decimeters to meters in the wide area and several centimeters in the regional area. These promising results would be helpful for the implementation and applications of Beidou satellite navigation system.
Keywords: Compass/BeiDou; PANDA; precise orbit determination (POD); Beidou difference
来源出版物:Science China-Earth Sciences, 2012, 55(7): 1079-1086
被引频次:29
Two-step method for the determination of the differential code biases of Compass satellites
Li Zishen; Yunbin Yuan; Lihui; et al.
Abstract: The differential code bias (DCB) in satellites of the Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) should be precisely corrected when designing certain applications, such as ionospheric remote sensing, precise point positioning, and time transfer. In the case of Compass system, the data used for estimating DCB are currently only available from a very limited number of global monitoring stations. However, the current GPS/GLONASS satellite DCB estimation methods generally require a large amount of geographically well-distributed data for modeling the global ionospheric vertical total electron content (TEC) and are not particularly suitable for current Compass use. Moreover, some satellites with unstable DCB (i.e., relatively large scatter) may affect other satellite DCB estimates through the zero-mean reference that is currently imposed on all satellites. In order to overcome the inadequacy of data sources and to reduce the impact of unstable DCB, a new approach, designated IGGDCB, is developed for Compass satellite DCB determination. IGG stands for the Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics, which is located in Wuhan, China. In IGGDCB, the ionospheric vertical TEC of each individual station is independently modeled by a generalized triangular series function, and the satellite DCB reference is selected using an iterative DCB elimination process. By comparing GPS satellite DCB estimates calculated by the IGGDCB approach based on only a handful (e.g., seven) of tracking stations against that calculated by the currently existing methods based on hundreds of tracking stations, we areable to demonstrate that the accuracies of the IGGDCB-based DCB estimates perform at the level of about 0.13 and 0.10 ns during periods of high (2001) and low (2009) solar activity, respectively. The iterative method for DCB reference selection is verified by statistical tests that take into account the day-to-day scatter and the duration that the satellites have spent in orbit. The results show that the impact of satellites with unstable DCB can be considerably reduced using the IGGDCB method. It is also confirmed that IGGDCB is not only specifically valid for Compass but also for all other GNSS.
Keywords: differential code bias (DCB); Compass; total electron content (TEC); ionosphere; IGGDCB
来源出版物:Journal of Geodesy, 2012, 86(11): 1059-1076
被引频次:28
Orbit and clock analysis of Compass GEO and IGSO satellites
Steigenberger, P; Hugentobler, U; Hauschild, A; et al.
Abstract: China is currently focussing on the establishment of its own global navigation satellite system called Compass or BeiDou. At present, the Compass constellation provides four usable satellites in geostationary Earth orbit (GEO) and five satellites in inclined geosynchronous orbit (IGSO). Based on a network of six Compass-capable receivers, orbit and clock parameters of these satellites were determined. The orbit consistency is on the 1-2 dm level for the IGSO satellites and on the several decimeter level for the GEO satellites. These values could be confirmed by an independent validation with satellite laser ranging. All Compass clocks show a similar performance but have a slightly lower stability compared to Galileo and the latest generation of GPS satellites. A Compass-only precise point positioning based on the products derived from the six-receiver network provides an accuracy of several centimeters compared to the GPS-only results.
Keywords: GNSS; BeiDou-2; satellite orbits; Allan deviation
来源出版物:Journal of Geodesy, 2013, 87(6): 515-525
被引频次:24
The performance comparison between GPS and BeiDou-2/Compass: A perspective from Asia
Chen, He-Chin; Huang, Yu-Sheng; Chiang, Kai-Wei; et al.
Abstract: The next decade promises drastic improvements to global navigation satellite systems. The USA is modernizing GPS, Russia is refreshing GLONASS, Europe is moving ahead with its own Galileo system, and The People’s Republic of China is expanding its BeiDou-1 system from a regional navigation system to a full constellation global navigation satellite system known as BeiDou-2/Compass, which consists of thirty five satellites including geostationary satellites, MEO satellites and geosynchronous satellites in the coming year. Extra satellites will make possible improved performance for all applications, and especially where satellite signals can be obscured, such as in urban canyons, under tree canopies or in open-pit mines. The benefits of the expected extra satellites and their signals can be evaluated in terms of availability, accuracy, continuity, and reliability issues. The advent of a hybrid GNSS constellation has drawn a lot of attention to study compatibility and interoperability. A number of performance analyses have been conducted on a global scale with respect to availability, reliability, accuracy and integrity in different simulated scenarios (such as open sky and urban canyons) for each system individually as well as for combined systems with all the possible combinations. Since the BeiDou-2/Compass has gained more attention from GNSS communities, the main objective of this paper is to study the performance of BeiDou-2/Compass comparied to GPS in the greater Asia region; and also to explore whether the combination of BeiDou-2/Compass with GPS would yield performance improvements in this region. The performance analysis can be analyzed by either the signal or the geometrical conditions. However, the scope of this study is limited to investigating the impact of current and future GNSS based on geometrical conditions. Therefore, the satellite visibility and DOP (Dilution of Precision) values of each system or possible combinations between them are used as the major indices for performance evaluation with the emphasis on the addition of Compass. In addition, those indices are further analyzed in terms of their spatial and temporal distributions with the emphasis on the greater Asia region. Moreover, the spatial performance analyses are conducted on both global and regional scales to provide more insightful comparisons to illustrate the importance of future Compass for users in the greater Asia region.
Keywords: global navigation satellite systems; compass; dilution of precision; GPS
来源出版物:Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, 2009, 32(5): 679-689
被引频次:23
Preliminary assessment of the navigation and positioning performance of BeiDou regional navigation satellite system
Yang YuanXi; Li JinLong; Wang AiBing; et al.
Abstract: BeiDou regional navigation satellite system (BDS) also called BeiDou-2 has been in full operation since December 27, 2012. It consists of 14 satellites, including 5 satellites in Geostationary Orbit (GEO), 5 satellites in Inclined Geosynchronous Orbit (IGSO), and 4 satellites in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO). In this paper, its basic navigation and positioning performance are evaluated preliminarily by the real data collected in Beijing, including satellite visibility, Position Dilution of Precision (PDOP) value, the precision of code and carrier phase measurements, the accuracy of single point positioning and differential positioning and ambiguity resolution (AR) performance, which are also compared with those of GPS. It is shown that the precision of BDS code and carrier phase measurements are about 33 cm and 2 mm, respectively, which are comparable to those of GPS, and the accuracy of BDS single point positioning has satisfied the design requirement. The real-time kinematic positioning is also feasible by BDS alone in the opening condition, since its fixed rate and reliability of single-epoch dual-frequency AR is comparable to those of GPS. The accuracy of BDS carrier phase differential positioning is better than 1 cm for a very short baseline of 4.2 m and 3 cm for a short baseline of 8.2 km, which is on the same level with that of GPS. For the combined BDS and GPS, the fixed rate and reliability of single-epoch AR and the positioning accuracy are improved significantly. The accuracy of BDS/GPS carrier phase differential positioning is about 35% and 20% better than that of GPS for two short baseline tests in this study. The accuracy of BDS code differential positioning is better than 2.5 m. However it is worse than that of GPS, which may result from large code multipath errors of BDS GEO satellite measurements.
Keywords: BeiDou navigation satellite system; service area; dilution of precision; precision of code and carrier phase measurement; single point positioning; code differential positioning; ambiguity resolution; carrier phase differential positioning
来源出版物:Science China-Earth Sciences, 2014, 57(1): 144-152
被引频次:22
Instantaneous BeiDou plus GPS RTK positioning with high cut-off elevation angles
Teunissen, P. J. G.; Odolinski, R; Odijk, D
Abstract: As the Chinese BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) has become operational in the Asia-Pacific region, it is of importance to better understand as well as demonstrate the capabilities that a combination of BeiDou with GPS brings to positioning. In this contribution, a formal and empirical analysis is given of the single-epoch RTK positioning capabilities of such a combined system. This will be done for the single- and dual-frequency case, and in comparison with the BDS- and GPS-only performances. It will be shown that with the combined system, when more satellites are available, much larger than the customary cut-off elevations can be used. This is important, as such measurement set-up will significantly increase)the)GNSS)applicability)in)constrained environments, such as e.g. in urban canyons or when low-elevation multipath is present.
Keywords: BeiDou (BDS); GPS; multi-GNSS; integer ambiguity resolution; real time kinematic (RTK) positioning; cut-off elevation
来源出版物:Journal of Geodesy, 2014, 88(4): 225-250
被引频次:21
Precise point positioning with the BeiDou navigation satellite system Fruh, C; Zakhor, A
Li, Min; Qu, Lizhong; Zhao, Qile; et al.
Abstract: By the end of 2012, China had launched 16 BeiDou-2 navigation satellites that include six GEOs, five IGSOs and five MEOs. This has provided initial navigation and precise pointing services ability in the Asia-Pacific regions. In order to assess the navigation and positioning performance of the BeiDou-2 system, Wuhan University has built up a network of BeiDou Experimental Tracking Stations (BETS) around the World. The Position and Navigation Data Analyst (PANDA) software was modified to determine the orbits of BeiDou satellites and provide precise orbit and satellite clock bias products from the BeiDou satellite system for user applications. This article uses the BeiDou/GPS observations of the BeiDou Experimental Tracking Stations to realize the BeiDou and BeiDou/GPS static and kinematic precise point positioning (PPP). The result indicates that the precision of BeiDou static and kinematic PPP reaches centimeter level. Theprecision of BeiDou/GPS kinematic PPP solutions is improved significantly compared to that of BeiDou-only or GPS-only kinematic PPP solutions. The PPP convergence time also decreases with the use of combined BeiDou/GPS systems.
Keywords: BeiDou navigation satellite system; Position and Navigation Data Analyst (PANDA); BeiDou Experimental Tracking Stations (BETS); Precise Point Positioning (PPP)
来源出版物:Sensors, 2014, 14(1): 927-943
被引频次:21
Experimental study on the precise orbit determination of the BeiDou navigation satellite system
He, Lina; Ge, Maorong; Wang, Jiexian; et al.
Abstract: The regional service of the Chinese BeiDou satellite navigation system is now in operation with a constellation including five Geostationary Earth Orbit satellites (GEO), five Inclined Geosynchronous Orbit (IGSO) satellites and four Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) satellites. Besides the standard positioning service with positioning accuracy of about 10 m, both precise relative positioning and precise point positioning are already demonstrated. As is well known, precise orbit and clock determination is essential in enhancing precise positioning services. To improve the satellite orbits of the BeiDou regional system, we concentrate on the impact of the tracking geometry and the involvement of MEOs, and on the effect of integer ambiguity resolution as well. About seven weeks of data collected at the BeiDou Experimental Test Service (BETS) network is employed in this experimental study. Several tracking scenarios are defined, various processing schemata are designed and carried out; and then, the estimates are compared and analyzed in detail. The results show that GEO orbits, especially the along-track component, can be significantly improved by extending the tracking network in China along longitude direction, whereas IGSOs gain more improvement if the tracking network extends in latitude. The involvement of MEOs and ambiguity-fixing also make the orbits better.
Keywords: BeiDou; tracking network; precise orbit determination; ambiguity-fixing
来源出版物:Sensors, 2013, 13(3): 2911-2928
被引频次:21
BeiDou navigation satellite system and its time scales
Han, Chunhao; Yang, Yuanxi; Cai, Zhiwu; et al.
Abstract: The development and current status of BeiDou Navigation Satellite System are briefly introduced. The definition and realization of the system time scales are described in detail. The BeiDou system time (BDT) is an internal and continuous time scale without leap seconds. It is maintained by the time and frequency system of the master station. The frequency accuracy of BDT is superior to 2 × 10-14and its stability is better than 6 × 10-15/30 days. The satellite synchronization is realized by a two-way time transfer between the uplink stations and the satellite. The measurement uncertainty of satellite clock offsets is less than 2 ns. The BeiDou System has three modes of time services: radio determination satellite service (RDSS) one-way, RDSS two-way and radio navigation satellite service (RNSS) one-way. The uncertainty of the one-way time service is designed to be less than 50 ns, and that of the two-way time service is less than 10 ns. Finally, some coordinate tactics of UTC from the viewpoint of global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) are discussed. It would be helpful to stop the leap second, from our viewpoint, but to keep the UTC name, the continuity and the coordinate function unchanged.
来源出版物:Metrologia, 2011, 48(4): S213-S218
·推荐论文摘要·
多种测量技术条件下的GEO卫星定轨研究
郭睿,胡小工,唐波,等
摘要:提出了基于SLR和转发式测距数据的GEO卫星定轨方案,探讨了两种新的C波段转发式测距设备的系统时延精确标定方法,包括激光并置比对法和联合定轨法, 其中激光并置比对法的时延标定精度为0.5 ns,联合定轨法的时延标定精度优于1 ns。利用中国区域内的转发式测距跟踪网对 GEO卫星进行了联合定轨实验,结果表明经过事后精处理,定轨残差为 0.205 m,激光外符视向精度为0.133 m,三维位置精度优于5 m,预报2 h激光外符视向精度为0.373 m。
关键词:精密定轨;设备时延;GEO;SLR
来源出版物:科学通报, 2010, 55(6): 428-434
区域监测网精密定轨与轨道预报精度分析
周善石,胡小工,吴斌
摘要:我国导航系统采用区域监测网提供轨道预报等导航服务。由于区域网不能覆盖地球中轨轨道(Medium Earth Orbit, MEO)卫星全弧段,并且受卫星相对于监测网几何条件限制,若采用与全球网相同的定轨和预报策略,预报精度难以满足我国导航系统的指标要求。预报精度决定于定轨获得的初轨和力学模型的精度。针对MEO卫星星座的区域监测网定轨预报问题,本文提出两步法策略,即首先解算部分动力学参数和轨道参数,然后强约束这部分动力学参数的估值,重新解算所有动力学参数和轨道,并利用得到的初轨和动力学参数进行轨道预报。利用实测GPS数据的实验表明,采用两步法定轨策略可获得对动力学参数的合理解算结果,并可提高轨道预报精度,预报1天轨道的平均用户距离精度(User Range Error, URE)优于0.6 m。
关键词:区域网;定轨;预报;太阳辐射压;URE
来源出版物:中国科学:物理学 力学 天文学, 2010, 40(6):800-808
北斗卫星导航系统Klobuchar模型精度评估
张强,赵齐乐,章红平,等
摘要:目前,我国北斗卫星导航系统已完成星座区域组网,系统每2 h提供一组电离层延迟Klobuchar模型参数。利用欧洲定轨中心(CODE)的高精度电离层格网数据作为参考,对北斗卫星导航系统电离层参数性能进行了精度评估分析,并进行了定位分析。数据表明,其修正精度一般在70%以上,北半球的修正误差在1.5 m左右,而南半球的修正误差在3.5 m左右;在北半球中纬度地区的修正精度比高纬度、低纬度地区高;北斗单频伪距定位采用北斗Klobuchar模型在平面上的精度为3 m左右,高程上为7 m左右,与采用GPS的Klobuchar模型相比较,定位精度提高了约10%,高程方向尤为明显。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;电离层;Klobuchar模型;格网模型;单点定位
来源出版物:武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2014, 39(2): 142-146
多GNSS融合的北斗卫星精密定轨
刘伟平,郝金明,李建文,等
摘要:提供高精度的精密轨道产品对北斗卫星导航系统的推广应用具有重要意义。本文给出一种基于模糊度固定的北斗卫星多系统融合非差精密定轨方法,重点推导并论述模糊度固定的实现方法,结合实测数据,对其精密定轨效果进行了分析。初步分析结果表明:利用本文方法,北斗GEO、IGSO、MEO卫星三维定轨精度分别达到1.263 m、0.214 m、0.134 m,3类卫星径向定轨精度平均优于10 cm,IGSO和MEO已经基本优于5 cm;模糊度固定以后,北斗卫星三维定轨精度平均提高了21.8%,轨道切向精度改善最为明显,其中又以GEO卫星改进最大。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;模糊度固定;非差精密定轨;多系统融合;激光观测数据
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2014, 43(11): 1132-1138
BDS/GPS精密单点定位收敛时间与定位精度的比较
张小红,左翔,李盼,等
摘要:采用武汉大学卫星导航定位技术研究中心发布的北斗精密卫星轨道和钟差,在 TriP 2.0软件的基础上实现了 BDS PPP定位算法,并利用大量实测数据进行了BDS/GPS静态PPP和动态PPP浮点解试验。结果表明,BDS静态PPP的收敛时间约为80 min,动态PPP的收敛时间为100 min;对于3 h的观测数据,静态PPP收敛后定位精度优于5 cm,动态PPP收敛后水平方向优于8 cm,高程方向约12 cm;与GPS PPP类似,东分量上定位精度较北分量稍差。当前由于BDS的全球跟踪站有限,精密轨道和钟差精度不如GPS,因此BDS PPP的收敛时间较GPS长,但收敛后可实现厘米至分米级的绝对定位。
关键词:北斗卫星导航;精密单点定位;定位精度;收敛时间
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2015, 44(3): 250-256
北斗区域导航系统的PPP精度分析
朱永兴,冯来平,贾小林,等
摘要:北斗卫星导航系统的开放运行为其在高精度领域的应用提供了可能,系统精密单点定位性能受到了极大关注。本文首先介绍了北斗区域导航系统的星座和BDS/GPS跟踪网,分析了基于国内布站定轨的北斗卫星精密轨道和钟差精度。在此基础上研究了北斗区域导航系统静态、动态精密单点定位精度,并与GPS定位结果进行比较。实测算例表明:北斗精密单点定位可以实现静态厘米级、动态分米级的定位精度,达到目前GPS精密单点定位水平。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;BDS/GPS跟踪网;精密定轨;精密单点定位;精度分析
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2015, 44(4): 377-383
BeiDou、Galileo、GLONASS、GPS多系统融合精密单点
任晓东,张柯柯,李星星,等
摘要:随着中国BeiDou系统与欧盟Galileo系统的出现以及俄罗斯 GLONASS系统的恢复完善,过去单一的GPS导航卫星系统时代已经逐步过渡为多系统并存且相互兼容的全球性卫星导航系统(multi-constellation global navigation satellite systems, multi-GNSS)时代,多系统GNSS融合精密定位将成为未来GNSS精密定位技术的发展趋势。本文采用GPS、GLONASS、BeiDou、Galileo 4大卫星导航定位系统融合的精密单点定位(precise point positioning, PPP)实测数据,初步研究并分析了4系统融合PPP的定位性能。试验结果表明:在单系统观测几何构型不理想的区域,多系统融合能显著提高PPP的定位精度和收敛速度。4大系统融合的 PPP收敛速度相对于单 GNSS可提高30%~50%,定位精度可提高10%~30%,特别是对高程方向的贡献更为明显。此外,在卫星截止高度角大于30°的观测环境下,单系统由于可见卫星数不足导致无法连续定位,而多系统融合仍然可以获得PPP定位结果,尤其是水平方向具有较高的定位精度。这对于山区、城市以及遮挡严重的区域具有非常重要的应用价值。
关键词:精密单点定位;精度与收敛速度;BeiDou;Galileo;GLONASS;GPS;多频多系统
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2015, 44(12): 1307-1313
北斗三频宽巷组合网络RTK单历元定位方法
高旺,高成发,潘树国,等
摘要:利用三频超宽巷/宽巷模糊度波长较长从而易于固定的优势,提出了一种基于北斗三频宽巷组合的网络RTK单历元定位方法。数据处理中心利用基准站实时生成并播发包含双差对流层和电离层延迟改正信息的虚拟观测值;用户站利用载波、伪距组合及分步解算的TCAR方法基于单个卫星对、单历元可靠固定两个超宽巷或宽巷模糊度。最后利用已固定模糊度且噪声最小的宽巷观测值和内插得到的大气延迟改正进行实时动态定位解算。试验结果表明,对于本文提出的网络RTK单历元定位方法,用户站宽巷模糊度单历元解算准确率高于99.9%,统计的定位中误差平面为3~4 cm,高程方向约为5 cm。
关键词:北斗三频;宽巷组合;网络RTK;单历元定位
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2015, 44(6): 641-648
BDS/GPS/GLONASS组合的双频单历元相对定位性能对比分析
汪亮,李子申,袁洪,等
摘要:随着我国北斗卫星导航系统(Bei Dou Navigation Satellite System, BDS)的建成与运行,目前具备独立服务能力的系统包括GPS,GLONASS和BDS,多系统组合已成为GNSS导航定位发展的必然趋势。基于伪距或载波相位的相对定位是目前利用GNSS实现高精度定位的主要技术手段之一。本文重点分析对比了BDS/GPS/GLONASS单系统、双系统以及三系统组合共7种模式下双频伪距和单历元载波相位相对定位性能。结果表明:1)BDS/GPS/GLONASS组合伪距和单历元载波相位相对定位时,三系统观测值误差比分别设为1︰1︰2和1︰1︰1较合适;2)BDS/GPS组合的性能要优于GPS/GLONASS以及BDS/GLONASS组合,BDS/GPS/GLONASS三系统组合较双系统组合可进一步改善定位性能;3)短基线条件下(<20 km),BDS/GPS/GLONASS组合伪距和单历元载波相位相对定位精度较单BDS,GPS,GLONASS系统分别提高了48.4%,31.7%,65.7%和6.1%,12.5%,39.4%。
关键词:北斗;BDS/GPS/GLONASS;相对定位;单历元RTK
来源出版物:科学通报, 2015, 60(9): 857-868
基于通用钟差模型的北斗卫星钟预报精度分析
唐桂芬,许雪晴,曹纪东,等
摘要:卫星钟差参数的预报精度直接影响卫星导航系统的服务性能。影响卫星钟预报精度的因素有很多,其中钟差序列的建模质量是一个很重要的影响因子,只有最能反映星载原子钟自身物理特性和运行状态的模型才能获得更高的卫星钟预报精度。本文分析了北斗系统钟差序列的特性,提出了一种通用的钟差模型,该模型同时包含线性项、周期项和随机项,并且利用了AR模型对随机项进行建模,给出了周期项和AR模型参数的确定方法,该模型还能够根据实际星载钟特性进行退化与扩展。本文还给出了基于该模型的卫星钟预报方法,最后利用北斗实测数据进行了卫星钟预报精度分析试验,试验结果表明:所提出的通用模型能够最大限度地拟合钟差序列,从而大大提高卫星钟的预报精度,特别是针对一些稳定度较差的星载钟,实现了6 h预报精度2 ns,12 h预报精度5.5 ns。
关键词:卫星导航;在轨卫星钟;差预报
来源出版物:中国科学:物理学 力学 天文学, 2015, 45(7): 079502
北斗/GPS组合伪距单点定位性能测试和分析
唐卫明,徐坤,金蕾,等
摘要:讨论了北斗/GPS伪距单点定位联合解算的数学模型,并根据北京、武汉两地的北斗/GPS双系统实测数据,在多种模拟遮挡环境下将北斗/GPS联合解算结果与北斗、GPS单系统在可见卫星数、PDOP值、定位精度、定位可用性等方面进行了对比分析。结果表明,相对于单系统伪距单点定位,北斗/GPS组合定位大大增加了可见卫星数,减小了PDOP值,并在观测条件较差的环境下有效地改善了定位精度,显著提高了系统定位可用性。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;GPS;伪距单点定位;联合解算;可用性
来源出版物:武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2015, 40(4): 529-533
北斗系统短基线解算数据处理方法
高猛,徐爱功,祝会忠,等
摘要:北斗卫星导航系统基线解算和高精度定位中的关键问题是整周模糊度解算。针对北斗系统的相对定位问题,该文利用B1、B2载波相位观测值组成宽巷双差观测值,利用搜索算法固定宽巷双差整周模糊度,建立宽巷及B1、B2的双差观测方程,并利用搜索算法固定B1的整周模糊度,进而固定 B2的整周模糊度。以武汉大学PANDA软件处理结果作为参考值处理16 km以下的四段基线进行算法的试验检验,结果表明,四段基线在E方向、N方向、U方向的精度分别为1.5、2.0、5.0 cm,验证了利用宽巷组合观测值进行北斗系统基线解算是可行的,其精度和GPS系统相当。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;基线解算;双差;宽巷组合;整周模糊度;
来源出版物:测绘科学, 2015, 40(4): 28-33
北斗RNSS-RDSS组合模糊度解算方法
赵姣姣,曲江华,袁洪,等
摘要:电离层延迟较大是基线较长情况下的模糊度解算需要解决的关键问题。当基线较长时,由于基准站和流动站的电离层相关性弱使得双差电离层残差较大,易导致模糊度解算所需时间长且成功率不高。本文提出了一种模糊度解算方法,该方法将北斗无线电测定业务(radio determination satellite system, RDSS)的下行S频段信号测量值与无线电导航业务(radio navigation satellite system, RNSS)信号测量值组合来削弱电离层的影响。首先,通过RDSS信号测量值与RNSS信号测量值一起进行频率组合研究,确定了几组电离层延迟系数小且总噪声波长比(total noise level, TNL)较小的组合。然后,利用这些组合形成几何无关和电离层无关模型解算GEO卫星的窄巷模糊度。最后利用已知窄巷模糊度的GEO卫星测量值辅助求解非GEO卫星的窄巷模糊度。利用实测北斗星历对提出的方法进行了仿真验证,结果表明,本文方法可以从整体上提高模糊度解算的速度和成功率。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;RDSS-RNSS;模糊度解算;电离层延迟
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2016, 45(4): 404-410
GNSS互操作若干问题
杨元喜,陆明泉,韩春好
摘要:GNSS兼容与互操作是国际卫星导航领域的热点议题,也是用户实现多系统融合导航必须具备的条件。本文首先介绍了兼容与互操作的基本概念;简要分析了多GNSS系统互操作的基本趋势及GNSS4大核心系统信号互操作的现状;分析了现有北斗卫星导航系统(BDS)在信号互操作方面存在的问题,指出其对用户接收机制造商和多GNSS用户的影响;分析了坐标基准和坐标框架在互操作方面存在的问题及其可能带来的影响,指出坐标系统的实现、维持甚至更新策略带来的误差都可能给多GNSS互操作及导航定位结果带来影响;讨论了时间基准互操作存在的问题,以及可能的解决措施。最后归纳了本文的主要结论。
关键词:北斗;兼容与互操作;频率;坐标系统;时间基准
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2016, 45(3): 253-259
北斗卫星导航系统的毫米级精度变形监测算法与实现
肖玉钢,姜卫平,陈华,等
摘要:研究了北斗卫星导航系统(BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, BDS)毫米级精度变形监测算法。首先改进了TurboEdit方法,以能够探测到1周的小周跳;针对 BDS星座结构给出更为高效的独立双差观测值搜索方法;对于模糊度固定,采用决策函数和序贯模糊度固定相结合的方法。在此基础上,研制了BDS变形监测软件。最后,利用变形监测试验平台的实测数据,从星座分布、解算精度等方面分析了BDS在变形监测中应用的可行性。结果表明,目前在试验区域内BDS与GPS在卫星几何分布等方面基本相当。BDS的短基线解算精度略低于GPS,但仍可达到平面1 mm以内、高程2 mm以内的精度水平。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;变形监测;软件实现;精度分析
来源出版物:测绘学报, 2016, 45(1): 16-21
北斗在极区导航定位性能分析
杨元喜,徐君毅
摘要:北极蕴藏着丰富的资源,冰川融化使得夏季北极地区的航行成为可能,北极地区战略地位凸显。为了保障北极地区活动的安全性,精确导航定位是重要基础保障,本文分析了我国北斗卫星导航系统当前星座及未来全球星座在极区的可用性。详细分析了利用北斗卫星导航系统在极区进行导航、定位服务的基本性能,分析其优缺点,并提出了可能的应对方法。
关键词:北极;GNSS;北斗;极区导航
来源出版物:武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2016, 41(1): 15-20
基于北斗卫星的水汽探测性能分析
施闯,王海深,曹云昌,等
摘要:本文利用北斗试验网的数据,结合探空观测,对北斗系统与GPS系统,北斗、GPS与探空系统之间进行详细的比较分析,对北斗水汽探测性能及精度给出初步分析结果。北斗系统与GPS系统及探空系统大气可降水量的探测结果较一致,很好地反映了大气可降水量的变化情况;北斗系统解算出的大气可降水量大于GPS系统,两个系统间存在 2~3.3 mm的系统误差,水汽含量较低时,一致性更好;北斗系统与探空的系统误差和标准偏差较大,定位定轨模型有待优化,系统稳定性有待提高。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;水汽探测;大气延迟;大气可降水量
来源出版物:武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2016, 41(3): 285-289
BeiDou inter-satellite-type bias evaluation and calibration for mixed receiver attitude determination
Nadarajah, Nandakumaran; Teunissen, Peter J. G; Raziq, Noor; et al.
Abstract: The Chinese BeiDou system (BDS), having different types of satellites, is an important addition to the ever growing system of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS). It consists of Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO) satellites, Inclined Geosynchronous Satellite Orbit (IGSO) satellites and Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) satellites. This paper investigates the receiver-dependent bias between these satellite types, for which we coined the name inter-satellite-type bias (ISTB), and its impact onmixed receiver attitude determination. Assuming different receiver types may have different delays/biases for different satellite types, we model the differential ISTBs among three BeiDou satellite types and investigate their existence and their impact on mixed receiver attitude determination. Our analyses using the real data sets from Curtin's GNSS array consisting of different types of BeiDou enabled receivers and series of zero-baseline experiments with BeiDou-enabled receivers reveal the existence of non-zero ISTBs between different BeiDou satellite types. We then analyse the impact of these biases on BeiDou-only attitude determination using the constrained (C-)LAMBDA method, which exploits the knowledge of baseline length. Results demonstrate that these biases could seriously affect the integer ambiguity resolution for attitude determination using mixed receiver types and that a priori correction of these biases will dramatically improve the success rate.
Keywords: global navigation satellite systems (GNSS); BeiDou system (BDS); inter-satellite-type biases; attitude determination;)multivariate)constrained)integer least-squares (MC-LAMBDA); carrier phase ambiguity resolution
来源出版物:Sensors, 2013, 13(7): 9435-9463
GNSS multi-carrier fast partial ambiguity resolution strategy tested with real BDS/GPS dualand triple-frequency observations
He H; Li J; Yang Y; et al.
Abstract: The regional constellation of BeiDou navigation satellite system (BDS) has been officially in operation since December 27, 2012, and real-time kinematic positioning using BDS and GPS multi-frequency observations is feasible. A heavy computational problem arises when resolving ambiguities in the case of multi-system with multi-frequency observations. A multi-carrier fast partial ambiguity resolution strategy is developed with the property that the extra-wide-lane and wide-lane ambiguities in the multi-frequency case can be resolved reliably in advance. Consequently, the technique resolves ambiguities sequentially instead of the usual batch ambiguity resolution (AR) mode so as to improve the computational efficiency of AR significantly. The strategy is demonstrated with real BDS/GPS dual- and triple-frequency observations. The results have shown that the probability of correct AR by the proposed method is comparable to that of the batch AR. Experimentally, the new method is about 2.5 times as fast as the batch AR in the dual-frequency case, 3 times in the mixed dual- and triple-frequency case and 3.5 times in the triple-frequency case.
Keywords: global navigation satellite systems (GNSS); BeiDou navigation satellite system (BDS); multifrequency; computational efficiency; partial ambiguity resolution
来源出版物:GPS Solutions, 2013, 19(1):5-13
Estimating zenith tropospheric delays from BeiDou navigation satellite system observations
Xu, Aigong; Xu, Zongqiu; Ge, Maorong; et al.
Abstract: The GNSS derived Zenith Tropospheric Delay (ZTD) plays today a very critical role in meteorological study and weather forecasts, as ZTDs of thousands of GNSS stations are operationally assimilated into numerical weather prediction models. Recently, the Chinese BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) was officially announced to provide operational services around China and its neighborhood and it was demonstrated to be very promising for precise navigation and positioning. In this contribution, we concentrate on estimating ZTD using BDS observations to assess its capacity for troposphere remote sensing. A local network which is about 250 km from Beijing and comprised of six stations equipped with GPS-and BDS-capable receivers is utilized. Data from 5 to 8 November 2012 collected on the network is processed in network mode using precise orbits and in Precise Point Positioning mode using precise orbits and clocks. The precise orbits and clocks are generated from a tracking network with most of the stations in China and several stations around the world. The derived ZTDs are compared with that estimated from GPS data using the final products of the International GNSS Service (IGS). The comparison shows that the bias and the standard deviation of the ZTD differences are about 2 mm and 5 mm, respectively, which are very close to the differences of GPS ZTD estimated using different software packages.
Keywords: BeiDou navigation satellite system; precise point positioning; network solution; GNSS meteorology
来源出版物:Sensors, 2013, 13(4): 4514-4526
Design and experiment of onboard laser time transfer in Chinese Beidou navigation satellites
Meng, Wendong; Zhang, Haifeng; Huang, Peicheng; et al.
Abstract: High-precision time synchronization betweensatellites and ground stations plays the vital role in satellite navigation system. Laser time transfer (LTT) technology is widely recognized as the highest accuracy way to achieve time synchronization derived from satellite laser ranging (SLR) technology. Onboard LTT payload has been designed and developed by Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, and successfully applied to Chinese Beidou navigation satellites. By using the SLR system, with strictly controlling laser firing time and developing LTT data processing system on ground, the high precise onboard laser time transfer experiment has been first performed for satellite navigation system in the world. The clock difference and relative frequency difference between the ground hydrogen maser and space rubidium clocks have been obtained, with the precision of approximately 300 ps and relative frequency stability of 10E-14. This article describes the development of onboard LTT payload, introduces the principle, system composition, applications and LTT measuring results for Chinese satellite navigation system.
Keywords: navigation satellites; time synchronization; laser time transfer (LTT); measuring experiment; satellite laser ranging (SLR)
来源出版物:Advances in Space Research, 2013, 51(6): 951-958
Performance assessment of single- and dual-frequency BeiDou/GPS single-epoch kinematic positioning
H He; J Li; Y Yang; et al.
Abstract: The first results of the short baseline singleepoch kinematic positioning based on dual-frequency real BeiDou/GPS data are presented. The performance of the BeiDou/GPS single-epoch positioning is demonstrated in both static and kinematic modes and compared with corresponding GPS-only performance. It is shown that the availability and reliability of the single-frequency BeiDou/GPS and dual-frequency BeiDou single-epoch kinematic positioning are comparable to those of the dual-frequency GPS. The fixed rate and reliability of ambiguity resolution for the single- and dual-frequency BeiDou/GPS are remarkably improved as compared to that of GPS-only, especially in case of high cutoff elevations. For positioning accuracy with fixed ambiguities, the BeiDou/GPS single-epoch solutions are improved by 23 and 4% relative to the GPS-only case for two short baseline tests of 8 km, respectively. These results reveal that dual-frequency BeiDou real-time kinematic (RTK) is already applicable in Asia–Pacific areas and that single-frequency BeiDou/GPS RTK is also achievable but only with initialization of several seconds. More promisingly, the dual-frequency BeiDou/GPS RTK can overcome the difficulties with GPS-only RTK under the challenging conditions assuming, of course, that the additional BeiDou satellites are visible.
Keywords: ambiguity resolution; BeiDou; GPS; highprecision positioning; single-epoch RTK
来源出版物:GPS Solutions, 2014, 18(3):393-403
Triple-frequency carrier ambiguity resolution for BeiDou navigation satellite system
Zhong, Chen; Arisona, Stefan Mueller; Huang, Xianfeng; et al.
Abstract: The Chinese Beidou system, also known as Compass, has entered its trial operational stage and can already provide services for triple-frequency users. Using triple-frequency signals is expected to be of great benefit for ambiguity resolution. Based on error characteristic analysis of the Beidou frequencies, we introduce the procedure of selecting the best combinations of triple-frequency signals. The geometry-based model and geometry-free model of triple-frequency signals are presented. Three triplefrequency carrier ambiguity resolution (TCAR) methods are described, which include the cascading rounding method, the stepwise AR method and the modified stepwise AR method. In order to evaluate the performance of these methods, observations from baselines of various lengths were collected using Beidou triple-frequency receivers and were processed epoch-by-epoch using the three methods. The same observation data were also processed in a dual-frequency mode for comparison. The results show that, compared to the dual-frequency based solution, the single epoch ambiguity resolution success rate with triple frequency improved nearly 30% for the short baselines (< 20 km) and 100% for the mid-length baselines (20-50 km) using the proposed modified stepwise AR method.
Keywords: triple frequency; Beidou navigation satellite system; ambiguity resolution
来源出版物:GPS Solutions, 2014, 18(3): 335-344
Instantaneous BeiDou-GPS attitude determination:A performance analysis
Nadarajah, Nandakumaran; Teunissen, Peter J. G; Raziq, Noor; et al.
Abstract: The advent of modernized and new globalnavigation satellite systems (GNSS) has enhanced the availability of satellite based positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) solutions. Specifically, it increases redundancy and yields operational back-up or independence in case of failure or unavailability of one system. Among existing GNSS, the Chinese BeiDou system (BDS) is being developed and will consist of geostationary (GEO) satellites, inclined geosynchronous orbit (IGSO) satellites, and medium-Earth-orbit (MEO) satellites. In this contribution, a BeiDou-GPS robustness analysis is carried out for instantaneous, unaided attitude determination. Precise attitude determination using multiple GNSS antennas mounted on a platform relies on the successful resolution of the integer carrier phase ambiguities. The constrained Least-squares AMBiguity Decorrelation Adjustment (C-LAMBDA) method has been developed for the quadratically constrained GNSS compass model that incorporates the known baseline length. In this contribution the method is used to analyse the attitude determination performance when using the GPS and BeiDou systems. The attitude determination performance is evaluated using GPS/BeiDou data sets from a real data campaign in Australia spanning several days. The study includes the performance analyses of both stand-alone and mixed constellation (GPS/BeiDou) attitude estimation under various satellite deprived environments. We demonstrate and quantify the improved availability and accuracy of attitude determination using the combined constellation.
Keywords: GNSS; GPS; BeiDou; attitude determination; Constrained integer least-squares; C-LAMBDA
来源出版物:Advances in Space Research, 2014, 54(5): 851-862
First combined Compass/BeiDou-2 and GPS positioning results in Australia. Part I:Single-receiver and relative code-only positioning
Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, PJG; Odijk, D
Abstract: China’s BeiDou-2/Compass is expected to deliver global Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT) services by 2020. Australia is already a beneficiary of the regional BeiDou configuration, as enough satellites are available to perform PNT. The present contribution is Part I out of two parts that consider first combined BeiDou+GPS positioning results in Australia. In Part II, we will focus our attention on the single-baseline RTK model performance and the integer ambiguity success rates. Part I considers code-only single- and multiple-frequency single-receiver and relative point positioning. Our results show that the increased strength of the combined model allows for improved positioning robustness and accuracy over the BeiDou- and GPS-only solutions.
Keywords: GNSS; BeiDou; GPS; positioning navigation and timing (PNT); multipath; single-point positioning (SPP); relative point positioning (RPP)
来源出版物:Journal of Spatial Science, 2014, 59(1): 3-24
HPTS: Towards a new method for generating precise global ionospheric TEC map based on spherical harmonic and generalized trigonometric series functions
Li Zishen; Yuan Yunbiin; Ningbo Wang; et al.
Abstract: To take maximum advantage of the increasing Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) data to improve the accuracy and resolution of global ionospheric TEC map (GIM), an approach, named Spherical Harmonic plus generalized Trigonometric Series functions (SHPTS), is proposed by integrating the spherical harmonic and the generalized trigonometric series functions on global and local scales, respectively. The SHPTS-based GIM from January 1st, 2001 to December 31st, 2011 (about one solar cycle) is validated by the ionospheric TEC from raw global GPS data, the GIM released by the current Ionospheric Associate Analysis Center (IAAC), the TOPEX/Poseidon satellite and the DORIS. The present results show that the SHPTS-based GIM over the area where no real data are available has the same accuracy level (approximately 2-6 TECu) to that released by the current IAAC. However, the ionospheric TEC in the SHPTS-based GIM over the area covered by real data is more accurate (approximately 1.5 TECu) than that of the GIM (approximately 3.0 TECu) released by the current IAAC. The external accuracy of the SHPTS-based GIM validated by the TOPEX/Poseidon and DORIS is approximately 2.5-5.5 and 1.5-4.5 TECu, respectively. In particular, the SHPTS-based GIM is the best or almost the best ranked, along with those of JPL and UPC, when they are compared with TOPEX/Poseidon measurements, and the best (in addition to UPC) when they are validated with DORIS data. With the increase in the number of GNSS satellites and contributing stations, the performance of the SHPTS-based GIM can be further improved.
Keywords: global ionospheric TEC map (GIM); GNSS; TOPEX/Poseidon; DORIS
来源出版物:Journal of Geodesy, 2015, 89(4): 331-345
Combined BDS, galileo, QZSS and GPS single-frequency RTK
Odolinski, Robert; Teunissen, Peter J. G; Odijk, Dennis
Abstract: We will focus on single-frequency singlebaseline real-time kinematic (RTK) combining four Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) satellite systems. We will combine observations from the Chinese BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS), European Galileo, American Global Positioning System (GPS) and the Japanese Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS). To further strengthen the underlying model, attention will be given to overlapping frequencies between the systems. If one can calibrate the inter-system biases, a common pivot satellite between the respective systems can be used to parameterize double-differenced ambiguities. The LAMBDA method is used for ambiguity resolution. The instantaneous (singleepoch) single-frequency RTK performance is evaluated by a formal as well as an empirical analysis, consisting of ambiguity dilution of precision (ADOP), bootstrapped and integer least-squares success rates and positioning precisions. The time-to-correct-fix in some particular cases when instantaneous RTK is not possible will also be analyzed. To simulate conditions with obstructed satellite visibility or when low-elevation multipath is present, various elevation cut-off angles between 10 and 40 A degrees will be used. Four days of real data are collected in Perth, Western Australia. It will be shown that the four-system RTK model allows for improved integer ambiguity resolution and positioning performance over the single, dual or triple-systems, particularly for higher cut-off angles.
Keywords: Inter-system biases (ISBs); real-time kinematic (RTK); multi-global navigation satellite system (GNSS); integer ambiguity resolution; LAMBDA
来源出版物:GPS Solutions, 2015, 19(1): 151-163
The mixed-receiver BeiDou inter-satellite-type bias and its impact on RTK positioning Nadarajah, Nandakumaran; Teunissen, Peter J. G.;
Sleewaegen, Jean-Marie; et al.
Abstract: The inter-satellite-type bias (ISTB) is a receiver-dependent hardware delay/bias between different satellite types. Our recent research revealed the existence of nonzero mixed-receiver phase ISTBs for the Chinese BeiDou system. Triggered by this finding, global navigation satellite system receiver manufactures, who are in the early stage of BeiDou-enabled receiver developments, are working toward a mutually consistent measurement extraction procedure. We analyze the long-term stability and current status of the mixed-receiver ISTBs, as well as study their impact on BeiDou stand-alone real-time kinematic (RTK) positioning. Our results confirm that a recent update in one of the receiver types has aligned it with one of the other receiver types. However, since not all receiver types are aligned yet, nonzero mixed-receiver ISTBs are shown to be still present. Analyses of BeiDou stand-alone RTK positioning using mixed-receiver types demonstrate that ISTBs could seriously affect the integer ambiguity resolution performance and that a priori correction for these biases will dramatically improve the success rate. Our analyses using real data from three different receiver types also demonstrate the long-term stability of the ISTBs, thus showing that such a priori calibration is indeed possible.
Keywords: global navigation satellite system (GNSS); BeiDou system (BDS); inter-satellite-type bias (ISTB); real-time kinematic (RTK) positioning; carrier phase ambiguity resolution
来源出版物:GPS Solutions, 2015, 19(3): 357-368
Analysis on the long-term dynamical evolution of the inclined geosynchronous orbits in the Chinese BeiDou navigation system
Zhao, Chang-Yin; Zhang, Ming-Jiang; Wang, Hong-Bo; et al.
Abstract: Five inclined geosynchronous orbit (IGSO) satellites with the inclination of about 55 degrees in the Chinese BeiDou navigation system have been put in orbit until now. The Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC) has defined a geosynchronous orbit (GEO) protected region and recommended that the GEO satellite should be maneuvered to a disposal orbit high enough at end-of-mission to remain above the GEO protected region. The recommended disposal altitude is at least 235 km + (1000·CR·A/M) higher than the perigee altitude of the GEO satellite, where CRand A/M are radiation pressure coefficient and area-to-mass ratio respectively. Whether this recommendation is also adequate for the disposal of these IGSO satellites in the Chinese BeiDou navigation system at end-of-mission? And if not, is there any other possible strategy to do? In view of these considerations, the long-term dynamical evolution of these IGSO satellites is investigated by both theoretical analysis and numerical computation methods in this paper.Some qualitative orbital evolution characteristics and quantitative result of variation ranges of the semi-major axis a, the inclination i and the eccentricity e are presented respectively. Based on these results, a possible mitigation strategy to reduce the orbital lifetime of the IGSO satellites after end-of-mission is proposed.
Keywords: long-term dynamical evolution; inclined geosynchronous orbit; Chinese BeiDou navigation system; mitigation strategy
来源出版物:Advances in Space Research, 2015, 56(3): 377-387
Multiangle BSAR imaging based on BeiDou-2 navigation satellite system: Experiments and preliminary results
Zeng, Tao; Ao, Dongyang; Hu, Cheng; et al.
Abstract: This paper analyzes the multiangle imaging results for bistatic synthetic aperture radar (BSAR) based on global navigation satellite systems (GNSS-BSAR). Due to the shortcoming of GNSS-BSAR images, a multiangle observation and data processing strategy based on BeiDou-2 navigation satellites was put forward to improve the quality of images and the value of system application. Twenty-six BSAR experiments were conducted and analyzed in different configurations. Furthermore, a regionbased fusion algorithm using region-of-interest (ROI) segmentation was proposed to generate a high-quality fusion image. Based on the fusion image, typical targets such as water area, vegetation area, and artificial targets were compared and interpreted among single/multipleangle images. The results reveal that the multiangle imaging method was a good technique to enhance image information, which might extend the applications of GNSS-BSAR.
Keywords: bistatic synthetic aperture radar (BSAR); global navigation satellite system (GNSS); image fusion; image interpretation; multiangle
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(10): 5760-5773
Determination of differential code biases with multi-GNSS observations
Wang Ningbo; Yuan Yunbin; Li Zishen; et al.
Abstract: In order to better understand the differential code biases (DCBs) of global navigation satellite system, the IGGDCB method is extended to estimate the intra-and inter-frequency biases of the global positioning system (GPS), GLONASS, BeiDou navigation satellite system (BDS), and Galileo based on observations collected by the multi-GNSS experiment (MGEX) of the international GNSS service (IGS). In the approach of IGGDCB, the local ionospheric total electronic content is modeled with generalized triangular series (GTS) function rather than using a global ionosphere model or a priori ionospheric information. The DCB estimated by the IGGDCB method is compared with the DCB products from the Center for Orbit Determination in Europe (CODE) and German Aerospace Center (DLR), as well as the broadcast timing group delay (TGD) parameters over a 2-year span (2013 and 2014). The results indicate that GPS and GLONASS intra-frequency biases obtained in this work show the same precision levels as those estimated by DLR (about 0.1 and 0.2-0.4 ns for the two constellations, respectively, with respect to the products of CODE). The precision levels of IGGDCB-based inter-frequency biases estimated over the 24-month period are about 0.29 ns for GPS, 0.56 ns for GLONASS, 0.36 ns for BDS, and 0.24 ns for Galileo, respectively. Here, the accuracies of GPS and GLONASS biases are assessed relative to the products of CODE, while those of BDS and Galileo are compared with the estimates of DLR. In addition, the monthly stability indices of IGGDCB-based DCBs are 0.11 (GPS), 0.18 (GLONASS), 0.17 (BDS), and 0.14 (Galileo) ns for the individual constellation.
Keywords: multi-GNSS experiment (MGEX); differential code bias (DCB); timing group delay (TGD); intrafrequency bias; inter-frequency bias; IGGDCB; total electronic content (TEC)
来源出版物:Journal of Geodesy, 2016, 90(3): 209-228
Comprehensive comprisons of satellite data,signals, and measurements between the BeiDou navigation satellite system and the global positioning system
Jan, Shau-Shiun; Tao, An-Lin
Abstract: The Chinese BeiDou navigation satellite system (BDS) aims to provide global positioning service by 2020. The combined use of BDS and Global Positioning System (GPS) is proposed to provide navigation service with more stringent requirements. Actual satellite data, signals and measurements were collected for more than one month to analyze the positioning service qualities from both BDS and GPS. In addition to the conversions of coordinate and timing system, five data quality analysis (DQA) methods, three signal quality analysis (SQA) methods, and fourmeasurement quality analysis (MQA) methods are proposed in this paper to improve the integrated positioning performance of BDS and GPS. As shown in the experiment results, issues related to BDS and GPS are resolved by the above proposed quality analysis methods. Thus, the anomalies in satellite data, signals and measurements can be detected by following the suggested resolutions to enhance the positioning performance of the combined use of BDS and GPS in the Asia Pacific region.
Keywords: global navigation satellite system (GNSS); BeiDou navigation satellite system (BDS); global positioning system (GPS); navigation data; ephemeris; almanac; signal; measurement
来源出版物:Sensors, 2016, 16(5): 689
Estimation of differential code biases for Beidou navigation system using multi-GNSS observations:How stable are the differential satellite and receiver code biases?
Xue, Junchen; Song, Shuli; Zhu, Wenyao; et al.
Abstract: Differential code biases (DCBs) are important parameters that must be estimated accurately and reliably for high-precision GNSS applications. For optimal operational service performance of the Beidou navigation system (BDS), continuous monitoring and constant quality assessment of the BDS satellite DCBs are crucial. In this study, a global ionospheric model was constructed based on a dual system BDS/GPS combination. Daily BDS DCBs were estimated together with the total electron content from 23 months’ multi-GNSS observations. The stability of the resulting BDS DCB estimates was analyzed in detail. It was found that over a long period, the standard deviations (STDs) for all satellite B1-B2 DCBs were within 0.3 ns (average: 0.19 ns) and for all satellite B1-B3 DCBs, the STDs were within 0.36 ns (average: 0.22 ns). For BDS receivers, the STDs were greater than for the satellites, with most values 2 ns. The DCBs of different receiver families are different. Comparison of the statistics of the short-term stability of satellite DCBs over different time intervals revealed that the difference in STD between 28-and 7-day intervals was small, with a maximum not exceeding 0.06 ns. In almost all cases, the difference in BDS satellite DCBs between two consecutive days was 0.8 ns. The main conclusion is that because of the stability of the BDS DCBs, they only require occasional estimation or calibration. Furthermore, the 30-day averaged satellite DCBs can be used reliably for the most demanding BDS applications.
Keywords: differential code bias; GNSS; Beidou navigation system; global ionospheric model
来源出版物:Journal of Geodesy, 2016, 90(4): 309-321
BDS/GPS dual systems positioning based on the modified SR-UKF algorithm
Kong, JaeHyok; Mao, Xuchu; Li, Shaoyuan
Abstract: The Global Navigation Satellite System can provide all-day three-dimensional position and speed information. Currently, only using the single navigation system cannot satisfy the requirements of the system’s reliability and integrity. In order to improve the reliability and stability of the satellite navigation system, the positioning method by BDS and GPS navigation system is presented, the measurement model and the state model are described.)Furthermore,)the)modified)square-root Unscented Kalman Filter (SR-UKF) algorithm is employed in BDS and GPS conditions, and analysis of single system/multi-system positioning has been carried out, respectively. The experimental results are compared with the traditional estimation results, which show that the proposed method can perform highly-precise positioning. Especially when the number of satellites is not adequate enough, the proposed method combine BDS and GPS systems to achieve a higher positioning precision.
Keywords: Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS); positioning algorithm; modified square-root Unscented Kalman filter (modified SR-UKF); BeiDou Navigation System (BDS)
来源出版物:Sensors, 2016, 16(5): 35
编辑:卫夏雯
Precise orbit determination of BeiDou satellites with precise positioning
Shi Chuang; Zhao QiLe; Li Min; et al.
Chinese Beidou satellite navigation system constellation currently consists of eight BeiDou satellites and can provide preliminary service of navigation and positioning in the Asia-Pacific Region. Based on the self-developed software Position And Navigation Data Analysis(PANDA) and BeiDou Experimental Tracking Stations (BETS), which are built by Wuhan University, the study of BeiDou precise orbit determination, static precise point positioning (PPP), and high precision relative positioning, and differential positioning are carried out comprehensively. Results show that the radial precision of the Beidou satellite orbit determination is better than 10 centimeters. The RMS of static PPP can reach several centimeters to even millimeters for baseline relative positioning. The precision of kinematic pseudo-range differential positioning and RTK mode positioning are 2-4 m and 5-10 cm respectively, which are close to the level of GPS precise positioning. Research in this paper verifies that, with support of ground reference station network, Beidou satellite navigation system can provide precise positioning from several decimeters to meters in the wide area and several centimeters in the regional area. These promising results would be helpful for the implementation and applications of Beidou satellite navigation system.
compass/BeiDou; PANDA; precise orbit determination (POD); BeiDou difference
